ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS INDUSTRIAL AND CONTROL ENGINEERING APPLICATIONS
…
490 pages
1 file

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
Artificial neural networks may probably be the single most successful technology in the last two decades which has been widely used in a large variety of applications. The purpose of this book is to provide recent advances of artificial neural networks in industrial and control engineering applications. The book begins with a review of applications of artificial neural networks in textile industries. Particular applications in textile industries follow. Parts continue with applications in materials science and industry such as material identification, and estimation of material property and state, food industry such as meat, electric and power industry such as batteries and power systems, mechanical engineering such as engines and machines, and control and robotic engineering such as system control and identification, fault diagnosis systems, and robot manipulation. Thus, this book will be a fundamental source of recent advances and applications of artificial neural networks in industrial and control engineering areas. The target audience includes professors and students in engineering schools, and researchers and engineers in industries.
Figures (404)












































































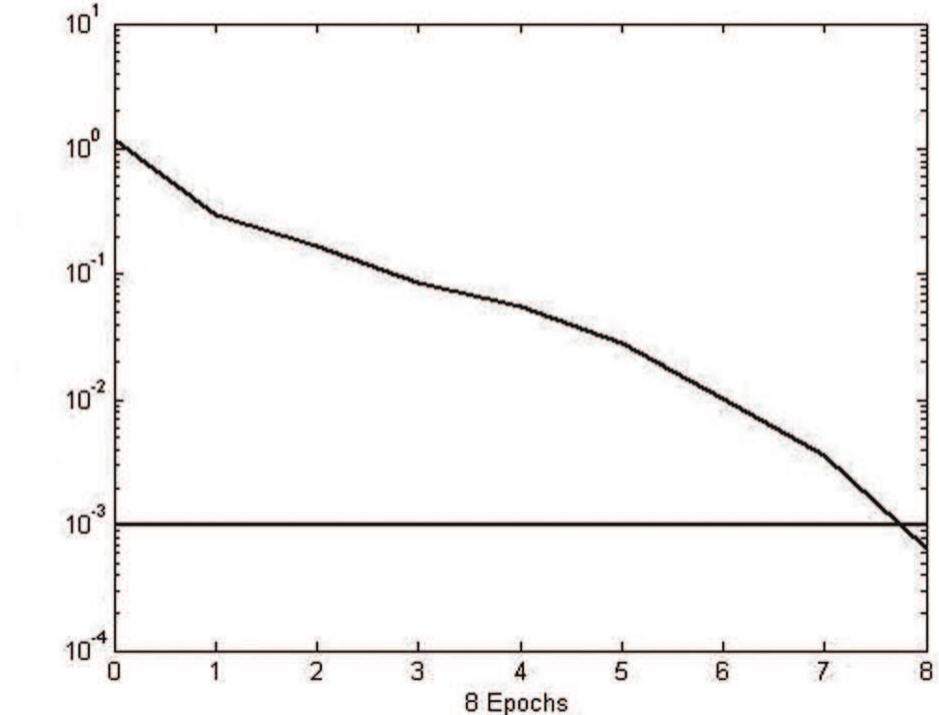
































































































































































































![presented in [Rivera et al., 1986]. IMC for nonlinear systems is introduced in [Economou et al.,
1986] and IMC with neural networks is described e.g. in [Norgaard et al., 2000].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/54267271/figure_176.jpg)














































































































Related papers
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences
The textile process involves the interaction of a large number of variables. The relations between these variables and the product properties could not be established conclusively. Different techniques have been suggested to determine these relations but with limited success. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) represent a promising step in this field. In this research, a survey of the application of ANN from fibers through yarn; fabric, garments as well as finishing processes is performed. A comparison between the traditional techniques and ANN in textiles is conducted and a preview for the expected future of ANN in the textile field is also presented.
2015
The artificial neural network (ANN) is increasingly used as a powerful tool for many real world problems. ANN has proved its usefulness for resolving many problems in textiles such as prediction of yarn properties, analysis of fabric defects, process optimization etc. The power of neural networks lies in their ability to represent complex relationships and learn them directly from the data being modeled. The prediction of properties or performance of a process in advance is required to minimize the setup cost and time. The ability to predict these properties accurately has become a challenge due to highly non-linear and interactive behaviour of textile materials. This paper presents basics of ANN and its applications in different textile domains.
Neural Network is an intelligent system that finds widespread applications in many research and engineering fields. Artificial neural network systems is one of the hopes available to textile industry to integrate the elements such as production, quality, cost, information, statistical process control, just-in-time manufacturing computer integrated manufacturing etc,. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is a field of computer science that seeks to understand and implement computer based technology that can simulate characteristics of human intelligence (that include learning, adapting, reasoning, self-correction and automatic improvement) and human sensory capabilities. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) are finding applications in textile industry in areas such as fabric engineering, lay planning in garment industry, market prediction, fashion prediction etc The Basics involved in the understanding of the Neural Networks, their properties, construction, Classification - based on application, advantages of neural computing. Next to the basics, Applications of Neural Networks in the area of fabric engineering is covered extensively. To have a clear-cut idea on exactly how the Neural Network works, a real time expert system (using NN) used in Prediction of Fabric end-uses is presented with the principle involved, Prediction network modeling, Training the network, the logic behind the prediction technique etc. Then, the application list extends and covers the use of NN in detecting the fabric faults, grading the color fastness of the fabric, Measurement / Prediction of comfort properties of the fabric.
Neural network is a computational structure. A neural network is a massively parallel distributed processor made up of simple processing units, which has a neural propensity for storing experiential knowledge and making it available for use. It has capability to organize its structural constituents, known as “Neurons”. It can perform certain computations (e.g. fabric pattern, fabric defects, fabric wrinkle, etc.) many times faster than the fastest computer. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is a field of computer science that seeks to understand and implement computer based technology. The Neural Network is understood on the basis of their properties, construction, classification - based on application, advantages of neural computing. Fabric engineering needs a thorough understanding of the functional properties and their construction parameters. When the relationship between a set of interrelated properties goes beyond the complete comprehension of the human brain, neural networks (NNs) could be used to find the unknown function. Neural network describes the method, for the prediction of both construction and performance parameters of fabrics. Accordingly, constructional parameters are used as input for predicting the performance parameter in forward engineering, and the parameters are reversed for the reverse engineering prediction. Comparison between actual results and predicted results is made. An expert system with an embedded artificial neural network (ANN) is also used, with its functionality toward engineered fabric manufacturing.
… Science & IT …, 2009
Neural Network (NN) has emerged over the years and has made remarkable contribution to the advancement of various fields of endeavor. The purpose of this work is to examine neural networks and their emerging applications in the field of engineering, focusing more on Controls. In this work, we have examined the various architectures of NN and the learning process. The needs for neural networks, training of neural networks, and important algorithms used in realizing neural networks have also been briefly discussed. Neural network application in control engineering has been extensively discussed, whereas its applications in electrical, civil and agricultural engineering were also examined. We concluded by identifying limitations, recent advances and promising future research directions.
IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1992
Abstruct-This paper describes the theory and the applications of artificial neural networks, especially in a control field. Artificial neural networks try to mimic the nerve system in a mammalian brain into a mathematical model. Therefore, neural networks have some desirable characteristics and capabilities similar to the brain system, such as parallel processing, learning, nonlinear mapping, and generalization. Recently, many researchers have developed neural networks as new tools in many fields such as pattern recognition, information processing, design, planning, diagnosis, and control. We survey hybrid systems of the neural networks, fuzzy sets, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies. Fuzzy sets and technologies have been also implemented as new tools in many fields and shown to be useful. Therefore, we deal with the hybrid systems as key technologies in the future.
Indonesian Journal of Computer Science, 2022
The neural network model is an advanced and effective tool aims at simulating the manufacturing operations. An important number of researchers have utilized artificial neural network (ANN) to optimising multiple response metrics in manufacturing applications. In the majority of situations, the use of ANN enables the prediction of the mechanical and physical properties of manufacturing goods based on provided technical data. To this end, the deployment of ANN in manufacturing sector is tremendously significant in terms of cost and material resource savings. Thus, Artificial neural network as a key component regarding the optimization of the manufacturing processes.
2003
This paper presents a comprehensive review of the industrial applications of artificial neural networks (ANNs), in the last 12 years. Common questions that arise to practitioners and control engineers while deciding how to use NNs for specific industrial tasks are answered. Workable issues regarding implementation details, training and performance evaluation of such algorithms are also discussed, based on a judiciously chronological organization of topologies and training methods effectively used in the past years. The most popular ANN topologies and training methods are listed and briefly discussed, as a reference to the application engineer. Finally, ANN industrial applications are grouped and tabulated by their main functions and what they actually performed on the referenced papers. The authors prepared this paper bearing in mind that an organized and normalized review would be suitable to help industrial managing and operational personnel decide which kind of ANN topology and training method would be adequate for their specific problems.
Computers & Industrial Engineering, 1992
Advanced manufacturing systems are becoming too complex and dynamic for traditional rule-based decision support systems. Neural network technology application is gathering momentum in all aspects of manufacturing processes. This paper overviews the technology and surveys the literature on its application in manufacturing processes.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (559)
- Golob, D.; Osterman, D. P. & Zupan, J. (2008). Determination of Pigment combinations for Textile Printing Using Artificial Neural Networks. Fibers & Textiles in Eastern Europe, Vol.16, No.3, pp. 93-98, ISSN 1230-3666
- Guruprasad, R. & Behera, B. K. (2010). Soft Computing in Textiles. Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research, Vol.35, pp. 75-84, ISSN 0971-0426
- Hadizadeh, M.; Jeddi, A. A. A. & Amani Tehran, M. (2009). The Prediction of Initial Load- Extension Behavior of Woven Fabrics using Artificial Neural Network. Textile Research Journal, Vol.79, No.17, pp. 1599-1609, ISSN 0040-5175
- Huang, C. C. & Chang, K. T. (2001). Fuzzy Self-Organizing and Neural Network Control of Sliver Linear Density in a Drawing Frame. Textile Research Journal, Vol.71, No.11, pp. 987-992, ISSN 0040-5175
- Hui, C. L.; Lau, T. W.; Ng, S. F. & Chan, K. C. C. (2004). Neural Network Prediction of Human Psychological Perceptions of Fabric Hand. Textile Research Journal, Vol.74, No.5, pp. 375-383, ISSN 0040-5175
- Jeon, B. S.; Bae, J. H. & Suh, M. W. (2003). Automatic Recognition of Woven Fabric Patterns by an Artificial Neural Network. Textile Research Journal, Vol.73, No.7, pp. 645-650, ISSN 0040-5175
- Kang, T. J. & Kim, S. C. (2002). Objective Evaluation of the Trash and Color of Raw Cotton by Image Processing and Neural Network. Textile Research Journal, Vol.79, No.
- 9, pp. 776-782, ISSN 0040-5175
- Karras, D. A.; Karkanis, S. A. & Mertzios, B. G. (1998). Supervised and Unsupervised Neural Network Methods applied to Textile Quality Control based on Improved Wavelet Feature Extraction Techniques. International Journal of Computer Mathematics, Vol.67, No.1&2, pp. 169-181, ISSN 0020-7160
- Keshavaraj, R.; Tock, R.W. & Haycook, D. (1996).Airbag Fabric Material Modeling of Nylon and Polyester Fabrics Using a Very Simple Neural Network Architecture. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, Vol.60, pp. 2329-2338, ISSN 0021-8995
- Khan, Z.; Lim, A. E. K.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. & Beltran, R. (2002). An Artificial Neural Network-based Hairiness Prediction Model for Worsted Wool Yarns. Textile Research Journal, Vol.79, No.8, pp. 714-720, ISSN 0040-5175
- Kumar, A. (2003). Neural Network Based Detection of Local Textile Defects. Pattern Recognition, Vol.36, pp. 1645-1659, ISSN 0031-3203
- Kuo, C. F. J.; Hsiao, K. I. & Wu, Y. S. (2004). Using Neural Network Theory to Predict the Properties of Melt Spun Fibers. Textile Research Journal, Vol.74, No.9, pp. 840-843, ISSN 0040-5175
- Kuo, C. F. J. & Lee, C. J. (2003). A Back-Propagation Neural Network for Recognizing Fabric Defects. Textile Research Journal, Vol.73, No.2, pp. 147-151, ISSN 0040-5175
- Kuo, C. F. J.; Lee, C. J. & Tsai, C. C. (2003). Using a Neural Network to Identify Fabric Defects in Dynamic Cloth Inspection. Textile Research Journal, Vol.73, No.3, pp. 238 244, ISSN 0040-5175
- Kuo, C. F. J.; Su, T. L. & Huang, Y. J. (2007). Computerized Color Separation System for Printed Fabrics by using Backward-Propagation Neural Network. Fibers and Polymers, Vol.8, No.5, pp. 529-536, ISSN 1229-9197
- Leonard, J.; Pirotte, F. & Knott, J. (1998). Classification of Second Hand Textile Waste Based on Near-infrared Analysis and Neural Network. Melliand International, Vol.4, pp. 242-244, ISSN 0947-9163
- Lien, H. C. & Lee, S. (2002). A Method of Feature Selection for Textile Yarn Grading Using the Effective Distance Bettween Clusters. Textile Research Journal, Vol.72, No.10, pp. 870-878, ISSN 0040-5175
- Lin, J. J. (2007). Prediction of Yarn Shrinkage Using Neural Nets. Textile Research Journal, Vol.77, No.5, pp. 336-342, ISSN 0040-5175
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W. & Zhang, Y. (2001). Inspection of Defects in Optical Fibers based on Back- Propagation Neural Networks. Optics Communications, Vol.198, pp. 369-378, ISSN 0030-4018
- Liu, J.; Zuo, B.; Zeng, X.; Vroman, P. & Rabenasolo, B. (2010). Nonwovens Uniformity Identification using Wavelet Texture Analysis and LVQ Neural Network. Expert Systems with Applications, Vol.37, pp.2241-2246, ISSN 0957-4174
- Liu, J.; Zuo, B.; Vroman, P.; Rabenasolo, B.; Zeng, X. & Bai, L. (2010). Visual Quality Recognition of Nonwovens using Wavelet Texture Analysis and Robust Bayesian Neural Network. Textile Research Journal, Vol.80, No.13, pp.1278-1289, ISSN 0040-5175
- Majumdar, P. K. & Majumdar, A. (2002). Predicting the Breaking Elongation of Ring Spun Cotton Yarns using Mathematical, Statistical, and Artificial Neural Network Models. Textile Research Journal, Vol.74, No.7, pp. 652-655, ISSN 0040-5175
- Mokhtari Yazdi, M.; Semnani, D. & Sheikhzadeh, M. (2009). Moisture and Heat Transfer in Hybrid Weft Knitted Fabric with Artificial Intelligence. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, Vol.114, pp. 1731-1737, ISSN 0021-8995
- Moradian, S. & Amani Tehran, M. (2000). Predicting the Degree of Metamerism by Artificial Neural Network, Proceedings of Fifth Seminar on Polymer Science and Technology, pp. 153-156, Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran, September 12-14, 2000
- Mori, T. & Komiyama, J. (2002). Evaluating Wrinkled Fabrics with Image Analysis and Neural Networks. Textile Research Journal, Vol.72, No.5, pp. 417-422, ISSN 0040-5175
- Murrells, C. M.; Tao, X. M.; Xu, B. G. & Cheng, K. P. S. (2009). An Artificial Neural Network Model for the Prediction of Spirality of Fully Relaxed Single Jersey Fabrics. Textile Research Journal, Vol.79, No.3, pp. 227-234, ISSN 0040 5175
- Nirmal, U. (2010). Prediction of Friction coefficient of Treated Betelnut Fiber Reinforced polyester (T-BFRP) Composite using Artificial Neural Networks. Tribology International, Vol.43, pp. 1417-1429, ISSN 0301-679X
- Onal, L.; Zeydan, M.; Korkmaz, M. & Meeran, S. (2009). Predicting the Seam Strength of Notched Webbings for Parachute Assemblies using the Taguchi's Design of Experiment and Artificial Neural Networks. Textile Research Journal, Vol.79, No.5, pp. 468-478, ISSN 0040-5175
- Pynckels, F.; Kiekens, P.; Sette, S.; Van Langenhove, L. & Impe, K. (1995). Use of NeuralNets for Determining the Spinnability of Fibers. Journal of Textile Institute, Vol.86, No.3, pp. 425-437, ISSN 0040-5000
- Rawal, A.; Majumdar, A.; Anand, S. & Shah, T. (2009). Predicting the Properties of Needlepunched Nonwovens using Artificial Neural Network. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, Vol.112, pp. 3575-3581, ISSN 0021-8995
- Semnani, D. & Vadood, M. (2010). Improvement of Intelligent Methods for Evaluating the Apparent Quality of Knitted Fabrics. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Vol.23, pp. 217-221, ISSN 0952-1976
- References
- Box, G. E. P. & Behnken, D. W. (1960). Some New Three Level Designs for the Study of Quantitative Variables. Technometrics, Vol.2, No.4, 455-475, ISSN 0040-1706
- Debnath, C. R. & Roy, A. N. (1999). Mechanical behaviour of needle punched textiles of jute nonwovens. Indian Textile Journal, Vol.110, No.3, 50-53, ISSN 0019-6436
- Debnath, S.; Madhusoothanan, M. & Srinivasmoorthy, V. R. (2000a). Modelling of tensile properties of needle-punched nonwovens using artificial neural networks. Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research, Vol.25, No.1, 31-36, ISSN 0971-0426
- Debnath, S.; Madhusoothanan, M. & Srinivasmoorthy, V. R. (2000b). Prediction of air permeability of needle-punched nonwoven fabrics using artificial neural network and empirical models. Indian Journal of Fibre and Textile Research, Vol.25, No.4, 251- 255, ISSN 0971-0426
- Debnath, S., Nag, D., De, S. S., Ganguly, P. K., & Ghosh, S. K. (2006). Studies on mechanical and hydraulic properties of JGT for geo-technical applications. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India), Vol.TX86, No.2, 46-49, ISSN 0257-4438
- Debnath, S. & Madhusoothanan, M. (2007). Compression behaviour of jute-polypropylene blended needle-punched nonwoven fabrics. Indian Journal of Fibre and Textile Research, Vol.32, No.4, 427-433, ISSN 0971-0426
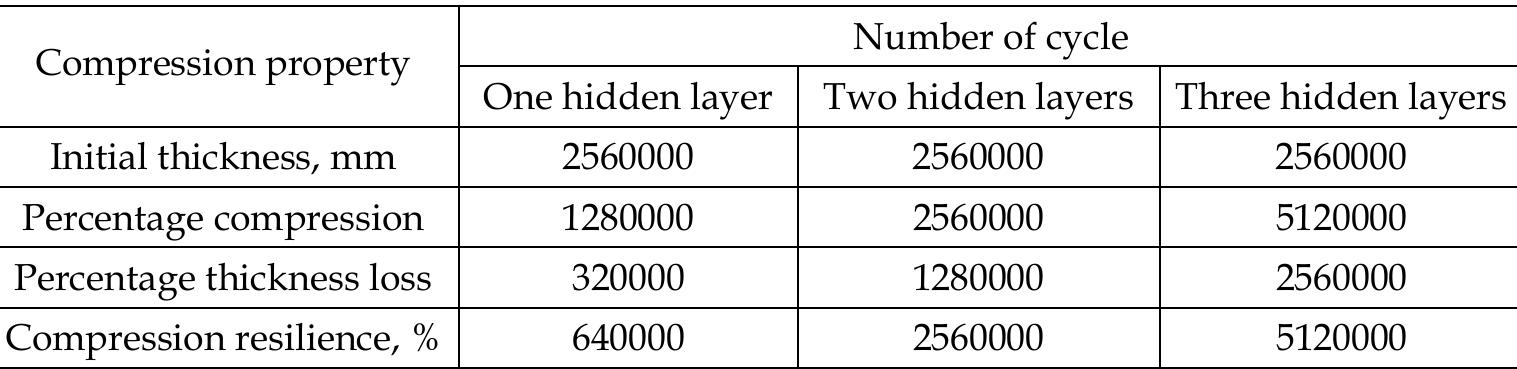
- Debnath, S. & Madhusoothanan, M. (2008). Modeling of compression properties of needle- punched nonwoven fabrics using artificial neural network. Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research, Vol.33, No.4., 392-399, ISSN 0971-0426
- Debnath, Sanjoy & Madhusoothanan, M. (2009a). Compression properties of polyester needlepunched fabric. Journal of Engineered Fibres and Fabrics, Vol.4, No.4, 14-19, ISSN 1558-9250
- Debnath, S. & Madhusoothanan, M. (2009b). Studies on compression behaviour of polypropylene needle punched non-woven fabrics. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India), Vol.TX89, No.2, 34-37, ISSN 0257-4438
- Debnath, Sanjoy & Madhusoothanan, M. (2010a). Water absorbency of jute-polypropylene blended needle-punched nonwoven. Journal of Industrial Textiles, Vol.39, No.3, 215- 231, ISSN 1528-0837, DOI: 10.1177/1528083709347121.
- Debnath, Sanjoy & Madhusoothanan, M. (2010b). Thermal insulation, compression and air permeability of polyester needle-punched nonwoven. Indian Journal of Fibre and Textile Research, Vol.35, No.1, 38-44, ISSN 0971-0426
- Fan, J. & Hunter, L. (1998). A worsted fabric expert system, Part-2: An artificial neural network model for predicting the properties of worsted fabrics. Textile Research Journal, Vol.68, No.10., 763-771, ISSN 0040-5175
- Gong, R. H. & Chen, Y. (1999). Predicting the performance of fabrics in garment manufacturing with artificial neural networks. Textile Research Journal, Vol.69, No.7., 477-482, ISSN 0040-5175
- Hearle, J.W.S. & Sultan, M.A.I. (1967). A study of needled fabrics, Part-I: Experimental methods and properties. Journal of Textile Institute, Vol.58, Part-1, No.6, 251-265, ISSN 0040-5000
- Kothari, V. K., & Das, A. (1992). Compression behaviour of nonwoven geotextiles. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, Vol.11, 235-253, ISSN 0266-1144
- Kothari, V. K., & Das, A. (1993). Compression behaviour of layered needle-punched nonwoven geotextiles. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, Vol.12, 179-191, ISSN 0266- 1144
- Luo, C., and David, A. L. (1995). Yarn strength prediction using neural networks, Part I: Fibre properties and yarn strength relationship. Textile Research Journal, Vol.65, No.9., 495-500, ISSN 0040-5175
- Midha, V. K., Alagirusamy, R. & Kothari, V. K. (2004). Studied on properties of hollow polyester needle-punched fabrics. Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research, Vol.29, No.4., 391-399, ISSN 0971-0426
- Park, S. W., Hwang, Y. G., Kang, B. C. & Yeo, S. W. (2000). Applying fuzzy logic and neural networks to total hand evaluation of knitted fabrics. Textile Research Journal, Vol.70, No.8., 675-681, ISSN 0040-5175
- Postle, R. (1997). Fabric catagorisation by means of objective measurement and neural networks. Textile Asia, Vol.28, No. 2, 33-34, ISSN 0049-3554
- Rajamanickam, R., Hansen, S. M. & Jayaraman, S. (1997). Analysis of the modelling methodologies for predicting the strength of air-jet spun yarns. Textile Research Journal, Vol.67, No.1., 39-44, ISSN 0040-5175
- Ramesh, M. C., Rajamanickam, R., & Jayaraman, S. (1995). The Prediction of yarn tensile properties by using artificial neural networks. Textile Research Journal, Vol.86, No.3., 459-469, ISSN 0040-5175
- Sao, K.P. & Jain, A. K. (1995). Mercerization and crimp formation in jute. Indian Journal of Fibre and Textile Research, Vol.20, No.4, 185-191, ISSN 0971-0426
- Sengupta, A. K., Sinha, A. K. & Debnath, C. R. (1985). Needle-punched non-woven jute floor coverings: Part III -Air permeability and thermal conductivity. Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research, Vol.10, No.4., 147-151, ISSN 0971-0426
- Subramaniam, V., Malathi, Lokanadam, B., Kumari. N. & Chandramohan, G. (1990). A simple method of measuring the handle of fabrics and softness of yarns. Journal of Textile Institute, Vol.81, Part-1, No.1., 94-97, ISSN 0040-5000
- Vangheluwe, L., Sette, S., & Pynckels, F. (1993). Assessment of set marks by means of neural nets. Textile Research Journal, Vol.63, No.4., 244-246, ISSN 0040-5175
- Vangheluwe, L., Sette, S., & Kiekens P. (1996). Modelling relaxation behaviour of yarns, Part-II: Backpropagation neural network model. Journal of Textile Institute, Vol.87, Part-1, No.2., 305-310, ISSN 0040-5000
- Wen Chen P., Chun Liang T., Fai You H., Li Sun W., Chueh Wang N., Chyilin H. and Cherng Lien R. (1998). Classifying textile faults with a back propagation neural network using power spectra. Textile Research Journal, Vol.68, No.2., 121-126, ISSN 0040-5175
- Xu, B., Fang, C. & Watson, M. D. (1999). Clustering analyses for cotton trash classification. Textile Research Journal, Vol.69, No.9., 656-662, ISSN 0040-5175
- Zhu, R. & Ethridge, M. D. (1997). Predicting hairiness for ring and rotor spun yarns and analysing the impact of fibre properties. Textile Research Journal, Vol.67, No.9., 694- 698, ISSN 0040-5175
- References
- Aguilera, J.A.; Aragón, C.; Cristoforetti, G. & Tognoni, E. (2009) Application of calibration- free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy to radially resolved spectra from a copper-based alloy laser-induced plasma, Spectrochimica Acta Part B, Vol. 64, No. 7, (July 2009) pp. 685-689, ISSN: 05848547
- Belkov, M.V.; Burakov, V.S.; De Giacomo, A.; Kiris, V.V.; Raikov, S.N. & Tarasenko, N.V. (2009) Comparison of two laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy techniques for total carbon measurement in soils, Spectrochimica Acta Part B, Vol. 64, No. 9, (September 2009) pp. 899-904, ISSN: 05848547
- Bousquet, B.; Sirven, J.-B. & Canioni, L. (2007) Towards quantitative laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis of soil samples, Spectrochimica Acta Part B, Vol. 62, No. 12, (December 2007) pp. 1582-1589, ISSN: 05848547
- Cho, H.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Jo, Y.S.; Kitagawa, K.; Arai, N. & Lee, Y.I. (2001) Application of laser- induced breakdown spectrometry for direct determination of trace elements in starch-based flours, Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, Vol. 16, No. 6, (June 2001) pp. 622-627, ISSN: 02679477
- Ciucci, A.; Corsi, M.; Palleschi, V.; Rastelli, S.; Salvetti, A. & Tognoni, E. (1999) New procedure for quantitative elemental analysis by laser-induced plasma spectroscopy, Applied Spectroscopy, Vol. 53, No. 8, (August 1999) pp. 960-964, ISSN: 00037028
- Clegg, S.M.; Sklute, E.; Dyar, M.D.; Barefield, J.E. & Wien, R.C (2009) Multivariate analysis of remote laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy spectra using partial least squares principal, component analysis, and related techniques, Spectrochimica Acta Part B, Vol. 64, No. 1, (January 2009) pp. 79-88, ISSN: 05848547
- Cremers, D.A. & Radziemski, L.J. (2006) Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN: 978-0-470-09299-6, USA
- Eppler, A.S.; Cremers, D.A.; Hickmott, D.D.; Ferris, M.J. & Koskelo, A.C. (1996) Matrix effects in the detection of Pb and Ba in soils using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, Applied Spectroscopy, Vol. 50, No. 9, (September 1996) pp. 1175-1181, ISSN: 00037028
- Escudero-Sanz, I.; Ahlers, B. & Courrèges-Lacoste, G.B. (2008) Optical design of a combined Raman-laser-induced-breakdown-spectroscopy instrument for the European Space Agency ExoMars Mission, Optical Engineering, Vol. 47. No. 3, (March 2008) pp. 033001-1 -033001-11, ISSN: 00913286
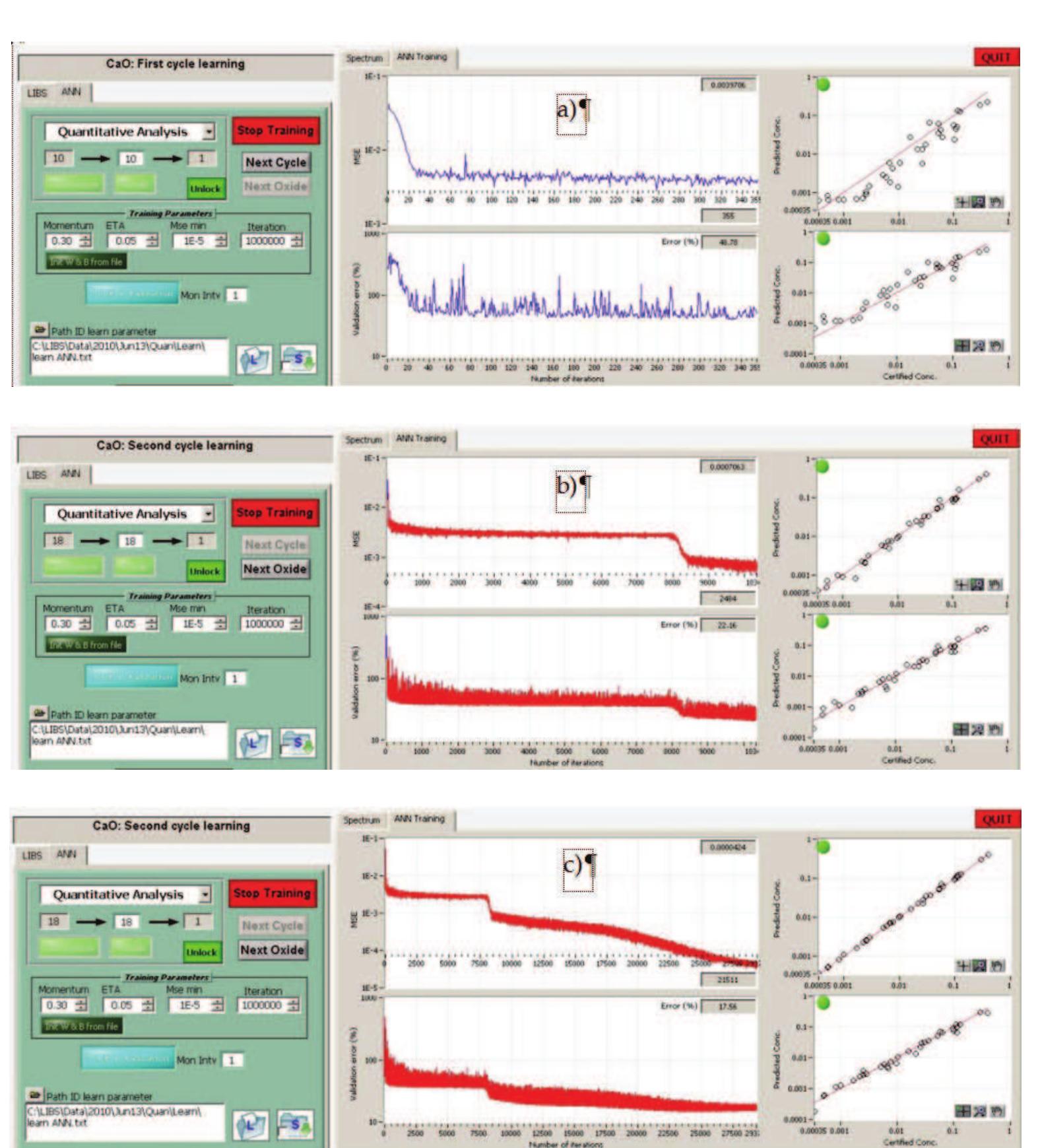
- Ferreira, E. C.; Milori, D.M.B.P.; Ferreira, E.J.; Da Silva, R.M. & Martin-Neto, L. (2008) Artificial neural network for Cu quantitative determination in soil using a portable laser induced breakdown spectroscopy system, Spectrochimica Acta Part B, Vol. 63., No. 10, (October 2008) pp. 1216-1220, ISSN: 05848547
- Gaft, M.; Nagli, L.; Fasaki, I.; Kompitsas, M. & Wilsch, G. (2009) Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for on-line sulfur analyses of minerals in ambient conditions, Spectrochimica Acta Part B, Vol. 64, No. 10, (October 2009) pp. 1098-1104, ISSN: 05848547
- Garrelie, F. & Catherinot, A. (1999) Monte Carlo simulation of the laser-induced plasma- plume expansion under vacuum and with a background gas, Applied Surface Science, Vol. 138-139, No. 1-4, (January 1999) pp. 97-101, ISSN: 01694332
- Gurney K. (1997) An Introduction to Neural Networks, UCL Press, ISBN: 0-203-45151-1, UK Harmon, R.S.; DeLucia, F.C.; McManus, C.E.; McMillan, N.J.; Jenkins, T.F.; Walsh, M.E. & Miziolek, A. (2006) Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy -An emerging chemical sensor technology for real-time field-portable, geochemical, mineralogical, and environmental applications, Applied Geochemistry, Vol. 21, No. 5, (May 2006) pp. 730-747, ISSN: 08832927
- References
- Abdalla, J. A., & Hawileh, Rami., (in press). Modeling and simulation of low-cycle fatigue life of steel reinforcing bars using artifiial neural network. Journal of the Franklin Institute, ISSN 0016-0032
- Bahrami, A., Mousavi Anijdan, S. H., & Ekrami, A., (2005). Prediction of Mechanical Properties of DP Steels Using Neural Network Model. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, Vol.392, No.1-2, (April 2005), pp. 177-182, ISSN 0925-8388
- Bucar, T., Nagode, M., & Fajdiga, M., (2006). A Neural Network Approach to Describing the Scatter of S-N Curves. International Journal of Fatigue, Vol.28, No.4, (April 2006), pp. 311-323, ISSN 0142-1123
- Fogel, D. B., (1994). An Introduction to Simulated Evolutionary Optimization. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, Vol.5, No.1, (1994), pp. 3-14, ISSN 1045-9227
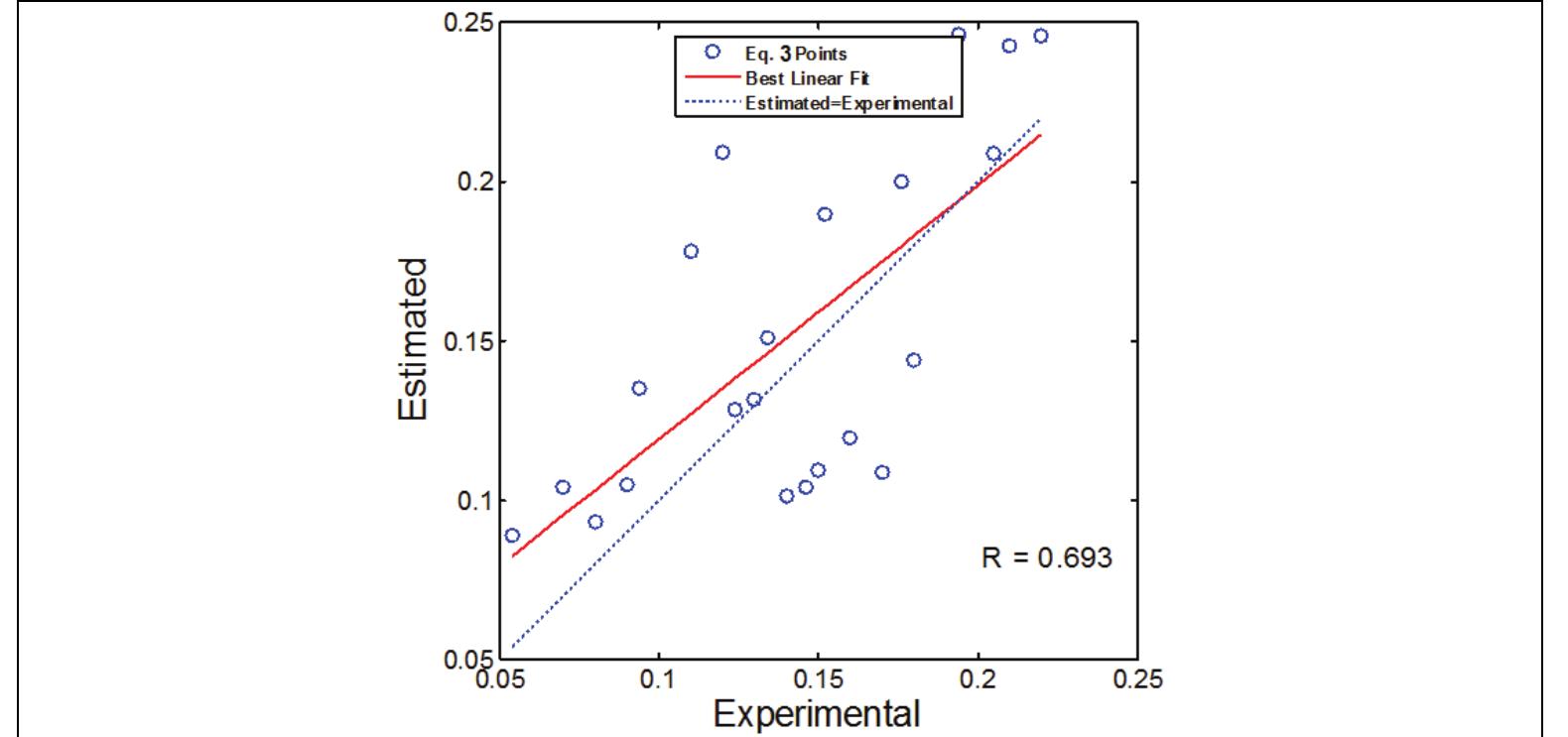
- Genel, K., (2004). Application of Artificial Neural Network for Predicting Strain-Life Fatigue Properties of Steels on the Basis of Tensile Data. International Journal of Fatigue, Vol.26, No.10, (October 2004), pp. 1027-1035, ISSN 0142-1123
- Ghajar, R.; Alizadeh, J., & Naserifar, N., (2008). Estimation of cyclic strain hardening exponent and cyclic strength coefficient of steels by artificial neural networks, Proceedings of ASME 2008 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, pp. 639-648, ISBN 978-0-7918-4873-9, Boston, Massachusetts, USA, November 2-6, 2008.
- Hagan, M. T., & Menhaj, M. B., (1994). Training Feedforward Networks with the Marquardt Algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, Vol.5, No.6, (1994), pp. 989-993, ISSN 1045-9227
- Han, Y. L., (1995). Artificial Neural Network Technology as a Method to Evaluate the Fatigue Life of Weldments with Welding Defects. International Journal of Pressure Vessels & Piping, Vol.63, No.2, (1995), pp. 205-209, ISSN 0308-0161
- Kim, K. S., Chen, X., Han, C., & Lee, H. W., (2002). Estimation Methods for Fatigue Properties of Steels under Axial and Torsional Loading. International Journal of Fatigue, Vol.24, No.7, (July 2002), pp. 783-793, ISSN 0142-1123
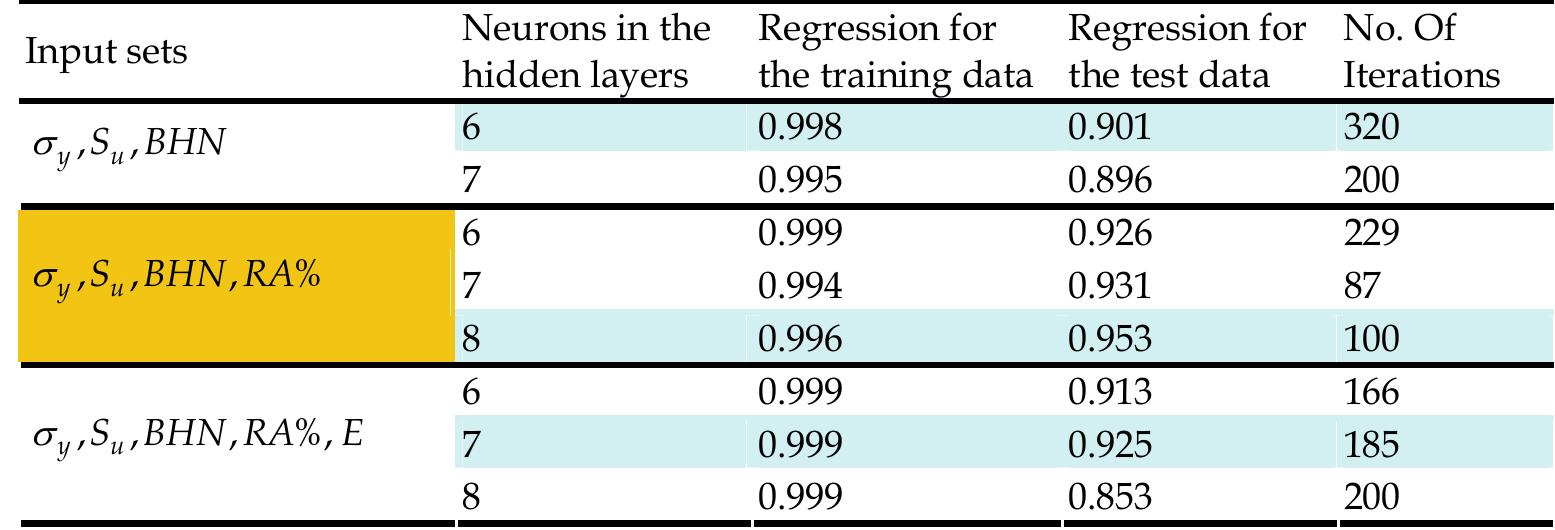
- Koker, R., Altinkok, N., & Demir, A., (2007). Neural network based prediction of mechanical properties of particulate reinforced metal matrix composites using various training algorithms. Materials and Design, Vol.28, No.2, (2007), pp. 616-627, ISSN 0264-1275
- Lee, J. A., Almond, D. P., & Harris, B., (1999). The Use of Neural Networks for the Prediction of Fatigue Lives of Composite Materials. Composites: PartA: Applied Scienceand Manufacturing, Vol.30, No.10, (October 1999), pp. 1159-1169, ISSN 1359-835X
- Liao, X., Xu, W., & Gao, Z., (2008). Application of Artificial Neural Network to Forecast the Tensile Fatigue Life of Carbon Material. Key Engineering Materials, Vol.385-387, (July 2008), pp. 385-387, ISSN 1662-9795
- Malinov, S., Sha, W., & McKeown, J. J., (2001). Modelling the Correlation Between Processing Parameters and Properties in Titanium Alloys Using Artificial Neural Network. Computational Materials Science, Vol.21, No.3, (July 2001), pp. 375-394, ISSN 0927-0256
- Mathew, M. D., Kim, D. W., & Ryu, W. S., (2008). A neural network model to predict low cycle fatigue life of nitrogen-alloyed 316L stainless steel. Materials Science and Engineering A, Vol.474, No.1-2, (February 2008), pp. 247-253, ISSN 0921-5093
- Mathur, S., Gopeand, P. C., & Sharma, J. K., (2007). Prediction of Fatigue Lives of Composites Material by Artificial Neural Network, Proceedings of the SEM2007 Annual Conference and Exposition, Paper 260, Springfield, Massachusetts, USA, June4-6, 2007
- Mousavi Anijdan, S. H., Bahrami, A., & Mater, J., (2005). A New Method in Prediction of TCP Phases Formation in Superalloys. Materials Science and Engineering A, Vol.396, No.1-2, (April 2005), pp. 138-142, ISSN 0921-5093
- Muc, A., & Gurba, W., (2001). Genetic Algorithms and Finite Element Analysis in Optimization of Composite Structures. Composite Structures, Vol.54, No.2-3, (November-December 2001), pp. 275-281, ISSN 0263-8223
- Park, J. M., & Kang, H. T., (2007). Prediction of Fatigue Life for Spot Welds Using Back- Propagation Neural Networks. Materials and Design, Vol.28, No.10, (2007), pp. 2577- 2584, ISSN 0261-3069
- Pleune, T. T., & Chopra, O. K., (2000). Using Artificial Neural Networks to Predict the Fatigue Life of Carbon and Low-Alloy Steels. Nuclear Engineering and Design, Vol.197, No.1-2, (April 2000), pp. 1-12, ISSN 0029-5493
- Roessle, M. L., & Fatemi, A., (2000). Strain-Controlled Fatigue Properties of Steels and Some Simple Approximations. International Journal of Fatigue, Vol.22, No.6, (July 2000), pp. 495-511, ISSN 0142-1123
- SAE Standards (2002). Technical Report on Low Cycle Fatigue Properties: Ferrous and Nonferrous Materials, SAE, Report Number: J1099, Warren dale, PA
- Sha, W., & Edwards, K. L., (2007). The use of artificial neural networks in materials science based research. Materials and Design, Vol.28, No.6, (2007), pp. 1747-1752, ISSN 0261- 3069
- Song, R. G., Zhang, Q. Z., Tseng, M. K., & Zhang, B. J., (1995). The Application of Artificial Neural Networks to the Investigation of Aging Dynamics in 7175 Aluminium Alloys. Materials Science and Engineering C, Vol.3, No.1, (October 1995), pp. 39-41, ISSN 0928-4931
- Srinivasan, V. S., Valsan, M., Roa, K. B. S., Mannan, S. L., & Raj, B., (2003). Low Cycle Fatigue and Creep-Fatigue Interaction Behavior of 316L(N) Stainless Steel and Life Prediction by Artificial Neural Network Approach. International Journal of Fatigue, Vol.28, No.12, (December 2003), pp. 1327-1338, ISSN 0142-1123
- Stephens, R. I., Fatemi, A., Stephens, R. R., & Fuchs, H. O., (2001). Metal Fatigue in Engineering, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 9780471510598, Canada
- Venkatessh, V., & Rack, H. J., (1999). A Neural Network Approach to Elevated Temperature Creep-Fatigue Life Prediction. International Journal of Fatigue, Vol.21, No.3, (March 1999), pp. 225-234, ISSN 0142-1123
- Wong, K. P., & Wong, Y. W., (1995). Thermal Generator Scheduling Using Hybrid Genetic/ Simulated-Annealing Approach. IEEE Proceedings on Generation, Transmission and Distribution, Vol.142, No.4, (July 1995), pp. 372-380, ISSN 1350-2360
- References
- Altinkok N. & Korker R. N. (2004). Neural Network Approach to Prediction of Bending Strength and Hardening Behaviour of Particulate Reinforced (Al-Si-Mg)
- Aluminium Matrix Composites. Materials and Design, Vol. 25, No. 7, Oct, 2004, pp. 595-602, ISSN 0261-3069
- Altinkok N. & Korker R. N. (2005). Mixture and Pore Volume Fraction in Al 2 O 3 /SiC Ceramic Cake Using Artificial Neural Networks. Materials and Design, Vol. 26, No. 4, Jun, 2005, pp. 305-311, ISSN 0261-3069
- Gen M. & Cheng R. (2000). Genetic algorithm and Engineering Optimization, Wiley, ISBN 0-471- 31531-1, New York
- Gu X.Q.; Yi D.X & Liu C.H. (2006). Optimization of Topological Structure and Weight Value of Artifical Neural Network using Genetic Algorithm. Journal of Guangdong University of Technology, Vol. 23, No. 4, 2006, pp. 64-69, ISSN 1007-7162 (in Chinese)
- Gupta J.N.D. & Sexton R.S. (1999). Comparing Back propagation with a Genetic Algorithm for Neural Network Training. The International Journal of Management Science. Vol. 27, Dec, 1999, pp. 679-684, ISSN 1226-0797
- Huang C.Z.; Zhang L.; He L.; Sun J.; Fang B. & B. Zou. J. (2002). A Study on the Prediction of the Mechanical Properties of a Ceramic Tool Based on an Artificial Neural Network. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 129, Oct, 2002, pp. 399-402, ISSN 0924-0136
- Jiang X. & Adeli H. (2004). Clustering-Neural Network Models for Freeway Work Zone Capacity Estimation. International Journal of Neural Systems, Vol. 14, No. 3, Jun, 2004, pp. 147-163, ISSN 0129-0657
- Kim B. & Bae J. (2005). Prediction of Plasma Processes Using Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. Solid-State Electronics, Vol. 49, Oct, 2005, pp. 1576-1580, ISSN 0038-1101
- Mousavi Anijdan S.H.; Madaah-Hosseini H.R. & Bahrami A. (2007). Flow stress Optimization for 304 Stainless Steel under Cold and Warm Compression by Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. Materials and Design, Vol. 28, 2007, pp. 609-615, ISSN 0261-3069
- Ozcelik B.; Oktem H. & Kurtaran H. (2005). Surface Roughness in End Milling Inconel 718 by Coupling Neural Network Model and Genetic Algorithm. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 27, 2005, pp. 234-241, ISSN 0268- 3768
- Scott D.J.; Coveney P.V.; Kilner J.A.; Rossing J.C.H.; Alford N.M. & Ceram J. (2007). Prediction of the Functional Properties of Ceramic Materials from Composition Using Artificial Neural Networks. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, Vol. 27, Dec, 2007, pp. 4425-4435, ISSN 0955-2219
- Sexton R.S.; Dorsey R.E. & Johnson J.D. (1998). Toward Global Optimization of Neural Network: A Comparison of the Genetic Algorithm and Backpropagation. Decision Support Systems. Vol. 22, Feb, 1998, pp. 171-185, ISSN 0167-9236
- Yao X. (1999). Evolving Artificial Neural Network, Proceedings of IEEE, pp. 1423-1447, ISBN 0018-9219, Sep 1999, IEEE Press. Vol. 87
- Yen G.& Lu H. M. (2002). Hierarchical Genetic Algorithm for Near-Optimal Feed Forward Neural Network Design. International Journal Neural Systems, Vol. 12, No. 1, Feb, 2002, pp. 31-43, ISSN 0129-0657
- Zemin F.; Jianhua M. & Lin C. (2010). Using Genetic Algorithm-Back Propagation Neural Network Prediction and Finite-element Model Simulation to Optimize the Process of Multiple-step Incremental Air-bending Forming of Sheet Metal. Materials and Design, Vol. 31, Jan, 2010, pp. 267-277, ISSN 0261-3069
- Zhu D.Q. & Shi H. (2006). The Principle and Application of Artificial Neural Networks, Science Press, ISBN 7-03-016570-5, Beijing (in Chinese)
- Botlani-Esfahani.
- M, Toroghinejad. M. R. and Abbasi. Sh. (2009b) Artificial Neural Network Modeling the Tensile Strength of Hot Strip Mill Products. ISIJ International 49:10, 1583-1587
- Doan. C. D. and Yuiliong. S. (2004) Generalization for Multilayer Neural Network Bayesian Regularization or Early Stopping. Proc. of Asia Pacific Association of Hydrology and Water Resources 2nd Conference, APHW, Singapore, 1
- Gonzalez. JEG. (2002) Study of the effect of hot rolling processing parameters on the variability of HSLA steels, Master thesis, University of Pittsburgh, USA Hulka. K. (2003): Niobium Information, 17/98, http://www.cbmm.com.br Keytosteel.com. Control of high strength low alloy (HSLA) steel properties. www. keytosteel.com
- Lampinen. J. and Vehtari. A. (2001) Bayesian techniques for neural networks -review and case studies. In K. Wang, J Grundespenkis, and A. Yerofeyev, editors, Applied Computational Intelligence to Engineering and Business, 7-15.
- MacKay DJC. (1992) A practical Bayesian framework for back-propagation networks. Neural Computation. 4, 415-47.
- MathWorks,Inc.http://www.mathworks.com/access/helpdesk/help/pdf- doc/nnet/nnet.pdf, Nat-ick, MA, USA
- MEYER, L (2001). History of Niobium as a microalloying element." In: Proceedings of the International Symposium Niobium 2001. Niobium Science and Technology. Niobium 2001 Ltd. Bridgeville: Pa, USA. 359-377
- Preloscan. A., Vodopivec. F., Mamuzic. I. (2002) Fine-Grained Structural Steel with Controlled Hot Rolling. Materiali in Tehnologije, 36, 181.
- Parker. S.V. (1997) Modeling phase transformation in hot-rolling steels. PhD Thesis, University of Cambridge, UK
- Ryu. J. (2008). Model for mechanical properties of hot-rolled steels, Master thesis, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Korea
- Singh. S. B., Bhadeshia. H. K. D. H, MacKay. D. J. C., Carey. H, and Martin. I. (1998) Neural Network Analysis of Steel Plate Processing. Ironmaking Steelmaking, 25, 355.
- Umemoto. M., Liu. Z.G., Masuyama. K., Tsuchiya. K. (2001): Influence of Alloy Additions on Production and Propeties of Bulk Centite. Scripta. Materialia., 45, 39.
- Zhang. Y. B., Ren. D.Y. (2003) Distribution of strong carbide forming elements in hard facing weld metal. Materials. Science and Technology., 19:8. 1029-103.
- Vehtari. A., and Lampinen. J. (2002), Bayesian model assessment and comparison using cross-validation predictive densities, Neural Computation, 14, 2439.
- Xu. M., Zeng. G., Xu. X., Huang. G., Jiang. R. and Sun. W. (2006) Application of Bayesian Regularized BP Neural Network Model for Trend Analysis, Acidity and Chemical Composition of Precipitation in North Carolina. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 172, 167. artificial neural network . International Journal of Coal Geology, Volume 73, Issue 2, 130-138.
- Bragg, L.J. ; Oman, J.K. ; Tewalt, S.J. ; Oman, C.J. ; Rega, N.H. ; Washington, P.M. & Finkelman, R.B. (2009). U.S. Geological Survey Coal Quality (COALQUAL) database version 2.0. open-file report 97-134, http://energy.er.usgs.gov/ products/databases/CoalQual/index.htm.
- Chong-lin, W. ; Cao-yuan, M. ; Jian-hua, L. ; Guo-xin, L. ; Dong-liang, Z. & Jie-jie, T. (2009). Study on coal face stray current safety early warning based on ANFIS, Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, Volume 1, Issue 1, 1332-1336.
- Chen, S. ; Cowan, C.F.N. & Grant, P.M. (1991). Orthogonal least squares learning algorithm for radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks, 2 (2), 302-309.
- Custer, V.F. (1951). Uber die Berechnung des Heizwertes von Kohlen der Immediatzusammensetzung. Brennst.-Chem, 32, 19-20.
- Channiwala, S.A. & Parikh, P.P. (2002). A unified correlation for estimating HHV of solid, Liquid and gaseous fuels. Fuel, 81, 1051-1063.
- Chehreh Chelgani, S. ; Hower, J.C. ; Jorjani, E. ; Mesroghli, Sh. & Bagherieh, A.H. (2008). Prediction of coal grindability based on petrography, proximate and ultimate analysis using multiple regression and artificial neural network models, Fuel Processing Technology, Volume 89, Issue 1, 13-20.
- Chehreh Chelgani, S. ; Mesroghli, Sh. & Hower, J.C. (2010). Simultaneous prediction of coal rank parameters based on ultimate analysis using regression and artificial neural network. International Journal of Coal Geology, Volume 83, Issue 1, 31-34.
- Esen, H. & Inalli, M. (2010). ANN and ANFIS models for performance evaluation of a vertical ground source heat pump system , Expert Systems with Applications, Volume 37, Issue 12, 8134-8147.
- Given, P.H. ; Weldon, D. & Zoeller, J.H. (1986). Calculation of calorific values of coals from ultimate analyses: theoretical basis and geochemical implications. Fuel, 65, 849-854.
- Hower, J.C. & Eble, C.F. (1996). Coal quality and coal utilization. Energy Miner. Div. Hourglass 30 (7), 1-8.
- Hansen, J.V. & Meservy, R.D. (1996). Learning experiments with genetic optimization of a generalized regression neural network. Decis. Support Syst., 18 (3-4), 317-325.
- Jorjani, E., Chehreh Chelgani, S. & Mesroghli, Sh. (2007). Prediction of microbial desulfurization of coal using artificial neural networks , Minerals Engineering, Volume 20, Issue 14, 1285-1292.
- Jorjani, E. ; Mesroghli, Sh. & Chehreh Chelgani, S. (2008). Prediction of operational parameters effect on coal flotation using artificial neural network. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, Mineral, Metallurgy, Material, Volume 15, Issue 5, 528-533.
- Jantzen J. (1998). Neurofuzzy modelling, Technical University of Denmark, Department of Automation, Tech. report no 98-H-874, 1-28.
- Jang, J.S.R. & Sun, C.T. (1995). Neuro-fuzzy modeling and control, Proceedings of the IEEE, 83(3): 378-406.
- Khandelwal, M. & Singh, T.N. (2010). Prediction of macerals contents of Indian coals from proximate and ultimate analyses using artificial neural networks, Fuel, Volume 89, Issue 5, 1101-1109.
- Karacan, C.O. (2007). Development and application of reservoir models and artificial neural networks for optimizing ventilation air requirements in development mining of coal seams, International Journal of Coal Geology, Volume 72, Issues 3-4, 221-239.
- Mason, D.M. & Gandhi, K.N. (1983). Formulas for calculating the calorific value of coal and chars. Fuel Process. Technol. 7, 11-22.
- Miller, B.G. (2005). Coal Energy Systems, Elsevier Academic Press, ISBN: 0-12-497451-1, USA.
- Mazumdar, B.K. (1954). Coal systematics: deductions from proximate analysis of coal part I. J. Sci. Ind. Res., 13B (12), 857-863.
- Majumder, A.K. ; Jain, R. ; Banerjee, J.P. & Barnwal, J.P. (2008). Development of a new proximate analysis based correlation to predict calorific value of coal. Fuel, 87, 3077-3081.
- Mesroghli, Sh. ; Jorjani, E. & Chehreh Chelgani, S. (2009). Estimation of gross calorific value based on coal analysis using regression and artificial neural networks. International Journal of Coal Geology, 79, 49-54.
- Patel, S.U. ; Kumar, B.J. ; Badhe, Y.P. ; Sharma, B.K. ; Saha, S. ; Biswas, S. ; Chaudhury, A. ; Tambe, S.S. & Kulkarni, B.D. (2007). Estimation of gross calorific value of coals using artificial neural. Fuel, Volume 86, Issue 3, 334-344.
- Pena, B. ; Teruel, E. & Diez, L.I. (2010). Soft-computing models for soot-blowing optimization in coal-fired utility boilers, Applied Soft Computing, In Press, Corrected Proof.
- Parikh, J. ; Channiwala, S.A. & Ghosal, G.K. (2005). A correlation for calculating HHV from proximate analysis of solid fuels. Fuel, 84, 487-494.
- Soltani, F. ; Kerachian, R. & Shirangi, E. (2010). Developing operating rules for reservoirs considering the water quality issues: Application of ANFIS-based surrogate models, Expert Systems with Applications, Volume 37, Issue 9, 6639-6645.
- Specht, D.F. (1991). A generalized regression neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw., 2(5), 568-576.
- Salehfar, H. & Benson, S.A. (1998). Electric utility coal quality analysis using artificial neural network techniques, Neurocomputing, Volume 23, Issues 1-3, 195-206.
- Spooner, C.E. (1951). Swelling power of coal. Fuel, 30, 193-202. SPSS. (2004). Help Files, Version 13, SPSS Inc.
- Wu, Q.; Ye, S. & Yu, J. (2008). The prediction of size-limited structures in a coal mine using Artificial Neural Networks. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, Volume 45, Issue 6, 999-1006.
- Wasserman, P.D. (1993). Advanced methods in neural computing. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 155-161.
- Zhenyu, Z. & Yongmo, X. (1996). Introduction to fuzzy theory, neural networks, and their applications. Beijing/Nanning: Tsinghua University Press/Guangxi Science and Technology Press, in Chinese.
- Sahu, H.B. ; Padhee, S. & Mahapatra, S.S. (2010). Prediction of spontaneous heating susceptibility of Indian coals using fuzzy logic and artificial neural network models, Expert Systems with Applications, In Press, Uncorrected Proof.
- References
- Brown, B. M. (1987). A Comparison of AC and DC Resistance Welding of Automotive Steels. The Welding Journal, Vol. 66, No. 1, January 1987, pp. 8-23
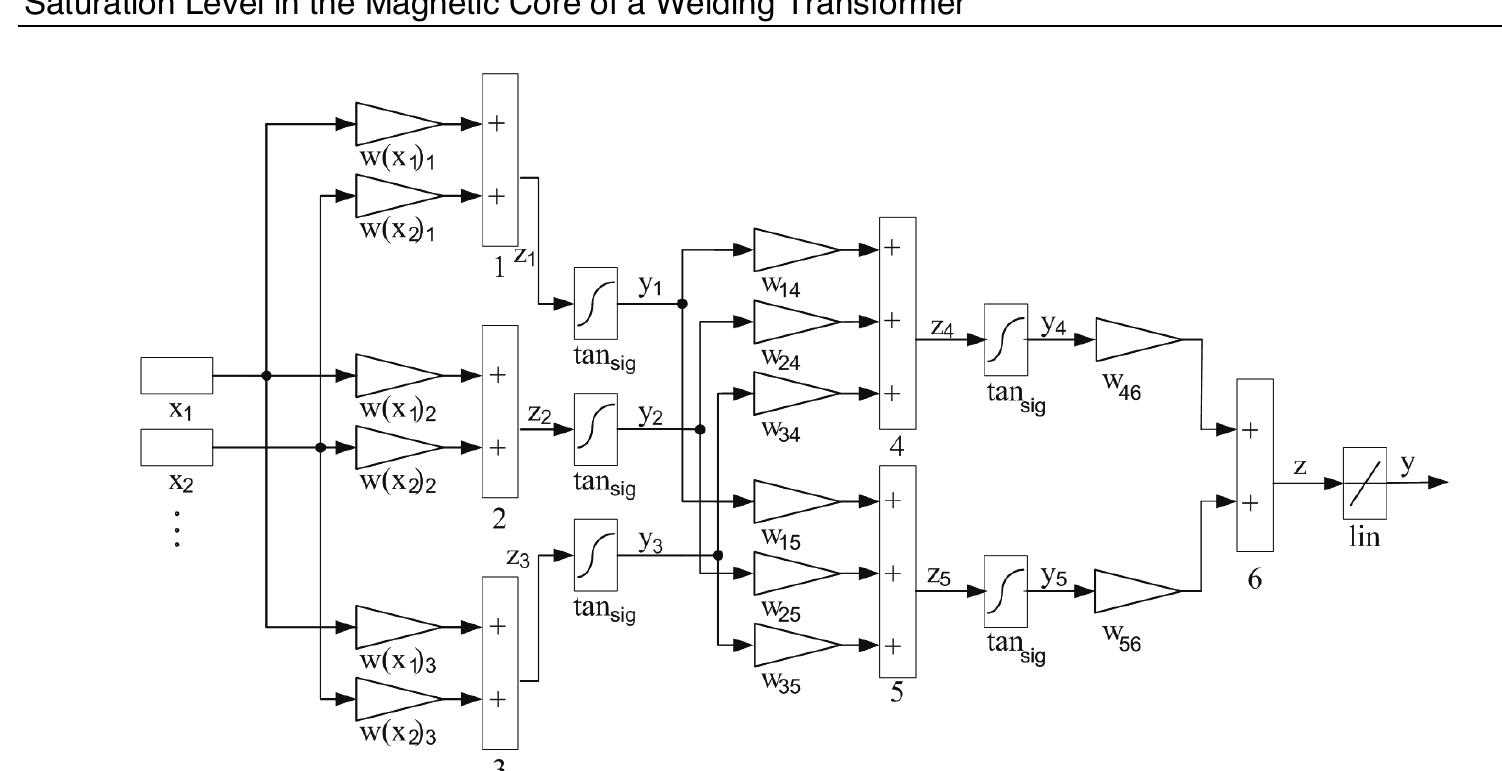
- Deželak, K.; Pihler, J.; Štumberger, G.; Klopčič, B. & Dolinar, D. (2010). Artificial Neural Network Applied for Detection of Magnetization Level in the Iron core of a Welding Transformer. IEEE Trans. On Magnetics, Vol. 46, No. 2, February 2010, pp. 634-637
- Deželak, K.; Klopčič, B.; Štumberger, G. & Dolinar, D. (2008). Detecting Saturation Level in the Iron Core of a Welding Transformer in a Resistance Spot-Welding System. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 320, No. 20, October 2008, pp. 878- 883
- Deželak, K.; Štumberger, G.; Klopčič, B.; Dolinar, D. & Pihler, J. (2008). Iron Core Saturation Detector Supplemented by an Artificial Neural Network. Prz. Elektrotech., Vol. 84, No. 12, 2008, pp. 157-159
- Hassoun, H. M. (1995). Fundamentals of Artificial Neural Networks, Library of Congress Cataloging, 0-262-08239-X, Massachusetts Institute of Technology Hoyong, K.; Yunseok, K. & Kyung-Hee, J. (1993). Artificial Neural Network Based Feeder Reconfiguration for Loss Reduction in Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. On Power Delivery, Vol. 8, No. 3, 1993, pp. 1356-1366
- Klopčič, B.; Dolinar, D. & Štumberger, G. (2008). Advanced Control of a Resistance Spot Welding System. IEEE Trans. On Power Electronics, Vol. 23, No. 1, January 2008, pp. 144-152
- Leon, F. & Semlyen, A. (1994). Complete Transformer Model for Electromagnetic Transients. IEEE Trans. On Power Delivery, Vol. 9, No. 1, January 1994, pp. 231-239
- Pihler, J.; Grčar, B. & Dolinar, D. (1997). Improved Operation of Power Transformer Protection Using Artificial Neural Network. IEEE Trans. On Power Delivery, Vol. 12, No. 3, 1997, pp. 1128-1136
- Ramboz, D. J. (1996). Machinable Rogowski Coil, Design, and Calibration. IEEE Trans. Instrumentation and Measurement, Vol. 45, No. 2, April 1996
- Sabate, J. A.; Vlatkovic, V.; Ridley, R. B.; Lee, F. C. & Cho, B. H. (1990). Design Considerations for High-voltage High-power Full Bridge Zero Voltage-switching PWM Converter. IEEE Appl. Power Electron., Conference, 1990, pp. 275-284
- Štumberger, G.; Klopčič, B.; Deželak, K. & Dolinar, D. (2010). Prevention of Iron Core Saturation in Multi-Winding Transformer for DC-DC Converters. IEEE Trans. On Magnetics, Vol. 46, No. 2, February 2010, pp. 582-585 Paper 1.2, 8-9 th August 2002 Nagpur , organized by Laxminarayan Institute of Technology, Nagpur, India
- Beluhan Damir, & Beluhan Sunica (2000). Hybrid modeling approach to on-line estimation of yeast biomass concentration in industrial bioreactor, Biotechnology Letters 22(8), pp. 631-635
- Bhattacharya Suvendu, Patel Bhavesh K, & Agarwal Kalpesh (2003). Enrobing of foods: Simulation study and application of artificial neural network for development of products. Proceedings of International Food Convention "Innovative Food Technologies and Quality Systems Strategies for Global Competitiveness" IFCON 2003, Poster no TC- 32, pp 172, Mysore, December 2003.(AFSTI), Mysore India Carapiso Ana I, Ventanas Jesus, Jurado Angela, & Garcia Carmen (2001). An Electronic Nose to Classify Isberian Pig Fats with different Fatty Acid Composition, Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 78(4), pp. 415-418
- Deshpande SK, Bhotmange MG, Chakrabarti T, & Shastri PN (2008). Production of cellulase and xylanase by T. reesei (QM9414 mutant), A. niger and mixed culture by Solid State Fermentation (SSF) of Water Hyacinth (Eicchornia crassipes), Indian Journal of Chemical Technology, 15(5), pp. 449-456
- Eberhart, R. C., & Dobbins, R.W. (1990). Network analysis. In Neural Network PC Tools. A. Practical Guide, R.C. Eberhart and R.W. Dobbins (Ed.), Academic Press, San Diego, CA. Gardner, JW, Hines, EL, & Wilkinson M (1990). Application of artificial neural networks to an electronic olfactory system, Journal Measurement Science and Technology, 1(5), pp. 446.
- Gupta R, Pandharipande SL, & Shastri PN (2005). Optimization of the process of extraction of fiber from defatted soyflour using ANN, National Seminar on Global perspectives for India Food Industry by 2020-Food Vision 2020, organized by Laxminarayan Institute of Technology, Nagpur University, Nagpur.
- Harimoto Y, Durance T, Nakai S, & Lukow O.M. (1995). Neural Networks Vs Principal Component Regression for Prediction of Wheat Flour Loaf Volume in Baking Tests, Journal of Food Science, 60(3), pp. 429-433
- Herv's, C. G.,Zurera, Garcfa, R M., & Martinez J. A. (2001). Optimization of Computational Neural Network for Its Application in the Prediction of Microbial Growth in Foods Food Science and Technology International, 7: 159-163
- Hong Yan, G.V., & Barbosa-Canovas (2001). Attrition Evaluation for selected Agglomerated Food Powders: The effect of agglomerate size and water activity, Journal of Food Process Engineering, 24(1), pp. 37-49
- Hornik, K, Stichcombe, M, & White , H (1989). Multilayer Feed forward Neural Network are universal Approximate . Neural Network. 2, pp. 359-366 Huang Y, Kangas LJ, & Rasco BA. (2007). Applications of artificial neural networks (ANNs) in food science. Crit. Rev Food Sci. Nutr. 47(2), pp. 113-26
- Huiling Tai, Guangzhong Xie, & Yadong Jiang (2004). An Artificial Olfactory system based on Gas Sensor Array and Back-Propogation Neural Network, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Advances in Neural Networks, Vol. 3174, pp. 323-339
- Igor V. Kovalenko, Glen R. Rippke, & Charles R. Hurburgh (2006). Measurement of soybean fatty acids by near-infrared spectroscopy: Linear and nonlinear calibration methods Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 83(5)
- İsmail Hakkı Boyacı, Gulum Sumnu, & Ozge Sakiyan (2008). Estimation of Dielectric Properties of Cakes Based on Porosity, Moisture Content, and Formulations Using Statistical Methods and Artificial Neural Networks, Food Bioprocess Technol 2(4), pp. 353-360
- Jenzsch, Marco, Simutis, Rimvydas, Eisbrenner, Günter, Stückrath, Ingolf, & Lübbert, Andreas (2006). Estimation of biomass concentrations in fermentation processes for recombinant protein production, Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 29(1), pp. 19-27
- Jose Alberto Gallegos-Enfante, Nuria E.Roha Guzman, Ruben F.Gonzalez-Laredo, & Ramiro Rico-Martinez (2007). The kinetics of crystallization of tripalmitin in olive oil: an artificial neural network approach Journal of Food Lipids, 9(1), pp. 73-86
- Kılıç, K., Boyacı, İ.-H., Köksel, H., & Küsmenoğlu, İ. (2007). A classification system for beans using computer vision system and artificial neural networks. Journal of Food Engineering, 78, pp. 897-904.
- References and further reading may be available for this article. To view references and further reading you must this article.
- Kulkarni Savita G., Chaudhary Amit Kumar Nandi , Somnath Tambe, & Kulkarni Bhaskar D. (2004). Modeling and monitoring of batch processes using principal component analysis (PCA) assisted generalized regression neural networks (GRNN), Biochemical Engineering Journal, 18(3), pp. 193-210
- Lenz, J, Hofer, M, Krasenbrink, J, B, & Holker U (2004). A Survey of Computational and physical methods applied to solid state fermentation, Applied Microbiology and biotechnology, 65(1), pp. 9-17
- Lopes, M.F.S., Pereira C. I., Rodrigues F.M.S., Martins M. P., Mimoso M.C., Barros T. C., Figueiredo Marques J. J., Tenreiro R. P., Almeida J. S., & Barreto Crespo M. T. (1999). Registered designation of origin areas of fermented food products defined by microbial phenotypes and artificial neural networks. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 65, pp. 4484-4489
- Lou, W., & Nakai, S. (2001). Application of artificial neural networks for predicting the thermal inactivation of bacteria: A combined effect of temperature, pH and water activity. Food Research International, 34, pp. 573-579
- Mazzuti Marcio M, Corrazza Marcos L, Filho Francisco Maugeri, Rodrigues Marai Isabel, Corraza Fernanda C, & Triechel Helen (2009). Inulinase production in a batch bioreactor using agroindustrial residues as the substrate: experimental data and modeling, Bioprocess and Biosystems engineering, 32(1), pp. 85-95
- Meshram C.N. (2008). Studies on dehydration of agro based products using radio frequency dryer, M.Tech (ChemTech.) Thesis sumitted to Nagpur University Mittal G.S., & Zhang , J. (2000). Prediction of temperature and moisture content of frankfurters during thermal processing using neural network, Meat Science, 55(1), pp. 13-24
- Molkentin Joachim, Meisel Hans, Lehmann Ines, & Rehbein Hartmut (2007). Identification of Organically Farmed Atlantic Salmon by Analysis of Stable Isotopes and Fatty acids, European food Research and Technology, 224 (5) pp. 535-543
- Pandharipande, M.S., Pandharipande, S.L., Bhotmange, M.G., & Shastri P.N. (2003). Application of ANN for prediction of Amylase production by Aspergillus oryzae under SSF conditions; Proceedings of International Food Convention"Innovative Food by A. niger in solid state fermentation. Asian Journal of Microbiology Biotechnology Environmental Science, 11(4), pp. 777-782
- Sousa Ruy, Resende Mariaam M, Giordano Raquel L.C., & Giordano Roberto C, (2003). Hydrolysis of cheese whey proteins by alcalase immobilized in agarose gel particles, Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 106(1-3)
- Vallejo-Cordoba B., Arteaga G.E., & Nakai S. (1995). Predicting Milk Shelf-life Based on Artificial Neural Networks and Headspace Gas Chromatographic Data, Journal of Food Science, 60(5), pp. 885-888
- Vassileva S., B. Tzvetkova B., Katranoushkova C. and Losseva L.(2000) Neuro-fuzzy prediction of uricase production Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering 22,( 4), pp 363-367
- Wongsapat Chokananporn, & Ampawan Tansakul (2008). Artificial Neural Network Model for Estimating the Surface Area of Fresh Guava, Asian Journal of Food and Agro- Industry, 1(3), pp. 129 -136
- Yadav Sangeeta, Shastri N.V., Pandharipande S.L., & Shastri P. N. (2003). Optimization of water and DOP level for production of pectin trans eliminase by Penicillium oxalatum under SSF condition by Artificial Neural Network, Proceedings of International Food Convention"Innovative Food Technologies and Quality Systems Strategies for Global Competitiveness" IFCON 2003, Poster no FB 28, pp. 48, Mysore , December 2003.(AFSTI) Mysore, India
- Yasuo Saito, Toshiharu Hatanaka, Katsuji Uosaki, & Hidekazu Shigeto (2003). Neural Network application to Eggplant Classification, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 2774, pp. 933-940
- Yeh Jeffrey C.H., Hamey Leonard G. C., Westcott Tas, & Sung Samuel K.Y. (2005). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks 2005, pp. 37--42, {IEEE}
- Zhang, Jun, & Chen, Yixin (1997). Food sensory evaluation employing artificial neural networks Sensor Review, 17(2), pp. 150-158(9)
- References
- Argyri, A. A., Panagou, E. Z., Tarantilis, P. A., Polysiou, M. & Nychas, G. J. E. (2010). Rapid qualitative and quantitative detection of beef fillets spoilage based on Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy data and artificial neural networks. Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical, 145, 1, 146-154, ISSN: 0925-4005
- Balasubramanian, S., Panigrahi, S., Logue, C. M., Gu, H. & Marchello, M. (2009). Neural networks-integrated metal oxide-based artificial olfactory system for meat spoilage identification. Journal of Food Engineering, 91, 1, 91-98, ISSN: 0260-8774
- Beattie, J. R., Bell, S. E. J., Borggaard, C., Fearon, A. M. & Moss, B. W. (2007). Classification of adipose tissue species using Raman spectroscopy. Lipids, 42, 7, 679-685, ISSN: 0024- 4201
- Berg, E. P., Engel, B. A. & Forrest, J. C. (1998). Pork carcass composition derived from a neural network model of electromagnetic scans. Journal of Animal Science, 76, 1, 18-22, ISSN: 0021-8812
- Borggaard, C., Madsen, N. & Thodberg, H. (1996). In-line image analysis in the slaughter industry, illustrated by beef carcass classification. Meat Science, 43, 151-163, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Brethour, J. (1994). Estimating marbling score in live cattle from ultrasoud images using pattern-recognition and neural-network procedures. Journal of Animal Science, 72, 6, 1425-1432, ISSN: 0021-8812
- Broomhead, D. S. & Lowe, D. (1998). Multivariable functional interpolation and adaptive networks. Complex Systems, 2, 312-355, ISSN: 0891-2513
- Cartwright, H. M. (2008). Artificial neural networks in biology and chemistry. In: Artificial neural networks : methods and applications. Livingstone, D. (Ed.), 1-13, Humana Press, ISBN: 978-1-58829-718-1, New York
- Chandraratne, M. R., Samarasinghe, S., Kulasiri, D. & Bickerstaffe, R. (2006). Prediction of lamb tenderness using image surface texture features. Journal of Food Engineering, 77, 3, 492-499, ISSN: 0260-8774
- Chandraratne, M., Kulasiri, D. & Samarasinghe, S. (2007). Classification of lamb carcass using machine vision: Comparison of statistical and neural network analyses. Journal of Food Engineering, 82, 1, 26-34, ISSN: 0260-8774
- Chao, K., Park, B., Chen, Y. R., Hruschka, W. R. & Wheaten, F. W. (2000). Design of a dual-camera system for poultry carcasses inspection. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 16, 5, 581-587, ISSN: 0883-8542
- Chao, K., Chen, Y. R., Hruschka, W. R. & Gwozdz, F. B. (2002). On-line inspection of poultry carcasses by a dual-camera system. Journal of Food Engineering, 51, 3, 185-192, ISSN: 0260-8774
- Chen, Y. R., Huffman, R. W., Park, B. & Nguyen, M. (1996). Transportable spectrophotometer system for on-line classification of poultry carcasses. Applied Spectroscopy, 50, 7, 910-916, ISSN: 0003-7028
- Chen, Y. R., Nguyen, M. & Park, B. (1998a). Neural network with principal component analysis for poultry carcass classification. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 21, 5, 351-367, ISSN: 0145-8876
- Chen, Y. R., Park, B., Huffman, R. W. & Nguyen, M. (1998b). Classification o in-line poultry carcasses with back-propagation neural networks. Journal of Food Processing Engineering, 21, 1, 33-48, ISSN: 1745-4530
- Cheroutre-Vialette, M. & Lebert, A. (2002). Application of recurrent neural network to predict bacterial growth in dynamic conditions. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 73, 2-3, 107-118 ISSN: 0168-1605
- Christensen, S. S., Andersen, A. W., Jørgensen, T. M. & Liisberg, C. (1996). Visual guidance of a pig evisceration robot using neural networks. Pattern Recognition Letters, 17, 4, 345-355, ISSN: 0167-8655
- Craven, M. A., Gardner, J. W. & Bartlett, P. N. (1996). Electronic noses -Development and future prospects. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 15, 9, 486-493, ISSN: 0167-2940
- Del Moral, F. G., Guillén, A., del Moral, L. G., O'Valle, F., Martínez, L. & del Moral, R. G. (2009). Duroc and Iberian pork neural network classification by visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Journal of Food Engineering, 90, 4, 540-547, ISSN: 0260-8774
- Díez, J., Bahamonde, A., Alonso, J., López, S., del Coz, J. J., Quevedo, J. R., Ranilla, J., Luaces, O., Alvarez, I., Royo, L. J. & Goyache, F. (2003). Artificial intelligence techniques point out differences in classification performance between light and standard bovine carcasses. Meat Science, 64, 3, 249-258, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Dong, Q. L. (2009). BP neural network for evaluating sensory texture properties of cooked sausage. Journal of Sensory Studies, 24, 6, 833-850, ISSN: 0887-8250
- Eklöv, T., Johansson, G., Winquist, F. & Lundström, I. (1998). Monitoring sausage fermentation using an electronic nose. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 76, 4, 525-532, ISSN: 0022-5142
- Ellis, D. I. & Goodacre, R. (2001). Rapid and quantitative detection of the microbial spoilage of muscle foods: Current status and future trends. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 12, 11, 414-424, ISSN: 0924-2244
- Galdikas, A., Mironas, A., Senuliené, D., Strazdiené, V., Šetkus, A. & Zelenin, D. (2000). Response time based output of metal oxide gas sensors applied to evaluation of meat freshness with neural signal analysis. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 69, 3, 258-265, ISSN: 0925-4005
- Harper, W. J. (2001). The strengths and weaknesses of the electronic nose. In: Headspace analysis of foods and flavours, Rouseff R. L. & Cadwallader K. R. , (Ed.), 59-71, Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publ., ISBN: 978-0-306-46561-1, New York
- Hatem, I., Tan, J. & Gerrard, D. E. (2003). Determination of animal skeletal maturity by image processing. Meat Science, 65, 3, 999-1004, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Hill, B. D., Jones, S. D. M., Robertson, W. M. & Major, I. T. (2000). Neural network modeling of carcass measurements to predict beef tenderness. Canadian Journal of Animal Science, 80, 2, 311-318, ISSN: 0008-3984
- Huang, Y., Lacey, R. & Whittaker, A. (1998). Neural network prediction modeling based on elastographic textural features for meat quality evaluation. Transactions of the ASAE, 41, 4, 1173-1179, ISSN: 0001-2351
- Hwang, H., Park, B., Nguyen, M. & Chen, Y. R. (1997). Hybrid image processing for robust extraction of lean tissue on beef cut surfaces. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 17, 3, 281-294, ISSN: 0168-1699
- Ibarra, J. G., Tao, Y. & Xin, H. W. (2000). Combined IR imaging-neural network method for the estimation of internal temperature in cooked chicken meat. Optical Engineering, 39, 11, 3032-3038, ISSN: 0091-3286
- Ibarra, J. G., Tao, Y., Newberry, L. & Chen, Y. R. (2002). Learning vector quantization for color classification of diseased air sacs in chicken carcasses. Transactions of the ASAE, 45, 5, 1629-1635, ISSN: 0001-2351
- Josell, Å., Martinsson, L., Borggaard, C., Andersen, J. R. & Tornberg, E. (2000). Determination of RN-phenotype in pigs at slaughter-line using visual and near- infrared spectroscopy. Meat Science, 55, 3, 273-278, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Li, J., Tan, J., Martz, F. A. & Heymann, H. (1999). Image texture features as indicators of beef tenderness. Meat Science, 53, 1, 17-22, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Li, J., Tan, J. & Shatadal, P. (2001). Classification of tough and tender beef by image texture analysis. Meat Science, 57, 4, 341-346, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Lohninger, H. (1993). Evaluation of neural networks based on radial basis functions and their application to the prediction of boiling points from structural parameters. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 33, 736-744, ISSN: 0095-2338
- Lohninger, H. (1999). Teach/Me Data Analysis, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-New York-Tokyo, ISBN: 978-3-54014-743-5
- Lou, W. & Naka, S. (2001). Artificial Neural Network-based predictive model for bacterial growth in a simulated medium o modified-atmosphere-packed coked meat products. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49, 4, 1799-1804, ISSN: 0021-8561
- Lu, J., Tan, J., Shatadal, P. & Gerrard, D. E. (2000). Evaluation of pork color by using computer vision. Meat Science, 56, 1, 57-60, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Lu, W. & Tan, J. (2004). Analysis of image-based measurements and USDA characteristics as predictors of beef lean yield. Meat Science, 66, 2, 483-491, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Ma, L. & Tao, Y. (2005). An infrared and laser range imaging system for non-invasive estimation of internal temperatures in chicken breasts during cooking. Transactions of the ASAE, 48, 2, 681-690, ISSN: 0001-2351
- Mittal, G. S. & Zhang, J. (2000). Prediction of temperature and moisture content of frankfurters during thermal processing using neural network. Meat Science, 55, 1, 13-24, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Novič, M. (2008). Kohonen and counter-propagation neural networks applied for mapping and interpretation of IR spectra. In: Artificial neural networks : methods and applications. Livingstone, D. (Ed.), 45-60, Humana Press, ISBN: 978-1-58829-718-1, New York Palanichamy, A., Jayas, D. S. & Holley, R. A. (2008). Predicting survival of Escherichia coli O157 : H7 in dry fermented sausage using artificial neural networks. Journal of Food Protection, 71, 1, 6-12, ISSN: 0362-028X
- Panigrahi, S., Balasubramanian, S., Gu, H., Logue, C. M. & Marchello, M. (2006). Design and development of a metal oxide based electronic nose for spoilage classification of beef. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 119, 1, 2-14, ISSN: 0925-4005
- Park, B. & Chen, Y.-R. (1994). Intensified multispectral imaging system for poultry carcass inspection. Transactions of the ASAE, 37, 6, 1983-1988, ISSN: 0001-2351
- Park, B. Chen, Y. R., Nguyen, M. & Hwang, H. (1996). Characterizing multispectral images of tumorous, bruised, skin-torn, and wholesome poultry carcasses. Transactions of the ASAE, 39, 5, 1933-1941, ISSN: 0001-2351
- Park, B., Chen, Y. R. & Nguyen, M. (1998). Multi-spectral Image Analysis using Neural Network Algorithm for Inspection of Poultry Carcasses. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 69, 4, 351-363, ISSN: 1095-9246
- Park, B. & Chen, J. Y. (2000). Real-time dual-wavelength image processing for poultry safety inspection. Journal of Food Processing Engineering, 23., 5., 329-351, ISSN: 1745-4530
- Peres, A. M., Dias, L. G., Joy, M. & Teixeira, A. (2010). Assessment of goat fat depots using ultrasound technology and multiple multivariate prediction models. Journal of Animal Science, 88, 2, 572-580, ISSN: 0021-8812
- Prevolnik, M., Čandek-Potokar, M., Novič, M. & Škorjanc, D. (2009). An attempt to predict pork drip loss from pH and colour measurements or near infrared spectra using artificial neural networks. Meat Science, 83, 3, 405-411, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Qiao, J., Ngadi, M. O., Wang, N., Gariépy, C. & Prasher, S. O. (2007a). Pork quality and marbling level assessment using a hyperspectral imaging system. Journal of Food Engineering, 83, 1, 10-16, ISSN: 0260-8774
- Qiao, J., Wang, N., Ngadi, M. O., Gunenc, A., Monroy, M., Gariépy, C. & Prasher, S.O. (2007b). Prediction of drip-loss, pH, and color for pork using a hyperspectral imaging technique. Meat Science, 76, 1, 1-8, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Rosenblatt, F. (1961). Principles of neurodynamics: perceptrons and the theory of brain mechanisms. Spartan Books, Washington D. C., Washington
- Santé, V. S., Lebert, A., Le Pottier, G. & Ouali, A. (1996). Comparison between two statistical models for prediction of turkey breast meat colour. Meat Science, 43, 3-4, 283-290, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Santos, J. P., García, M., Aleixandre, M., Horrillo, M. C., Gutiérrez, J., Sayago, I., Fernández, M. J. & Arés, L. (2004). Electronic nose for the identification of pig feeding and ripening time in Iberian hams. Meat Science, 66, 3, 727-732, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Sebastián, A., Viallon-Femandez, C., Toumayre, P., Berge, P., Sañudo, C., Sánchez, A. & Berdague, J.-L. (2004). Evaluation of collagen and lipid contents and texture of meat by Curie point pyrolysis-mass spectrometry. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 72, 2, 203-208, ISSN: 0165-2370
- Sheridan, C., O'Farrell, M., Lewis, E., Flanagan, C., Kerry, J. & Jackman, N. (2007). A comparison of CIE L*a*b* and spectral methods for the analysis of fading in sliced cured ham. Journal of Optics A-Pure and Applied Optics, 9, 6, 32-39, ISSN: 1464-4258
- Shiranita, K., Hayashi, K., Otsubo, A., Miyajima, T. & Takiyama, R. (2000). Grading meat quality by image processing. Pattern Recognition, 33, 1, 97-104, ISSN: 0031-3203.
- Tan, F. J., Morgan, M. T., Ludas, L. I., Forrest, J. C. & Gerrard, D. E. (2000). Assessment of fresh pork color with color machine vision. Journal of Animal Science, 78, 12, 3078-3085, ISSN: 0021-8812
- Tian, Y. Q., McCall, D. G., Dripps, W., Yu, Q. & Gong, P. (2005). Using computer vision technology to evaluate the meat tenderness of grazing beef. Food Australia, 57, 8, 322-326, ISSN: 1032-5298
- Valous, N. A., Mendoza, F., Sun, D.-W. & Allen, P. (2010). Supervised neural network classification of pre-sliced cooked pork ham images using quaternionic singular values. Meat Science, 84, 3, 422-430, ISSN: 0309-1740
- Wang, Y., Yang, W., Winter, P. & Walker, L. (2008). Walk-through weighing of pigs using machine vision and an artificial neural network. Biosystems Engineering, 100, 1, 117-125, ISSN: 1537-5110
- Winquist, F., Hörnsten, E. G., Sundgren, H. & Lundström, I. (1993). Performance of an electronic nose for quality estimation of ground meat. Measurement Science & Technology, 4, 12, 1493-1500, ISSN: 0957-0233
- Zheng, C., Sun, D.-W. & Zheng, L. (2007). Predicting shrinkage of ellipsoid beef joints as affected by water immersion cooking using image analysis and neural network. Journal of Food Engineering, 79, 4, 1243-1249, ISSN: 0260-8774
- Zou, J., Han, Y. & So, S.-S. (2008). Overview of artificial neural networks. In: Artificial neural networks : methods and applications. Livingstone, D. (Ed.), 15-23, Humana Press, ISBN: 978-1-58829-718-1, New York.
- Zupan, J. (1994). Introduction to artificial neural network (ANN) methods: What they are and how to use them. Acta Chimica Slovenica, 41, 3, 327-352, ISSN: 1318-0207
- Zurera-Cosano, G., Garcia-Gimeno, R. M, Rodriguez-Perez, M. R. & Hervas-Martinez, C. (2005). Validating an artificial neural network model of Leuconostoc mesenteroides in vacuum packaged sliced cooked meat products for shelf-life estimation. European Food Research and Technology, 221, 5, 717-724, ISSN: 1438-2377
- References
- Li Hongjian;Lin Yuchun. (2007). Vigorously the development and promotion of our natural gas vehicles. MAGNIFICENT WRTING, No.4, (2007) page numbers (174), ISSN l009-5489
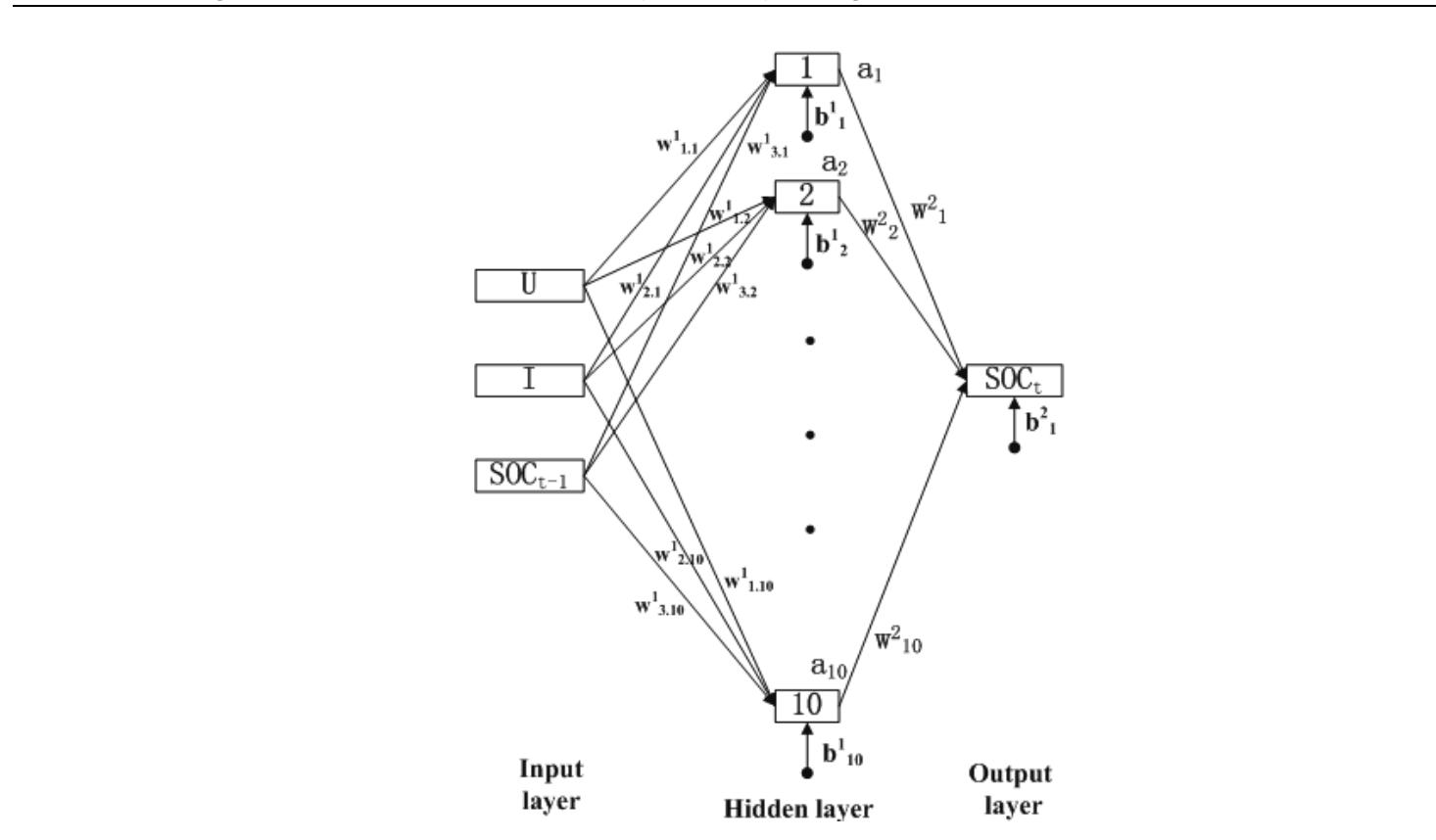
- MA Youliang; CHEN Quanshi; QI Zhanning. (2001). Research on the SOC definition and measurement method of batteries used in EVs. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), Vol.41, No.11, (2001) page numbers (95-98), ISSN 1000-0054
- Piao Changhao, Yang Xiaoyong, Teng Cong and Yang Huiqian(2010), An Improved Model Based on Artificial Neural Networks and Thevenin Model for Nickel Metal Hydride Power Battery, 2010 International Conference on Optics, Photonics and Energy Engineering, March 2010, Wuhan, China , pp.
- T.Shinpo. Development of Battery Management System for Electric Vehicle.Proc.of the 14 International Electric Vehicle Sysposium(1997)
- Lin Chengtao; CHEN Quanshi; WANG Junping. (2006). Improved Ah counting method for state of charge estimation of electric vehicle batteries. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), Vol.26, No.2, (2006) page numbers (76-79), ISSN 1000-0054
- Zhao Huiyong; Luo Yongge; Yang Qiliang; She Jianqiang. (2004). Situation and Development on the Vehicle NiMHBattery Management System. Journal of Hubei Automotive Industries Institute, Vol.18, No.3, (SEP2004) page numbers (23-26), ISSN 1008-5483
- Jiang Jiuchun,Niu Liyong,Zhang Xin. (2004). Research 0n Battery Management System for Hybrid Electric Vehicle. High Technology Letters, Vol.11, No.2, (2004) page numbers (75-77), ISSN 1002-0470
- Chen Jun;Tao Zhanliang. (2006). Nickel-Metal Hydride Secondary Battery, Chemical Industry Press, ISBN 9787502583859,Bei Jing
- PILLER S, PERRIN M, JOSSEN A. Methods for state of charge determination and their application[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001,96(5):113-120.
- Zhang Hongmei, DENG Zhenglong. UKF-based attitude determination method for gyro less satellite[J]. Journal of System Engineering and Electronics, 2004, 15(2): 105-109.
- Tian Xiaohui;Diao Hainan;Fan Bo;Qiu Yunpeng. (2010). Research on estimation of lithium-ion battery SOC for electric vehicle. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, Vol.6, No.1, (2010) page numbers (51-54), ISSN 1002-087X
- Meng Siqi; Yang Honggeng. (2008). Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on Second- Order Correction of Kalman Filter. Advances of Power System & Hydroelectric Engineering, Vol.24, No.2, (200802) page numbers (73-75), ISSN 1674-0009
- LIN Chengtao, WANG Junping, CHEN Quanshi, Methods for state of charge estimation of EV batteries and their application[J], 2004, 34(5):772-774.
- SIMMONDS N, Device for indicating the residual capacity of secondary cells: U.S. Patent 5 518 835[P], 1996-5-21.
- SALAMEH M, CASACCA A. A mathematical model for lead2acid batteries [J]. IEEE Trans Energy Conversion, 1992 ,7 (1): 93 -97.
- Shen Wenxue, State of available capacity estimation for lead-acid batteries in electric vehicles using neural network[J], Energy Conversion and Management, 2007, 48(2):433-442.
- A. Salkind, C. Fennie, P. Singh, T. Atwater, D. Reisner, Determination of state-of-charge and state-of-health of batteries by fuzzy logic methodology[J], Journal of Power Sources , 1999, 80(2): 293-300.
- Simon Haykin. (2001). Neural network: A comprehensive foundation (Second edition), Tsinghua University Press, ISBN 730204936, Bei Jing
- Chang-hao Piao, Wen-li Fu, Gai-hui Lei and Chong-du Cho, Online Parameter Estimation of the Ni-MH Batteries Based on Statistical Methods, Energies, Volume 3, Issue 2 (February 2010), pp.206-215
- Martin T.Hagan. (2002). Neural network design, Machinery Industry Press, ISBN 7111075854., Bei Jing
- Jiao Huimin; Yu Qunming. Research on Capacity Predication of Battery based on BP network and Genetic Algorithm. Computer Simulation, Vol.26, No.11, (2006) page numbers (218-220), ISSN 1006-9348
- Wen Xin; Zhou Lu. (2000). MATLAB Neural network application and design, Science and Technology Press, ISBN 7030084802, Bei Jing
- Gao Juan. (2003). Artificial neural network theory and simulation, Machinery Industry Press, ISBN 9787111125914, Bei Jing
- Lin C, Reinforcement structure/parameter learning for neural network based fuzzy logic control systems [J], IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst, 1994, 2(1): 46-63
- References J.K. Wu, Frequency tracking techniques of power systems including higher order harmonics devices, Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE International Caracas Conference, vol. 1, (3-5 Nov. 2004), pp. 298-303.
- M. Akke, Frequency estimation by demodulation of two complex signals, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 12, no. 1, (Jan. 1997), pp. 157-163.
- P.J. Moore, R.D. Carranza and A.T. Johns, Model system tests on a new numeric method of power system frequency measurement, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 11, no. 2, (Apr. 1996), pp. 696-701.
- M.M. Begovic, P.M. Djuric, S. Dunlap and A.G. Phadke, Frequency tracking in power networks in the presence of harmonics, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 8, no. 2, (April 1993), pp. 480-486.
- C.T. Nguyen and K.A. Srinivasan, A new technique for rapid tracking of frequency deviations based on level crossings, IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst., vol. 103, no. 8, (April 1984), pp. 2230-2236.
- I. Kamwa and R. Grondin, Fast adaptive schemes for tracking voltage phasor and local frequency in power transmission and distribution systems, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 7, no. 2, (April 1992), pp.789-795.
- M.S. Sachdev and M.M. Giray, A least error square technique for determining power system frequency, IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst., vol. 104, no. 2, (Feb. 1985), pp. 437-443.
- M.M. Giray and M.S. Sachdev, Off-nominal frequency measurements in electric power systems, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 4, no. 3, (July 1989), pp. 1573-1578.
- V.V. Terzija, M.B. Djuric and B.D. Kovacevic, Voltage phasor and local system frequency estimation using Newton-type algorithm, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 9, no. 3, (Jul. 1994), pp. 1368-1374.
- M.S. Sachdev, H. C. Wood and N. G. Johnson, Kalman filtering applied to power system measurements for relaying, IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst., vol. 104, no. 12, (Dec. 1985), pp. 3565-3573.
- A.A. Girgis and T.L.D. Hwang, Optimal estimation of voltage phasors and frequency deviation using linear and nonlinear Kalman filter: Theory and limitations, IEEE Tran. Power App. Syst., vol. 103, no. 10, (1984), pp. 2943-2949.
- A.A. Girgis and W.L. Peterson, Adaptive estimation of power system frequency deviation and its rate of change for calculating sudden power system overloads, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 5, no. 2, (Apr. 1990), pp. 585-594.
- T. Lobos and J. Rezmer, Real time determination of power system frequency, IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., vol. 46, no. 4, (Aug. 1997), pp. 877-881.
- A.G. Phadke, J.S. Thorp and M.G. Adamiak, A new measurement technique for tracking voltage phasors, local system frequency, and rate of change of frequency, IEEE Trans. Power App. and Systems, vol. 102, no. 5, (May 1983), pp. 1025-1038.
- J.Z. Yang and C.W. Liu, A precise calculation of power system frequency, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 16, no. 3, (July 2001), pp. 361-366.
- J.Z. Yang and C.W. Liu, A precise calculation of power system frequency and phasor, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 15, no. 2, (Apr. 2000), pp. 494-499.
- S.L. Lu, C.E. Lin and C.L. Huang, Power frequency harmonic measurement using integer periodic extension method, Elect. Power Syst. Res., vol. 44, no. 2, (1998), pp. 107- 115.
- P.J. Moore, R.D. Carranza and A.T. Johns, A new numeric technique for high speed evaluation of power system frequency, IEE Gen. Trans. Dist. Proc., vol. 141, no. 5 (Sept. 1994), pp. 529-536.
- J. Szafran and W. Rebizant, Power system frequency estimation, IEE Gen. Trans. Dist. Proc., vol. 145, no. 5, (Sep. 1998), pp. 578-582.
- A.A. Girgis and F.M. Ham, A new FFT-based digital frequency relay for load shedding, IEEE Trans. Power App. Syst., vol. 101, no. 2, (Feb. 1982), pp. 433-439.
- H.C. Lin and C. S. Lee, Enhanced FFT-based parameter algorithm for simultaneous multiple harmonics analysis, IEE Gen. Trans. Dist. Proc., vol. 148, no. 3, (May 2001), pp. 209- 214.
- W.T. Kuang and A.S. Morris, Using short-time Fourier transform and wavelet packet filter banks for improved frequency measurement in a Doppler robot tracking system, IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., vol. 51, no. 3, (June 2002), pp. 440-444.
- V.L. Pham and K. P. Wong, Wavelet-transform-based algorithm for harmonic analysis of power system waveforms, IEE Gen. Trans. Dist. Proc., vol. 146, no. 3, (May 1999), pp. 249-254.
- V.L. Pham and K.P. Wong, Antidistortion method for wavelet transform filter banks and nonstationary power system waveform harmonic analysis, IEE Gen. Trans. Dist. Proc., vol. 148, no. 2, (March 2001), pp. 117-122.
- M. Wang and Y. Sun, A practical, precise method for frequency tracking and phasor estimation, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 19, no. 4, (Oct. 2004), pp. 1547-1552.
- D.W.P. Thomas and M.S. Woolfson, Evaluation of a novel frequency tracking method, Transmission and Distribution Conference, vol. 1, (11-16 April 1999), pp. 248-253.
- M.I. Marei, E.F. El-Saadany and M.M.A. Salama, A processing unit for symmetrical components and harmonics estimation based on a new adaptive linear combiner structure, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 19, no. 3, (July 2004), pp. 1245-1252.
- P.J. Moore, J.H. Allmeling and A.T. Johns, Frequency relaying based on instantaneous frequency measurement, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 11, no. 4, (Oct. 1996), pp. 1737-1742.
- D.W.P. Thomas and M.S. Woolfson, Evaluation of frequency tracking methods, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 16, no. 3, (July 2001), pp. 367-371.
- G. J. Retter, Matrix and Space-Phasor Theory of Electrical Machines, Akademiai Kiado, Budapest, Rumania, (1987).
- G.H. Hostetter, Recursive discrete Fourier transformation, IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process., vol. 28, no, 2, (1980), pp. 184-190.
- R.R. Bitmead, A.C. Tsoi and P.J. Parker, A Kalman filtering approach to short-time Fourier analysis, IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process., vol. 34, no. 6, (1986), pp. 1493-1501
- T. Kailath, Linear Systems, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, (1980). Application of ANN to Real and Reactive Power Allocation Scheme S.N. Khalid, M.W. Mustafa, H. Shareef and A. Khairuddin Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Malaysia
- References
- Abdullah, S.S (2008). A Short Course in Artificial Neural Network, Desktop, ISBN, Malaysia Bialek, J. ; (1996). Tracing the flow of electricity, IEE Proceedings Generation, Transmission & Distribution, Vol.,143 No., 4 (313-320)
- Chu, W.; Chen, B. & Liao, C. (2004). Allocating the Costs of Reactive Power Purchased in an Ancillary Service Market by Modified Y-Bus Matrix Method, IEEE Transaction on Power system, Vol.,19 No., 1 (174-178)
- Cheng, J.W.M. (1998). Studies of Bilateral Contracts with Respects to Steady-State Security in a Deregulated Environment, IEEE Transaction on Power system, Vol.,13 No.,3 (1020- 1025)
- Haque, R .; & Chowdhury, N. (2005). An Artificial Neural Network Based Transmision Loss Allocation For Bilateral Contracts, Proceedings of the 18th Annual Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, pp.2197-2201, Canada, May 2005
- Tsoukalas, LH.; & Uhrig, RE. (1997). Fuzzy and Neural Approaches in Engineering, Wiley, ISBN, New York
- Reta, R. ; & Vargas,A . (2001). Electricity Tracing and Loss Allocation Methods Based on Electric Concepts, IEE Proceedings Generation, Transmission & Distribution, Vol.,148 No., 6 (518-522)
- Sharkey, A. J. C. (1999), Combining Artificial Neural Nets, ensemble and modular multi net systems, Springer, London
- Thompson, G.; Atkinson, C.; Clark, N.; Long, T. and Hanzevack, E. (2000), Neural Network Modelling of the Emissions and Performance of a Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine, Proceedings of the Institute of Mechanical Engineers, Vol. 214, Part D, No. D04499, 2000
- Wu, B.; Filipi, Z.; Assanis, D.; Kramer, D. M.; Ohl, G. L.; Prucka, M. J. and Divalentin, E. (2004). Using artificial neural networks for representing the air flow rate through a 2.4 litre VVT engine, SAE paper no. 2004-01-3054
- References
- Arghavani, J.; Derenne, M. & Marchand, L. (2001). Fuzzy logic application in gasket selection and sealing performance. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 18, (67-78).
- Chau, Kwokwing (2006). A review of the integration of artificial intelligence into coastal modelling. Journal of Environmental Management, Vol. 80, (47-57).
- Cus, Franci & Zuperl, Uros (2006). Approach to optimization of cutting conditions by using artificial neural networks. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 173, (281-290)
- El Baradie, M.A. (1997). A fuzzy logic model for machining data selection. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 37, No. 9, (1353-1372).
- Ghiassi, M. & Saidene, H. (2005). A dynamic architecture for artificial neural networks. Neurocomputing, Vol. 63, (397-413).
- Hashmi, K.; Graham, I.D. & Mills, B. (2003). Data selection for turning carbon steel using a fuzzy logic approach. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 135, (44-58).
- Hashmi, K.; Graham, I.D. & Mills, B. (2000). Fuzzy logic based Data selection for the drilling process. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 108, (55-61).
- Hashmi, K.; El Baradie, M.A. & Ryan, M. (1999). Fuzzy logic based intelligent selection of machining parameters. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 94, (94-111).
- Hashmi, K.; El Baradie, M.A. & Ryan, M. (1998). Fuzzy logic based intelligent selection of machining parameters. Computers and Industrial Engineering, Vol. 35, No. (3-4), (571-574).
- Kim, Jae Kyeong & Park, Kyung Sam (1997). Modelling a class of decision problems using artificial neural networks. Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 12, (195-208).
- Kuo, R.J.; Chi, S.C. & Kao, S.S. (2002). A decision support system for selecting convenience store location through integration of fuzzy AHP and artificial neural network. Computers in Industry, Vol. 47, (199-214).
- Lee, B.Y. & Tarng, Y.S. (2000). Cutting parameter selection for maximizing production rate or minimizing production cost in multistage turning operations. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 105, (61-66).
- Liu, T.I.; Singonahalli, J.H. & Iyer, N.R. (1996). Detection of roller bearing defects using expert system and fuzzy logic. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 10, No. 5, (595-614).
- Malakooti, B. & Deviprasad, J. (1989). An interactive multiple criteria approach for parameter selection in metal cutting. Operations Research, Vol. 37, No. 5, (805-818).
- Medsker, Larry R. (1996). Microcomputer applications of hybrid intelligent systems. Journal of Network and Computer applications, Vol. 63, (213-234).
- Metcut Research Associates Inc. (1980). Machining Data Handbook, 3 rd edition, Vol. 1 & 2, Cincinnati.
- Nian, C.Y.; Yang, W.H. & Tarng, Y.S. (1999). Optimization of turning operations with multiple performance characteristics. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 95, (90-96).
- Park, Kyung Sam & Kim, Soung Hie (1998). Artificial intelligence approaches to determination of CNC machining parameters in manufacturing: a review. Artificial Intelligence in Engineering, Vol. 12, (127-134).
- Saravanan, R.; Asokan, P. & Vijayakumar, K. (2003). Machining parameters optimization for turning cylindrical stock into a continuous finished profile using genetic algorithm (GA) and simulated annealing (SA). International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 21, (1-9).
- Singh, Rajiv & Raman, Shivakumar (1992). METEX-an expert system for machining planning. International Journal of Production Research, Vol. 30, No. 7, (1501-1516).
- Sivanandam, S.N.; Sumathi, S. & Deepa, S.N. (2007). Introduction to Fuzzy Logic using MATLAB, Springer, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
- The MathWorks, Inc. (2009). MATLAB Fuzzy Logic Toolbox, User's guide.
- Vitanov, V.I.; Harrison, D.K.; Mincoff, N.H. & Vladimirova, T.V. (1995). An expert system shell for the selection of metal cutting parameters. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 15, (111-116).
- Wong, S.V. & Hamouda, A.M.S. (2003a). The development of an online knowledge-based expert system for machinability data selection. Knowledge-based Systems, Vol. 16, (215-229).
- Wong, S.V. & Hamouda, A.M.S. (2003b). Machinability data representation with artificial neural network. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 138, (538-544).
- Wong, S.V.; Hamouda, A.M.S. & El Baradie, M.A. (1999). Generalized fuzzy model for metal cutting data selection. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 89-90, (310-317).
- Yazgan, Harun Resit; Boran, Semra & Goztepe, Kerim (2009). An ERP software selection process with artificial neural network based on analytic network process approach. Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 36, (9214-9222).
- Yilmaz, Oguzhan; Eyercioglu, Omer & Gindy, Nabil N.Z. (2006). A user-friendly fuzzy based system for the selection of electro discharge machining process parameters. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 172, (363-371).
- Zadeh, L.A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, Vol. (8), (338-353).
- Zuperl, Uros & Cus, Franci (2003). Optimization of cutting conditions during cutting by using neural networks. Robotics and Computer Integrated Manufacturing, Vol. 19, (189-199).
- References
- Baotic, M.; Christophensen, F.; Morari , M. (2006). Constrained Optimal Control of Hybrid Systems With a Linear Performance Index. IEEETrans. on Automatic Control, Vol.51, No 12., ISSN 1903-1919.
- Camacho, E.F.; Bordons, C. (2007). Model Predictive Control, Springer-Verlag, ISBN 1-85233- 694-3, London
- Coello, C. A. C.; Lamont, G. B. (2002). Evolutionary Algorithms for Solving Multi-Objective problems, Springer, ISBN 978-0-387-33254-3, Boston
- Dolezel, P.; Taufer, I. (2009a). PSD controller tuning using artificial intelligence techniques, Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Process Control '09, pp. 120-124, ISBN 978-80-227-3081-5, Strbske Pleso, june 2009, STU, Bratislava.
- Dolezel, P.; Mares, J. (2009b). Reactor Furnace Control using Artificial Neural Networks and Genetic Algoritm, Proceedings of the International Conference on Applied Electronics, pp. 99-102, ISBN 978-80-7043-781-0, Plzen, september 2009, ZCU, Plzen.
- Dwarapudi, S.; Gupta, P. K.; Rao, S. M. (2007). Prediction of iron ore pellet strength using artificial neural network model, ISIJ International, Vol. 47, No 1., ISSN 0915-1559.
- Economou, C.; Morari, M.; Palsson, B. (1986). Internal Model Control: extension to nonlinear system, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, Vol. 26, No 1, pp. 403-411, ISSN 0196-4305.
- Fletcher, R. (1987). Practical Methods of Optimization, Wiley, ISBN 978-0-471-91547-8, Chichester, UK.
- Lichota, J. ; Grabovski, M. (2010). Application of artificial neural network to boiler and turbine control, Rynek Energii, ISSN 1425-5960.
- Mares, J., Dusek, F., Dolezel, P.(2010a) Nelinearni a linearizovany model reaktorové pece. In Proceedings of Conference ARTEP'10", 24.-26. 2 2010.Technicka univerzita Kosice, 2010. Pp. 27-1 -27-14. ISBN 978-80-553-0347-5.
- Mares, J., Dusek, F., Dolezel, P.(2010b). Prediktivni rizeni reaktorove pece. In Proceedings of XXXVth Seminary ASR'10 "Instruments and Control", VSB-Technical University Ostrava, 2010. Pp. 269 -279. ISBN 978-80-248-2191-7.
- Montague, G.; Morris, J. (1994). Neural network contributions in biotechnology, Trends in biotechnology, Vol. 12, No 8., ISSN 0167-7799.
- Nguyen, H.; Prasad, N.; Walker, C. (2003). A First Course in Fuzzy and Neural Control, Chapman & Hall/CRC, ISBN 1-58488-244-1, Boca Raton.
- Norgaard, M.; Ravn, O.; Poulsen, N. (2000). A Neural Networks for Modelling and Control of Dynamic Systems, Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-1-85233-227-3, London.
- Rivera, D.; Morari, M.; Skogestad, S. (1986). Internal Model Control: PID Controller Design, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, Vol. 25, No 1., pp. 252-265, ISSN 0196-4305.
- Teixeira, A.; Alves, C.; Alves, P. M. (2005). Hybrid metabolic flux analysis/artificial neural network modelling of bioprocesses, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Hybrid Intelligent Systems, ISBN 0-7695-2457-5, Rio de Janeiro.
- References
- Bavarian B. (1988). Introduction to Neural Networks for Intelligent Control, IEEE Control Systems Magazine, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 3-7.
- Ebrahim Osama S., Mohamed A. Badr, Ali S. Elgendy, and Praveen K. Jain,(2010). ANN- Based Optimal Energy Control of Induction Motor Drive in Pumping Applications. IEEE Transactions On Energy Conversion, Vol. 25, No. 3, (Sept. 2010), pp. 652-660.
- Fukuda T. & Shibata T. (1992). Theory and Application of Neural Networks for Industrial Control Systems, IEEE Trans. on Industrial Electronics, Vol. 39, No. 6, pp. 472-489.
- Henneberger G. and B. Otto (1995). Neural network application to the control of electrical drives. Proceeding of Confrence of Power Electronics Intelligent Motion, pp. 103-123, Nuremberg, Germany.
- Karanayil B.; Rahman M. F. & Grantham C. (2003). Implementation of an on-line resistance estimation using artificial neural networks for vector controlled induction motor drive, Proceeding of IECON '03 29th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vol. 2, pp. 1703-1708.
- Kulawski G. and Mietek A. Brdyś (2000). Stable adaptive control with recurrent networks. Automatica A Journal of IFAC, the International Federation of Automatic Control, vol. 36, No. 1, (Jan. 2000), pp. 5-22.
- Kung Y. S., C. M. Liaw, and M. S. Ouyang (1995). Adaptive speed control for induction motor drive using neural network. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 42, no. 1, (Feb. 1995), pp. 9-16.
- Lippman R. P. (1987). An Introduction to Computing with Neural Nets, IEEE ASSP Magazine, Vol. 4, pp. 4-22.
- Ljung L. & Guo L. (1997). Classical model validation for control design purposes, Mathematical Modelling of Systems, 3, 27-42.
- Ljung L. & Sjöberg J. (1992). A System Identification Perspective on Neural Nets, Technical Report, Report No. LiTH-ISY-R-1373, At the location: www.control.isy.liu.se, May 27.
- Ljung L. (1995). System Identification, Technical Report, Report No. LiTH-ISY-R-1763, At the location: www.control.isy.liu.se.
- Ma X. & Na Z. (2000). Neural network speed identification scheme for speed sensor-less DTC induction motor drive system, PIEMC 2000 Proceeding. 3rd Int. Conference on Power Electronics and Motion Control, Vol. 3, pp. 1242-1245.
- Mehrotra P. ; Quaicoe J. E. & Venkatesan R. (1996a). Development of an Artificial Neural Network Based Induction Motor Speed Estimator, PESC '96 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Vol. 1, pp. 682-688.
- Mehrotra P.; Quaicoe J. E. & Venkatesan R. (1996b). Induction Motor Speed Estimation Using Artificial Neural Networks, IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, Vol. 2, pp. 607-610,
- Merabet Adel, Mohand Ouhrouche and Rung-Tien Bui (2006). Neural Generalized Predictive Controller for Induction Motor, International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Computer Sciences, Vol. 1, 1 (2006), pp. 83-100.
- Mohamed H. A. F.; Yaacob S. & Taib M. N. (1997). Induction Motor Identification Using Artificial Neural Networks, APEC 97 Electric Energy Conference, pp. 217-221, 29-30th Sep..
- Ninness B. & Goodwin G. C. (1994). Estimation of Model Quality, 10th IFAC Symposium Proceeding. on System Identification, 1, pp. 25-44.
- Orłowska-Kowalska T. and C. T. Kowalski (1996). Neural network based flux observer for the induction motor drive. Proceedingceding of International Confrence of Power Electronics Motion Control, pp. 187-191, Budapest, Hungary, 1996.
- Patterson D. W. (1996). Artificial Neural Networks: Theory and Applications, Simon and Schuster (Asia) Pte. Ltd., Singapore: Prentice Hall.
- Raison B., F. Francois, G. Rostaing, and J. Rogon (2000). Induction drive monitoring by neural networks. Proceeding of IEEE International Conference of Industrial Electronics,Control Instrumentation, pp. 859-863, Nagoya, Japan, 2000.
- Sharma A. K., R. A. Gupta, Laxmi Srivastava (2007). Performance of Ann Based Indirect Vector Control Induction Motor Drive, Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, Vol. 3, No. 3, (2007), pp 50-57.
- Simoes M. G. and B. K. Bose (1995).Neural network based estimation of feedback signals for a vector controlled induction motor drive. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications., vol. 31, no. 3, (May/Jun. 1995), pp. 620-629.
- Sjöberg J.; Zhang Q., Ljung L., Benveniste A., Deylon B., Glorennec P. Y., Hjalmarsson H., & Juditsky A. (1995). Nonlinear Black-Box Models In System Identification: A Unified Overview, Automatica, Vol. 31, No. 12, pp. 1691-1724.
- Toqeer R. S. & Bayindir N. S. (2000). Neurocontroller for induction motors, ICM 2000. Proceeding. 12th Int. Conference on Microelectronics, pp. 227-230.
- Vas P. (1990). Vector Control of AC Machines, Clarendon Press, Oxford.
- Weber M.; Crilly P. B. & Blass W. E. (1991). Adaptive Noise Filtering Using an Error- Backpropagation Neural Network, IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., Vol. 40(5), pp. 820-825.
- Wishart M. T. & Harley R. G. (1995). Identification And Control Of Induction Machines Using Artificial Neural Networks, IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, Vol. 31(3), pp. 612-619.
- Wlas M.; Krzeminski, Z.; Guzinski, J.; Abu-Rub, H.; Toliyat, H.A. (2005). Artificial- Neural-Network-Based Sensorless Nonlinear Control of Induction Motors, IEEE Transection of Energy conversion, Vol. 20, 3 (Sept 2005), pp. 520-528.
- Yabuta T. & Yamada T. (1991). Learning Control Using Neural Networks. Proceeding of the 1991 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Vol. 1, pp. 740-745. Reference Control of RUAV during Hover Bhaskar Prasad Rimal 1 , Idris E. Putro 2 , Agus Budiyono 2 , Dugki Min 3 and Eunmi Choi 1
- References
- A. U. Levin, k. s Narendra," Control of Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Using Neural Networks: Controllability and Stabilization", IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1993, Vol. 4, pp.192-206
- A. U. Levin, k. s Narendra," Control of Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Using Neural Networks-Part II: Observability, Identification and Control", IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1996, Vol. 7, pp. 30-42
- David E. Rumelhart et al., "The basic ideas in neural networks", Communications of the ACM, v.37 n.3, p.87-92, March 1994
- E. R. Mueller, "Hardware-in-the-loop Simulation Design for Evaluation of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Control Systems", AIAA Modeling and Simulation Technologies Conference and Exhibit , 20 -23 August, 2007, Hilton Head, South Carolina
- E. N. Johnson and S. Fontaine, "Use of flight simulation to complement flight testing of low-cost UAVs", AIAA Modeling and Simulation Technologies Conference and Exhibit, Montreal, Canada, 2001
- MATLAB and Simulink for Technical Computing, Available from: http://www.mathworks.com
- Oliver Nelles, "Nonlinear System Identification: From Classical Approaches to Neural Networks and Fuzzy Models, Springer
- Cybenko, G., "Approximation by Superposition of a Sigmoidal Function, Mathematics of Control, Signals and Systems, 303-314.
- N. K. and K. Parthasarathy, Gradient methods for the optimization of dynamical systems containing neural networks. IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, 252-262.
- B.G Martzios and F.L. Lewis, "An algorithm for the computation of the transfer function matrix of generalized two-dimensional systems " Journal of Circuit, System, and Signal Processing, Volume 7, Number 4 / December, 1988
- Budiyono A, Sudiyanto T, Lesmana H., "First Principle Approach to Modelling of Small Scale Helicopter", International Conference on Intelligent Unmanned System, 2007
- B. Mettler, T. Kanade, M.B. Tischler, "System Identification Modeling of a Model-Scale Helicopter", CMU-RI-TR-00-03. 2000.
- E. D. Beckmann, G. A. Borges, "Nonlinear Modeling, Identification and Control for a Simulated Miniature Helicopter," Robotic Symposium. LARS'08, pp.53-58, 2008.
- D. W. Marquardt. "An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters". SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, Vol. 11 No.2 pp. 431-441, 1963.
- S. Haykin, "Neural networks: A comprehensive foundation", IEEE Press, New York, USA, 1994
- K. S. Narendra and K. Parthasarathy, "Identification and control of dynamical systems using neural networks," IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 4-27, 1990.
- La Civita, M., G., P., Messner, W. C., and Kanade, T., "Design and Flight Testing of a High-Bandwidth H∞ Loop Shaping Controller for a Robotic Helicopter," Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference, No. AIAA 2002-4836, 2002.
- Sahasrabudhe, V., & Celi, R., "Improvement of off-design characteristics in integrated rotor-flight control system optimization". AHS, annual forum 53rd Virginia Beach, VA, April 29-May 1, 1997, Proceedings. Alexandria, VA, American Helicopter Society, 1997. Vol. 1 (A97-29180 07-01).
- Smerlas, A., Postlethwaite, I., Walker, D. J., Strange, M. E., Howitt, J., Horton, R. I., Gubbels, A. W., & Baillie, S. W. , "Design and flight testing of an H-infinity controller for the NRC Bell 205 experimental fly-by-wire helicopter. AIAA GNC conference, 1998.
- Li-Xin Wang, "Design and analysis of fuzzy identifiers of nonlinear dynamic systems". IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 40(1), 1995.
- Shaaban A. Salman, Vishwas R. Puttige, and Sreenatha G. Anavatti, "Real-time Validation and Comparison of Fuzzy Identification and State-space Identification for a UAV Platform" Proceeding of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, pages 2138-2143, 2006.
- R. Pintelon and J. Schoukens, "System Identification: A Frequency Domain Approach" Wiley-IEEE Press, 1st edition, 2001.
- Kumpati S. Narendra and Kannan Parthasarathy, "Identification and Control of Dynamical Systems Using Neural Networks" IEEE transaction on Neural Networks, 1(1), 1990.
- Magnus Norgaard, "Neural Network Based System Identification Tool Box", Version 2, 2000
- Budiyono, A. and Sutarto, H.Y., Linear Parameter Varying Model Identification for Control of Rotorcraft-based UAV, Fifth Indonesia-Taiwan Workshop on Aeronautical Science, Technology and Industry, Tainan, Taiwan, November 13-16, 2006
- M. M. Korjani, O.Bazzaz, M. B. Menhaj, "Real time identification and control of dynamics systems using recurrent neural network", Journal of Artificial Intelligence Review, Springer, August 2009
- W. Yu, X. Li, "Recurrent fuzzy neural networks for nonlinear system identification", 22nd IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control Part of IEEE Multi- conference on Systems and Control, Singapore, 1-3 October 2007.
- Shim D. H., Kin H. J., Sastry. "Control System Design for Rotorcraft-based Unmanned Aerial Vehicles using Time-domain System Identification". IEEE International Conference on Control Application, 2000. pp. 808-813
- References
- Singh, G. K. & Kazzaz, S. A. S. A. (2003). Induction Machine Drive Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Research -a Survey, Electric Power Systems Research, Vol. 64, pp. 145- 158.
- Huang, H. -H. (1993). Transputer-Based Machine Fault Diagnostic, Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of Industrial Engineering, The University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa.
- Knapp, G. M. and Wang, H. -P. (1992). Machine Fault Classification: A Neural Network Approach, International Journal of Production Research, Vol. 30, No. 4, pp. 811-823.
- Knapp, G. M., (1992). Hierarchical Integrated Maintenance Planning for Automated Manufacturing Systems, Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of Industrial Engineering, The University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa.
- Carpenter, G. A. & Grossberg, S. (1987b). ART2: Self-Organization of Stable Category Recognition Codes for Analog Input Patterns, Applied Optics, Vol. 26, No. 23, December, pp. 4919-4930.
- Carpenter, G. A.; Grossberg, S. & Reynolds, J. H. (1991). ARTMAP: Supervised Real-Time Learning and Classification of Non-stationary Data by a Self-Organizing Neural Network, Neural Networks, Vol. 4, pp. 565-588.
- Spoerre, J. K. (1993). Machine Performance Monitoring and Fault Classification Using an Exponentially Weighted Moving Average Scheme, Master Thesis, Department of Industrial Engineering, The University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA.
- Monk, R. (1972). Vibration Measurement Gives Early Warning of Mechanical Faults, Process Engineering, November, pp. 135-137.
- Wheeler, P. G. (1968). Bearing Analysis Equipment Keeps Downtime Down, Plant Engineering, Vol. 25, pp. 87-89.
- Gersch, W. & Liu, T. S. (1976). Time Series Methods for the Synthesis of Random Vibration Systems, ASME Journal of Applied Mechanical, Vol. 43, No. 1, pp. 159-165.
- Akaike, H. (1969). Power Spectrum Estimation through Autoregression Model Fitting, Ann. Inst. Stat. Math., Vol. 21, pp. 407-419.
- Akaike, H. (1974). A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification, IEEE Transactions on Automation Control, Vol. AC-19, December, pp. 716-723.
- Gersch, W.; Brotherton, T. & Braun, S. (1983). Nearest Neighbor-Time Series Analysis Classification of Faults in Rotating Machinery, Transactions of the ASME, Vol. 105, April, pp. 178-184.
- Swingler, D. N. (1980). Frequency Errors in MEM processing, IEEE Transactions on Acoustic, Speech, Signal Processing, Vol. ASSP-28, April, pp. 257-259.
- Kay, S. M. (1988). Modern Spectral Estimation: Theory and Application, Prentice Hall Inc., NJ.
- Marple, S. L. Jr. (1987). Digital Spectral Analysis with Applications, Prentice Hall Inc., NJ.
- Mathew, J. & Alfredson, R. J. (1984). The Condition Monitoring of Rolling Element Bearings Using Vibration Analysis," Journal of Vibration, Acoustics, Stress, and Reliability in Design, Vol. 106, July, pp. 447-453.
- Mathew, J. (1989). Monitoring the Vibrations of Rotating Machine Elements--An Overview, ASME, DE Vol. 18-5, pp. 15-22.
- Dyer, D. & Stewart, R. M. (1978). Detection of Rolling Element Bearing Damage by Statistical Vibration Analysis, Transactions of the ASME Journal of Mechanical Design, Vol. 100, April, pp. 229-235.
- Grossberg, S. (1976a). Adaptive Pattern Classification and Universal I: Parallel Development and Coding of Neural Feature Detectors, Biological Cybernetics, Vol. 23, pp. 121-134.
- Grossberg, S. (1976b). Adaptive Pattern Classification and Universal II: Feedback Expectation Olfaction and Illusions, Biological Cybernetics, Vol. 23, pp. 187-202.
- Grossberg, S. (1987a). Competitive Learning: from Interactive Activation to Adaptive Resonance, Cognitive Science, Vol. 11, pp. 23-63.
- Banquet, J. P. & Grossberg, S. (1987). Probing Cognitive Processes Through the Structure of Event-related Potentials during Learning: an Experimental and Theoretical Analysis, Applied Optics, Vol. 26, No. 23, December, pp. 4931-4944.
- Air compressor
- Service Unit
- SPC 200 Controller
- Analog Pressure Transducers 5. Gripper
- NI Compact FieldPoint System 10. Power Supply other. Since they did not need training, they are very convenient for industrial applications. However, it is unrealistic to expect them to assign different categories for the normal operation and each fault modes, and classify all the incoming cases accurately.
- References
- Aykut, S., Demetgul, M. & Tansel, I. N. (2010). Selection of Optimum Cutting Condition of Cobalt Based Alloy with GONN. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 46, No. 9-12, pp. 957-967.
- Beale, M. H., Hagan, M. T. & Demuth, H. B. (2010). Neural Network Toolbox 7 User Guide, Mathworks. http://www.mathworks.com/help/pdf_doc/nnet/nnet.pdf.
- Belforte, G., Mauro, S. & Mattiazzo, G. (2004). A method for increasing the dynamic performance of pneumatic servo systems with digital valves, Mechatronics, Vol.14, pp. 1105-1120.
- Bryson, A. E., Ho, Y. C. (1975). Applied optimal control: optimization, estimation, and control. Taylor & Francis Publishing, pp. 481.
- Bouamama, B.O. et al. (2005). Fault detection and isolation of smart actuators using bond graphs and external models, Control Engineering Practice, Vol. 13, pp.159-175.
- Carpenter, G. A & Grossberg, S. (1987). ART-2: Self-Organization of Stable Category Recognition Codes for Analog Input Pattern, Applied Optics, Vol. 26, pp. 4919-4930.
- Carpenter, G. A., Grossberg S., & Reynolds J. H. (1991). ARTMAP: Supervised real-time learning and classification of nonstationary data by a self-organizing neural network, Neural Networks , Vol. 4, pp.565-588.
- Carpenter, G. A., Grossberg, S. & Rosen, D. B. (1991a). ART 2-A: An adaptive resonance algorithm for rapid category learning and recognition, Neural Networks , Vol. 4, pp. 493-504.
- Carpenter, G. A., Grossberg, S. & Rosen, D. B. (1991b). Fuzzy ART: Fast stable learning and categorization of analog patterns by an adaptive resonance system, Neural Networks , Vol. 4, pp. 759-771.
- Carpenter, G. A. et al. (1992). Fuzzy ARTMAP: A neural network architecture for incremental supervised learning of analog multidimensional maps, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, Vol. 3, pp. 698-713.
- Chen, C. & Mo, C. (2004). A method for intelligent fault diagnosis of rotating machinery, Digital Signal Processing, Vol. 14, pp. 203-217.
- Chena, P. et al. (2007). A study of hydraulic seal integrity. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 21, pp.1115-1126.
- Demetgul M.; Tansel IN. & Taskin S. (2009). Fault Diagnosis of Pneumatic Systems with Artificial Neural Network Algorithms. Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 36, No. 7, pp. 10512-10519.
- Garrett, A. (2003). Fuzzy ART and Fuzzy ARTMAP Neural Networks, http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/4306.
- Gary M. & Ning, S., (2007). Experimental Comparison of Position Tracking Control Algorithms for Pneumatic Cylinder Actuators, IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, October 2007.
- Grossberg S. (1987). Competitive learning: From interactive activation to adaptive resonance, Cognitive Science, Vol. 11, pp. 23-63.
- Huang, R.; Xi, L.; Li, X.; Liu, C.R.; Qiu, H. & Lee, J. (2007). Residual life predictions for ball bearings based on self-organizing map and back propagation Neural network methods, Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 21, pp.193-207.
- Karpenko, M.; Sepehri, N. & Scuse, D. (2003). Diagnosis of process valve actuator faults using a multilayer Neural network. Control Engineering Practice, Vol. 11, pp.1289- 1299.
- Lee, I. S.; Kim, J. T.; Lee, J. W.; Lee, D. Y. & Kim, K. Y. (2003). Model-Based Fault Detection and Isolation Method Using ART2 Neural Network, International Journal of Intelligent Systems, Vol.18, pp. 1087-1100.
- Li, X. & Kao, I. (2005). Analytical fault detection and diagnosis (FDD) for pneumatic systems in robotics and manufacturing automation. Intelligent Robots and Systems, IEEE/RSJ International Conference, pp.2517-2522.
- Lu, P. J.; Hsu, T. C.; Zhang, M. C. & Zhang, J. (2000), An Evaluation of Engine Fault Diagnostics Using Artificial Neural Networks, ASME J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power, Vol. 123, pp. 240-246.
- McGhee, J.; Henderson, I. A. & Baird, A. (1997). Neural networks applied for the identification and fault diagnosis of process valves and actuators, Measurement, Vol. 20, No. 4, pp. 267-275.
- Mendonça, L. F.; Sousa, J. M. C. & Costa, J. M. G. (2009). An architecture for fault detection and isolation based on fuzzy methods, Expert Systems with Applications. Vol. 36 pp. 1092-1104.
- Na, C. & Lizhuang, M. (2008). Pattern Recognition Based on Weighted and Supervised ART2. International Conference on Intelligent System and Knowledge Engineering, Xiamen, China, Nov. 17-18, 2008,Vol. 2, pp. 98-102.
- Nakutis, Ž., Kaškonas, P. (2005). Application of ANN for pneumatic cylinder leakage diagnostics. Matavimai, Vol. 36, No.4, pp.16-21.
- Nakutis, Ž. & Kaškonas, P. (2007. Pneumatic cylinder diagnostics using classification methods. Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, Warsaw, 1-3 May 2007, pp.1-4.
- Nakutis, Ž. & Kaškonas, P. (2008). An approach to pneumatic cylinder on-line conditions monitoring. Mechanika. Kaunas: Technologija, Vol. 4, No. 72, pp.41-47.
- Nazir, M. B. & Shaoping, W. (2009). Optimization Based on Convergence Velocity and Reliability for Hydraulic Servo System, Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, Vol. 22, pp. 407-412.
- Ning, S. & Bone, G. M. (2005). Development of a nonlinear dynamic model for a servo pneumatic positioning system, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Mechatronics Autom., pp. 43-48.
- Nogami, T. et al. (1995). Failure diagnosis system on pneumatic control valves by neural networks. IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Vol. 2, pp. 724-729.
- Rajakarunakaran, S.; Venkumar, P.; Devaraj, D. & Rao, K.S.P. (2008). Artificial neural network approach for fault detection in rotary system, Applied Soft Computing, Vol. 8, No. 1, pp.740-748.
- Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E., and Williams, R. J. (1976). Learning internal representations by error propagation. In Rumelhart, D. E. and McClelland, J. L., editors, Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition. Volume 1: Foundations, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. pp 318-362.
- Sepasi, M. & Sassani, F. (2010). On-line Fault Diagnosis of Hydraulic Systems Using Unscented Kalman Fitler, International Journal of Control and Automation Systems, Vol. 8, No. 1, pp. 149-156.
- Shi, L. & Sepehri, N. (2004). Adaptive Fuzzy-Neural-Based Multiple Models for Fault Diagnosis of a Pneumatic Actuator, Proceeding of the 2004 American Control Conference, Boston. Massachusetts, June 30 -July 2, 2004.
- Song, S. O.; Lee, G. & Yoon, E.N. (2004). Process Monitoring of an Electro-Pneumatic Valve Actuator Using Kernel Principal Component Analysis, Proceedings of the International Symposium on Advanced Control of Chemical Processes. Hong Kong, China, 11-14 January 2004.
- Taghizadeh, M.; Ghaffari, A. & Najafi, F. (2009). Improving dynamic performances of PWM- driven servo-pneumatic systems via a novel pneumatic circuit, ISA Transactions, Vol.48, pp. 512-518.
- Takosoglu, J. E.; Dindorf, R. F. & Laski, P. A. (2009). Rapid prototyping of fuzzy controller pneumatic servo-system. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 40, No.3/4, pp. 349-361.
- Tansel, I. N. ; Demetgul, M. ; Leon, R. A. ; Yenilmez, A. & Yapici A. (2009). Design of Energy Scavengers of Structural Health Monitoring Systems Using Genetically Optimized Neural Network Systems, Sensors and Materials, Vol. 21, No. 3, pp. 141-153.
- Tansel I. N.; Demetgul M. & Sierakowski R. L. (2009). Detemining Initial Design Parameters By Using Genetically Optimized Neural Network Systems. Sapuan SM, Selangor S, Mujtaba IM(ed) Composite Materials Technology: Neural Network Applications. Taylor & Francis(CRC Press).
- Tsai Y. C. & Huang, A. (2008). Multiple-surface sliding controller design for pneumatic servo systems, Mechatronics, Vol. 18, pp. 506-512.
- Uppal, F.J.; Patton, R.J. & Palade, V. (2002). Neuro-fuzzy based fault diagnosis applied to an electro-pneumatic valve, Proceedings of the 15th IFAC World Congress, Barcelona, Spain, 2002, pp. 2483-2488.
- Uppal, F. J.; & Patton, R. J. (2002). Fault Diagnosis of an Electro-pneumatic Valve Actuator Using Neural Networks With Fuzzy Capabilities, European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Bruges, Belgium, 24-26 April 2002, pp. 501-506.
- Wang, J. et al. (2004). Identification of pneumatic cylinder friction parameters using genetic algorithms. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, Vol. 9, No.1, pp. 100-104.
- Yang, B. S.; Han, T. & An J. L. (2004). ART-KOHONEN neural network for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery, Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, Vol. 18, pp. 645-657.
- Yang, W.X. (2006). Establishment of the mathematical model for diagnosing the engine valve faults by genetic programming. Journal of Sound and Vibration, Vol. 293, pp.213-226.
- References
- Al-Assadi, H.M.A.A.; Hamouda, A.M.S.; Ismail, N. & Aris, I. (2007). An adaptive learning algorithm for controlling a two-degree-of-freedom serial ball-and-socket actuator. Proceedings of the IMechE Part I Journal of Systems & Control Engineering, Vol.221, No. 7,pp.1001-1006.
- Antonelli, G.; Chiaverini, S. & Fusco, G. (2003). A new on-line algorithm for inverse kinematics of robot manipulators ensuring path-tracking capability under joint limits. IEEE Transaction on Robotics and Automation, Vol.19, No.1, pp. 162-167.
- Bingual, Z.; Ertunc, H.M. & Oysu, C. (2005). Comparison of Inverse Kinematics Solutions Using Neural Network for 6R Robot Manipulator with Offset. ICSC congress on Computational Intelligence.
- Driscoll, J.A. (2000). Comparison of neural network architectures for the modeling of robot inverse kinematics. Proceedings of the IEEE, south astcon, pp. 44-51.
- D'Souza, A.; Vijayakumar, S. & Schaal, S. (2001). Learning Inverse Kinematics. Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE/ RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp.298- 303, Maui, Haw-USA.
- Fu, K.S.; Gonzalez, R.C. & Lee, C.S.G. (1987). Robotics control, Sensing, Vision and intelligence, McGraw-Hill Book Co, New York.
- Funahashi, K.I., 1998. On the approximate realization of continuous mapping by neural networks. Journal of Neural Networks, Vol.2, No.3, pp.183-192.
- Graca, R.A. & Gu, Y. (1993). A Fuzzy Learning Algorithm for Kinematic Control of a Robotic System. Proceeding of the 32nd Conference on Decision and Control, pp.1274-1279, San Antonio, Texas, USA.
- Hasan, A.T.; Hamouda, A.M.S.; Ismail, N. & Al-Assadi, H.M.A.A. (2007). A new adaptive learning algorithm for robot manipulator control. Proceeding of the IMechE, Part I: Journal of System and Control Engineering, Vol.221, No.4, pp. 663-672.
- Hasan, A.T.; Hamouda, A.M.S.; Ismail, N. & Al-Assadi, H.M.A.A.(2006). An adaptive- learning algorithm to solve the inverse kinematics problem of a 6 D.O.F serial robot manipulator. Journal of Advances in Engineering Software, Vol.37, pp. 432-438.
- Haykin S. (1994). Neural Networks. A Comprehensive Foundation. New York: Macmillan.
- Hornik, K. (1991). Approximation capabilities of multi-layer feed forward networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks, Vol.4, No.2, pp. 251-257.
- Hu, Z.; FU, Z. & Fang, H. (2002). Study of singularity robust inverse of Jacobian matrix for manipulator, Proceedings of the First International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, pp. 406-410,China, Beijing.
- Kalogirou, S.A. (2001) Artificial Neural Networks In Renewable Energy Systems Applications: a review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. Vol. 5,pp.373-401.
- Karilk, B. & Aydin, S. (2000). An improved approach to the solution of inverse kinematics problems for robot manipulators. Journal of Engineering applications of artificial intelligence, Vol.13, pp.159-164.
- Köker, R. (2005). Reliability-based approach to the inverse kinematics solution of robots using Elman's networks. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Vol.18, pp. 685-693.
- Köker, R.; Öz, C.; Çakar.T. & Ekiz, H. (2004). A study of neural network based inverse kinematics solution for a three-joint robot. Journal of Robotics and Autonomous Systems, Vol.49, pp. 227-234.
- Kuroe, Y.; Nakai, Y. & Mori, T. (1994). A new Neural Network Learning on Inverse Kinematics of Robot Manipulators, International Conference on Neural Networks, IEEE world congress on computational Intelligence. Vol.5, pp. 2819-2824.
- Nakamura, Y. & Hanafusa, H. (1986). Inverse kinematic solutions with singularity robustness for robot manipulator control, Journal of Dynamic Systems Measurements Control, Vol. 108,pp. 163-171.
- Ogawa, T.; Matsuura, H. & Kanada, H. (2005). A Solution of Inverse Kinematics of Robot Arm Using Network Inversion. Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Modelling, Control and Automation.
- Santosh, A. ;Devendra P. Garg. (1993). Training back propagation and CMAC neural networks for control of a SCARA robot. Journal of Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence. Vol.6.No.2. pp.105-115.
- Wampler, C. W. & Leifer, L. J. (1988). Applications of damped least-squares methods to resolved-rate and resolved-acceleration control of manipulators. Journal of Dynamic Systems Measurements Control, Vol. 110,pp. 31-38.
- Wampler, C. W. (1986). Manipulator inverse kinematic solutions based on vector formulations and damped least-squares methods, IEEE Transaction Syst., Man, Cybernetics. Vol. 16,pp. 93-101.
- Whitney. E. (1969). Resolved motion rate control of manipulators and human prostheses. IEEE Transaction Man-Mach. Systems, Vol. MMS-10,pp.47-53.
- Zurda, M. J. (1992). Introduction to Artificial Neural System Network. West Publishing Companies, ISBN 0-314-93397-3, St. Paul, MN, USA.
Related papers
Advances in Computational Intelligence
Proceedings of 10th World Congress on Computational Mechanics, 2014
Tekstil Ve Konfeksiyon, 2017
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2008
Fibres and Textiles in Eastern Europe, 2017
Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2008
Journal of the Textile Institute, 2006
Current Trends in Fashion Technology & Textile Engineering, 2020
Shock and Vibration, 1993
MATEC Web of Conferences
Textile Research Journal, 2013
Reviews in Chemical Engineering, 2013
 Kenji Suzuki
Kenji Suzuki
