Copolymerization of lactones and bioaromatics via concurrent ring-opening polymerization/polycondensation

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
Concurrent ring-opening polymerization/polycondensation of lactones and bioaromatic hydroxy-acids yields random copolymers with improved and controlled thermal properties.
Figures (418)





![Figure S1. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 1).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_003.jpg)
![Figure 82. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_004.jpg)
![Figure S3. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_005.jpg)
![Figure S4. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 4).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_006.jpg)
![Figure S5. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_007.jpg)
![Figure S6. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 6).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_008.jpg)
![Figure $7. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_009.jpg)
![Figure S8. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_010.jpg)
![Figure S9. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 8 and Table S2 entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_011.jpg)

![Figure S11. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 2)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_013.jpg)
![Figure S12. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_014.jpg)
![Figure S13. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 4)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_015.jpg)
![Figure § S14. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_016.jpg)
![Figure $15. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 6)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_017.jpg)
![Figure S16. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 7)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_018.jpg)
![Figure S17. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_019.jpg)
![Figure $18. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 10).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_020.jpg)

![Figure $20. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanilic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 12). Figure S19. GPC Chromatogram of polyethylene syringate (Table S2, entry 21).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_022.jpg)
![Figure | $21. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanilic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 13)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_023.jpg)
![Figure $22. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanilic acid) [70:30] (Table 2, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_024.jpg)
![Figure $23. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanilic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_025.jpg)

![Figure $25. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanilic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 17).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_027.jpg)
![Figure | $26. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanilic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 18).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_028.jpg)
![Figure S27. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanilic acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 19](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_029.jpg)
![Figure $28. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanilic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 20).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_030.jpg)
![Figure S29. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 22).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_031.jpg)

![Figure | $31. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 24).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_033.jpg)
![Figure $32. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 25).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_034.jpg)
![Figure | $33. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 26)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_035.jpg)
![Figure S34. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 27).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_036.jpg)
![Figure $35. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 28)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_037.jpg)
![Figure $36. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 29).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_038.jpg)
![Figure | S837. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 30).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_039.jpg)

![Figure S39. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 32)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_041.jpg)


![Figure S41. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 34)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_044.jpg)
![Figure $43. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [80:20] (Table S3, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_045.jpg)

![Figure S45. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [40:60] (Table S3, entry 4).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_047.jpg)
![Figure S46. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S3, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_048.jpg)
![Figure S47. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [80:20] (Table S3, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_049.jpg)

![Figure S49. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [40:60] (Table S3, entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_051.jpg)

![Figure S51. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [90:10] (Table S3, entry 12).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_053.jpg)

![Figure S53. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [70:30] (Table S3, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_055.jpg)


![Figure S56. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [90:10] (Table S3, entry 18) Figure S55. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [20:80] (Table S3, entry 16).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_058.jpg)

![Figure S58. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [70:30] (Table S3, entry 20).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_060.jpg)
![Figure S59. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 21).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_061.jpg)

![‘igure $61. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 10 min. (Table S4, entry 1).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_063.jpg)
![Figure S62. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 20 min. (Table S4, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_064.jpg)
![‘igure. $63. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 30 min. (Table S4, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_065.jpg)
![Figure S64. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 1 hour (Table S4, entry 4)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_066.jpg)
![Figure S65. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 1.5 hours (Table S4, entr 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_067.jpg)
![Figure S66. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2 hours (Table S4, entry 6).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_068.jpg)
![Figure S67. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2.5 hours (Table S4, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_069.jpg)
![Figure | S68. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 3 hours (Table S4, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_070.jpg)
![Figure S69. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 3.5 hours (Table S4, entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_071.jpg)
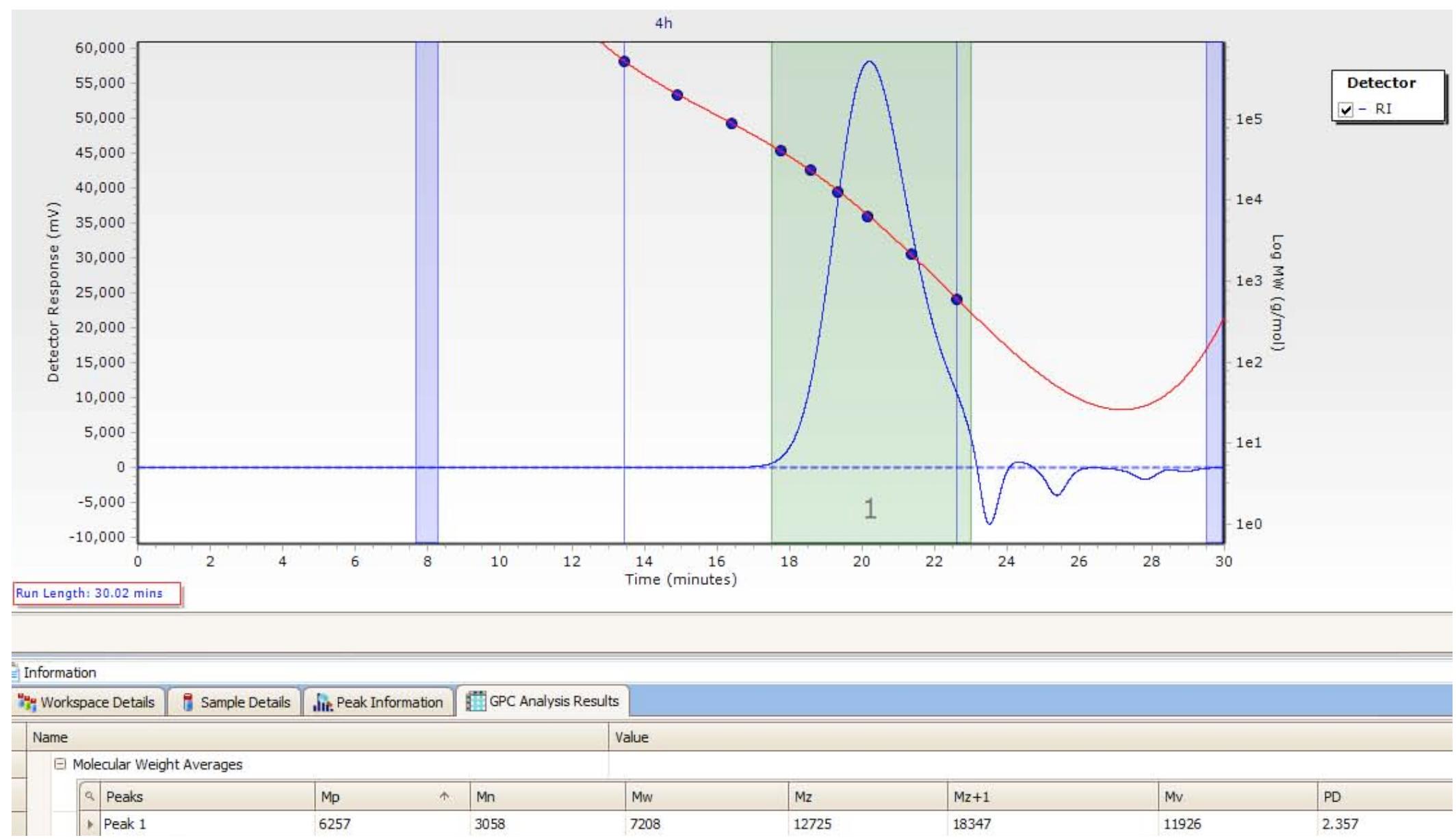
![Figure S71. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 4.5 hours (Table S4, entr 11).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_073.jpg)
![Figure $72. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 5 hours (Table S4, entry 12).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_074.jpg)
![Figure S73. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 6 hours (Table S4, entry 13](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_075.jpg)
![Figure S74. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 7 hours (Table S4, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_076.jpg)
![‘igure S75. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 8 hours (Table S4, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_077.jpg)
![Figure S76. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 9 hours (Table S4, entry 16)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_078.jpg)
![Figure S77 . GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 10 hours (Table S4, entry 17).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_079.jpg)
![Figure $78. GPC Chromatogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 13 hours (Table S4, entr 18).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_080.jpg)
![Figure S79. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 1).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_081.jpg)

![Figure S81. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_083.jpg)

![Figure S82. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_085.jpg)


![Figure S84. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 7). Figure S83. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 6).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_088.jpg)
![Figure S85. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_089.jpg)
![Figure S86. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S1, entry 9 and Table S2. entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_090.jpg)


![Figure S88. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_093.jpg)
![Figure S90. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 4).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_094.jpg)




![Figure S92. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 6).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_099.jpg)
![Figure $93. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_100.jpg)

![Figure S94. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_102.jpg)

![Figure S95. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 10).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_104.jpg)
![Figure S97. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 12).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_105.jpg)
![Figure S98. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 13).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_106.jpg)
![Figure S99. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_107.jpg)

![Figure $101. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 16).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_109.jpg)
![Figure $102. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 17).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_110.jpg)
![Figure $103. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 18).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_111.jpg)
![Figure $104. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 19).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_112.jpg)
![Figure $105. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 20).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_113.jpg)


![Figure $108. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 23). Figure $107. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [90:10] (Table $2, entry 22).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_116.jpg)
![Figure $109. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 24).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_117.jpg)
![Figure $110. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 25).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_118.jpg)

![Figure $112. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 27). Figure S111. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 26).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_120.jpg)

![Figure $114. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 29). Figure $113. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 28).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_122.jpg)
![Figure $115. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 30).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_123.jpg)


![Figure $118. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 33). Figure $117. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 32).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_126.jpg)

![Figure $119. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 34).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_128.jpg)


![Figure $122. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [80:20] (Table S3, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_131.jpg)
![Figure $123. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_132.jpg)

![Figure S125. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S3, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_134.jpg)
![Figure $126. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [80:20] (Table S3, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_135.jpg)
![Figure $127. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [60:40] (Table $3, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_136.jpg)

![Figure $129. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [20:80] (Table S3, entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_138.jpg)


![Figure $132. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [70:30] (Table S3, entry 14). Figure $131. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [80:20] (Table S3, entry 13).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_141.jpg)
![Figure $133. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_142.jpg)


![Figure $136. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [80:20] (Table S3, entry 19). Figure $135. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [90:10] (Table $3, entry 18).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_145.jpg)
![Figure $137. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [70:30] (Table S3, entry 20).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_146.jpg)
![Figure $138. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 21).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_147.jpg)
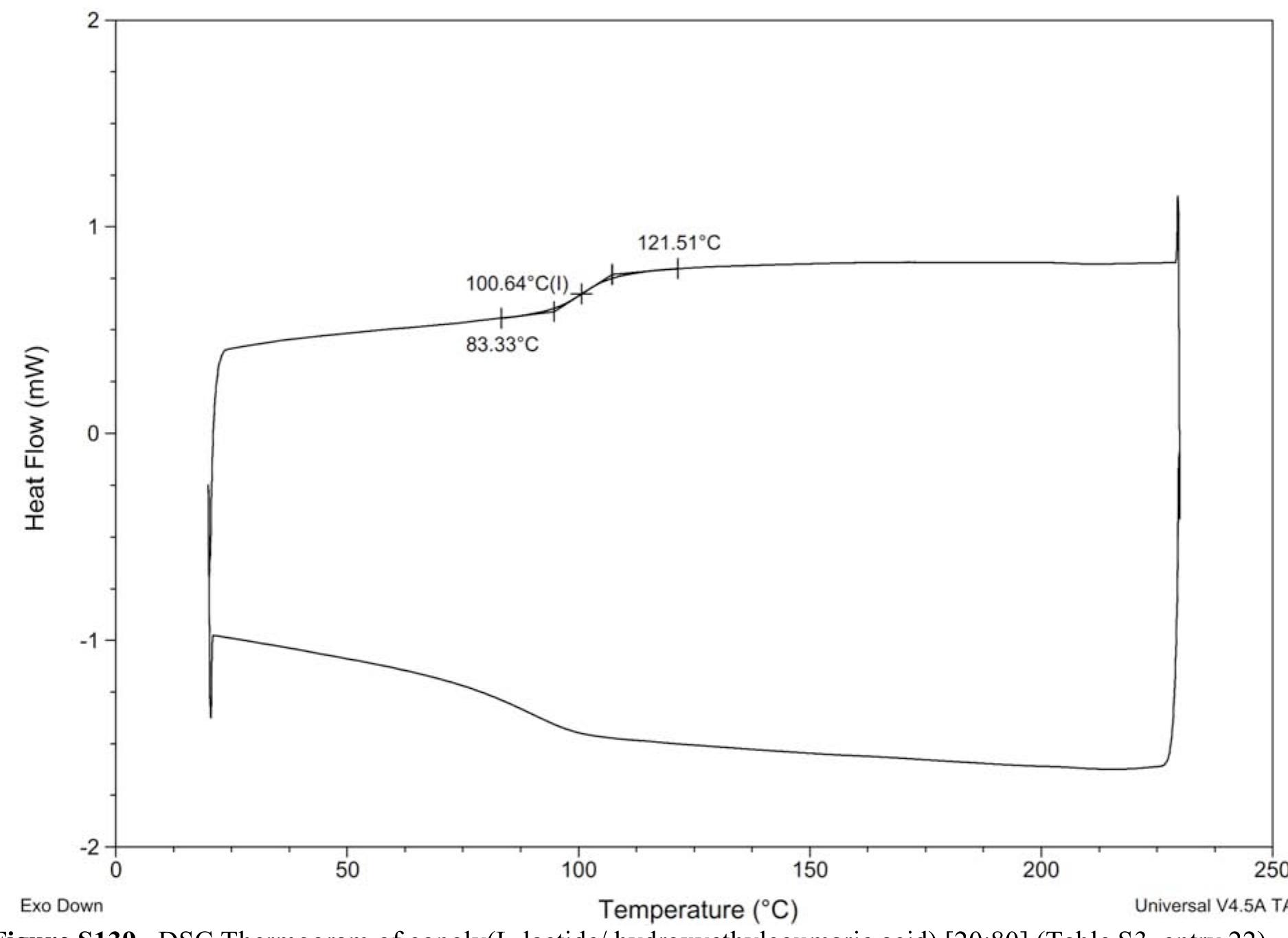
![Figure $140. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 10 min. (Table S4, entry 1). Figure S139. DSC Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [20:80] (Table S3, entry 22).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_149.jpg)
![Figure $141. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 20 min. (Table S4, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_150.jpg)
![Figure $8142. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 30 min. (Table S4, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_151.jpg)
![Figure $143. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 1 hour (Table S4, entry 4).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_152.jpg)
![Figure $144. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 1.5 hours (Table S4, entr 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_153.jpg)
![Figure $145. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2 hours (Table S4, entry 6).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_154.jpg)
![Figure S146. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2.5 hours (Table S4, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_155.jpg)


![Figure S148. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 3.5 hours (Table S4, entry 0) Figure $147. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 3 hours (Table S4, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_158.jpg)
![ee ee: eee Figure $149. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ ‘hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 4 hours (Table S4, entry 10).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_159.jpg)

![Figure $150. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 4.5 hours (Table $4, entry 11).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_161.jpg)

![Figure S152. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 6 hours (Table S4, entry 13). Figure $151. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 5 hours (Table S4, entry 12).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_163.jpg)
![Figure $153. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 7 hours (Table S4, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_164.jpg)
![Figure $154. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 8 hours (Table S4, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_165.jpg)
![Re ee Figure $155. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 9 hours (Table S4, entry 16)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_166.jpg)
![Figure $156. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 10 hours (Table S4, entr 17).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_167.jpg)
![Figure $157. DSC Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 13 hours (Table S4, entry 18).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_168.jpg)


![Figure $159. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_171.jpg)
![Figure S160. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_172.jpg)

![Figure $162. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_174.jpg)

![Figure S163. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 6).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_176.jpg)
![Figure $164. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_177.jpg)
![Figure $165. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_178.jpg)
![Figure $166. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_179.jpg)
![Figure S167. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 10).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_180.jpg)

![Figure $169. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 12).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_182.jpg)
![Figure $170. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 13).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_183.jpg)
![Figure $171. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_184.jpg)
![Figure $172. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_185.jpg)

![Figure $174. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 17).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_187.jpg)
![Figure $175. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 18).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_188.jpg)
![Figure S176. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 19).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_189.jpg)


![Figure $179. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 22).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_192.jpg)
![Figure S180. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 23).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_193.jpg)
![Figure $181. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 24).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_194.jpg)
![Figure $182. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 25).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_195.jpg)
![Figure $183. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 26).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_196.jpg)
![Figure S184. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [40:60] (Table S3, entry 37).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_197.jpg)
![Figure $185. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 28).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_198.jpg)
![Figure $186. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 29).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_199.jpg)
![Figure 8187. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 30).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_200.jpg)


![Figure $189. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 32). Figure S188. TGA Thermogram of polyethylene ferulate (Table 82, entry 31).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_203.jpg)
![Figure 8190. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 33).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_204.jpg)
![Figure $191. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 34).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_205.jpg)


![tigure $194. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [80:20] (Table $3, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_208.jpg)

![Figure $196. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [40:60] (Table $3, entry 4).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_210.jpg)

![Figure S198. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [80:20] (Table $3, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_212.jpg)
![Figure $199. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_213.jpg)
![Figure S200. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [40:60] (Table S3, entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_214.jpg)

![Figure $202. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethyl ferulic acid) [90:10] (Table $3, entry 12).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_216.jpg)
![Figure $203. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [80:20] (Table $3, entry 13).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_217.jpg)
![Figure $204. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [70:30] (Table $3, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_218.jpg)
![Figure S205. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_219.jpg)
![Figure S206. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [20:80] (Table S3, entry 16).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_220.jpg)

![Figure S208. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [80:20] (Table S3, entry 19).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_222.jpg)
![Figure S209. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [70:30] (Table S3, entry 20).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_223.jpg)
![Figure 8210. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 21).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_224.jpg)
![Figure S211. TGA Thermogram of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [20:80] (Table S3, entry 22).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_225.jpg)
![Figure $8212. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 10 min. (Table S4, entry 1).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_226.jpg)

![Figure 8214. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 30 min. (Table S4, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_228.jpg)

![Figure S216. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 1.5 hours (Table S4, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_230.jpg)

![Figure $218. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2.5 hours (Table S4, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_232.jpg)

![Figure $8220. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 3.5 hours (Table S4, entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_234.jpg)

![Figure $222. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 4.5 hours (Table S4, entry 11).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_236.jpg)

![Figure $224. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 6 hours (Table S4, entry 13)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_238.jpg)
![Figure 8225. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 7 hours (Table S4, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_239.jpg)
![Figure 8226. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 8 hours (Table S4, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_240.jpg)
![Figure 8227. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 9 hours (Table S4, entry 16).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_241.jpg)
![ere wee AES we gay Figure $228. TGA Thermogram of copoly(caprolactone/ ‘hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 10 hours (Table S4, entry 17).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_242.jpg)
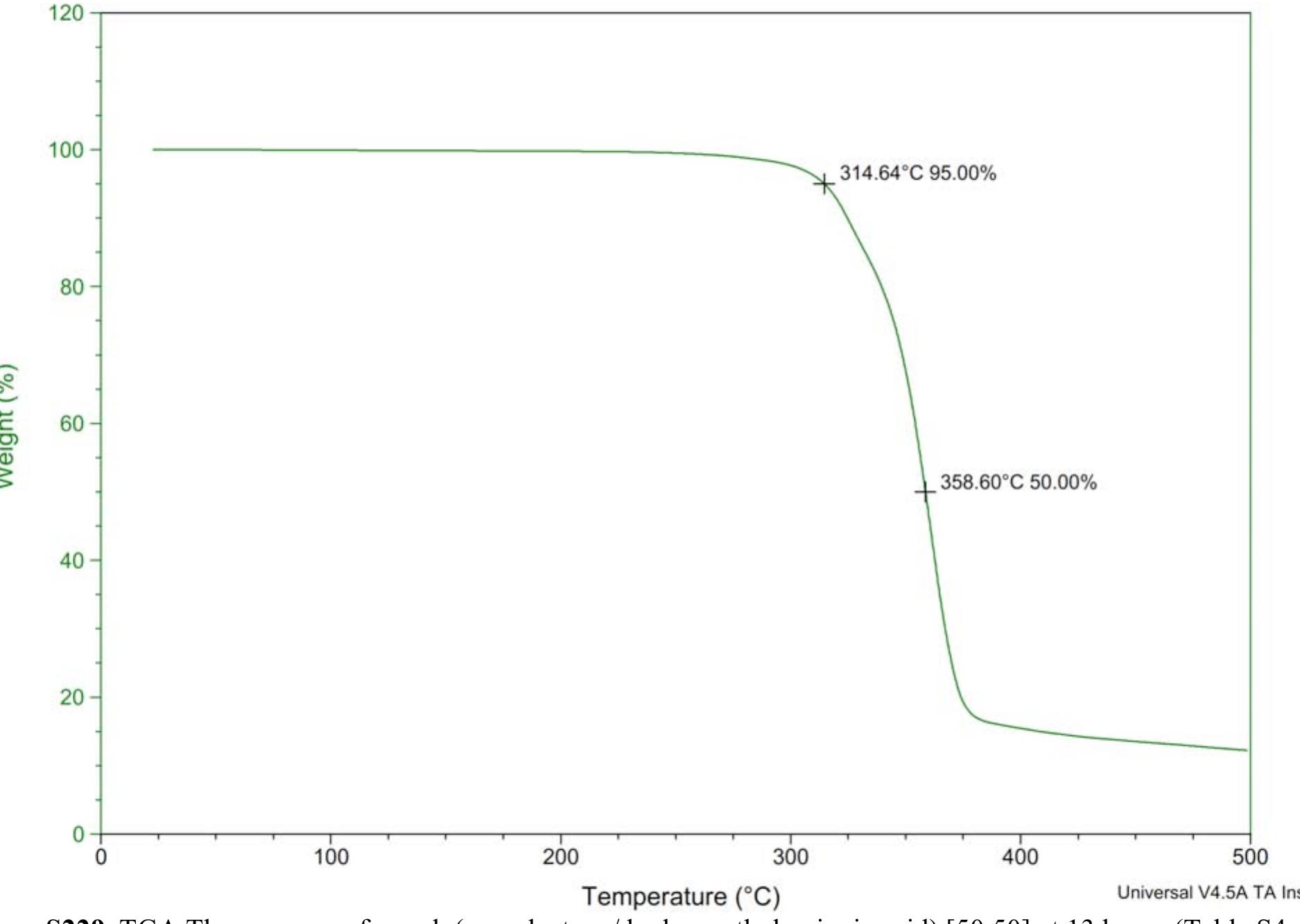


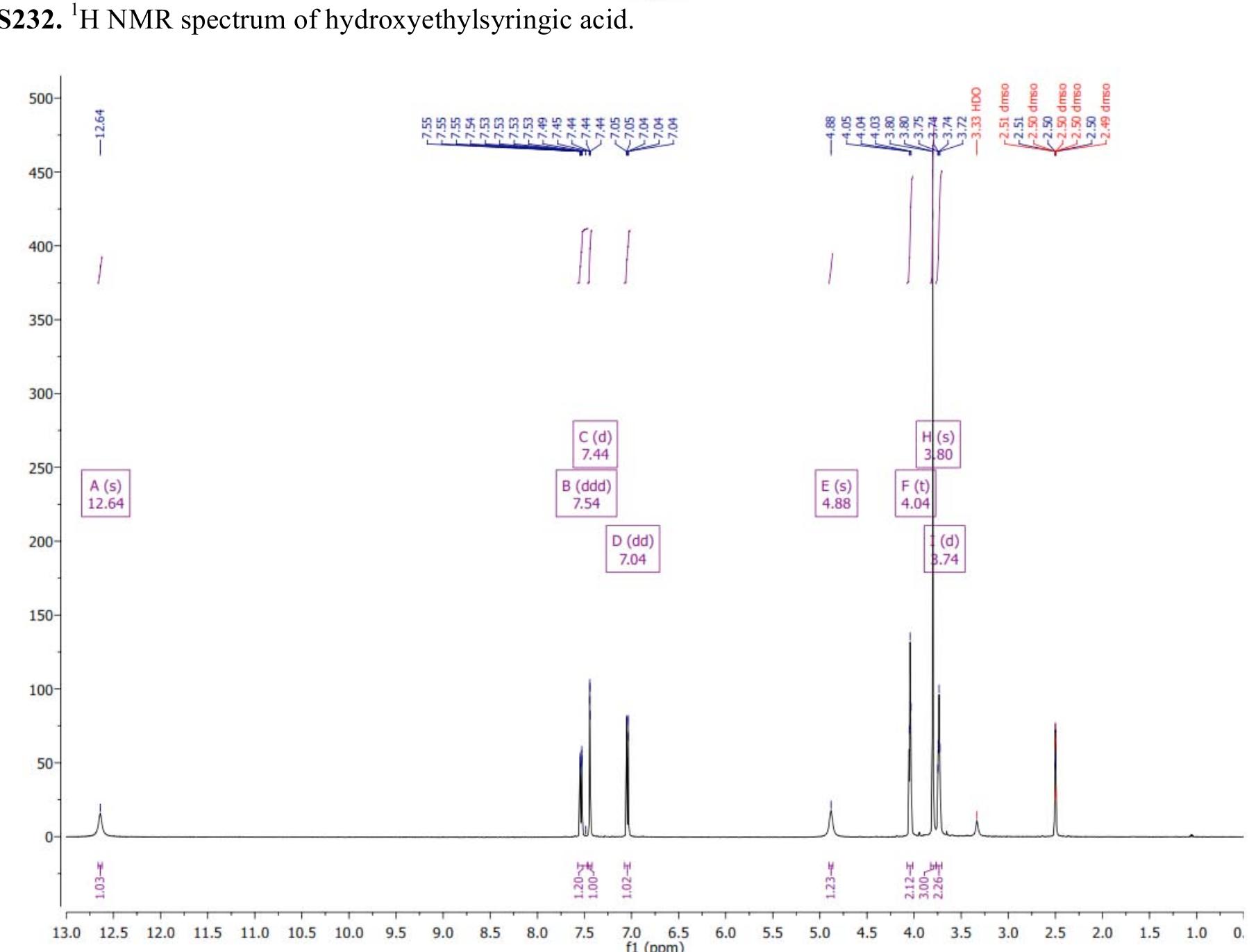
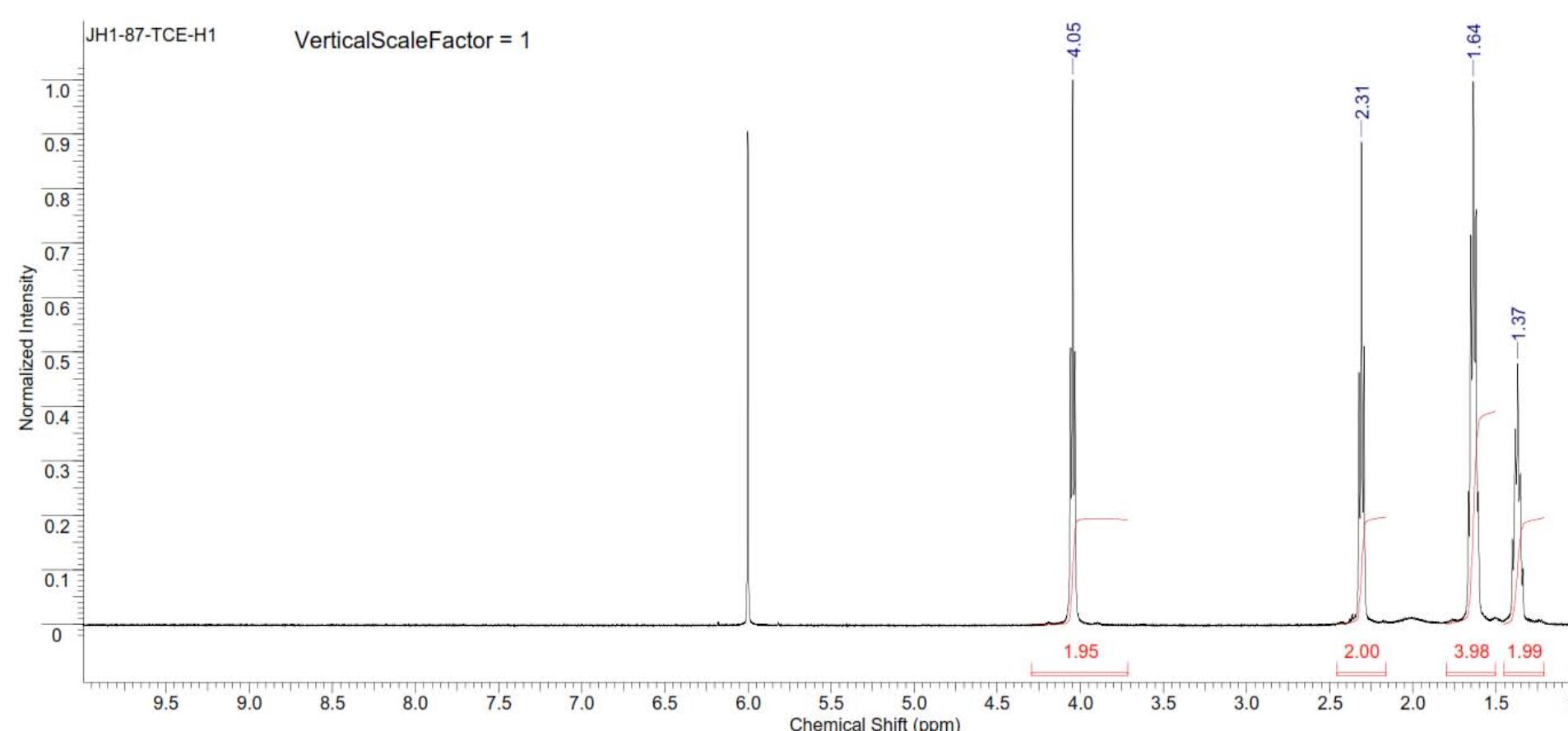
![Figure 8235. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_248.jpg)
![Figure S236. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_249.jpg)
![i al i | Figure $237. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [70:30] (Table $2, entry 4).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_250.jpg)
![Figure 8238. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_251.jpg)

![Figure $239. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 6).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_253.jpg)
![ee eT a Dee ee SU ee Figure $240. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [40:30] (Table S2, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_254.jpg)


![ee a we ne ee ee Figure $242. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table 82, entry 9). Figure $241. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_257.jpg)
![Figure $243. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 10).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_258.jpg)


![Figure $245. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 12). $132](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_261.jpg)
![Figure S246. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 13).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_262.jpg)
![a ae Figure $247. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_263.jpg)
![Figure $248. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_264.jpg)
![Figure S249. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 16).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_265.jpg)
![Figure $250. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 17).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_266.jpg)

![Figure $251. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 18)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_268.jpg)
![Figure $252. 'd NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 19).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_269.jpg)
![Figure $253. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 20).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_270.jpg)
![Figure $254. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 22).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_271.jpg)
![Figure S255. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 23).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_272.jpg)
![Figure $256. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 24).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_273.jpg)

![POT ENCSES me OPES Apres Figure $257. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 25).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_275.jpg)
![‘igure $258. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 26).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_276.jpg)
![Figure $259. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 27).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_277.jpg)
![Figure S260. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 28).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_278.jpg)
![Figure $261. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 29).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_279.jpg)
![Figure $262. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 30).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_280.jpg)

![Figure $264. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 32).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_282.jpg)
![Figure $265. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 33).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_283.jpg)
![Figure $266. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 34).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_284.jpg)


![Figure S270. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_287.jpg)
![Figure $271. 'd NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [40:60] (Table S3, entry 4)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_288.jpg)
![Figure S272. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table $3, entry 5)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_289.jpg)
![Ee ee eee ee Ee Figure S273. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [80:20] (Table S3, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_290.jpg)
![Figure $274. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_291.jpg)
![Figure $275. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [40:60] (Table $3, entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_292.jpg)
![Figure $276. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [20:80] (Table $3, entry 10).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_293.jpg)
![Figure $277. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [90:10] (Table $3, entry 12).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_294.jpg)
![Figure S278. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [80:20] (Table $3, entry 13).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_295.jpg)
![NSE TSEC TINEES COU TEER A Epee ely Figure S279. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [70:30] (Table S3, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_296.jpg)
![Figure S280. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [60:40] (Table $3, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_297.jpg)
![Figure $281. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [20:80] (Table $3, entry 16).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_298.jpg)
![Figure $282. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [90:10] (Table S3, entry 18).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_299.jpg)
![Figure $283. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [80:20] (Table $3, entry 19).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_300.jpg)
![Figure S284. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [70:30] (Table S3, entry 20).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_301.jpg)

![a eee ee ee ee Figure $285. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 21).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_303.jpg)
![Figure S286. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [20:80] (Table S3, entry 22).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_304.jpg)
![Figure S287. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 10 min. (Table S4, entry 1).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_305.jpg)
![Figure $288. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 20 min. (Table S4, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_306.jpg)
![Figure $289. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 30 min. (Table S4, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_307.jpg)
![Figure 8290. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 1 hour (Table S4, entry 4).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_308.jpg)
![Figure $291. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 1.5 hours (Table S4, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_309.jpg)
![Figure S292. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2 hours (Table S4, entry 6)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_310.jpg)
![Figure S293. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2.5 hours (Table S4, entry 7 C1412](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_311.jpg)
![Figure $294. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 3 hours (Table S4, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_312.jpg)
![Figure $295. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 3.5 hours (Table S4, entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_313.jpg)
![Figure $296. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 4 hours (Table S4, entry 10). $149](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_314.jpg)
![Figure 8297. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 4.5 hours (Table S4, entry 11).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_315.jpg)
![Figure $298. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 5 hours (Table S4, entry 12).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_316.jpg)
![Figure S299. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 6 hours (Table S4, entry 13).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_317.jpg)
![Figure $300. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 7 hours (Table S4, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_318.jpg)
![Figure $301. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 8 hours (Table S4, entry 15). g](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_319.jpg)
![Figure S302. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 9 hours (Table S4, entry 16).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_320.jpg)
![Figure $303. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 10 hours (Table S4, entry 17).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_321.jpg)
![Figure $304. 'H NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 13 hours (Table $4, entry 18).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_322.jpg)






![Figure $311. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 3). Figure $310. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_329.jpg)
![Figure $312. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 4).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_330.jpg)


![Figure $313. ‘°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_333.jpg)
![Figure $315. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 7) Figure S314. ‘°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 6).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_334.jpg)

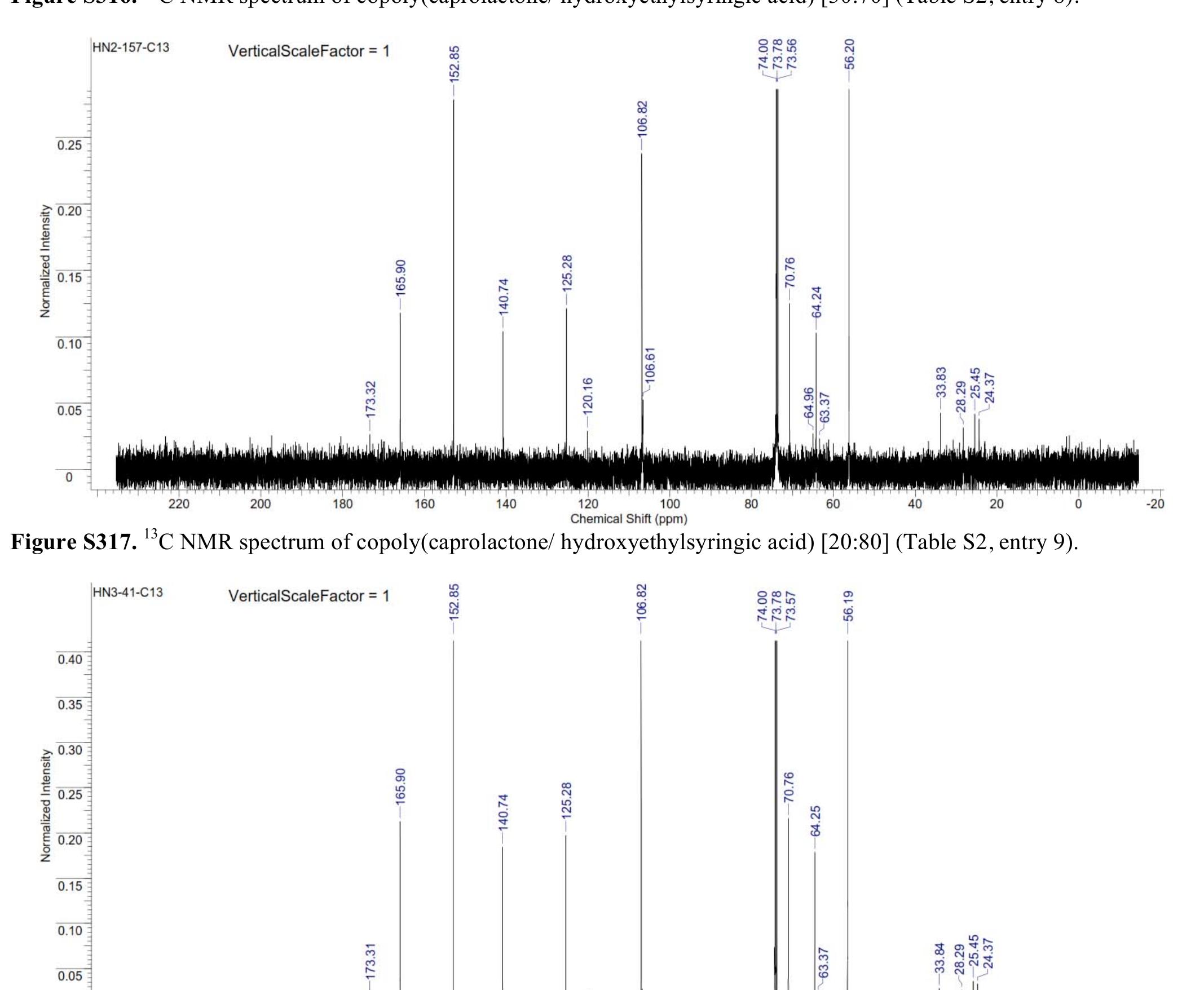
![Figure $316. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_337.jpg)
![Figure $318. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [10:90] (Table S2, entry 10). Figure $317. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S2, entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_338.jpg)


![Figure $320. ‘°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [90:10] (Table S3, entry 12).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_341.jpg)
![Figure S321. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 13).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_342.jpg)
![Figure $322. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_343.jpg)
![Figure $323. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_344.jpg)
![Figure $324. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 16).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_345.jpg)
![Figure $325. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 17).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_346.jpg)
![Figure S326. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 18).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_347.jpg)

![Figure $327. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethyl ferulic acid) [90:10] (Table S2, entry 22).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_349.jpg)
![Figure $328. ‘°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 23).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_350.jpg)
![Figure $329. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [70:30] (Table S2, entry 24).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_351.jpg)
![Figure S330. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [60:40] (Table S2, entry 25).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_352.jpg)
![Figure $331. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 26).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_353.jpg)
![Figure $332. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [40:60] (Table S2, entry 27).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_354.jpg)
![Figure S333. '*C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [30:70] (Table S2, entry 28).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_355.jpg)

![Figure $334. '°C NMR spectrum of polyethylene ferulate (Table S2, entry 31). Figure $335. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [80:20] (Table S2, entry 32).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_357.jpg)
![Figure S336. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [50:50] (Table S2, entry 33).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_358.jpg)



![Figure $339. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [80:20] (Table $3, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_362.jpg)
![Figure $340. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_363.jpg)
![Figure S341. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [40:60] (Table S3, entry 4).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_364.jpg)
![Figure $342. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [20:80] (Table S3, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_365.jpg)
![Figure S343. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [80:20] (Table $3, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_366.jpg)
![Figure $344. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [60:40] (Table S3, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_367.jpg)
![Figure $345. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylvanillic acid) [40:60] (Table S3, entry 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_368.jpg)
![Figure S346. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [90:10] (Table S3, entry 12).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_369.jpg)
![Figure $347. °C NMR spectrum of c copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [80:20] (Table $3, entry 13).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_370.jpg)
![Figure $348. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [70:30] (Table $3, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_371.jpg)
![Figure $349. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylferulic acid) [60:40] (Table $3, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_372.jpg)
![Figure $350. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [90:10] (Table S3, entry 18).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_373.jpg)
![Figure $351. '°C NMR spectrum of c copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethyleoumaric acid) [80:20] (Table S3, entry 19).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_374.jpg)
![Figure S352. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [70:30] (Table S3, entry 20).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_375.jpg)
![Figure S353. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(L-lactide/ hydroxyethylcoumaric acid) [60:40] (Table 3, entry 21).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_376.jpg)
![Figure $354. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 10 min. (Table S4, entry 1).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_377.jpg)
![Figure S355. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 20 min. (Table S4, entry 2).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_378.jpg)
![Figure $356. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 30 min. (Table $4, entry 3)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_379.jpg)
![Figure $357. ‘°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 1 hour (Table S4, entry 4).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_380.jpg)
![Figure $358. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 1.5 hours (Table S4, entry 5).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_381.jpg)
![Figure $359. ‘°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2 hours (Table S4, entry 6). 0171 ‘igure S359. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2 hours (Table S4, entry 6).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_382.jpg)
![Figure $360. ‘°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2.5 hours (Table S4, entry 7).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_383.jpg)
![Figure $361. ‘°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 3 hours (Table S4, entry 8).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_384.jpg)
![Figure S362. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 3.5 hours (Table S4, entr 9).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_385.jpg)
![Figure $363. ‘°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 4 hours (Table S4, entry 10).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_386.jpg)
![Figure $364. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 4.5 hours (Table S4, entry 11).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_387.jpg)
![Figure S365. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 5 hours (Table S4, entry 12).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_388.jpg)
![Figure S366. '*C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 6 hours (Table S4, entry 13).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_389.jpg)
![Figure $367. ‘°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 7 hours (Table S4, entry 14).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_390.jpg)

![Figure S368. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 8 hours (Table S4, entry 15).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_392.jpg)
![Figure $369. '°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 9 hours (Table S4, entry 16).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_393.jpg)
![Figure S370. °C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 10 hours (Table S4, entry 17).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_394.jpg)
![Figure $371. ‘°C NMR spectrum of copoly(caprolactone/ hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 13 hours (Table S4, entry 10\](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_395.jpg)










![Figure S380. ESI spectra of copoly(caprolactone/hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 10 min. (Table S4, entry 1)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_404.jpg)
![Figure S381. ESI spectra of copoly(caprolactone/hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 20 min. (Table S4, entry 2)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_405.jpg)
![Figure $382. ESI spectra of copoly(caprolactone/hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 30 min. (Table S4, entry 3)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_406.jpg)
![Figure $383. ESI spectra of copoly(caprolactone/hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 1 hour (Table S4, entry 4)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_407.jpg)
![Figure S384. ESI spectra of copoly(caprolactone/hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 1.5 hours (Table S4, entry 5)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_408.jpg)
![Figure S385. ESI spectra of copoly(caprolactone/hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2 hours (Table S4, entry 6)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_409.jpg)
![Figure $386. ESI spectra of copoly(caprolactone/hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 2.5 hours (Table S4, entry 7)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_410.jpg)
![Figure $387. ESI spectra of copoly(caprolactone/hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 3 hours (Table S4, entry 8)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_411.jpg)
![Figure S388. ESI spectra of copoly(caprolactone/hydroxyethylsyringic acid) [50:50] at 3.5 hours (Table S4, entry 9)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/97857879/figure_412.jpg)

Key takeaways
AI
AI
- Concurrent ring-opening polymerization and polycondensation yield random copolymers with tailored thermal properties.
- Monomer yields range from 62% to 94.9% across different formulations of hydroxyethyl derivatives.
- Polymerization conditions include temperatures up to 250 °C and dynamic vacuum to enhance degree of polymerization.
- Characterization techniques utilized include NMR, DSC, TGA, and GPC for comprehensive analysis of copolymers.
- This study aims to develop sustainable copolymers from bioaromatic hydroxy-acids and lactones.
Related papers
Biomacromolecules, 2003
Aliphatic polyesters prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactones are now used worldwide as bioresorbabale devices in surgery (orthopaedic devices, sutures, stents, tissue engineering, and adhesion barriers) and in pharmacology (control drug delivery). This review presents the various methods of the synthesis of polyesters and tailoring the properties by proper control of molecular weight, composition, and architecture so as to meet the stringent requirements of devices in the medical field. The effect of structure on properties and degradation has been discussed. The applications of these polymers in the biomedical field are described in detail.
Macromolecules, 2006
Metal-free catalysis was successfully applied to polymerize -pentadecalactone (PDL) by ring-opening polymerization (ROP) using several amino-ended initiators, namely hexylamine, allylamine and O, O′-bis(3-aminopropyl)diethylene glycol. This polymerization method was suitable to prepare telechelic polyesters carrying functional-end groups. The technique was then extended to the synthesis of block copolymers by ROP of PDL using bisamino-ended poly(ethylene glycol) (M n =2600) as macroinitiator. PPDL x -PEG 56 -PPDL x triblock copolymers with M n ranging between ~4000 and ~90000 g•mol -1 were synthesized and extensively characterized by NMR, DSC, TGA and XRD. The amphiphilic copolymers thus produced were demonstrated to be able to self-assemble in nanoparticles with average diameters of ~100-200 nm and morphologies highly depending on blocks lengths. The described synthetic route distinguishes in providing "clean" amphiphilic copolymers, which are attractive candidates for biomedical applications.
Chemical Reviews, 2004
2017
The aim of this work was the study of several polymerization systems using lactones as monomers, such as, Ɛ-caprolactone and ɣ-butyrolactone, by a ring opening mechanism. The experiments were performed with acidic catalysts such as, methanesulfonic acid and triflic acid. As indicated in the literature, the ring opening polymerizations with these types of catalysts and ɣ-lactones were not possible under the operating conditions due to the thermodynamic stability of this type of monomer. Thus, to obtain an efficient system, the copolymerization of the two monomers, Ɛ-caprolactone and ɣ-butyrolactone, was performed at different temperatures (-40 °C to 30 °C) and with the two catalysts mentioned above. Novel copolymers, γbutyrolactone-co-Ɛ-caprolactone were obtained at all tested temperatures showing the incorporation of ɣbutyrolactone as desired.
Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2007
ABSTRACT ABA triblock copolymers of L-lactide (LL) and ε-caprolactone (CL), designated as PLL-P(LL-co-CL)-PLL, were synthesized via a two-step ring-opening polymerization in bulk using diethylene glycol and stannous octoate as the initiating system. In the first-step reaction, an approximately 50:50 mol% P(LL-co-CL) random copolymer (prepolymer) was prepared as the middle (B) block. This was then chain extended in the second-step reaction by terminal block polymerization with more L-lactide. The percentage yields of the triblock copolymers were in excess of 95%. The prepolymers and triblock copolymers were characterized using a combination of dilute-solution viscometry, gel permeation chromatography (GPC), 1H- and 13C-NMR, and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). It was found that the molecular weight of the prepolymer was controlled primarily by the diethylene glycol concentration. All of the triblock copolymers had molecular weights higher than their respective prepolymers. 13C-NMR analysis confirmed that the prepolymers contained at least some random character and that the triblock copolymers consisted of additional terminal PLL end (A) blocks. From their DSC curves, the triblock copolymers were seen to be semi-crystalline in morphology. Their glass transition, solid-state crystallization, and melting temperature ranges, together with their heats of melting, all increased as the PLL end (A) block length increased. Copyright © 2005 John Wiley &amp; Sons, Ltd.
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2012
A series of di-and triblock copolymers [poly(L-lactide-b-e-caprolactone), poly(D,L-lactide-b-e-caprolactone), poly (e-caprolactone-b-L-lactide), and poly(e-caprolactone-b-L-lactideb-e-caprolactone)] have been synthesized successfully by sequential ring-opening polymerization of e-caprolactone (e-CL) and lactide (LA) either by initiating PCL block growth with living PLA chain end or vice versa using titanium complexes supported by aminodiol ligands as initiators. Poly(trimethylene carbonate-b-e-caprolactone) was also prepared. A series of random copolymers with different comonomer composition were also synthesized in solution and bulk of e-CL and D,L-lactide. The chemical composition and microstructure of the copoly-mers suggest a random distribution with short average sequence length of both the LA and e-CL. Transesterification reactions played a key role in the redistribution of monomer sequence and the chain microstructures. Differential scanning calorimetry analysis of the copolymer also evidenced the random structure of the copolymer with a unique T g .
Macromolecules
Statistical copolymers of L-lactide (L-LA) and ε-caprolactone (CL) are of major interest as a result of the desired combination of properties they exhibit for high-added-value applications, including in the biomedical field and in microelectronics. However, the high difference of reactivity between the two monomers makes difficult their statistical insertion in copolymer chains. Here, the ring-opening polymerization and copolymerization (ROP and ROcP, respectively) of L-LA and CL mediated by benzoic acid (BA) are investigated by means of density functional theory (DFT). It is first evidenced that the mechanism involves a hydrogen-bonding dual activation, where the acidic proton of BA activates the carbonyl moiety of the monomer, while the conjugated base of BA activates the alcohol initiator. In accordance with experimental findings, DFT calculations have then revealed a kinetically favored energetic profile for the BA-organocatalyzed ROP of CL compared to L-LA. In addition, energetic profiles of the BA-mediated ROcP of CL and L-LA does not show any preference of the insertion between CL and L-LA, irrespective of the type of growing species. Even though the caproyl unit insertion is kinetically favored by the primary nature of the growing chain end alcohol, this is eventually mitigated by the stabilizing effect of the ester moieties of the lactidyl unit, which is thermodynamically favored. As one effect compensates for the other, the dual activation mechanism involved in this organocatalytic pathway using BA as a weak organic acid is shown to be crucial to achieve truly statistical copolymers based on L-LA and CL.
Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 2009
2014
This project analyzed the ring opening chemistry of D, L-lactide, γ-butyrolactone, valerolactone, dodecalactone and caprolactone. Starting with each of the above monomers, Sn(Oct)2,SnCl2, Zn(acac)2, ZnCL2, and AlCl3 were used as catalysts in the polymerization process. Initiators included benzyl alcohol, 2-phenylethanol and 1-butanol. The results of each reaction were analyzed by 1H-NMR and IR spectroscopy and dynamic light scattering (DLS). The results were collated to determine the most promising candidates for a student project in the teaching laboratory.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (1)
- 9,200 23,200 2.5 13 293 355 14 7 200 14,700 33,600 2.3 15 301 354 15 8 200 20,300 45,600 2.2 15 304 353 16 9 200 23,200 50,500 2.2 17 311 353 17 10 200 27,100 55,800 2.1 20 314 353 18 13 200 28,800 57,200 2.0 20 315 359 a 1.2 eq. of P2O5; mixture was melted under argon for 5 hour temperature ramp from 150 to 200 °C; then dynamic vacuum was applied for 8 hours at 200 °C. b Obtained by GPC in hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) at 40 °C versus polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) standards. c Determined by DSC. d Temperature at which 5% mass loss is observed under nitrogen. f Temperature at which 50% mass loss is observed under nitrogen.
Related papers
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 1999
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2009
Macromolecular Bioscience, 2004
Polymer Chemistry, 2013
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2011
Macromolecules, 2002
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2016
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2012
Polymer Degradation and Stability - POLYM DEGRAD STABIL, 1998
Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2002
Polym. Chem., 2015
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2009
Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2009
Materials Research, 2015
Macromolecules, 2001
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 1998
Journal of Polymer Science Part A-polymer Chemistry, 2008
Related topics
Cited by
Polymers
Green Chemistry
Current Organic Synthesis
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022
Polymers, 2021
 Pengxu Qi
Pengxu Qi
