Hydraulics, Water Resources, Coastal and Environmental Engineering( HYDRO 2014 International)
…
306 pages
1 file

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
Department of Civil Engineering, MANIT Bhopal Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh) India Pin -462051
Figures (452)

































































































































































![Figure 1: Command Area of Nashik Left Bank Canal [NLBC Source: Nasik Irrigation Departmen Nashik district of Maharashtra state is one of the leading districts in the field of agriculture. The new experiments and use of advanced technology have empowered the farmers to increase export of agro based products. Gangapur Dam is most important and the oldest earthen dam in Nashik. It was constructed on Godavari River. Two canals namely Nashik [NRBC] and Nashik Left Bank Canal [NLBC] dam. The GRBC is closed due to high civiliz The present paper focuses on the case study of Canal of Nashik district, Maharashtra state w 20° 38’ Lattitude and 73° 19’ Longitude. The r is 64 km which is running open to atmosphere. take off ation in ashik L each of t in 1965 Right Bank Canal from the the area. eft Bank hich is located at his canal The alignment of canal and its command area is shown in Figure 1.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47841551/figure_131.jpg)
![TABLE II: Crop Pattern and Crop Water Requirement Details for NLBC [6]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47841551/table_038.jpg)

![Table III: Actual Details of Conveyance Losses and Efficiency for NLBC [6]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47841551/figure_133.jpg)
![Figure 2: Closed Circular Conduit [GRP] @ 1.82m](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47841551/figure_134.jpg)


















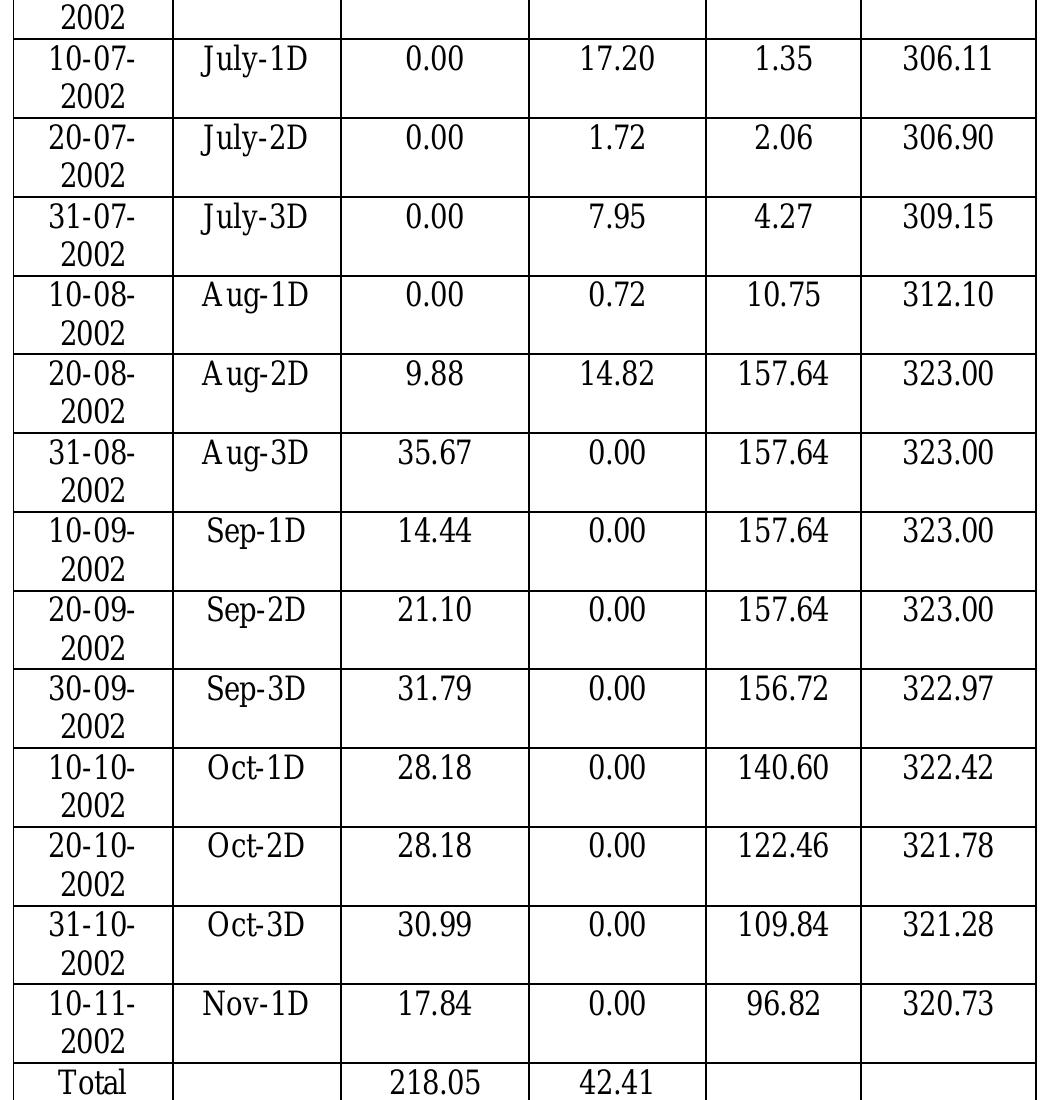

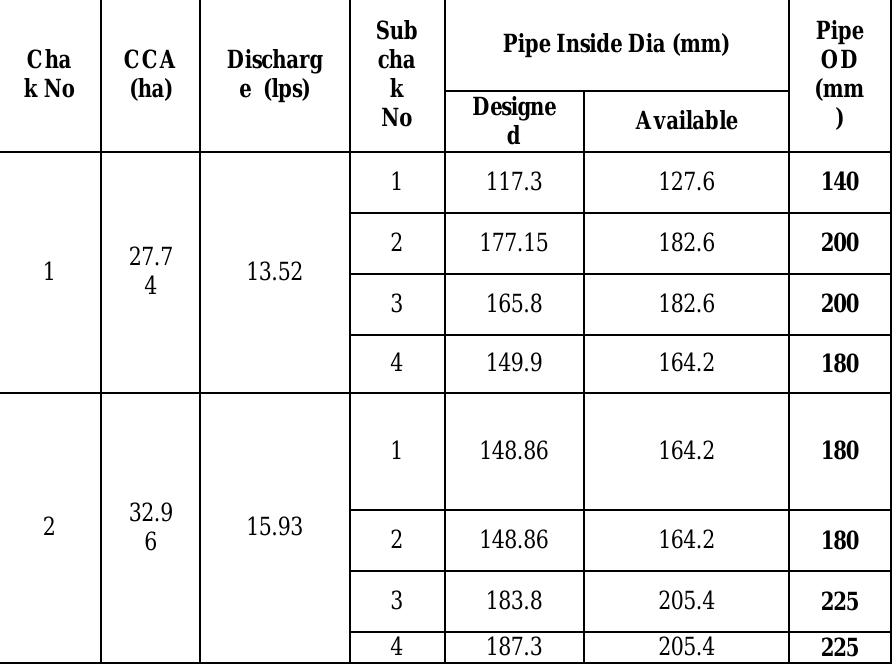

























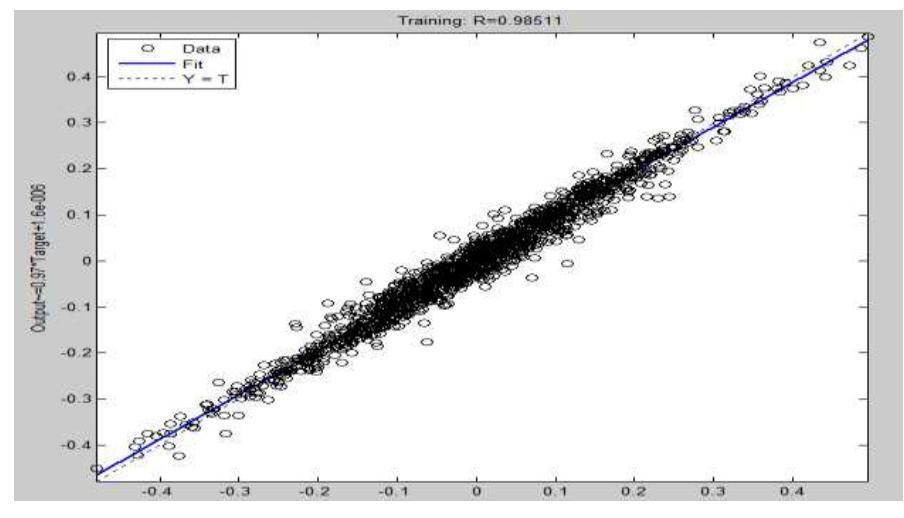




























































































































































![[Zp=Value (1000) 104 Rs ] [Zp= 10’Value in Quintal] Table -7 Objective Function value for benefit and production](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47841551/figure_277.jpg)



























































Related papers
SPECIAL ISSUE OF 5th Indian National Conference on Harbour and Ocean Engineering (INCHOE 2014) 5 - 7 February, 2014 Organized by CSIR-National Institute of Oceanography (CSIR-NIO), Goa, INDIA
The National Institute of Hydrology (NIH) is a premier research Institute in India in the area of hydrology and water resources. The Institute was established in 1978 with the main objective of undertaking, aiding, promoting and coordinating systematic and scientific work in all aspects of hydrology. The Institute has its headquarters at Roorkee (Uttarakhand), four regional centres at Belagavi, Jammu, Kakinada and Bhopal and two centres for flood management studies at Guwahati and Patna. The Institute is well equipped to carry out computer, laboratory and field oriented studies. This article presents an overview of research activities being undertaken by the Institute.
GREEN METHOD OF STEMMING THE TIDE OF INVASIVE MARINE AND FRESHWATER ORGANISMS BY NATURAL FILTRATION OF SHIPPING BALLAST WATER, 2022
Marine and freshwater pollution caused by the transport of invasive species in shipping ballast water is a major global problem and will increase in magnitude as the shipping of commodities increases in the future. An economical method to preclude biological organisms in the seawater used for ballast is to exclude them at the source port. Integrated natural filtration using onshore wells or seabed gallery systems has been thoroughly investigated for use as pretreatment for seawater desalination systems and has proven to be environmentally acceptable and economic. Thus, the use of this proven filtration technology for another issue, ballast water treatment, is an innovative method of providing marine organism free seawater by non-destructive means in port-based facilities. This method is ecosystem-friendly in that no chemicals or destructive processes are used. Design and construction of well or seabed gallery intake systems for the production of ballast seawater is feasible in virtually all global port facilities
International Journal of Advanced Engineering Research and Science, 2020
It covers a wide variety of research outcomes related to groundwater assessment; seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers; numerical modelling of unsaturated flow, groundwater flow and contaminant transport; management of aquifer recharge; and impact of climate change on groundwater etc.
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution and sharing with colleagues. Other uses, including reproduction and distribution, or selling or licensing copies, or posting to personal, institutional or third party websites are prohibited. In most cases authors are permitted to post their version of the article (e.g. in Word or Tex form) to their personal website or institutional repository. Authors requiring further information regarding Elsevier's archiving and manuscript policies are encouraged to visit: http://www.elsevier.com/copyright
As communities grow, the need for diverting water increases. Storm water runoff overwhelms city sewers and can damage nearby streams and rivers through erosion. Handling the storm water near its source can save millions in costly repairs that would otherwise be directed at correcting erosion or controlling flooding. A common method for managing storm water is to build a basin. Basins are meant to collect the water, and release it at a rate the prevents flooding or erosion.
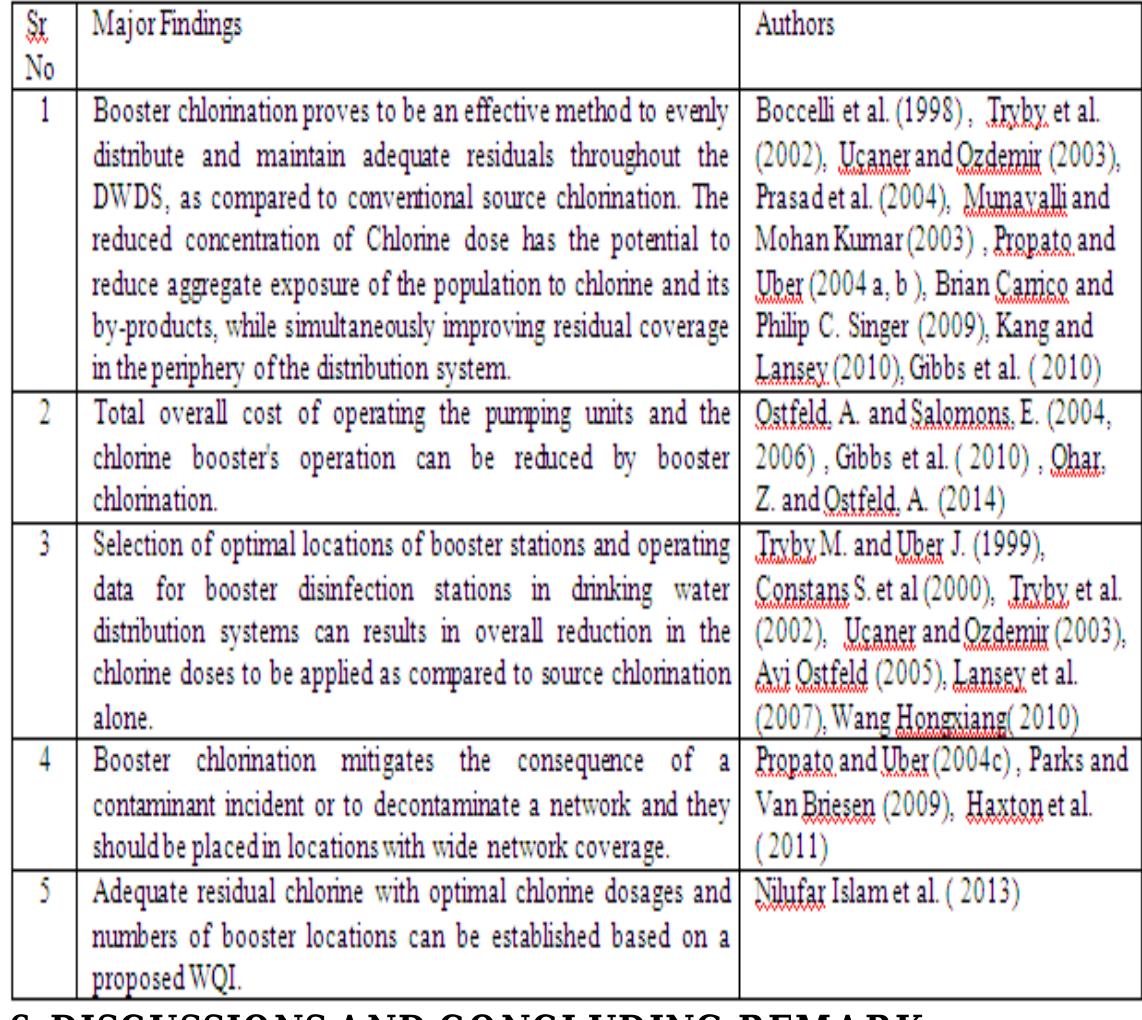
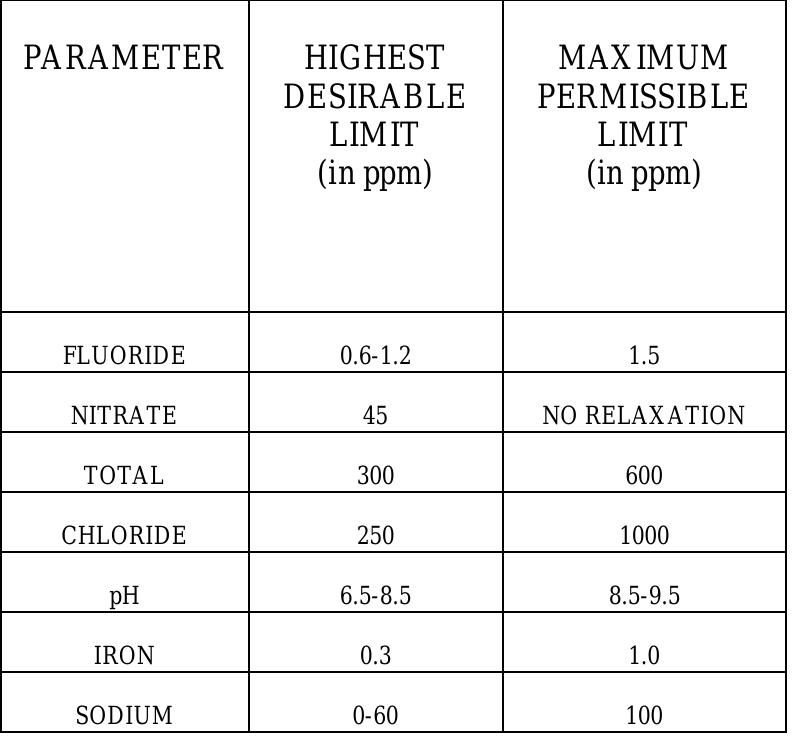
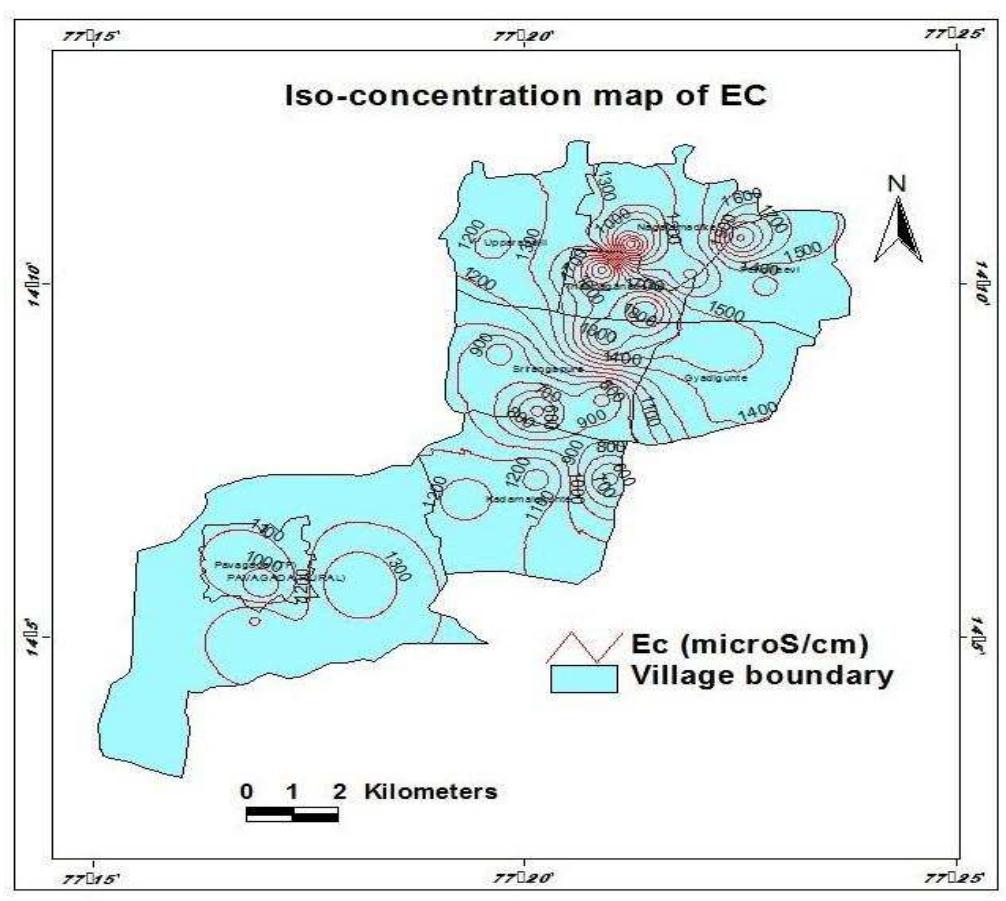
Editorial Note - IJEE-sp issue- on -HWRE-2013- HYDROLOGY AND WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING P.R. REDDY1 and D.VENKAT REDDY2 1Scientist ‘G’ (Ret), CSIR-NGRI, Hyderabad-500 007, India 2, Department of Civil Engineering, NITK, Surathkal, Srinivasnagar,-575025 Mangalore-D.K-India Email: parvatarreddy@gmail.com,dvr1952@gmail.com Hydrology is study of water. Water present on surface and subsurface columns of solid earth, in the oceans and in the atmosphere is linked through hydrological cycle. Nature controls various processes that contribute to the hydrological cycle. However, Man has been playing a significant role in managing water resources and in the process has unwittingly interfered with the natural process of generation and usage of this vital natural resource that is essential for sustenance of life on this planet. Since the management of water resources implies an ability to predict the quality and amount of the resource that is available, it is imperative that Man has to judiciously develop apt methodologies to optimally utilise the available resource to help himself and the flora and fauna. Keeping this in view IJEE has decided to bring out a special issue ….” Hydrology and Water Resource Engineering”. The topic is important for not only engineering community but also to earth scientists, as judicious conjunctive use of surface and ground waters alone can help us to use the 3 % of usable water on earth to quench the thirst, to provide food and to make commodities. The management of available water resources, assumes greater importance in India as it has more than 17% of the world`s population, but only 4 % of world`s renewable water resources with 2.6 % of world`s land area .Despite having reasonably assured annual rainfall( compared to Middle East, major parts of Australia and Africa ), we are having recurring floods and droughts in many parts of the country. This is attributed to uneven distribution of rainfall over time and space. Managing the available water potential effectively becomes therefore necessary. To ensure integrated water resource management helping to conserve water, minimize wastage and ensure equitable distribution both across and within different states of the country we need to have both major and minor water storage and distribution projects, without adversely affecting the environment. We need to develop a frame work to optimize water use by increasing water use efficiency through regulatory mechanisms with differential entitlements .To achieve these targets we need to evolve apt strategies, under an organized Mission mode. We need to optimize the efficiency of existing irrigation systems, including rehabilitation of systems that have been run down and also expand irrigation, where feasible, with a special effort to increase storage capacity. Incentive structures need to be designed to promote water-neutral or water- positive technologies, recharging of ground water resources and adoption of large scale irrigation programmes that rely on sprinkler, drip , ridge and furrow irrigation. Harvesting the optimal runoff volume available during the monsoon for artificial recharge to augment the groundwater resources for achieving water security is a viable methodology and to be up-scaled with scientific approaches and strategies. Understanding and standardization of catchments characterestics of watershed in hard rock areas becomes essential for implementing the water resources part of watershed development programme. In addition to major irrigation projects localized and traditional surface water management over hard rock areas through effectively practiced tank systems need to be encouraged. These strategies and organized plans can be used properly only when quality scientific management is adopted following apt water resources engineering. In the special issue major focus is made in addressing groundwater quality and quantity issues. Out of 23 papers 20 have covered various aspects of groundwater. Details pertaining to aquifer dynamics, watershed monitoring through remote sensing and GIS approaches, morphometric analysis using spatial information technology, assessment of ground water quality for drinking and irrigation, problems associated with Fluoride contamination, ground water potentialities in in Basaltic terrain, assessment of ground water resources through different geophysical techniques, delineation of ground water potential zones in hard rock terrain, sea water intrusion and coastal aquifer management , conceptualization of the hydrological system of southern Caspian Coastal aquifer of Iran, have significantly added to the existing knowledge base. The 3 papers on surface water ; impact of stream flow regulation on the downstream of rivers in the tropics, overview of regional flood frequency analysis, statistical approach towards Physico chemical characterestics of river water quality have added quality to the publication. Since water management needs to take in to consideration the area specific design characteristics in building major, medium and minor storage facilities ; meeting water demand in the urban sector needs through apt engineering techniques for storage and distribution of different grades of water and as eradication of water pollution of surface water bodies through area specific treatment methodologies is paramount and as wastewater management has to be given importance to meet ever increasing demand IJEE wishes to bring out a second special issue during 2014, to cover specifically the above cited topics .While thanking the authors who have contributed to the present special issue, we solicit support from learned scientists from engineering and earth science to contribute to the second special issue.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
Related papers
Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research), 2023
Journal of the Indian Society of Coastal Agricultural Research, 2022
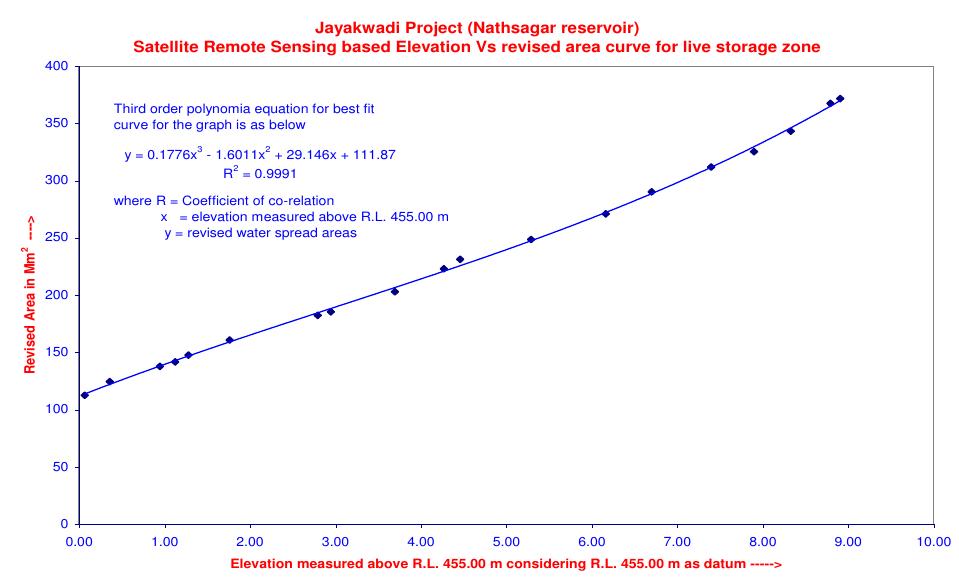
Lakes & Reservoirs: Science, Policy and Management for Sustainable Use, 2015
ISH Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2012
Proceedings to 29th Technical Sessions of Geological Society of Sri Lanka, 2013,, 2013
Journal of Hydraulic and Water Engineering, 2024
Journal of Hydraulic Engineering
 Innovative Research Publications
Innovative Research Publications
