Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control
2000, Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control
…
247 pages
1 file

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
Transactions of the ASME® Dynamic Systems and Control Division Technical Editor, A. GALIP ULSOY Past Editors, W. BOOK M. TOMIZUKA DM AUSLANDER JL SHEARER KN REID Y. TAKAHASHI MJ RABINS Associate Technical Editors, Y. CHAIT „2002… F. CONRAD „2001… E. FAHRENTHOLD „2001… S. FASSOIS „2001… Y. HURMUZLU „2001… R. LANGARI „2002… E. MISAWA „2002… S. NAIR „2001… N. OLGAC „2001… C. RAHN „2002… S. SIVASHANKAR „2002… J. TU „2002… P. VOULGARIS „2001… Book Review Editor A. GALIP ULSOY Executive ...
Figures (383)














![Application of the Passivity Theorem. Using the notion of multipliers [2], the feedback systems shown in Fig. | are equiva- lent from the point of view of stability. The passivity theorem states that if G is passive and H is strictly passive then r eL,=yeL,. Using Lemma 1 and the passivity theorem, the original system is stable if either H= Y, TH or H= HY, is strictly passive. A possible design strategy would select H,,, a strictly Therefore G(s) is passive if and only if w<* When «= p*, the summation over the vibration modes vanishes (all vibration modes become unobservable) and the output p,,+=C,i7, becomes propor- tional to the rigid body modal rate. It 1s instructive to consider a small negative rate feedback u(t) = — ep,,. Using a simple eigen- value perturbation argument, it is readily shown that the closed- loop eigenvalues of each vibration mode are given by —€Y Cr lratja- All modes are stabilized when u<p* (Y, >0) and all of them are destabilized when p> (Y ,<0) as- suming controllability and observability, i.e., ¢.,#0.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_015.jpg)


![The noncollocated degree of freedom is taken to be p,.= 03= 9 +[1 1]q, so that C,=1, C,=[11]. The collocated degree o' freedom is p.o= 9, and p,=wA,;+(1—) 4. If g-=6,, de) = 92.— 9, and g,.= 03— 9» are selected as gen- eralized coordinates and f(t) as the motor torque, the matrices defined in Eq. (2) are given by](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_018.jpg)








![Fig. 4 Simulation results for x(0)=[0 0.71 0.71]? and B=0.79, 2.29, and 3.23 conditions is a limited number of points in state space, it is pos- sible to obtain 6,,, quite accurately. The accuracy is determined by the size of the change in the parameter 8 used when searching for Boot -](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_026.jpg)


















![The two dynamical Eqs. (12) complete the transformation from the state [x1(1),....x,(D ]7 to the state [21 (1),.--5Z,—1(t),e1(t),e2(t)]’.. With implicit symbol defini- tions, system (12) can be rewritten as The idea is now that of steering both e,(ft) and the unmeasurable (ft) to zero (to attain the sliding regime on S(t)=S(t)=0) ina finite time, that is, a second order sliding mode control problem has to be solved. In Bartolini et al. [26], it has been proved that, by analogy to the well-known solution to the time optimal control problem, the control u(t) can be chosen as a bang-bang control switching be- tween two values — Uy, and +Uy,,. The classical switching logic for a double integrator (H(e,(t), e2(t))=0, Bj, =B,=1) is](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_045.jpg)










![Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of direct-drive robot As shown in Fig. 1, this study constructs a three-axis R— 6 —Z direct-drive robot manipulator, where the first link is driven by a NSK Megatorque motor [14], the second by a NSK Mega- thrust motor, and the third by an electrothrust motor together with ball screw.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_057.jpg)











![and where use was made of the definition of E(x) and of the fact that po;#0, ie J,. Next consider the matrices [[9(x) Ao(x)] and [T,(x) A,(x)] defined as](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_069.jpg)





![Space station dynamics: Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Conirol NE Rg OE Ley © Example 5.4. The nonlinear equations of motion of the space station rotating in circular orbit with constant orbital rate, in terms of components along the body-fixed control axes can be written as [28]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_076.jpg)
![Assuming a constant orbital rate and differentiating (5.5), we obtain Solving (5.3) with respect to the vector [w, w w3]|, we obtait](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_077.jpg)




















![In principle, given geometric measurements z at 4n locations (y,y) on the part surface, and the respective predictions z of the deposition model from Eq. (8), the resulting deviation values can be used in Eq. (10) to form a linear system of 4n equations, to be solved for the deposition parameter changes (Du; ,Dv;,Dw;,Dr;),i=1...n. Notice that in order to obtain such a well-conditioned system of equations for robust parameter identification, sufficiently rich data must be obtained at respective 4n positions (y,), located close and scattered around the current material deposition region. In the vicinity of the mass source (X,Y), however, real-time measurements, e.g., by mechanical pro- filometry or optical scanner sensing, are technically problematic because of the material deposition interference with the sensor. Moreover, the precision of the geometry model is challenged by the variable source influences, due to the dominating surface ten- sion assumption. For this reason, in-process geometry measure- ments at m locations are conducted on the solidified surface at a safe distance behind the mass source, as explained below. On the basis of these m measurements, the 4n deposition parameter changes are evaluated by a least-squares identification technique (Astrom and Wittenmark [24]). This method minimizes a qua- dratic index *e(t) of the deposition error ¢ values at the m mea- surement locations, analogous to that of Eq. (6). The resulting corrections Du;,Dv;,Dw;,Dr;,i=1...n, are subsequently used every time period Dt to update the deposition field param- eters u;,U;,W;,r;, to their new values u;+Du;,v;+Dv;,w; +Dw;,,r;+Dr;. identify the parameters (u; ,v; ,w;,7;) of the composite deposition field approximation Z, Eq. (5). For this purpose, Eq. (9) can be rewritten over the full process duration ¢, as a linearized expres- sion of the deviation field ¢ sensitivity on the parameter variations Dy. Dn. Dw. Dr. j=1.. 2 -n-](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_097.jpg)


























































![Fig. 1 The proposed ER damper: (a) Schematic configuration; (b) photograph Here E is the electric field. The a and @ are intrinsic values of the ER fluid to be experimentally determined. In this study, for the ER fluid, the commercial one (Rheobay, TP Al 3565) is used and its yield stress at room temperature is reported by 591E!“? Pa [7]. Here the unit of E is kV/mm. It is herein noted that the Bingham model of the ER fluid [8] is adopted for the derivation of Eqs. (1) and (3).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_150.jpg)





![Table 1 Parameters of the full-car ER suspension system rithm to the ER damper. Then, the damping force of the ER damper is measured from the hydraulic damper tester and the measured damping force is fed back into the computer simulation. In short, the computer simultaneously runs both the hydraulic damper tester and high voltage amplifier during simulation loop, and the computer simulation is performed based on the measured data. In this study, the ER damper at rear right side is chosen for the HILS by considering the capacity of the hydraulic damper tester. (=0.856 m/s). The second type of road excitation, normally used to evaluate the frequency response, is a stationary random process [14] with zero mean described by](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/table_014.jpg)



![Let us for simplicity define the time dependent gas velocity of the inlet port, v, (x,,)=v,.. The inlet port gas velocity, v,, can be approximated (Broome [16], Moraal et al. [13]) by the solution to a second order forced differential equation with known initial values:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_159.jpg)





![Fig. 6 Model (dashed line) versus experimental data (solid line) at 1500 rpm The model described in this paper was evaluated using experi- mental data for a 4-cylinder engine (Moraal et al. [13]) during wide open throttle operation. The valves of the experimental en- gine are cam-driven, therefore, the intake valve profile is the con- ventional sinusoidal profile with the following specifications: (i)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_166.jpg)

![Fig. 8 Model (dashed line) versus experimental data (solid line) at 4000 rpm In Figs. 6, 7, and 8 we compare the model with the actual engine data for wide open throttle (f in Eq. (15) is fixed to 90 deg) and engine speeds of 1500, 3000, and 4000 rpm, respec- tively. The manifold and cylinder pressures are plotted for the model (dashed curve) and the experimental engine (solid curve). The model Helmholtz resonator parameters were determined as w,=27*176, €,=0.005 for an engine speed of 1500 rpm, and w,=27*190, €,=0.15 for engine speed of 3000 and 4000 rpm. These values are similar to the ones identified in (Moraal et al. [17]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_168.jpg)


![The input-output behavior is derived for fixed intake valve tim- ing, u,, and parametrically varying intake valve maximum lift u, and duration uw, in the crankangle-domain model. We fix u, to zero degrees ATDC, because neither advancing nor retarding u, affects the performance variables in a favorable way (Ashhab et al. [11]). This result is in agreement with the work of Miller et al. [20] where uw, was set to zero at all loads and medium engine speed. Note, that by setting u,=0 deg ATDC, valve closing is approximately equal to the valve duration. The input-output mean-value model can now be described by a static nonlinearity that is identified by fitting data attained by simulation, and a de- lay:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_170.jpg)

![Fig. 11 Investigation of the effects of the higher order inertial and acoustic dynamics to the mean-value model at an engine speed of 1500 rpm Figure 12 shows the discrepancy between the two models for 6000 rpm. At high engine speed, Helmoltz resonator dynamics increase the cylinder air charge during late intake valve closing (ram effect as in Broome [11]). This is achieved with no adverse effect in specific pumping losses. For early valve closing, how- ever, Helmholtz resonator dynamics reduce the cylinder air charge and increase the pumping losses. To explain this behavior we plot part of the P-V diagram for three different intake valve closing timings in Fig. 13. Specifically, Fig. 13 shows the P-V diagrams for early (IVC=80 deg), at the event (IVC=180 deg), and late](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_172.jpg)
















![Fig. 10 Nominal engine tracking Fig. 11 Air charge regulation during engine speed changes The control signals (uz and u,) are shown in subplots 2 and 3. The control signals for the four cylinders are identical because the cylinders are balanced. The step changes in the demanded cylin- der air charge forces the feedforward controller to switch between the branches of the ‘‘L’’ shape (see Section 3). In the first engine cycle (t=[0,0.08]), the value of m**’ is larger than the critical air charge (m,,) and thus the feedforward controller selects u, =7 mm (subplot 2) and computes the corresponding u,= 134 deg (subplot 3) that satisfies m“°’. The small difference between the desired and individual cylinder air charge is due to errors in the curve fitting used in the feedforward controller. The closed-loop controller algorithm balances the four cylinders within three en- gine cycles. The next value of m** is less than m,,. Thus, the feedforward controller selects u,z=80 deg (subplot 3) and com- putes u;= 1.36 mm (subplot 2) that satisfies m“*’. As the desired](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_189.jpg)



![The details are omitted here because of the journal page constraints; see Wang et al. [11] for an outline of the main steps. After extensive calculations, employing MATHEMATICA to solve integrals in closed form,* the compressor model becomes](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_193.jpg)












![For a cubic characteristic, these conditions have already been re- vealed by Krener [14]. Since these conditions involve not only the shape parameters S$, and S, of the compressor characteristic but also the value of pressure at the peak, 2+W eo, we are of the opinion that controller (23), in which I’ is the bifurcation param- eter, is preferable to the controller (98). where yo is a set point/disturbance parameter and the gains kp, kp, ky, and kq are required to satisfy For right-skew compressors, for which S,;>0 and S,<0, the conditions (99)—(101), in particular, allow controllers of the fol- lowing types:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_204.jpg)












![The Q model is used when transmission lines are connected together or to fluid volumes (e.g., hydraulic cylinder) by compo- nents of negligible volume such as directional control valves (Fig. 2). Such connectors are modeled as orifices as in Piché & Ellman [18] and Ellman and Piché [19]. The Q-model transfer functions are A 4-mode SIMULINK realization of the Q model is shown in Fig. 3.” Implementation in other simulation environments should be straight forward. Because the models are decoupled, the model has an obvious parallellization. The approximate transfer function (59) are rational polynomials thus inverse Laplace transformation can be calculated giving constant coefficient ordinary differential equations. For ODE-based simulators the following state space realization can be used (with n modes):](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_215.jpg)




![The PQ model is used when the connections at the ends of the transmission line are of different types. One end can be connected to an orifice and the other directly to a volume. The PO-model transfer functions are The P model is used when transmission lines are connected together to fluid volumes by components of negligible resistance (Fig. 4). Such connectors are modeled as hydraulic volumes (Piché and Ellman [7]). The P-model transfer functions are](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_218.jpg)





![Fig. 7 Water hammer example pressure response at valve for first cycle of water hammer in high-viscosity oil Table 4 The physical properties of water hammer system in Sl units (Holmboe and Rouleau [20])](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_224.jpg)
![Substituting the Ritz approximation into Eq. (70) and simplifying yields the ordinary differential equation system of second order Equations (66a) and (66b) do not include frequency dependent friction effect, since the equations are one-dimensional. Equations (71)—(73) can be modified to include frequency dependent friction effects (2D friction), if we assume that for small flow rate and pressure perturbations the turbulence flow behave the same way as laminar flow. This assumption is related to turbulent mean flow condition in Trikha, [12]. Comparing the Q model (59) and Eq. (72) and (73) we can modify the matrices as follows (2D friction):](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_225.jpg)

![Fig. 1 Diagram of a pneumatic vibration exciter It was experimentally found that in real flow conditions present in a working generator temperature changes can be omitted and Pressure p,, controlled by valves f; and f,,, mainly depends on the quantity of air mass in chamber V,. Changes in the chamber volume caused by piston vibrations have little effect on pressure P1, in the open chamber and air stiffness in such a chamber is, inter alia, dependent on frequency w and is smaller than in the closed chamber [1]. The component of pressure function pj, re- sulting from varying volume of chamber V, is a feedback signal in the generator. When the feedback is compensated, changes in the chamber volume do not cause the air pressure in this chamber to change, thus the air temperature remains unchanged, too. This leads to a conclusion that the air temperature 7, in chamber V, depends mainly (or exclusively after feedback compensation) on air flow processes. _ «2 a el oe In ee](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_227.jpg)

















![Fig. 8 Unsteady flow rate measurement with the isothermal chamber (f=5 [Hz])](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_246.jpg)
![Fig.9 Unsteady flow rate measurement with isothermal cham- ber (f=40 [Hz])](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_247.jpg)
![Fig. 10 Unsteady flow rate measurement with the normal chamber (f= 40 [Hz])](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_248.jpg)


![Fig. 3 Frequency responses of the servovalve The experimental system consists of a Moog servovalve utiliz- ing a cantilever feedback spring and a 0.9 kg double-ended actua- tor with an effective area of 3.613 e * m? (0.56 in’). The supply pressure is 18.6 MPa (2700 psi). Mobil DTE Light oil is used at an average temperature of 90°F. The actuator and spool are con- nected to linear variable differential transducers (LVDT) with +3 mV noise level. The range of the actuator LVDT is +2.5 V for the total stroke of 0.0254 m (+1 in). While the servo valve physical parameters are not available for model verification, the experi- mental frequency responses for the servovalve and the actuator are measured with a signal analyzer, using a ‘“‘swept sine’’ method that generates fixed-amplitude sine waves of varying fre- quencies. This is then used to validate the model order and struc- ture. It is desired to measure this data near the equilibrium actua- tor position x,,=0. Since the actuator is of type 1 as Eq. (22) indicates, it is difficult to keep the actuator near the equilibrium position in open loop. Therefore, a proportional control loop (gain= 1) is used to create a stabilized plant, as shown in Fig. 2. With different input amplitude levels (15 mV, 30 mV, and 50 mV), the frequency responses of the servovalve and actuator are measured and shown in Figs. 3 and 4, respectively. Using the frequency responses from the three input amplitudes, an averaged frequency response is computed for the servovalve and the actua- tor, and nominal models are fitted through the use of an equation- error method [17].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_251.jpg)


















![(II): r(k)=0 since S(q~')y,e(k)=0. Also since ||¢(k)|| is bounded from (I), we have D(k) €1,5D €1,>D(k)—0. With X=max(A.Ay), (A2) and (A3) imply that The RHS of the above inequality is nondecreasing. Provided that e<X(1—X)/(k,||v|]) we have Further, § has no common factor with B, by assumption, there exist polynomials 7 and A, such that yS+AB,=1. Therefore, xSu+ABu=u and xi+A(A,y—C,d)=u. Therefore u(k) is bounded since the left hand side of the above is bounded. Since || @(n)||Skgl|x(n)|| and D(n) €1,, by the discrete form of the Bellman-Gronwall’s lemma (see Lemma 3), ||x(k)|| is bounded. Therefore # and y are bounded.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_270.jpg)






























![Fig. 1 Cylinder head arrangement of a digital-displacement pump-motor Figure 3 shows a schematic representation of a motoring cycle [4]. To enable a cylinder for motoring the controller closes the low-pressure valve shortly before the piston reaches the top-dead- center (TDC). Once the valve is closed, the cylinder pressure rises to equal to that of the high-pressure manifold by the time it reaches TDC. The high-pressure valve can then be opened and latched. The piston is then propelled by the fluid pressure toward BDC. In a similar fashion to the TDC valve-sequence, the high- pressure valve is closed prior to BDC such that the residual piston stroke can de-pressurize the cylinder and allow the low-pressure](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_300.jpg)






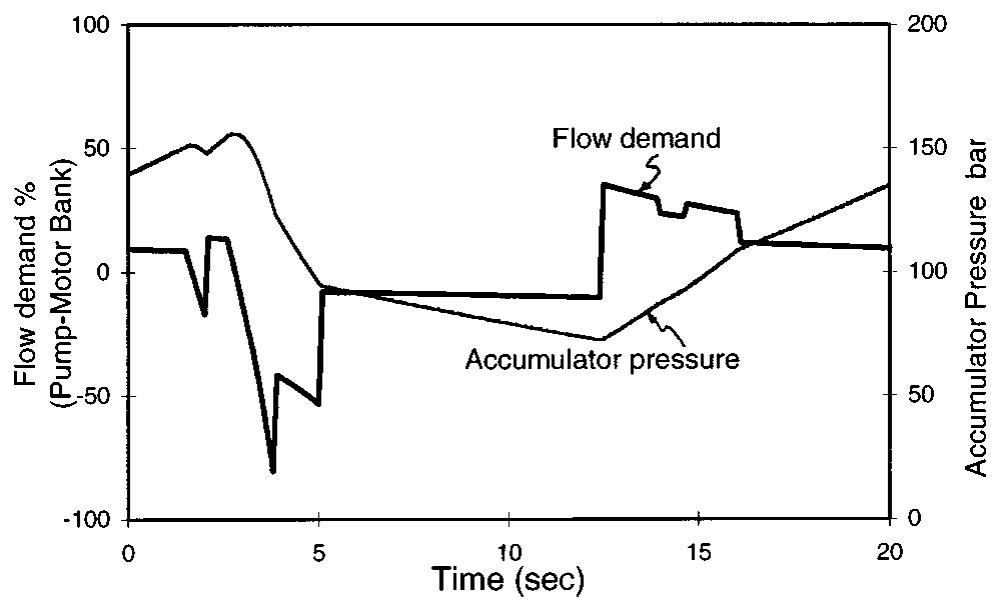
![The digital-displacement technology has advanced in the last few years both in terms of compu ter simulation and the building of prototypes. The first prototype of a six-cylinder pump was built in 1990. The single cylinder pump-motor prototype (1994) was followed by a six-cylinder axial pump-motor (1996). Figure 13 shows a photograph of the various components used for a six- cylinder radial pump-motor whic writing. Experimental work has simulations, some of which have Figure 14 shows the experimenta motor, running at 1500 rpm und h is under test at the time of shown good agreement with already been published [3,4]. results of a 6-cylinder pump- er pressure-control mode. The pressure is held constant (about 70 bars) while the pump flow follows an increase from 10 to 90 percent of the capacity in about 30 ms. The experimentally measured response time of the digital- Fig. 9 Power requirement of the pump-motor bank](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_307.jpg)





















![Fig. 3 Following a discontinuous wall: real (solid line) and es- timated (dashed-line) robot trajectory where g is a positive threshold value, P,(k|k) is an estimate of the covariance matrix of the state (used by the EKF) and Xx (k|k—1) is the time update of the EKF. Moreover, [F(k) — G(X(k|k- 1))] will produce incorrelated time series. On the other hand, if the model is wrong, both the aforementioned conditions will fail. Henceforth, by including the test (23) and the correlation test in a higher level controller, it is possible to perform a wall-following task of discontinuous profiles, by alternatively selecting whether to use the environmental model information to get better estimates of the robot position, or to upgrade the model itself. Figure 3](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_331.jpg)



![By LaSalle’s theorem [7], the tracking errors e; and e4 converge to zero globally. In addition, if the condition of persistent excita- tion is satisfied, the parameter estimate will converge to its true value.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_336.jpg)









![Differentiating J with respect to K (see p. 592 of [15]), we obtain the optimum value of K.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_346.jpg)



![-ig. 3 Phase portrait for the unperturbed system Let us consider the system in Eq. (8), where the parameters have been set as follows [3]:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/68067948/figure_350.jpg)







Related papers
1987
Transactions of the ASME® Dynamic Systems and Control Division Technical Editor, A. GALIP ULSOY Past Editors, W. BOOK M. TOMIZUKA DM AUSLANDER JL SHEARER KN REID Y. TAKAHASHI MJ RABINS Associate Technical Editors, Y. CHAIT „2002… F. CONRAD „2001… E. FAHRENTHOLD „2001… S. FASSOIS „2001… Y. HURMUZLU „2001… R. LANGARI „2002… E. MISAWA „2002… S. NAIR „2001… N. OLGAC „2001… C. RAHN „2002… S. SIVASHANKAR „2002… J. TU „2002… P. VOULGARIS „2001… Book Review Editor A.
2010
The use of general descriptive names, registered names, trademarks, etc. in this publication does not imply, even in the absence of a specific statement, that such names are exempt from the relevant protective laws and regulations and therefore free for general use.
Abstract: This issue includes six articles they are; P1111410320 by Simon O. Omekanda and Todd Perkins and Mohamed A. Zohdy which entitled "Robustness Analysis of Linear Time-Invariant Dynamic State Observers". P1111351312 by N.SambaSivaRao and J.Amarnath andV.PurnaChandrarao which entitled "Comparison of Voltage Stability Using FACTS Devices in Deregulated Power System". Paper P1111431335 by Sridevi Tirunagari and Ramesh Reddy Kolli which entitled "Suppression & Comparison of Magnetizing Current of a Transformer with PWM Voltage Source Converter". Paper P1111438344 by T. A. Perkins and M.A. Zohdy which entitled "Nonlinear State Control Optimized by Lyapunov and Riccati via Piecewise Linear Transformations Applied to Transmission Torque Converter Clutches", paper P1111440346 by P Srinath Rajesh and J Amarnath which entitled "Dynamics of Metallic Particle movement in a Gas Insulated Substation Employing SF6/N2, SF6/CO2 and SF6/Air Dielectric Gas Mixtures ". Paper P1111444352 by Jala M. El-Azab and Hamed M. Kandel and Mohamed A. Khedr which entitled "Numerical Study of Auto-Control and Stabilization of Pulse Repetition Rate of Passively Q-Switched Laser Systems".
This issue presents several interesting article on emerging research topics in automatic control and system engineering, they are; Xiaomin Zhou, Yunfeng Wu from University of Science and Technology Beijing and china presented an article on "The Control Capability Analysis and Decoupling Control of Flatness and Edge Drop for Cold Rolling Mill". P.Nagarjuna Reddy and J. Amarnath from JNT University, Hyderabad, India presented an article on "SIMULATION OF PARTICLE TRAJECTORIES IN A 3-PHASE COMMON ENCLOSURE GAS INSULATED BUSDUCT WITH EPOXY COATED ELECTRODES". N. Samba Siva Rao, J. Amarnath, V. Purna Chandrarao from Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Hyderabad, India presented an article on "Effect of Multi FACTS Devices on the Enhancement of Available Transfer Capability in a Deregulated Power System". S.O. Omekanda and M.A. Zohdy from Oakland University, USA presented an article on "An Efficient Novel Reduced Order Observer for State Estimation of an Internal Combustion Engine Model". Dipesh D Patel and Ziyad M Salameh from University of Massachusetts Lowell, USA presented an article on on "A Two Branch SIMULINK Model of the Lithium Polymer Battery". J. S. Piasecki and M. A. Zohdy from Oakland University, USA presented an article on "Hybrid Dynamic System Control of Sequential Motion in Biped Robots".
This issue (DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.1.1624.2642) includes the following papers; P1111025142, M.A. Eltantawie, “Forward and Inverse Fuzzy Magnetorheological Damper Models for Control Purposes” P1111026152, V. Naga Bhaskar Reddy and V. Narasimhulu and Dr. Ch. Sai Babu, “CONTROL OF CASCADED MULTILEVEL INVERTER BY USING CARRIER BASED PWM TECHNIQUE AND IMPLEMENTED TO INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE” P1110942894, Yousof Gheisari, “Improved Analysis and Simulation of Micro-Technology based on Frequency-Domain Hybrid Reduction Method: Micro-Electromechanical Optical Filter Benchmark” P1111026154, K. Satyanarayana and J. Amarnath and A. Kailasa Rao, “Hybrid PWM Algorithm with Low Computational Overhead for Induction Motor Drives for Reduced Current Ripple” P1111025143, R.Karthikeyan and Tapio Pahikkala and Seppo Virtanen and Jouni Isoaho and K. Manickavasagam and KVV. Murthy, “Fuzzy Logic Based Control for Parallel Cascade Control” P1111018061, Chafi Anas and Herrou Brahim and Harras Bilal and El Hammoumi Mohammed, “Geometrical Non-Linear Steady State Forced Periodic Vibration of Fully Clamped Composite Laminated Rectangular Plates: a Multi Mode Approach” P1110922764, BEN HAMED Mouna and SBITA Lassaâd and MESSAOUDI Mustapha, “A Robust Adaptive Control Algorithm for Sensorless Induction Motor Drives” P1111036271, Hassan Faida and Janah Saadi, “Study of a Project for Producing of Wind Energy: Design, Monitoring and Impact on the Electricity Grid”
The control concept on the electro-hydraulic servovalve system focuses on the pressure control, position control and velocity control. The servovalve and the system components are needed to be considered in the proposed control strategy. The control concepts on the electro-hydraulic servovalve systems in this work are divided into two parts: 1. Theoretical and experimental investigation for pressure control on the electro-hydraulic servovalve systems. The pressure control study in this work is concerned with the modeling and controlling of the hydraulic fluid pressure value at the end of long transmission line (TL) by using the electro-hydraulic servovalve. The input voltage signals to the amplifier, designed by C++ program, are used to control the pressure reference signal at the end of TL. The electrical analogy method is used to simulate the effect of the TL, as well as the first order transfer function to simulate the servovalve effect. Therefore, the whole system is represented mathematically in MATLAB m-file program. The mathematical model is seen as a good simulation approach compared with the experimental open loop control test. The on-line adjustable control strategy, Ziegler & Nichols method and Astrom & Hagglund method, can be used experimentally to find the proportional and integral control gain values for acceptable control system behavior. The servovalve succeeds to reduce and overcome the negative effect of the TL on the hydraulic fluid pressure value at the chosen control point. 2. Theoretical and experimental investigation for velocity and position control by the electro-hydraulic servovalve system. The C++ language programs are designed to control the position and velocity of the road simulator (single-rod, double acting linear cylinder actuator) with variable load (quarter car suspension system). The whole system is analyzed mathematically and experimentally. The mathematical model of the electro-hydraulic servovalve system is represented and analyzed successfully by designing the SIMULINK program. The dynamics modeling of the servovalve and the single road cylinder actuator under variable load which are controlled as a closed loop position control method with existence of the actuator internal leakage is done successfully by using the SIMULINK environments. So, the transfer function and the state-space model of the system in open and closed loop control are presented. Also, the Bode diagram is done for the system as well as the stability characteristics are found for the system by the Nyquist Diagram. The on-line adjustable PID control tuning is employed experimentally to find the best control gain values which are applied to the system. In the mathematical SIMULINK program, the PID gains values are tuned manually and automatically by computing a linear model of the plant. The tuning strategies are done automatically for the P, PI and PID strategies for three different response time values. The comparison figures in the P strategy show that the simulation programs give a good and accurate prediction results and enhance the system behavior. On the other hand, the PI strategy shows incompatible results between the actual test and the simulation program. The PID strategy shows a good prediction results. To analyze the actual fully system behaviors for a large spectrum frequency, the numbers of sinusoidal voltage input signal are used with unity compensator to create actual Bode plot. The tracking closed loop control method is done experimentally by designing C++ program and it is done theoretically by the SIMULINK simulation program for the system. The comparison result with the previous research clarifies that the mathematical solution method proposed in this dissertation shows that the prediction of the system behavior is acceptable and improve the system behavior.
This issue (DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.1.4824.2647) includes several articles they are; P1111209135, by: Tarun Varshney and Satya Sheel, on: "PID Control of MIMO Turbo – Generator Plant Based on Genetic Algorithm" P1111217176, by: Mohamed F. Hassan and Hala A. Mourad, on: "Closed Loop Controller for Stochastic Systems with Uncertain Parameters" P1111210136, by: O. Chandra Sekhar, Dr.K.Chandra sekhar Member, IEEE, on: "A Novel Nine-Level MPC Inverter for Direct Torque Control Induction Motor Drive " P1111219191, by: Akram Abu-aisheh and Sameer Khader, on: "Hybrid MPPT-Controlled LED Illumination Systems" P1111212142, by: G. Sambasiva Rao and K. Chandra Sekhar, on: "A sophisticated Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation Signal Generation for Nine-Level Inverter system for Dual-Fed Induction Motor Drive" P1111223205, by: H. Bellahsene and I. F. E. Fatani, on: "Amélioration du temps de convergence de l’algorithme de calcul du filtre optimal par HOS en DMT" P1111217174, by: C. Harikrihsna and T. Bramhananda Reddy and J. Amarnath and S. Kamakshaiah, on: "Simple and Novel Generalized Scalar PWM Algorithm for Multilevel Inverter Fed Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor"
This issue (DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.1.4949.9769) includes the following articles; P1111536402, Author="Soukaina ETTARFAOUI and Haitham Jabbar TAHA and Mohamed Majid HIMMI", Title="Performance Comparison of Golden and Silver code for STBC MIMO system" P1171221198, Author="F. CHIROUF and R. BRENDEL and M. ADDOUCHE and D. GILLET", Title="Amplitude Limitation Mechanisms in Quartz Crystal Oscillators: A Simulation Study Using Nonlinear Dipolar Method " P1181603464, Author="Sunita Badave and Anjali Bhalchandra", Title="Optimized Look-up-table for minimizing Critical Path in Distributed Arithmetic based FIR Filters" P1111610484, Author="Prof. Kamen M. Yanev", Title="Design and Analysis of a Robust Accurate Speed Control System by Applying a Digital Compensator" P1111620496, Author="N.Chaitanya and K.Chandra Sekhar and K.S.R Anajaneyulu ", Title="Current controller based Power Management Strategy of Grid Connected Parallel Inverters for Distributed Generation Applications"
This Issue (DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.1.1154.2482) includes several papers they are; P1111146024, Sunil kumar Chava and J. Amarnath and P. S Subramanyam, "Available Transfer Capability based Transmission Loading Relief (TLR) in Deregulated Power System" P1111205105, Y. A. Mobarak, and M. M. Hussien, Voltage Instability and Voltage Collapse as Influenced by Cold Inrush Current" P1111205106, AUTHOR="Y. A. Mobarak ", TITLE="Novel Controllers for Reactive Power Compensation by using STATCOM " P1111212143, Bellahsene Hatem Noura Razika and Mostefai Mohamed and Aktouf Oum El Kheir, "Nouvelle approche de diagnostic des états redoutés dans un système dynamique hybride", P1111203101, Kamen Yanev and George Anderson and Shedden Masupe, "Strategy for Analysis and Design of Digital Robust Control Systems " P1111134768, John O'Brien, "Trends in Region 3 Control System Performance as Wind Turbine Size Increases"
This issue includes several strong papers, they are; P1111451356, authored by Mohd Syakirin Ramli and Shigeru Yamamoto, which entitled "A Lyapunov Function Approach to Dynamic Stable Matching in A Multi-agent system". Paper P1111510361, authored by Vinay S. Prabhavalkar and Vijay R. Ghorpade, which entitled "A Novel Approach to Reduce the Spectral Ping-Pong Effect for the Mobility Management Framework in a Cognitive Radio Cellular Network". Paper P1111518375, authored by Kottam Pranay Kumar and K.Uday reddy and G.Jithendra Naidu and S.Siva Prasad, which entitled "DESIGN OF SOLAR POWERED MOBILE CHARGER WITH POWERBANK USING SUPERCAPACITOR AND STORAGE BATTERY FOR FAST CHARGING". Paper P1111521381, authored by N. Krishna Kumari and G. Tulasi Ram Das and M.P.Soni, which entitled "Online Stator Reference Flux Approach to Torque Ripple Minimization for SPM Drive using Fuzzy and PI Controllers", Paper P1111519376, authored by Ranuva Nageswararao and S.S. Tulasi Ram, which entitled "Effect of Multiple Particles and Collisions in a 3-Phase Gas Insulated Bus Duct under Switching Impulse Voltage". Paper P1111447354, authored by J.E.Muralidhar and P.Varanasi, which entitled "An Exotic Robust Performance of PI-Fuzzy Controller Fed BLDC Drive".

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (506)
- Newcomb, R. W., 1966, Linear Multiport Synthesis, McGraw-Hill, New York.
- Desoer, C. A., and Vidyasagar, M., 1975, Feedback Systems: Input-Output Properties, Academic Press, New York.
- ͓3͔ Gevarter, W. B., 1970, ''Basic Relations for Control of Flexible Vehicles,'' AIAA J., 8, pp. 666-672.
- ͓4͔ Hughes, D., and Wen, J. T., 1996, ''Passivity Motivated Controller Design for Flexible Structures,'' AIAA J. Guid. Control Dynam., 19, pp. 726-729.
- Lee, F. C., Flashner, H., and Safonov, M. G., 1995, ''Positivity-Based Control System Synthesis Using Alternating LMIs,'' Proceedings of American Control Conference, Seattle, WA, American Automatic Control Council, Evanston, IL, pp. 1469-1473.
- ͓6͔ Benhabib, R. J., Iwens, R. P., and Jackson, R. L., 1981, ''Stability of Large Space Structure Control Systems Using Positivity Concepts,'' AIAA J. Guid. Control, 4, pp. 487-494.
- ͓7͔ McLaren, M. D., and Slater, G. L., 1987, ''Robust Multivariable Control of Large Space Structures Using Positivity,'' AIAA J. Guid. Control Dynam., 10, pp. 393-400.
- Lozano-Leal, R. and Joshi, S. M., 1988, ''On the Design of Dissipative LQG- Type Controllers,'' Proc. 27th IEEE Decision and Control Conference, Dec., 2, pp. 1645-1646.
- ͓9͔ Haddad, W. M., Bernstein, D. S., and Wang, Y. W., 1994, ''Dissipative H 2 /H ϱ Controller Synthesis,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., 39, pp. 827- 831.
- Damaren, C. J., 1996, ''Gain Scheduled SPR Controllers for Nonlinear Flex- ible Systems,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 118, pp. 698-703.
- ͓11͔ Takegaki, M. and Arimoto, S., 1981, ''A New Feedback Method for Dynamic Control of Manipulators,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 103, pp. 119- 125.
- Ortega, R. and Spong, M. W., 1989, ''Adaptive Motion Control of Rigid Robots: A Tutorial,'' Automatica, 25, pp. 877-888.
- Damaren, C. J., 1995, ''Passivity Analysis for Flexible Multilink Space Ma- nipulators,'' AIAA J. Guid. Control Dynam., 18, pp. 272-279.
- Damaren, C. J., 1998, ''Modal Properties and Control System Design for Two-Link Flexible Manipulators,'' Int. J. Robot. Res., 17, pp. 667-678.
- References ͓1͔ Tyan, F., and Bernstein, D. S., 1994, ''Antiwindup Compensator Synthesis for Systems with Saturating Actuators,'' Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Decision and Control, 1, pp. 150-155.
- ͓2͔ Nicolao, D. G., Scattolini, R., and Sala, G., 1996, ''An Adaptive Predictive Regulator with Input Saturations,'' Automatica, 32, pp. 597-601.
- ͓3͔ Feng, T., 1995, ''Robust Stability and Performance Analysis for Systems with Saturation and Parameter Uncertainty,'' Ph.D. thesis, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
- Teel, A. R., and Kapoor, N., 1997, ''Uniting Local and Global Controllers for the Caltech Deducted Fan,'' Am. Control Conference, 3, pp. 1539-1543.
- Peng, Y., Vrancic, D., and Hanus, R., 1996, ''Anti-Windup, Bumpless, and Conditioned Techniques for PID Controllers,'' IEEE Control Syst. Mag., 16, pp. 48-57.
- ͓6͔ Khayyat, A. A., Heinrichs, B., and Sepehri, N., 1996, ''A Modified Rate- Varying Integral Controller,'' Mechatronics, 6, pp. 367-376.
- ͓7͔ Yang, S., and Leu, M. C., 1989, ''Stability and Performance of a Control System with an Intelligent Limiter,'' Proceedings of the 1989 American Con- trol Conference, pp. 1699-1705.
- ͓8͔ Yang, S., and Leu, M. C., 1993, ''Anti-Windup Control of Second-Order Plants with Saturation nonlinearity,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 115, pp. 715-720.
- ͓9͔ Fertik, H. A., and Ross, S. W., 1967, ''Direct Digital Control Algorithm with Anti-Windup Feature,'' ISA Trans., 6, pp. 317-328.
- Gilbert, E. G., and Kolmanovsky, I., 1995, ''Discrete-Time Reference Gov- erners for Systems with State and Control Constraints and Disturbance In- puts,'' Proceedings of the 34th Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 1189-1194.
- Wredenhagen, G. F., and Belanger, P. R., 1994, ''Piecewice-Linear LQ Con- trol for Systems with Input Constraints,'' Automatica, 30, pp. 403-416.
- ͓12͔ Larsson, P. T., ''Controller Design for Linear Systems Subject to Actuator Saturation,'' Ph.D. thesis, University of Michigan.
- Gutman, P.-O., and Hagander, P., 1985, ''A New Design of Constrained Con- trollers for linear systems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., 30, Jan, pp. 22-33.
- ͓14͔ Bernstein, D. S., 1995, ''Optimal Nonlinear, but Continuous, Feedback Con- trol of Systems with saturating actuators,'' Int. J. Control, 62, pp. 1209-1216.
- ͓15͔ Kazunoba, Y., and Kawabe, H., 1992, ''A Design of Saturating Control with a Guaranteed Cost and its Application to the Crane Control System,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., 37, pp. 121-127.
- ͓16͔ Larsson, P. T., 1999, Controller Design for Linear Systems Subject to Actuator Constraints, Ph.D. thesis, University of Michigan.
- Larsson, P. T., and Ulsoy, A. G., 1998, ''Scaling the Speed of Response Using LQR Design,'' Proceedings of the Conference on Decision and Control, Vol. 1, pp. 1171-1176.
- ͓18͔ Goldfarb, M., and Sirithanapipat, T., 1997, ''Performance-Based Selection of PD Control Gains for Servo Systems with Actuator Saturation,'' Proc. ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control Division, 61, pp. 497-501.
- ͓19͔ Kamenetskiy, V. A., 1996, ''The Choice of a Lyapunov Function for Close Approximation of the set of Linear Stabilization,'' Proceedings of the 35th Conference on Decision and Control, Vol. 1, pp. 1059-1060.
- ͓20͔ Tarbouriech, S., and Burgat, C., 1992, ''Class of Globally Stable Saturated State Feedback Regulators,'' Int. J. Systems Sci., 23, pp. 1965-1976.
- ͓21͔ Burgat, C., and Tarbouriech, S., 1992, ''Global Stability of Linear Systems with Saturated Controls,'' Int. J. Syst. Sci., 23, pp. 37-56.
- Gyugyi, P. J., and Franklin, G., 1993, ''Multivariable Integral Control with Input Constraints,'' Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Decision and Control, 3, pp. 2505-2510.
- ͓23͔ Phelan, R. M., 1977, Automatic Control Systems, Cornell University Press, Ltd.
- Hsu, J. C., and Meyer, A. U., 1968, Modern Control Principles and Applica- tions, McGraw-Hill.
- References ͓1͔ Meieran, H. B., and Gelhaus, F. E., 1986, ''Mobile Robots Designed for Haz- ardous Environments,'' Robots and Engineering, 8, pp. 10-16.
- ͓2͔ Wilcox, B., et al., 1992, ''Robotic Vehicles for Planetary Exploration,'' IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 175-80.
- ͓3͔ Woodbury, R., 1990, ''Exploring the Ocean's Frontiers Robots and Miniature Submarines Take Oil Drillers to New Depths.'' Time, 17.
- Schneider, S. A., and Cannon, R. H., Jr., 1992, ''Object Manipulation Control for Cooperative Manipulation: Theory and Experimental Results,'' IEEE Trans. Rob. Autom., 8, No. 3, pp. 383-394.
- ͓5͔ Luk, B., Collie, A., and Bingsley, J., 1991, ''Robug II: An Intelligent Wall Climbing Robot,'' Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Ro- botics and Automation, Sacramento, CA, Vol. 3, pp. 2342-2347.
- ͓6͔ Gorinevsky, D., and Schneider, A., 1990, ''Force Control in Locomotion of Legged Vehicles over Rigid and Soft Surfaces,'' Int. J. Rob. Res., 9, No. 2, pp. 4-23.
- Yoneda, K., Iiyama, H., Hirose, and Shigeo, S., 1994, ''Sky Hook Suspension Control of a Quadruped Walking Vehicle,'' Proceedings of the IEEE Interna- tional Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Diego, CA, Vol. 2, pp. 999-1004.
- Fujimoto, Y. and Kawamura, A., 1996, ''Proposal of Biped Walking Control Based on Robust Hybrid Position/Force Control,'' Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Minneapolis, MN, Vol. 4, pp. 2724-2730.
- Celaya, E. and Porta, J., 1996, ''Control of a Six-Legged Robot Walking on Abrupt Terrain,'' Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Ro- botics and Automation, Minneapolis, MN, Vol. 4, pp. 2731-2736.
- Sunada, C., Argaez, D., Dubowsky, S., and Mavroidis, C., 1994, ''A Coordi- nated Jacobian Transpose Control for Mobile Multilimbed Robotic Systems,'' References ͓1͔ Kanellakopoulos, I., Kokotovic ´, P. V., and Morse, A. S., 1991, ''Systematic Design of Adaptive Controllers for Feedback Linearizable Systems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., 36, pp. 1241-1253.
- ͓2͔ Krstic ´, M., Kanellakopoulos, I., and Kokotovic ´, P. V., 1992, ''Adaptive Non- linear Control Without Over-Parameterization,'' Systems Control Lett., 19, pp. 177-185.
- Krstic ´, M., and Kokotovic ´, P. V., 1995, ''Adaptive Nonlinear Design with Controller-Identifier Separation and Swapping,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Con- trol., 40, pp. 426-440.
- ͓4͔ Nam, K., and Arapostathis, A., 1988, ''A Model Reference Adaptive Control Scheme for Pure-Feedback Non Linear Systems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Con- trol., 33, pp. 803-811.
- ͓5͔ Seto, D., Annaswamy, A. M., and Baillieul, J., 1994, ''Adaptive Control of a Class of Nonlinear Systems with a Triangular Structure,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., 39, pp. 1411-1428.
- ͓6͔ Utkin, V. I., 1992, Sliding Modes In Control And Optimization, Springer- Verlag, Berlin.
- Zinober, A. S. I. ed., 1994, Variable Structure and Lyapunov Control, Springer-Verlag, London.
- ͓8͔ Bartolini, G., and Ferrara, A., 1994, ''Model-Following VSC Using an Input- Output Approach,'' Variable Structure and Lyapunov Control, A.S.I. Zinober, ed., Springer-Verlag, London, pp. 289-312.
- ͓9͔ Narendra, K. S., and Boskovic, J. D., 1989, ''A Combined Direct, Indirect and Variable Structure Method for Robust Adaptive Control,'' IEEE Trans. Au- tom. Control., 37, pp. 262-268.
- ͓10͔ Bartolini, G. Ferrara, A., Giacomini, L., and Usai, E., 1996, ''A Combined Backstepping/Second Order Sliding Mode Approach to Control a Class of Nonlinear Systems,'' Proc. IEEE International Workshop on Variable Struc- ture Systems, Tokyo, Japan, pp. 205-210.
- ͓11͔ Sira-Ramirez, H., 1992, ''On the Sliding Mode Control of Nonlinear Sys- tems,'' Systems Control Lett., 19, pp. 303-312.
- ͓12͔ Zinober, A. S. I., and Rios-Bolivar, E. M., 1994, ''Sliding Mode Control for Uncertain Linearizable Nonlinear Systems: A Backstepping Approach,'' Proc. IEEE Workshop on Robust Control via Variable Structure and Lyapunov Techniques, Benevento, Italy, pp. 78-85.
- ͓13͔ Bartolini, G., Ferrara, A., and Usai, E., 1997, ''Applications of a Suboptimal Discontinuous Control Algorithm for Uncertain Second Order Systems,'' Int. J. Robust Nonlin. Control, 7, pp. 299-320.
- ͓14͔ Levant, A., 1993, ''Sliding Order and Sliding Accuracy in Sliding Mode Con- trol,'' Int. J. Control, 58, pp. 1247-1263.
- ͓15͔ Spong, M. W., and Vidyasagar, M., 1989, Robot Dynamics and Control, Wiley, New York.
- ͓16͔ Marino, R., and Nicosia, S., 1985, ''Singular Perturbation Techniques in the Adaptive Controls of Elastic Robots,'' Proc. 1st IFAC Symp. on Robot Con- trol, Barcelona, pp. 95-100.
- ͓17͔ Spong, M. W., 1987, ''Modeling and Control of Elastic Joint Robots,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 109, pp. 310-319.
- ͓18͔ Chang, Y., and Daniel, R. W., 1992, ''On the Adaptive Control of Flexible Joint Robots,'' Automatica, 28, pp. 969-974.
- ͓19͔ Ge, S. S., 1996, ''Adaptive Controller Design for Flexible Joint Manipula- tors,'' Automatica, 32, pp. 273-278.
- ͓20͔ Spong, M. W., 1989, ''Adaptive Control of Flexible Joint Robots,'' Systems Control Lett., 13, pp. 15-21.
- ͓21͔ Spong, M. W., 1995, ''Adaptive Control of Flexible Joint Manipulators: Com- ments on Two Papers,'' Automatica, 31, pp. 585-590.
- ͓22͔ Su, R., and Hunt, L. R., 1986, ''A Canonical Expansion for Nonlinear Sys- tems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., 31, pp. 670-673.
- Krstic ´, M., Kanellakopoulos, I., and Kokotovic ´, P. V., 1995, Nonlinear and Adaptive Control Design, Wiley, New York.
- Krstic ´, M., and Kokotovic ´, P. V., 1994, ''Observer-Based Schemes for Adap- tive Nonlinear State-Feedback Control,'' Int. J. Control, 59, No. 6, pp. 1373- 1381.
- Jankovic, M., 1997, ''Adaptive Nonlinear Output Feedback Tracking with a Partial High-Gain Observer and Backstepping,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., 42, No. 1, pp. 106-113.
- ͓26͔ Bartolini, G., Ferrara, A., and Usai, E., 1997, ''Output Tracking Control of Uncertain Nonlinear Second-Order Systems,'' Automatica, 33, No. 12, pp. 2203-2212.
- Li, Z., and Krstic ´, M., 1997, ''Maximizing Regions of Attraction Via Back- stepping and CLFs with Singularities,'' Systems Control Lett., 30, pp. 195- 207. References ͓1͔ Arimoto, S., Kawamura, S., and Miyazaki, F., 1984, ''Bettering Operation of Robots by Learning,'' J. Robotic Systems, 1, No. 2, pp. 123-140.
- ͓2͔ Kwong, W. A., and Passino, K. M., 1995, ''Dynamically Focused Fuzzy Learning Control,'' Proc. American Control Conf., pp. 3755-3759.
- ͓3͔ Teshnehlab, M., and Watanabe, K., 1995, ''Flexible Structural Learning Con- trol of a Robotic Manipulator Using Artificial Neural Networks,'' JSME Int. J., Series C, 38, No. 3, pp. 510-521.
- ͓4͔ Yang, B. H., and Asada, H., 1995, ''Progressive Learning for Robotic Assem- bly: Learning Impedance with an Excitation Scheduling Method,'' Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2538-2544.
- ͓5͔ Horowitz, R., 1993, ''Learning Control of Robot Manipulators,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 115, No. 2͑B͒, pp. 402-411.
- ͓6͔ Messner, W., Horowitz, R., Kao, W. W., and Boals, M., 1991, ''A New Adap- tive Learning Rule,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., 36, No. 2, pp. 188-197.
- ͓7͔ Guglielmo, K., and Sadegh, N., 1996, ''Theory and Implementation of a Re- petitive Robot Controller with Cartesian Trajectory Description,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 118, No. 1, pp. 15-21.
- ͓8͔ Guvenc, L., 1996, ''Stability and Performance Robustness Analysis of Repeti- tive Control Systems Using Structured Singular Values,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 118, No. 3, pp. 593-597.
- ͓9͔ Emelyanov, S. V., 1967, Variable Structure Control Systems, Nauka, Moscow ͑in Russian͒.
- Slotine, J.-J. E., and Li, W., 1991, Applied Nonlinear Control, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J. ͓11͔ Gao, W., and Hung, J. C., 1993, ''Variable Structure Control of Nonlinear System: A New Approach,'' IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 40, No. 1, pp. 45-56.
- ͓12͔ Strang, G., 1980, Linear Algebra and Its Applications, 2nd ed., Academic, Press.
- Burton, J. A., and Zinober, A. S. I., 1986, ''Continous Approximation of Variable Structure Control,'' Int. J. Syst. Sci., 17, No. 6, pp. 876-885.
- ͓14͔ NSK Corporation, 1989, Megatorque Motor System: User's Manual, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sadegh, N., Horowitz, R., and Tomizuka, M., 1990, ''A Unified Approach to Design of Adaptive and Repetitive Controllers for Robotic Manipulator,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 112, No. 4, pp. 618-629.
- Õ Vol. 122, MARCH 2000 Transactions of the ASME References ͓1͔ Falb, P. L., and Wolovich, W. A., 1967, ''Decoupling in the Design and Synthesis of Multivariable Control Systems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC-12, pp. 651-669.
- ͓2͔ Porter, W. A., 1969, ''Decoupling of and Inverses for Time-Varying Linear Systems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC-14, pp. 378-380.
- ͓3͔ Porter, W. A., 1970, ''Diagonalization and Inverses for Nonlinear Systems,'' Int. J. Control, 10, pp. 252-264.
- ͓4͔ Ha, I. J., and Gilbert, E. G., 1986, ''A Complete Characterization of Decou- pling Control Laws for a General Class of Nonlinear Systems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC-31, pp. 823-830.
- ͓5͔ Xia, X., 1993, ''Parametrization of Decoupling Control Laws for Affine Non- linear Systems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC-38, pp. 916-928.
- ͓6͔ Isidori, A., 1996, Nonlinear Control Systems: An Introduction, 3rd Ed., Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
- Tsirikos, A. S., 1996, ''Contribution to the Development of New Techniques for the Analysis and Design of Linear and Nonlinear Systems,'' Ph.D. thesis, National Technical University of Athens, Department of Electrical and Com- puter Engineering, Athens.
- Morgan, B. S., 1964, ''The Synthesis of Linear Multivariable Systems by State-Variable Feedback,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC-9, pp. 405-411.
- ͓9͔ Suda, N., and Umahashi, K., 1984, ''Decoupling of Nonsquare Systems: A Necessary and Sufficient Condition in Terms of Infinite Zeros,'' Proc. 9th IFAC World Congress, Budapest, 1, pp. 88-93.
- ͓10͔ Descusse, J., Lafay, J. F., and Malabre, M., 1986, ''A Survey on Morgan's Problem,'' Proc. 25th IEEE Conf. Decision Contr. (CDC), 2, pp. 1289-1294, Athens, Greece.
- Descusse, J., Lafay, J. F., and Malabre, M., 1988, ''Solution to Morgan's Problem,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC-33, pp. 732-739.
- ͓12͔ Commault, C., Descusse, J., Dion, J. M., Lafay, J. F., and Malabre, M., 1986, ''New decoupling invariants: The essential orders,'' Int. J. Control, 44, pp. 689-700.
- Herrera, H. A. N., and Lafay, J. F., 1993, ''New Results about Morgan's Problem,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC-38, pp. 1834-1838.
- ͓14͔ Glumineau, A., and Moog, C. H., 1992, ''Nonlinear Morgan's Problem: Case of (pϩ1) Inputs and p Outputs,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC-37, pp. 1067-1072.
- Kamiyama, S., and Furuta, K., 1976, ''Decoupling by Restricted State Feed- back,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC-21, pp. 413-415.
- ͓16͔ Descusse, J., Lafay, J. F., and Kucera, V., 1984, ''Decoupling by Restricted State Feedback: The General Case,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC-29, pp. 79-81.
- Arvanitis, K. G., 1997, ''Simultaneous Uniform Disturbance Localization and Decoupling of Nonsquare Linear Time-Dependent Analytic Systems via Re- stricted State Feedback,'' IMA J. Math. Control Inf., 14, pp. 371-383.
- ͓18͔ Arvanitis, K. G., 1998, ''Uniform Decoupling of Nonsquare Linear Time- Varying Analytic Systems via Restricted Static State Feedback,'' J. Franklin Inst., 335B, pp. 359-373.
- ͓19͔ Tarn, T. J., and Zhan, W., 1991, ''Input-Output Decoupling and Linearization via restricted Static State Feedback,'' Proc. 11th IFAC World Congress, Tal- lin, Estonia, 3, pp. 287-292.
- ͓20͔ Wonham, W. M., 1979, Linear Multivariable Control: A Geometric Approach, Springer-Verlag, New York.
- ͓21͔ Isidori, A., Krener, A. J., Gori-Giorgi, C., and Monaco, S., 1981, ''Nonlinear Decoupling via Feedback: A Differential Geometric Approach,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC-26, pp. 331-345.
- ͓22͔ Hirschorn, R. M., 1981, ''͑A, B͒-Invariant Distributions and Disturbance De- coupling of Nonlinear Systems,'' SIAM J. Control Optim., 19, pp. 1-19.
- ͓23͔ Nijmeijer, H., and Van der Schaft, A., 1983, ''The Disturbance Decoupling Problem for Nonlinear Control Systems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, AC- 28, pp. 331-345.
- ͓24͔ Krener, A. J., 1985, ''͑Adf, g͒, ͑adf, g͒ and Locally ͑adf, g͒ Invariant and Controllability Distributions,'' SIAM J. Control Optim., 23, pp. 523-549.
- ͓25͔ Huijberts, H., 1992, ''A Nonregular Solution to the Nonlinear Dynamic Dis- turbance Decoupling Problem with an Application to a Complete Solution of the Nonlinear Model Matching Problem,'' SIAM J. Control Optim., 30, pp. 350-366.
- ͓26͔ Arvanitis, K. G., 1994, ''Uniform Disturbance Localization with Simultaneous Uniform Decoupling for Linear Time-Varying Analytic Systems,'' Int. J. Syst. Sci., 25, pp. 1679-1694.
- ͓27͔ Narikiyo, V., and Izumi, T., 1991, ''On model feedback control for robot manipulators,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 113, pp. 371-378.
- ͓28͔ Wie, B., Byun, K. W., and Warren, V. W., 1989, ''New approach to attitude/ momentum control for the space station,'' AIAA J. Guidance, Contr. Dyn., 12, pp. 714-722.
- References ͓1͔ Book, W. J., 1993, ''Controlled Motion in an Elastic World,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 115, No. 2, June, pp. 252-261.
- ͓2͔ Junkins, J. L., and Kim, Y. 1993, Introduction to Dynamics and Control of Flexible Structures.
- Singer, N., and Seering, W., 1990, ''Preshaping Command Inputs to Reduce System Vibration,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 112, No. 1, Mar., pp. 76-82.
- Singh, T., and Vadali, S. R., 1994, ''Robust Time-Optimal Control: A Fre- quency Domain Approach,'' AIAA J. Guid., Contr., Dyn., 17, No. 2, Mar.- Apr., pp. 346-353.
- ͓5͔ Singhose, W., Seering, W., and Singer, N., 1994, ''Residual Vibration Reduc- tion Using Vector Diagrams to Generate Shaped Inputs,'' ASME J. Mech. Des., 116, No. 2, June, pp. 654-659.
- ͓6͔ Wie, B., Sinha, R., and Liu, Q., 1993, ''Robust Time-Optimal Control of Uncertain Structural Dynamic Systems,'' AIAA J. Guid., Contr., Dyn., 16, No. 5, Sept.-Oct., pp. 980-983.
- ͓7͔ Smith, O. J. M., 1957, ''Posicast Control of Damped Oscillatory Systems,'' Proc. of the IRE, Sept., pp. 1249-1255.
- ͓8͔ Singhose, W., Seering, W., and Singer, N., 1996, ''Input Shaping for Vibration Reduction With Specified Insensitivity to Modeling Errors,'' Proc. Japan-USA Symposium on Flexible Automation, Boston, MA.
- Magee, D. P., 1996, ''Optimal Arbitrary Time-Delay Filtering to Minimize Vibration in Elastic Manipulator Systems,'' PhD thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology.
- de Roover, D., and Sperling, F. B., 1997, ''Point-to-Point Control of a High Accuracy Positioning Mechanism,'' Proc. American Control Conf., Albuquer- que, NM, June, pp. 1350-1354.
- ͓11͔ Rappole, B. W., Singer, N. C., and Seering, W. P., 1994, ''Multiple-Mode Impulse Shaping Sequences for Reducing Residual Vibrations,'' 23rd ASME Biennial Mechanisms Conf., Minneapolis, MN, DE-71, pp. 11-16.
- ͓12͔ Singhose, W., Seering, W., and Singer, N., 1995, ''The Effect of Input Shap- ing on Coordinate Measuring Machine Repeatability,'' Proc. IFToMM World Congress on the Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, Milan, Italy, 4, pp. 2930-2934.
- Tuttle, T. D., and Seering, W. P., 1997, ''Experimental Verification of Vibra- tion Reduction,'' AIAA J. Guid., Contr., Dyn., 20, No. 4, July-Aug., pp. 658-664.
- Singer, N. C., Singhose, W. E., and Kriikku, E., 1997, ''An Input Shaping Controller Enabling Cranes to Move Without Sway,'' Proc. ANS Topical Meeting on Robotics and Remote Systems, Augusta, GA.
- Jansen, J. F., 1992, ''Control and Analysis of a Single-Link Flexible Beam with Experimental Verification,'' ORNL/TM-12198, Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
- Magee, D. P., and Book, W., 1995, ''Filtering Micro-Manipulator Wrist Com- mands to Prevent Flexible Base Motion,'' Proc. American Control Conf., Se- attle, WA, June, pp. 924-928.
- ͓17͔ Feddema, J., Dohrmann, C., Parker, G., Robinett, R., Romero, V., and Schmitt, D., 1997, ''Control for Slosh-Free Motion of an Open Container,'' IEEE Con- trol Systems Magazine, 17, No. 1, Feb., pp. 29-36.
- ͓18͔ Pao, L. Y., 1997, ''An Analysis of the Frequency, Damping, and Total Insen- sitivities of Input Shaping Designs,'' AIAA J. Guid., Contr., Dyn., 20, No. 5, Sept.-Oct., pp. 909-915.
- ͓19͔ Kirkpatrick, S., Gellet, C., and Vecchi, M., 1983, ''Optimization by Simulated Annealing,'' Science, pp. 671-680.
- van Laarhoven, P. J. M., and Aarts, E. H. L., 1987, Simulated Annealing: Theory and Applications, Reidel Publishing Company.
- Pao, L. Y., and Lau, M. A., 1999, ''Expected Residual Vibration of Traditional and Hybrid Input Shaping Designs,'' AIAA J. Guid., Contr., Dyn., 22, No. 1, Jan.-Feb., pp. 162-165.
- ͓22͔ Bhat, S. P., and Miu, D. K., 1991, ''Solutions to Point-to-Point Control Prob- lems Using Laplace Transform Technique,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Con- trol, 113, No. 3, Sept., pp. 425-431.
- ͓23͔ Pao, L. Y., and Singhose, W. E., 1995, ''On the Equivalence of Minimum Time Input Shaping with Traditional Time-Optimal Control,'' Proc. IEEE Conf. Control Applications, Albany, NY, Sept., pp. 1120-1125.
- ͓24͔ Tuttle, T. D., and Seering, W. P., 1994, ''A Zero-placement Technique for Designing Shaped Inputs to Suppress Multiple-mode Vibration,'' Proc. Ameri- can Control Conf., Baltimore, MD, June, pp. 2533-2537.
- ͓25͔ Pao, L. Y., Chang, T. N., and Hou, E., 1997, ''Input Shaper Designs for Minimizing the Expected Level of Residual Vibration in Flexible Structures,'' Proc. American Control Conf., Albuquerque, NM, June, pp. 3542-3546.
- References ͓1͔ Thomas, C. L., 1995, Introduction to Rapid Prototyping, Univ. of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT.
- Hartwig, G., 1997, ''Rapid 3D Modelers,'' Design Engineering, Mar., pp. 37-44.
- Prinz, F. B., et al., 1995, ''Processing, Thermal and Mechanical Issues in Microcasting Shape Deposition Manufacturing,'' Proc. of the SFF Symposium, Austin, TX, pp. 118-129.
- ͓4͔ Doumanidis, C. C., 1994, ''Modeling and Control of Timeshared and Scanned Torch Welding,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 116, pp. 387-395.
- ͓5͔ Kutay, A., and Weiss, L. E., 1992, ''A Case Study of a Thermal Spraying Robot,'' Robotics Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 9, No. 4, pp. 12-19.
- ͓6͔ Doumanidis, C., 1992, ''Hybrid Modeling for Control of Weld Pool Dimen- sions,'' ASME 1992 Japan-USA Symposium on Flexible Automation, San Francisco, CA, July, pp. 317-323.
- ͓7͔ Goldak, J., 1989, ''Modeling Thermal Stresses and Distortions in Welds,'' Trends in Welding Research, ASM Intl., Gatlinburg, TN, May, pp. 71-81.
- ͓8͔ Thorn, K., Feenstra, M., Young, J. C., Lawson, W. H. S., and Kerr, H. W., 1982, ''The Interaction of Process Variables,'' Metal Construction 14/3, Mar., pp. 128-133.
- Vroman, A. R., and Brandt, H., 1978, ''Feedback Control of GTA Welding Using Puddle Width Measurement,'' Weld. J. ͑Miami͒, 57, Sept, pp. 742-746.
- ͓10͔ Song, J. B., and Hardt, D. E., 1991, ''Multivariable Adaptive Control of Bead Geometry in GMA Welding,'' ASME Symposium on Welding, 1991, pp. 41- 48.
- Hale, M. B., and Hardt, D. E., 1992, ''Multi-Output Process Dynamics of GMAW: Limits to Control,'' Welding Science and Technology, ASM, Gatlin- burg, TN, pp. 1015-1020.
- ͓12͔ Dornfeld, D. A., Tomizuka, M., and Langari, G., 1982, ''Modeling and Adap- tive Control of Arc Welding Processes,'' Measurement & Control for Batch Manuf., Nov., pp. 53-64
- Zhang, Y. M., and Kovacevic, R., 1995, ''Modeling and Real-Time Identifi- cation of Weld Pool Characteristics for Intelligent Controll,'' Proc. 1st World Congress on Intelligent Manufacturing Processes and Systems, 2, pp. 1014- 1023.
- Tzafestas, S. G. editor, 1982, Distributed Parameter Control Systems, Perga- mon Press, Oxford, UK.
- Ray, W. H., and Lainiotis, D. G., 1978, DPS-Identification, Estimation and Control, Dekker, New York, NY, 1978.
- Curtain, R. F., and Pritchard, A. J., 1978, ''Infinite Dimensional Linear Sys- tems Theory,'' Springer-Systems, SIAM J. Control, 10, pp. 329-333.
- ͓17͔ Delfour, and Mitter, 1972, ''Controllability and Observability for Infinite- Dimensional Systems,'' SIAM J. Control, 10, pp. 329-333.
- ͓18͔ Alifanov, O. M., 1994, Inverse Heat Transfer Problems, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
- Murio, D. A., 1993, The Mollification Method and the Numerical Solution of III-Posed Problems, Wiley, New York, NY.
- ͓20͔ Beck, J. V., 1985, Inverse Heat Conduction: Ill-Posed Problems, Wiley, New York, NY.
- Marquis, B. P., and Doumanidis, C. C., 1993, ''Distributed-Parameter Simu- lation of the Scan Welding Process,'' IASTED Conf. on Modeling & Simula- tion, Pittsburgh, PA, pp. 146-149.
- ͓22͔ Batchelor, G. K., 1967, Introduction to Fluid Dynamics, Cambridge Press, London, U.K.
- Carslaw, H. S., and Jaeger, J. C., 1959, Conduction of Heat in Solids, 2nd Edition, Oxford Press, London, U.K.
- Astrom, K. J., and Wittenmark, B., 1995, Computer-Controlled Systems, 3rd Edition, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
- References ͓1͔ Ibrahim, R. A., 1992, ''Friction-Induced Vibration, Chatter, Squeal, and Chaos: Part I-Mechanics of Friction and Part II-Dynamics and Modeling,'' DE-Vol. 49, Friction-Induced Vibration, Chatter, Squeal, and Chaos, ASME 1992.
- Moore, D. F., 1972, ''On the Decrease in Contact Area for Spheres and Cyl- inders Rolling on a Viscoelastic Plane,'' Wear, 21, pp. 179-194.
- ͓3͔ Moore, D. F., and Geyer, W., 1974, ''A Review of Hysteresis Theories for Elastomers,'' Wear, 30, pp. 1-34.
- ͓4͔ Barquins, M., and Roberts, A. D., 1986, ''Rubber Friction Variation with Rate and Temperature: Some New Observations,'' J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 19, pp. 547-563.
- Briscoe, B. J., 1992, ''Friction of Organic Polymers,'' Fundamentals of Fric- tion: Macroscopic and Microscopic Processes, I. L. Singer and H. M. Pollock, eds., Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston.
- Schallamach, A., 1971, ''How Does Rubber Slide,'' Wear, 17, pp. 301-312.
- ͓7͔ Barquins, M., 1985, ''Sliding Friction of Rubber and Schallamach Waves-A Review,'' Mater. Sci. Eng., 73, pp. 45-63.
- ͓8͔ Lewis, M. W. J., 1986, ''Friction and Wear of PTFE-Based Reciprocating Seals,'' Lubr. Eng., 42, No. 3, pp. 152-158.
- ͓9͔ Ferry, J. D., 1980, Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers, Wiley, New York.
- Briscoe, B. J., 1986, ''Interfacial Friction of Polymer Composites: General Fundamental Principles,'' Friction and Wear of Polymer Composites, Friedrich, K., ed., Elesevier, New York, pp. 25-60.
- ͓11͔ Pipkin, A. C., 1986, Lectures on Viscoelasticity Theory, Springer-Verlag, New York.
- Ludema, K. C., and Tabor, D., 1996, ''The Friction and Viscoelastic Proper- ties of Polymeric Solids,'' Wear, 9, pp. 329-348.
- ͓13͔ Lee, L. H., ed., 1985, Polymer Wear and Its Control, ACS Symposium series 287.
- Thorp, J. M., 1986, ''Tribological Properties of Selected Polymeric Matrix Composites Against Steel Surfaces,'' Friction and Wear of Polymer Compos- ites, Freidrich, K., ed., Elsevier, New York, pp. 89-136.
- ͓15͔ Visscher, M., and Kanters, A. F. C., 1990, ''Literature Review and Discussion on Measurements of Leakage, Lubricant Film Thickness and Friction of Re- ciprocating Elastomeric Seals,'' Lubr. Eng., 46, No. 12, pp. 785-791.
- ͓16͔ Dowson, D., and Swales, P. D., 1967, ''An Elastohydrodynamic Approach to the Problem of the Reciprocating Seal,'' Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. Fluid Sealing, BHRA Fluid Eng., paper F3.
- Hirano, F., and Kanetar, M., 1971, ''Theoretical Investigation of Friction and Sealing Characteristics of Flexible Seals for Reciprocating Motion,'' Proceed- ings of 5th International Conference on Fluid Sealing, BHRA Fluid Eng., paper G2, pp. G2-17-G2-32.
- ͓18͔ Hirano, F., and Kanetar, M., 1971, ''Experimental Investigation of Friction and Sealing Characteristics of Flexible Seals for Reciprocating Motion,'' Pro- ceedings of the 5th International Conference on Fluid Sealing, BHRA Fluid Eng., paper G3, pp. G3-33-G3-48.
- ͓19͔ Hirano, F., and Kanetar, M., 1973, ''Elastohydrodynamic Condition in Elliptic Contact in Reciprocating Motion,'' Proc. 6th Int. Conf. on Fluid Sealing, BHRA Fluid Eng., paper C2, pp. C2-11-C2-24.
- Karaszkiewicz, A., 1987, ''Hydrodynamics of Rubber Seals for Reciprocating Motion, Lubricating Film Thickness, and Out-Leakage of O-Seals,'' Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 26, No. 11, pp. 2180-2185.
- ͓21͔ Dowson, D., and Jin, Z. M. 1992, ''Microelastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Low-elastic Modulus Solids on Rigid Substrates,'' Frontiers of Tribology, A. D. Roberts, ed., Adam Hilger, New York, pp. A116-A123.
- ͓22͔ Stachowiak, G. W., and A. W. Batchelor, 1993, Eng. Tribology, Elsevier, New York, pp. 218-220.
- ͓23͔ Kanters, A. F. C., and Visscher, M., 1990, ''Literature-Review and Discussion on Measurements of Leakage, Lubricant film thickness and Friction of Recip- rocating Elastomeric Seals,'' Lubr. Eng., 46, No. 12, pp. 785-791.
- Prati, E., and Strozzi, A., 1984, ''A Study of the Elastohydrodynamic Problem in Rectangular Elastomeric Seals,'' ASME J. Tribol., 106, pp. 505-512.
- ͓25͔ Ruskell, L. E., 1980, ''A Rapidly Converging Theoretical Solution of the Elastohydrodynamic Problem for Rectangular Rubber Seals,'' J. Mech. Eng. Sci., 22, No. 1, pp. 9-16.
- ͓26͔ Karnopp, D., 1985, ''Computer Simulation of Stick-Slip Friction in Mechani- cal Dynamic Systems,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 107, pp. 100- 103.
- Haessig, D. A., and Friedland, B., 1991, ''On the Modeling and Simulation of Friction,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 113, pp. 354-362.
- Canudas de Wit, C., Olsson, H., A ˚stro ¨m, K. J., and Lischinsky, P., 1995, ''A New Model for Control of Systems with Friction,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Con- trol., 40, No. 3, pp. 419-425.
- ͓29͔ Bo, L. C., and Pavelescu, D., 1982, ''The Friction-Speed Relation and Its Influence on the Critical Velocity of the Stick-Slip Motion,'' Wear, 82, No. 3, pp. 277-289.
- ͓30͔ Hess, D. P., and Soom, A., 1990, ''Friction at a Lubricated Line Contact Operating at Oscillating Sliding Velocities,'' ASME J. Tribol., 112, No. 1, pp. 147-152.
- ͓31͔ Armstrong-He ´louvry, B., 1993, ''Stick Slip and Control in Low-Speed Mo- tion,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., 38, No. 10, pp. 1483-1496.
- ͓32͔ Armstrong-He ´louvry, B., 1991, Control of Machine with Friction, Kluwer Academic, Boston.
- Kilburn, R. F., 1974, ''Friction Viewed as a Random Process,'' ASME J. Lubr. Technol., 96, pp. 291-299.
- ͓34͔ Hsu, G., 1995, Stochastic Modelling and Identification of Lubricated Polymer Friction Dynamics, Dissertation, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 1995.
- Richards, S. C., and Roberts, A. D., 1992, ''Boundary Lubrication of Rubber by Aqueous Surfactant'' Frontiers of Tribology, A. D. Roberts, ed., Adam Hilger, New York, pp. A76-A80.
- Granick, S., 1992, ''Molecular Tribology of Fluids,'' Fundamentals of Fric- tion: Macroscopic and Microscopic Processes, I. L. Singer and H. M. Pollock, eds., Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp. 387-403.
- ͓37͔ Israelachvili, J. N., 1992, ''Adhesion, Friction and Lubrication of Molecularly Smooth Surfaces,'' Fundamentals of Friction: Macroscopic and Microscopic Processes, I. L. Singer and H. M. Pollock, eds., Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp. 351-385.
- Guran, A., Pfeiffer F., and Popp, K., 1996, ed. Dynamics with Friction: Mod- eling, Analysis, and Experiment, World Scientific, New Jersey.
- ͓39͔ Ljung, L., 1987, System Identification: Theory for the User, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey.
- ͓40͔ So ¨derstro ¨m, T., and Stoica, P., 1989, System Identification, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey.
- Yang, Y. P., and Chu, J. S., 1993, ''Adaptive Velocity Control of DC Motors with Coulomb Friction Identification,'' J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 115, No. 1, pp. 95-102.
- Laura, R. R., 1995, ''Real Time Determination of Road Coefficient of Friction for IVHS and Advanced Vehicle Control,'' Proceedings of the American Con- trol Conference, Vol. 3, pp. 2133-2137.
- ͓43͔ Gustafsson, F., 1996, ''Estimation and Detection of Tire-Road Friction Using the Wheel Slip,'' Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computer Aided Control System Design, pp. 99-104.
- ͓44͔ Dennis, J. E., and Schnabel, R. B., 1983, Numerical Methods for Uncon- strained Optimization and Nonlinear Equations, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey.
- ͓45͔ Van Trees, H. L., 1968, Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory: Part I, Wiley, New York.
- ͓46͔ Anderson, B.D. O., and Moore, J. B., 1979 Optimal Filtering, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey.
- Õ Vol. 122, MARCH 2000 Transactions of the ASME References ͓1͔ Ulsoy, A. G., and Koren, Y., 1993, ''Control of Machining Process,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 115, pp. 301-308.
- ͓2͔ Du, R., Elbestawi, M. A., and Wu, S. M., 1995, ''Automated Monitoring of Manufacturing Processes, Part 1: Monitoring Methods,'' ASME J. Eng. Indus- try, 117, pp. 121-132.
- ͓3͔ Koren, Y., and Lenz, E., 1972, ''Mathematial Model for Flank Wear While Turning Steel with Carbide Tools,'' CIRP Proceedings on Manufacturing Sys- tems, 1, pp. 127-139.
- Usui, E., Shirakashi, T., and Kitagawa, T., 1978, ''Analytical Prediction of Cutting Tool Wear,'' Wear, 100, pp. 129-151.
- ͓5͔ Koren, Y., 1978, ''Flank Wear Model of Cutting Tools Using Control Theory,'' ASME J. Eng. Industry, 100, pp. 19-26.
- ͓6͔ Park, J. J., and Ulsoy, A. G., 1990, ''Methods for Tool Wear Estimation From Force Measurement Under Varying Cutting Conditions,'' Automation of Manufacturing Processes, Danai, K., and Malkin, S., eds, ASME Press, New York, pp. 13-22.
- ͓7͔ Park, J. J., and Ulsoy, A. G., 1993, ''On-Line Flank Wear Estimation Using an Adaptive Observer and Computer Vision, Part I: Theory,'' ASME J. Eng. Industry, 115, pp. 30-36.
- ͓8͔ Park, J. J., and Ulsoy, A. G., 1993, ''On-Line Flank Wear Estimation Using an Adaptive Observer and Computer Vision, Part II: Results,'' ASME J. Eng. Industry, 115, pp. 37-43.
- ͓9͔ Kamarthi, S. V., 1994, ''On-Line Flank Wear Estimation in Turning Using Multi-Sensor Fusion and Neural Networks,'' Ph.D. thesis, Department of In- dustrial and Manufacturing Engineering, University Park, PA.
- Elanayar, S., and Shin, Y. C., 1995, ''Robust Tool Wear Estimation with Radial Basis Function Neural Networks,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Con- trol, 117, pp. 459-467.
- ͓11͔ Bukkapatnam, S. T. S., Lakhtakia, A., and Kumara, S. R. T., 1995, ''Analysis of Sensor Signals Shows that Turning Process on a Lathe Exhibits Low- Dimensional Chaos,'' Phys. Rev. E, 52, pp. 2375-2387.
- ͓12͔ Moon, F. C., 1992, Chaotic and Fractal Dynamics, Wiley, New York.
- ͓13͔ Abarbanel, H. D. I., 1996, Analysis of Observed Chaotic Data, Springer- Verlag, New York, NY.
- Bukkapatnam, S. T. S., 1997, ''Monitoring and Control of Chaotic Processes: Application to Turning,'' Ph.D. thesis, Department of Industrial and Manufac- turing Engineering, University Park, PA.
- ͓15͔ Isham, V., 1993, ''Statistical Aspects of Chaos: A review,'' Networks and Chaos-Statistical and Probabilistic Aspects, Barndorff-Nielsen et al., eds, Chapman and Hall, London, UK.
- Bukkapatnam, S. T. S., Kumara, S. R. T., and Lakhtakia, A., 1999, ''Analysis of Acoustic Emission in Machining,'' ASME J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 121, pp. 568-576.
- Schouten, F. T., and van den Bleek, C. M., 1994, ''Estimation of the dimen- sion of a noise attractor,'' Phys. Rev. E 50, pp. 1851-1861.
- ͓18͔ Goldberg, A., 1993, ''Applications of Wavelets to Quantization and Random Process Representations,'' Ph.D. thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA.
- Bukkapatnam, S. T. S., Kumara, S. R. T., and Lakhtakia, A., 1999, ''Local Eigenfunctions Based Suboptimal Wavelet Packet Representation of Contami- nated Chaotic Signals,'' IMA J. Appl. Math., pp. 149-162.
- ͓20͔ Donoho, D., 1992, ''De-noising by soft-thresholding,'' Technical Report: De- partment of Statistics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA.
- Cutler, C., 1991, ''Some Results on the Behavior and Estimation of Fractal Dimensions of Distributions on Attractors,'' J. Stat. Phys., 62, pp. 651-708.
- ͓22͔ Liebovitch, L., and Toth, T., 1989, ''A Fast Algorithm to Determine Dimen- sions by Box Counting,'' Phys. Lett. A, 141, pp. 386-390.
- ͓23͔ Zbikowski, R. W., 1994, ''Recurrent Neural Networks: Some Control As- pects,'' Ph.D. thesis, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Glasgow Uni- versity, Glasgow, UK.
- References ͓1͔ Reddy, W. R., and Sharan, A. M., 1987, ''The Finite Element Modeled Design of Lathe Spindles: The Static and Dynamic Analyses,'' ASME J. Vibr. Acoust., Stress Reliab. Design, 109, pp. 417-415.
- Al-Shareef, K. J. H., and Brandon, J. A., 1990, ''On the Effects of the Varia- tions in the Design Parameters on the Dynamic Performance of Machine Tools Spindle Bearing Systems,'' Int. J. Machine Tools Manufact., 30, No. 3, pp. 432-445.
- ͓3͔ Wang, W. R., and Chang, C. N., 1994, ''Dynamic Analysis and Design of a Machine Tool Spindle Bearing System,'' ASME J. Vibr. Acoust., 116, pp. 280-285.
- ͓4͔ Brandon, J. A., and Al-Shareef, K. J. H., 1992, ''Optimization Strategies for Machine Tool Spindle Bearing Systems: Critical Review,'' ASME J. Eng. Ind., 114, pp. 244-253.
- ͓5͔ Yoshimura, M., 1979, ''Computer-Aided Design Improvement of Machine Tool Structure Incorporating Joint Dynamics Data,'' Ann. CIRP, 28, pp. 241- 246.
- Wang, K. W., Shin, Y. C., and Chen, C. H., 1992, ''On the Natural Frequen- cies of High-Speed Spindles with Angular Contact Bearings,'' Proceedings of Institutions of Mechanical Engineering, J. Mech. Eng. Sci., 205, pp. 147-154.
- ͓7͔ Shin, Y. C., 1992, ''Bearing Nonlinearity and Stability Analysis in High Speed Machining,'' ASME J. Eng. Ind., 114, pp. 23-30.
- ͓8͔ Chen, C. H., Wang, K. W., and Shin, Y. C., 1994, ''An Integrated Approach Toward the Dynamic Analysis of High Speed Spindles, Part 1: System Model,'' ASME J. Vibr. Acoust., 116, pp. 506-513.
- ͓9͔ Mottershead, J. E., and Friswell, M. I., 1993, ''Model Updating in Structural Dynamics: A Survey,'' J. Sound Vib., 167, No. 2, pp. 347-375.
- ͓10͔ Butner, M. F., Murphy, B. T., and Akian, R. A., 1991, ''The Influence of Mounting Compliance and Operating Conditions on the Radial Stiffness of Ball Bearings: Analytic and Test Results,'' ASME Rotat. Machin. Vehicle Dynam., DE-Vol. 35, pp. 155-162.
- ͓11͔ Goodwin, M. J., 1991, ''Experimental Technique for Bearing Impedance Mea- surement,'' ASME J. Eng. Ind., 113, pp. 335-342.
- ͓12͔ Hong, S. W., and Lee, C. W., 1991, ''Identification of Linearized Joint Struc- tural Parameters by Combined Use of Measured and Computed Frequency Responses,'' Mech. Syst. Sig. Proc., 5, No. 4, pp. 267-277.
- ͓13͔ Wang, J. H., and Horng, S. B., 1994, ''Investigation of the Tool Holder Sys- tem with a Taper Angle 7:24,'' Int. J. Machine Tools Manufact., 34, No. 8, pp. 1163-1176.
- ͓14͔ Ren, Y., and Beards, C. F., 1995, ''Identification of Joint Properties of a Structure Using FRF Data,'' J. Sound Vib., 186, No. 4, pp. 567-587.
- Marsh, E. R., and Yantek, D. S., 1997, ''Experimental Measurement of Preci- sion Bearing Dynamic Stiffness,'' J. Sound Vib., 202, No. 1, pp. 55-66.
- ͓16͔ Chen, J. H., and Lee, A. C., 1997, ''Identification of Linearized Dynamic Characteristics of Rolling Element Bearings,'' ASME J. Vibr. Acoust., 119, pp. 60-69.
- ͓17͔ Hong, S. W., Shamine, D. M., and Shin, Y. C., 1999, ''An Efficient Identifi- cation Method for Joint Parameters in Mechanical Structures,'' ASME J. Vibr. Acoust., 121, No. 3, pp. 363-372.
- ͓18͔ Kim, T. R., Wu, S. M., and Ehmann, K. F., 1989, ''Identification of Joint Parameters for a Taper Joint,'' ASME J. Eng. Ind., 111, pp. 282-287.
- ͓19͔ Jorgensen, B. R., and Shin, Y. C., 1997, ''Dynamics of Machine Tool Spindle/ Bearing Systems Under Thermal Growth,'' ASME J. Tribol., 119, No. 4, pp. 875-882.
- Jorgensen, B. R., and Shin, Y. C., 1998, ''Dynamics of Spindle-Bearing Sys- tems at High Speeds Including Cutting Load,'' ASME J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 120, No. 2, pp. 387-394.
- References ͓1͔ Chapman, P. D., 1985, ''A Capacitive based Ultraprecision Spindle Error Analyser,'' J. Prec. Eng., 7, No. 3, July, pp. 129-137.
- Salazar, A. O., Dunford, W., Stephan, R., and Watanabe, E., 1990, ''A Mag- netic Bearing System Using Capacitive Sensors for Position Measurement,'' IEEE Trans. Magn., 26, No. 5, pp. 2541-2543.
- ͓3͔ Chang I. B., 1994, ''A Study on the Performance Improvement of a Magnetic Bearing System Using Built-in Capacitive Type Transducers,'' Ph.D. thesis, Seoul National University, Korea.
- Chung, S. C., 1996, ''A Study on the Dynamic Characteristics and Control Performance Improvements of an Active Magnetic Bearing System for the High Speed Spindle,'' Ph.D. thesis, Seoul National University, Korea.
- Mitsui, K., 1982, ''Development of a New Measuring Method for Spindle Rotation Accuracy by Three-Points Method,'' Proceedings of the 23rd Inter- national MTDR, pp. 115-121.
- ͓6͔ Gao, W., Kiyono, S., and Sugawara, T., 1997, ''Roundness Measurement by New Error Separation Method,'' J. Prec. Eng., 21, pp. 123-132.
- ͓7͔ Jay, F. Tu, Bernd, Bossmanns, and Spring, C. C. Hung, 1997, ''Modeling and Error Analysis for Assessing Spindle Radial Error Motions,'' J. Prec. Eng., 21, pp. 90-101.
- ͓8͔ Hammond, Jr., J. L., and Glidewell, S. R., 1983, ''Design of Algorithms to Extract Data from Capacitance Sensors to Measure Fastener Hole Profiles,'' IEEE Trans Instrum. Meas., 32, pp. 343-349.
- ͓9͔ Ahn, H. J., Lee, S. H., and Han, D. C., 1999, ''Precision AMB Spindles with Cylindrical Capacitive Sensors,'' Proceedings of 10th World Congress on TMM(IFToMM), 5, pp. 2043-2048, Oulu, Finland, June 20-24.
- References ͓1͔ Bennett, S., 1991, ''Ship Stabilization: History,'' Concise Encyclopedia of Traffic and Transportation Systems, M. Papageorgiou, ed., Pergamon, New York, NY, pp. 454-459.
- Lewis, E. V., 1989, Principles of Naval Architecture, 2nd ed., SNAME, NJ.
- ͓3͔ Chadwick, J. H., 1955, ''On the Stabilization of Roll,'' SNAME Trans., 63, pp. 234-280.
- Fortuna, L., and Muscato, G., 1996, ''A Roll Stabilization System for a Mono- hull Ship: Modeling, Identification, and Adaptive Control,'' IEEE Trans. Con- trol Systems Technol., 4, pp. 18-28.
- Fossen, T. I., 1995, Guidance and Control of Ocean Vehicles, Wiley, New York, NY.
- van Amerongen, J., 1991, ''Ship rudder roll stabilization,'' Concise Encyclo- pedia of Traffic and Transportation Systems, M. Papageorgiou, ed., Pergamon, New York, NY, pp. 448-454.
- ͓7͔ Chen, Shyh-Leh, 1996, Modeling, Dynamics and Control of Large Amplitude Motions of Vessels in Beam Seas, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI.
- Hsieh, S. R., Shaw, S. W., and Troesch, A. W., 1994, ''A Nonlinear Probabi- listic Method for Predicting Vessel Capsizing in Random Beam Seas,'' Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 446, pp. 195-211.
- ͓9͔ Khalil, Hassan K., 1996, Nonlinear Systems, 2nd ed., Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
- ͓10͔ Chen, Shyh-Leh, Shaw, Steven, W., and Troesch, Armin W., 1999, ''A Sys- tematic Approach to Modeling Nonlinear Multi-DOF Ship Motions in Regular Seas,'' J. Ship Res., 43, pp. 25-37.
- ͓11͔ Kokotovic, Petar V., Khalil, Hassan K., and O'Reilly, J., 1986, Singular Per- turbations Methods in Control: Analysis and Design, Academic, New York, NY.
- Kristic, M., Kanellakopoulos, I., and Kokotovic, P., 1995, Nonlinear and Adaptive Control Design, Wiley-Interscience, New York, NY. References ͓1͔ Petek, N. K., 1992, ''An Electronically Controlled Shock Absorber Using Electro-Rheological Fluid,'' SAE Technical Paper Series 920275.
- Petek, N. K., Romstadt, D. J., Lizell, M. B., and Weyenberg, T. R., 1995, ''Demonstration of an Automotive Semi-Active Suspension Using Elec- trorheological Fluid,'' SAE Technical Paper Series 950586.
- Lou, Z., Ervin, R. D., and Filisko, F. E., 1994, ''A Preliminary Parametric Study of Electrorheological Dampers,'' ASME J. Fluids Eng., 116, pp. 570- 576.
- Sturk, M., Wu, X. M., and Jung, J. Y., 1995, ''Development and Evaluation of a High Voltage Supply Unit for Electrorheological Fluid Dampers,'' Vehicle Syst. Dyn., 24, pp. 101-121.
- ͓5͔ Nakano, M., 1995, ''A Novel Semi-Active Control of Automotive Suspension Using an Electrorheological Shock Absorber,'' Proceedings of the 5th Inter- national Conference on ER Fluid, MR Suspensions and Associated Technol- ogy, Sheffield, pp. 645-653.
- ͓6͔ Gordaninejad, F., Ray, A., and Wang, H., 1997, ''Control of Forced Vibration Using Multi-Electrode Electro-Rheological Fluid Dampers,'' ASME J. Vibr. Acoust., 119, pp. 527-531.
- ͓7͔ Bayer Provisional Product Information: Rheobay TP AI 3565 and Rheobay TP AI 3566, Bayer, 1997.
- Jordan, T. C., and Shaw, M. T., 1989, ''Electrorheology,'' IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul., 24, No. 5, pp. 849-878.
- ͓9͔ Karnopp, D. C., Margolis, D. L., and Rosenberg, R. C., 1991, System Dynam- ics: A Unified Approach, Wiley, New York.
- ͓10͔ Leitmann, G., 1981, ''On the Efficacy of Nonlinear Control in Uncertain Lin- ear Systems,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 102, pp. 95-102.
- ͓11͔ Hui, S., and Zak, S. H., 1992, ''Robust Control Synthesis for Uncertain/Nonlinear Dynamical Systems,'' Automatica, , 28, No. 2, pp. 289- 298. ͓12͔ Choi, S. B., Park, D. W., and Jayasuriya, S., 1994, ''A Time-Varying Sliding Surface for Fast and Robust Tracking Control of Second-Order Uncertain Sys- tems,'' Automatica, 30, No. 5, pp. 899-904.
- ͓13͔ Leitmann, G., 1994, ''Semiactive Control for Vibration Attenuation,'' J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct., 5, No. 5, pp. 841-846.
- ͓14͔ Nigam, N. C., and Narayanan, S., 1994, Applications of Random Vibrations, Springer-Verlag, New York.
- References ͓1͔ Elrod, A. C., and Nelson, M. T., 1986, ''Development of a Variable Valve Timing Engine to Eliminate the Pumping Losses Associated with Throttled Operation,'' SAE Paper No. 860537.
- Gray, C., 1988, ''A Review of Variable Engine Valve Timing,'' SAE Paper No. 880386.
- Ma, T. H., 1986, 1996, ''Recent Advances in Variable Valve Timing,'' Alter- native and Advanced Automotive Engines, Plenum Press, New York.
- ͓4͔ Schecter, M. M., and Levin, M. B., 1996, ''Camless engine,'' SAE Paper No. 960581.
- Meacham, G.-B., 1970, ''Variable Cam Timing as an Emission Control Tool,'' SAE Paper No. 700645.
- Moriya, Y., Watanabe, A., Uda, H., Kawamura, H., Yoshioka, M., and Adachi, M. 1996, ''A Newly Developed Intelligent Valve Timing System- Continuously Controlled Cam Phasing as Applied to A New 3 Liter Inline 6 Engine,'' SAE Paper No. 960579.
- Anderson, M., Tsao, T.-C., and Levin, M., 1998, ''Adaptive Lift Control for a Camless Electrohydraulic Valvetrain,'' SAE Paper No. 981029.
- Kim, D., Anderson, M., Tsao, T.-C., and Levin, M. 1997, ''A Dynamic Model of a Springless Electrohydraulic Camless Valvetrain System,'' SAE Paper No. 970248.
- Ahmad, T., and Theobald, M. A., 1989, ''A Survey of Variable Valve Actua- tion Technology,'' SAE Paper No. 891674.
- Sono, H., and Umiyama, H. 1994, ''A Study of Combustion Stability of Non- Throttling Sl Engine with Early Intake Valve Closing Mechanism,'' SAE Pa- per No. 945009.
- Ashhab, M. S., Stefanopoulou, A. G., Cook, J. A., and Levin, M., ''Camless Engine Control for Robust Unthrottled Operation,'' SAE Paper No. 981031.
- Urata, Y., Umiyama, H., Shimizu, K., Fujiyoshi, Y., Sono, H., and Fukuo, K., ''A Study of Vehicle Equipped with Non-Throttling SI Engine with Early Intake Valve Closing,'' SAE Paper No. 930820.
- Moraal, P. E., Cook, J. A., and Grizzle, J. W., 1995, ''Modeling the Induction Process of an Automobile Engine,'' Control Problems in Industry, I. Lasiecka and B. Morton, ed., Birkhauser, Basel, pp. 253-270.
- ͓14͔ Powell, B. K., and Cook, J. A. 1987, ''Nonlinear Low Frequency Phenomeno- logical Engine Modeling and Analysis,'' Proc. 1987 Amer. Contr. Conf. 1, pp. 332-340, June.
- Heywood, J. B., 1988, Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals, McGraw- Hill, New York, NY.
- Broome, D., 1969, ''Induction Ram: Part I, II, III,'' Automobile Engineer, Apr., May, June.
- Ohata, A., and Ishida, Y., 1982, ''Dynamic Inlet Pressure and Volumetric Efficiency of Four Cylinder Engine,'' SAE Paper No. 820407.
- Novak, J. M., 1977, ''Simulation of the Breathing Process and Air-Fuel Ratio Distribution Characteristics of Three-Valve, Stratified Charge Engines,'' SAE Paper No. 770881.
- Shampine, L. F., and Gear, C. W., 1979, ''A User's View of Solving Stiff Differential Equations,'' SIAM Rev., 21, No. 1, pp. 1-17.
- Miller, R. H., Davis, G. C., Newman, C. E., and Levin, M. B., 1997, ''Un- throttled Camless Valvetrain Strategy for Spark-Ignited Engines,'' Proc. ASME ICE 29-1, pp. 81-94.
- References ͓1͔ Ashhab, M. S., Stefanopoulou, A. G., Cook, J. A., and Levin, M., 1998, ''Camless Engine Control for Robust Unthrottled Operation,'' SAE Paper No. 981031.
- Urata, Y., Umiyama, H., Shimizu, K., Fujiyoshi, Y., Sono, H., and Fukuo, K., 1993, ''A Study of Vehicle Equipped with Non-Throttling SI Engine with Early Intake Valve Closing,'' SAE Paper No. 930820.
- Vogel, O., Rousssopoulos, K., Guzzella, L., and Czekai, J., 1996, ''An Initial Study of Variable Valve Timing Implemented with a Secondary Valve in the Intake Runner,'' SAE Paper No. 960590.
- Schecter, M. M., and Levin, M. B., 1996, ''Camless Engine,'' SAE Paper No. 960581.
- Astrom, K., and Wittenmark, B., 1989, Adaptive Control, Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA.
- Fig. 12 Cylinder balancing in the cylinder overlap case Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control MARCH 2000, Vol. 122 Õ 139
- References ͓1͔ Moore, F. K., and Greitzer, E. M., 1986, ''A Theory of Post-Stall Transients in Axial Compression Systems-Part I: Development of Equations,'' ASME J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power, 108, pp. 68-76.
- ͓2͔ Liaw, D.-C., and Abed, E. H., 1996, ''Active Control of Compressor Stall Inception: A Bifurcation-Theoretic Approach,'' Automatica, 32, pp. 109-115, also in Proceedings of the IFAC Nonlinear Control Systems Design Sympo- sium.
- Badmus, O. O., Chowdhury, S., Eveker, K. M., Nett, C. N., and Rivera, C. J., 1993, ''A Simplified Approach for Control of Rotating Stall, Parts I and II,'' Proceedings of the 29th Joint Propulsion Conference, AIAA papers 93-2229 & 93-2234.
- ͓4͔ Eveker, K. M., Gysling, D. L., Nett, C. N., and Sharma, O. P., 1995, ''Inte- grated Control of Rotating Stall and Surge in Aeroengines,'' 1995 SPIE Con- ference on Sensing, Actuation, and Control in Aeropropulsion.
- Krstic ´, M., Fontaine, D., Kokotovic ´, P. V., and Paduano, J. D., 1998, ''Useful Nonlinearities and Global Bifurcation Control of Jet Engine Surge and Stall,'' IEEE Trans Automatic Control, 43, pp. 1739-1745.
- ͓6͔ Mansoux, C. A., Setiawan, J. D., Gysling, D. L., and Paduano, J. D., 1994, ''Distributed Nonlinear Modeling and Stability Analysis of Axial Compressor Stall and Surge,'' 1994 American Control Conference.
- Behnken, R. L., D'Andrea, R., and Murray, R. M., 1995, ''Control of Rotating Stall in a Low-speed Axial Flow Compressor Using Pulsed Air Injection: Modeling, Simulations, and Experimental Validation,'' Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 3056-3061.
- ͓8͔ Jankovic, M., 1995, ''Stability Analysis and Control of Compressors with Noncubic Characteristic,'' PRET Working Paper B95-5-24.
- ͓9͔ Sepulchre, R., and Kokotovic ´, P. V., 1998, ''Shapes Signifiers for Control of Surge and Stall in Jet Engines,'' IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 43, pp. 1643-1648.
- ͓10͔ McCaughan, F. E., 1990, ''Bifurcation Analysis of Axial Flow Compressor Stability,'' SIAM ͑Soc. Ind. Appl. Math.͒ J. Appl. Math., 20, pp. 1232-1253.
- ͓11͔ Wang, H.-H., Krstic ´, M., and Larsen, M., 1997, ''Control of Deep-Hysteresis Aeroengine Compressors-Part I: A Moore-Greitzer Type Model,'' Proc. 1997 American Control Conference, pp. 1003-1007.
- ͓12͔ Meyers, M. R., Gysling, D. L., and Eveker, K. M., 1995, ''Benchmark for Control Design: Moore-Greitzer Model,'' PRET Working Paper, UTRC95-9- 18.
- Khalil, H. K., 1996, Nonlinear Systems, Second Edition, Prentice Hall, Engle- wood Cliffs, NJ.
- ͓14͔ Krener, A. J., 1995, ''The Feedbacks Which Soften the Primary Bifurcation of MG3,'' PRET Working Paper B95-9-11.
- ͓15͔ Badmus, O. O., Nett, C. N., and Schork, F. J., 1991, ''An Integrated, Full- Range Surge Control/Rotating Stall Avoidance Compressor Control System,'' Proceedings of the 1991 American Control Conference, pp. 3173-3180.
- ͓16͔ Simon, J. S., Valavani, L., Epstein, A. H., and Greitzer, E. M., 1993, ''Evalu- ation of approaches to active compressor surge stabilization,'' ASME J. Tur- bomachinery, 115, pp. 57-67.
- References ͓1͔ Stecki, J., and Davis, D., 1986, ''Fluid Transmission Lines-Distributed Param- eter Models, Part 1: A Review of the State of the Art,'' Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part A, 200, pp. 215-228.
- ͓2͔ Stecki, J., and Davis, D., 1986, ''Fluid Transmission Lines-Distributed Param- eter Models, Part 2: Comparison of Models,'' Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part A, 200, pp. 229-236.
- ͓3͔ Wylie, E., Streeter, V., and Suo, L., 1993, Fluid Transients in Systems, Prentice-Hall.
- Hsue, C., and Hullender, D., 1983, ''Modal Approximations for the Fluid Dynamics of Hydraulic and Pneumatic Transmission Lines,'' Fluid Transmis- sion Line Dynamics, M. Franke and T. Drzewiecki, eds. ASME, pp. 51-77.
- ͓5͔ Hullender, D., Woods, R., and Hsu, C., 1983, ''Time Domain Simulation of Fluid Transmission Lines using Minimum Order State Variable Models,'' Fluid Transmission Line Dynamics, M. Franke and T. Drzewiecki, eds., ASME, pp. 78-97.
- ͓6͔ Watton, J., and Tadmori, M., 1988, ''A Comparison of Techniques for the Analysis of Transmission Line Dynamics in Electrohydraulic Control Sys- tems,'' Appl. Math. Modelling, 12, pp. 457-466.
- ͓7͔ Piche ´, R., and Ellman, A., 1995, ''A Fluid Transmission Line Model for Use with ODE Simulators,'' The Eighth Bath International Fluid Power Work- shop.
- Brown, F., 1962, ''The Transient Response of Fluid Lines,'' ASME J. Basic Eng., 84, pp. 547-553.
- D'Souza, A., and Oldenberger, R., 1964, ''Dynamic Response of Fluid Lines,'' ASME J. Basic Eng., 86, pp. 589-598.
- ͓10͔ Goodson, R., and Leonard, R., 1972, ''A Survey of Modeling Techniques for Fluid Line Transients,'' ASME J. Basic Eng., 94, pp. 474-482.
- ͓11͔ Reddy, J., 1987, Applied Functional Analysis and Variational Methods in En- gineering, McGraw-Hill.
- Trikha, A., 1975, ''An Efficient Method for Simulating Frequency Dependent Friction in Transient Liquid Flow,'' ASME J. Basic Eng., 97, pp. 97-105.
- ͓13͔ Taylor, S., Johnston, D., and Longmore, D., 1997, ''Modelling of Transient Flow in Hydraulic Pipelines,'' Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part I, 211, pp. 447- 456.
- Woods, R., 1983, ''A First-Order Square-Root Approximation for Fluid Trans- mission Lines,'' Fluid Transmission Line Dynamics, M. Franke and T. Drze- wiecki, eds., ASME, pp. 37-49.
- ͓15͔ Yang, W., and Tobler, W., 1991, ''Dissipative Modal Approximation of Fluid Transmission Lines Using Linear Friction Model,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 113, pp. 152-162.
- ͓16͔ Lanczos, C., 1956, Applied Analysis, Prentice Hall.
- Harris, F., 1978, ''On the Use of Windows for Harmonic Analysis with the Discrete Fourier Transform,'' Proc. IEEE, 66, pp. 51-83.
- ͓18͔ Piche ´, R., and Ellman, A., 1994, ''Numerical Integration of Fluid Power Cir- cuit Models using Semi-Implicit Two-Stage Runge-Kutta Methods,'' Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part C: J. Mech. Eng. Sci., 208, pp. 167-175.
- Ellman, A., and Piche ´, R., 1996, ''A Modified Orifice Flow Formula for Nu- merical Simulation,'' 1996 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Con- gress and Exposition, Atlanta, GA.
- Holmboe, E., and Rouleau, W., 1967, ''The Effect of Viscous Shear on Tran- sients in Liquid Lines,'' ASME J. Basic Eng., 89, pp. 174-180.
- ͓21͔ Gottlieb, D., and Orszag, S., 1977, Numerical Analysis of Spectral Methods, Vol. 26, SIAM, Philadelphia.
- ͓22͔ Ma ¨kinen, J., et al., 1997, ''Dynamic Simulations of Flexible Hydraulic-Driven Multibody Systems using Finite Strain Theory,'' Fifth Scandinavian Interna- tional Conference on Fluid Power, Linko ¨ping. References ͓1͔ Kuz ´niewski, B., 1994, Dynamics and Principles of Designing Piston Pneu- matic Units Generating Periodic Signals, WSM, Studia Nr 19, Szczecin ͑in Polish͒.
- ͓2͔ Kuz ´niewski, B., 1995, ''Nonlinearity Compensation in a Pneumatic Vibration Generator With a Dual Chamber for the Variable Component'' Mechanical System and Signal Processing, 9, No. 4, pp. 439-443, Academic Press, Lon- don. References ͓1͔ Gurney, J. O., 1984, ''Photofluidic Interface,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 106, pp. 90-97.
- ͓2͔ Hockaday, B. D., and Waters, J. P., 1990, ''Direct Optical-to-Mechanical Ac- tuation,'' Appl. Opt., 29, No. 31. pp. 4629-4632.
- ͓3͔ Hu, F. Q., Watson, J. M., Page, M., and Payne, P. A., 1990, ''A High Speed Optopneumatic Digital Actuator,'' Appl. Optics Optoelectron., Sept., pp. 97- 98.
- Bramley, H. C., Hu, F. Q., and Walton, J. M., 1993, ''Optical Control of a Pneumatic Actuator,'' EUROϩPEAN. J. Fluid Power, March, pp. 16-19.
- Nakada T., Morikawa M., and Cao Dong-Hiu, 1994, ''Study on Opto- Pneumatic Control System,'' 11th Aachener International Colloquium, pp. 255-260.
- ͓6͔ Drzewiecki, M., Tada, K., and Gurney, J., 1985, ''Photofluidic Interface,'' USA Patent N.4.512.371.
- ͓7͔ Viktorov, V. V., 1990, ''An Optofluidic Converter,'' Transaction of the All- Union Conference Pneumohydroautomatic and Hydraulic Power, Suzdal, USSR ͑Russian͒.
- Yamamoto, K., 1991, ''Characteristic of an Optofluidic Converter Utilizing Photoacoustic Effect,'' Trans. Soc. Instrum. Control Engineers, 27, No. 12, pp. 1406-1411.
- Eula, G., Viktorov, V., and Ivanov, A., 1996, ''Valutazione della conduttanza in una cella fotoacustica,'' Oleodinamica-Pneumatica, Tecniche Nuove editor, No. 12, pp. 82-88.
- ͓10͔ Kutatekadze, S. S., and Borishanskii, V. M., 1966, A Concise Encyclopedia of Heat Transfer, Pergamon Press, New York.
- References ͓1͔ Miller, R. W., 1989, Flow Measurement Engineering Handbook, 2nd edition, McGraw-Hill, New York.
- Scott, R. W. W., 1982, Development in Flow Measurement, Applied Science, London.
- ͓3͔ ISO Standard 5024, 1981, Petroleum Liquids and Gases-Measurement- Standard Reference Conditions, ISO, Geneva.
- ͓4͔ ISO/DP 8959/2, 1986, Measurement of Gas Flow-Rate Volumetric Method, part 2, Bell Provers, ISO Standard, Doc. 442E, ISO TC30, Geneva.
- Otis, D. R., 1970, ''Thermal Damping in Gas-Filled Composite Materials Dur- ing Impact Loading,'' ASME J. Appl. Mech., 37, pp. 38-44.
- Kagawa, T. and Shimizu, M. 1988, ''Heat Transfer Effect on the Dynamic of Pneumatic RC Circuit,'' 2nd International Symposium on Fluid Control Mea- surement and Visualization.
- Pourmovahed, A., and Otis, D. R., 1984, ''Effects of Thermal Damping on the Dynamic Response of a Hydraulic Loading,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 106, pp. 21-26.
- Kagawa, T., 1985, ''Heat Transfer Effects on the Frequency Response of a Pneumatic Nozzle Flapper,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 107, pp. 332-336.
- References ͓1͔ Hori, N., Pannala, A. S., Ukrainetz, P. R., and Nikiforuk, P. N., 1989, ''Design of an Electrohydraulic Positioning System Using a Novel Model Reference Control Scheme,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 111, pp. 294-295.
- ͓2͔ Lee, S. R., and Srinivasan, K., 1990, ''Self-Tuning Control Application to Closed-Loop Servohydraulic Material Testing,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 112, pp. 682-683.
- ͓3͔ Thayer, W. J., 1958, ''Transfer Functions for Moog Servovalves,'' Moog Technical Bulletin 103, East Aurora, Moog Inc., Controls Division, New York.
- ͓4͔ Akers, A., and Lin, S. J., 1988, ''Optimal Control Theory Applied to a Pump with Single-Stage Electrohydraulic Servovalve,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 110, p. 121.
- Shichang, Z., Xingmin, C., and Yuwan, C., 1991, ''Optimal Control of Speed Conversion of a Valve Controlled Cylinder System,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 113, p. 693.
- Merritt, H. E., 1967, Hydraulic Control Systems, Wiley, New York, pp. 147- 150 and 312-318.
- ͓7͔ Watton, J., 1989, Fluid Power Systems: Modeling, Simulation, Analog and Microcomputer Control, Prentice Hall, New York, pp. 43-60 and 100-110.
- ͓8͔ Lin, S. J., and Akers, A., 1989, ''A Dynamic Model of the Flapper-Nozzle Component of an Electrohydraulic Servovalve,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 111, pp. 105-109.
- ͓9͔ Kim, D. H., and Tsao, Tsu-Chin, 1997, ''An Improved Linearized Model for Electrohydraulic Servovalves and its Usage for Robust Performance Control 186 Õ Vol. 122, MARCH 2000 Transactions of the ASME System Design,'' Proceedings of the American Control Conference, pp. 3807- 3808.
- Tsao, T.-C., Hanson, R. D., Sun, Z., and Babinski, A., 1998, ''Motion Control of Non-Circular Turning Process for Camshaft Machining,'' Proceedings of the Japan-U.S.A. Symposium on Flexible Automation, Otsu, Japan, pp. 485- 489.
- Zames, G., and Francis, B. A., 1984, ''On H ϱ Optimal Sensitivity Theory for SISO Feedback Systems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., AC-29, No. 4, pp. 11-13.
- Francis, B. A., 1987, A Course in H ϱ Control Theory, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 15-22 and 75-83.
- ͓13͔ Glover, K., and Doyle, J., 1988, ''State-Space Formulae for All Stabilizing Controllers That Satisfy an H ϱ Norm Bound and Relations to Risk Sensitiv- ity,'' Syst. Control Lett., 11, pp. 167-172.
- ͓14͔ Doyle, J. C., Glover, K., Khargonekar, P. P., and Francis, B. A., 1989, ''State- Space Solutions to Standard H 2 and H ϱ Control Problems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., AC-34, No. 8, pp. 831-847.
- ͓15͔ Kwakernaak, H., 1985, ''Minimax Frequency Domain Performance and Ro- bustness Optimization of Linear Feedback Systems,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., AC-30, No. 10, pp. 994-1004.
- ͓16͔ McCloy, D., and Martin, H. R., 1973, Control of Fluid Power, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, pp. 120-125, 180-185.
- ͓17͔ Smith, J. O., 1983, ''Techniques for Digital Filter Design and System Identi- fication with Application to the Violin,'' Ph.D. dissertation, Electrical Engi- neering Dept., Stanford University, p. 50.
- Chen, M. J., and Desoer, C. A., 1982, ''Necessary and Sufficient Condition for Robust Stability of Linear Distributed Feedback Systems,'' Int. J. Control, 35, pp. 255-267.
- ͓19͔ Doyle, J., Francis, B., and Tannenbaum, A., 1992, Feedback Control Theory, MacMillan Publishing Company, New York, pp. 88-91.
- ͓20͔ Balas, G., Doyle, J. C., Glover, K., Packard, A., and Smith, R., 1991, -Analysis and Synthesis Toolbox, The MathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA.
- Kim, D. H., and Tsao, Tsu-Chin 1997, ''Robust Performance Control of Elec- trohydraulic Actuators for Camshaft Machining,'' ASME publication FPST- Vol. 4/DSC-Vol. 63, Fluid Power Systems and Technology: Collected Papers. References ͓1͔ Francis, B. A., and Wonham, W. M., 1976, ''The Internal Model Principle of Control Theory,'' Automatica, 12, No. 5, pp. 457-465.
- ͓2͔ Hara, S., Yamamoto, Y., Omata, T., and Nakano, M., 1988, ''Repetitive Con- trol Systems: A New Type Servo System for Periodic Exogenous Signals,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., AC-31, No. 2, pp. 127-133.
- ͓3͔ Tomizuka, M., Tsao, T-C., and Chew, K. K., 1989, ''Analysis and Synthesis of Discrete-Time Repetitive Controllers,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Con- trol, 111, pp. 353-358.
- ͓4͔ Tsao, T-C., Tomizuka, M., 1988, ''Adaptive and Repetitive Digital Control Algorithms for Noncircular Machining,'' Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Atlanta, GA, pp. 115-120.
- ͓5͔ Tsao, T-C., and Tomizuka, M., 1994, ''Robust Adaptive and Repetitive Digital Control and Application to Hydraulic Servo for Noncircular Machining,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 116, pp. 24-32.
- ͓6͔ Kim, D. H., and Tsao, Tsu-Chin, 1997, ''An Improved Linearized Model for Electrohydraulic Servovalves and its Usage for Robust Performance Control System Design,'' Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Albuquer- que, NM, pp. 3807-3808.
- ͓7͔ Kim, D. H., and Tsao, Tsu-Chin, 1997, ''Robust Performance Control of Elec- trohydraulic Actuators for Camshaft Machining,'' ASME publication FPST- Vol. 4/DSC-Vol. 63, Fluid Power Systems and Technology: Collected Papers.
- Finney, J. M., de Pennington, A., Bloor, M. S., and Gill, G. S., 1985, ''A Pole-Assignment Controller for an Electro-hydraulic Cylinder Drive,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 107, pp. 145-150.
- ͓9͔ Bobrow, J. E., and Lum, K., 1996, ''Adaptive, High Bandwidth Control of a Hydraulic Actuator,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 118, pp. 714-720.
- ͓10͔ Plummer, A. R., and Vaughan, N. D., 1996, ''Robust Adaptive Control for Hydraulic Servosystems,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 118, pp. 237- 244.
- Elliott, H., and Goodwin, G. C., 1984, ''Adaptive Implementation of the In- ternal Model Principle,'' Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE Conference on Deci- sion and Control, pp. 1292-1297.
- ͓12͔ Palaniswami, M., and Goodwin, G. C., 1987, ''An Adaptive Implementation of the Internal Model Principle,'' Proceedings of the 7th American Control Conference, Minneapolis, MN, pp. 600-605.
- ͓13͔ Palaniswami, M., and Goodwin, G. C., 1988, ''Disturbance Rejection in Adap- 194 Õ Vol. 122, MARCH 2000 Transactions of the ASME tive Control of Industrial Process,'' Proceedings of the 14th IEEE Industrial Electronics Society Conference, Singapore, pp. 290-296.
- ͓14͔ Feng, G., and Palaniwami, 1990, ''An Stable Adaptive Implementation of Internal Model Principle,'' Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Conference on De- cision and Control, Honolulu, HI, pp. 3241-3246.
- ͓15͔ Middleton, R. H., Goodwin, G. C., Hill, D. J., and Mayne, D. Q., 1988, ''Design Issues in Adaptive Control,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., 33, No. 1, pp. 50-58.
- ͓16͔ Kreisselmeier, G., and Anderson, B. D. O., 1986, ''Robust Model Reference Adaptive Control,'' IEEE Trans. Autom. Control., AC-31, No. 2, pp. 127- 133. ͓17͔ Goodwin, G. C., and Sin, K. S., 1984, Adaptive Filtering Prediction and Control, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
- ͓18͔ Leal, L. R., and Ortega, R., 1987, ''Reformulation of the Parameter Identifi- cation Problem for System with Bounded Disturbances,'' Automatica, 23, No. 2, pp. 247-251.
- ͓19͔ Goodwin, G. C., Leal, L. R., Mayne, D. Q., and Middleton, R. H., 1986, ''Rapprochement Between Continuous and Discrete Model Reference Adap- tive Control,'' Automatica, 22, No. 2, pp. 199-208.
- ͓20͔ Desoer, C. A., 1970, ''Slowly Varying Discrete System x iϩ1 ϭA i x i ,'' Elec- tron. Lett., 6, No. 11, pp. 339-340.
- ͓21͔ Tsao, T-C., and Tomizuaka, M., 1987, ''Adaptive Zero Phase Error Tracking Algorithm for Digital Control,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 109, pp. 349-454.
- References ͓1͔ Burrows, C. R., 1972, Fluid Power Servomechanisms, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York.
- ͓2͔ Murrenhoff, H., and Versteegen, C., 1984, ''Einsatzbeispiele Motor Geregelter Antriebe mit der Mo ¨glichkeit der Energieru ¨ckgewinnung,'' O ¨lhydraulik und Pneumatik, 28, No. 7, pp. 427-434.
- Weishaupt, E., and Backe, W., 1993, ''Secondary Speed and Position Con- trolled Units with Adapation for Pressure and Inertia Load,'' presented at the Third Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power.
- Kim, C. S., and Lee, C. O., 1996, ''Speed Control of an Overcentered Variable-Displacement Hydraulic Motor with a Load-Torque Observer,'' Con- trol Engineering Practice, 4, No. 11, pp. 1563-1570.
- ͓5͔ Meditch, J. S., and Hostetter, G. H., 1974, ''Observers for Systems with Un- known and Inaccessible Inputs,'' Int. J. Control, 19, No. 3, pp. 473-480.
- ͓6͔ Gopinath, B., 1971, ''On the Control of Linear Multiple Input-Output Sys- tems,'' Bell Syst. Tech. J., 50, No. 3, pp. 1063-1081.
- ͓7͔ Merritt, H. E., 1967, Hydraulic Control Systems, Wiley, New York, NY, pp. 273-280.
- References ͓1͔ Watton, J., 1988, Fluid Power Systems, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
- ͓2͔ Lin, S. J., and Akers, A., 1989, ''A Dynamic Model of the Flapper-Nozzle Component of an Electrohydraulic Servo Valve,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 111, pp. 105-109.
- ͓3͔ Bullough, W. A., 1991, ''Liquid State Force and Displacement Devices,'' Mechatronics, 1, No. 1, pp. 1-10.
- ͓4͔ Petek, N. K., Rimstadt, D. J., Lizal, M. B., and Weyenberg, T. R., 1995, ''Demonstration of an Automotive Semi-Active Suspension Using Elec- trorheological Fluid,'' SAE paper, No. 950586.
- Morishita, S., and Mitsui, J., 1992, ''An Electronically Controlled Engine Mount Using Electro-Rheological Fluid,'' SAE Paper, No. 922290.
- Choi, S. B., Cheong, C. C., and Kim, G. W., 1997, ''Feedback Control of Tension in a Moving Tape Using an ER Brake Actuator,'' Mechatronics, 7, No. 1, pp. 53-66.
- ͓7͔ Choi, S. B., Cheong, C. C., and Park, Y. K., 1996, ''Active Vibration Control of Intelligent Composite Laminate Structures Incorporating an Electro- Rheological Fluid,'' J. Intell. Mat. Syst. Struct., 7, pp. 411-419.
- ͓8͔ Simmonds, A. J., 1991, ''Electro-Rheological Valves in a Hydraulic Circuit,'' IEE Proceeding-D, 138, No. 4, pp. 400-404.
- ͓9͔ Brooks, D. A., 1992, ''Design and Development of Flow Based Electro- Rheological Devices,'' J. Mod. Phys. B., 6, pp. 2705-2730.
- ͓10͔ Nakano, M., and Yonekawa, T., 1994, ''Pressure Response of ER Fluid in a Piston Cylinder-ER Valve System,'' Proceedings of the 4th International Con- ference on Electrorheological Fluids, pp. 477-489.
- ͓11͔ Whittle, M., Firoozian, R., and Bullough, W. A., 1994, ''Decomposition of the Pressure in an ER Valve Control System,'' J. Intell. Mat. Syst. Struct., 5, No. 1, pp. 105-111.
- Adriani, P. M., and Gast, A. P., 1988, ''A Microscopic Model of Electrorhe- ology,'' Phys. Fluids, 31, No. 10, pp. 2757-2768.
- ͓13͔ Miyamoto, H., Kawato, M., Setoyama, T., and Suzuki, R., 1988, ''Feedback- Error-Learning Neural Network for Trajectory Control of a Robotic Manipu- lator,'' Neural Networks, 11, pp. 251-265.
- ͓14͔ Venugopal, K. P., and Smith, S. M., 1993, ''A Feedback Scheme for Improv- ing Dynamic Response of Neuro-Controllers,'' Proceedings of the American Control Conference, pp. 84-88.
- ͓15͔ Tarng, Y. S., Hwang, S. T., and Wang, Y. S., 1994, ''A Neural Network Controller for Constant Turning Force,'' Int. J. Machine Tools Manufact., 34, No. 4, pp. 453-460.
- References ͓1͔ Ehsan, Md., Rampen, W. H. S, and Salter, S. H, 1996, ''Computer Simulation of the Performance of Digital-Displacement Pump-Motors'' ASME Interna- tional Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, FPST 3, pp. 19-24, Atlanta, Nov. 1996.
- Rampen, W. H. S., Salter, S. H., and Fussey, A., ''Constant Pressure Control of the Digital Displacement Pump,'' 4th Bath Intn'l Fluid Power Workshop, Fluid Power Systems and Modelling, Bath, Sept. 1991, RSP, pp. 45-62.
- ͓3͔ Rampen, W. H. S., and Salter, S. H., ''The Digital Displacement Hydraulic Piston Pump,'' Proc. 9th International Symposium on Fluid Power, BHR Group, Cambridge, April 1990, STI, pp. 33-46.
- ͓4͔ Rampen, W. H. S, Almond, J. P., and Salter, S. H, ''The Digital Displacement Pump/Motor Operating Cycle: Experimental Results Demonstrating the Fun- damental Characteristics,'' 7th International Fluid Power Workshop, Bath, 1994, pp. 321-331.
- ͓5͔ Salter, S. H., and Rampen, W. H. S., ''The Wedding Cake Multi-Eccentric Radial Piston Hydraulic Machine with Direct Computer Control of Displace- ment,'' Proc. 10th International Conference on Fluid Power, BHR Group, Brugge, April 1993, MEP, pp. 47-64.
- Post W. J. A. M., and Burgt, J. A. H. V, ''Energy saving and system optimi- zation in cyclic loaded hydraulic power transmissions,'' 7th International Fluid Power Workshop, Bath, 1994.
- Ehsan, Md., Rampen, W. H. S., and Taylor, J. R. M, 1995, ''Simulation and Dynamic Response of Computer Controlled Digital Hydraulic Pump/Motor System Used in Wave Energy Power Conversion,'' 2nd European Wave Power Conference, pp. 305-311, Lisbon, 8-10 Nov. 1995.
- Akers, A., and Lin, S. J., 1987, ''Dynamic Analysis of an Axial Piston Pump with a Two-Stage Controller and Swash-Plate Position Feedback,'' Proceed- ings of the 8th International Symposium of Fluid Power, BHRA, Birmingham, 1987, pp. 547-564.
- ͓9͔ System Build ͑MatrixX͒, Simulation Package, Integrated Systems, Inc., Santa Clara, CA.
- References ͓1͔ Manring, N., and Johnson, R., 1996, ''Modeling and designing a variable- displacement open-loop pump,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 118, pp. 267-271.
- ͓2͔ Schoenau, G., Burton, R., and Kavanagh, G., 1990, ''Dynamic Analysis of a Variable Displacement Pump,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 112, pp. 122-132.
- Kim, S., Cho, H., and Lee, C., 1987, ''A Parameter Sensitivity Analysis for the Dynamic Model of a Variable Displacement Axial Piston Pump,'' Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, 201, pp. 235-243.
- ͓4͔ Zeiger, G., and Akers, A., 1985, ''Torque on the Swashplate of an Axial Piston Pump,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 107, pp. 220-26.
- Pourmovahed, A., 1992, ''Uncertainty in the efficiencies of a hydrostatic pump/motor,'' Proceedings of the Winter Annual Meeting of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Anaheim, CA.
- Ezato, M., and Ikeya, M., 1986, ''Sliding Friction Characteristics Between a Piston and a Cylinder for Starting and Low-Speed Conditions in the Swashplate-Type Axial Piston Motor,'' 7th International Fluid Power Sympo- sium, Bath, England.
- McCandlish, D., and Dorey, R., 1981, ''Steady-State Losses in Hydrostatic Pumps and Motors.'' 6th International Fluid Power Symposium, St. Johns's Colleges, Cambridge, England.
- References ͓1͔ Swiecicki, I., 1961, ''Regulation of a Hydraulic Turbine Calculated by Step- By-Step Method,'' ASME J. Basic Eng., 83, pp. 445-455.
- ͓2͔ Hutarew, G., 1963, ''Tests on Turbine Governing Systems,'' Water Power, 15, pp. 243-248.
- ͓3͔ Parnaby, J., 1964, ''Dynamic and Steady-State Characteristics of a Centrifugal Speed Governor,'' The Engineer, 218, pp. 879-881.
- ͓4͔ Schiott, H., and Winther, J., 1965, ''Simulation of a Water Turbine on an Analogue Computer,'' Water Power, 17, pp. 410-412.
- ͓5͔ Thorne, D., and Hill, E., 1975, ''Extensions of Stability Boundaries of a Hy- draulic Turbine Generating Unit,'' IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst., PAS-94, pp. 1401-1409.
- Hagihara, S., Yokota, H., Goda, K., and Isobe, K., 1979, ''Stability of a Hy- draulic Turbine Generating Unit Controlled by P.I.D. Governor,'' IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst., PAS-98, pp. 2294-2298.
- ͓7͔ Sanathanan, C., 1986, ''Double Loop Control of a Hydro Turbine Unit,'' Int. Water Power Dam Construction, 38, pp. 25-27.
- Upchurch, E., 1994, ''Determining the Stability of a Pneumatic Turbine Speed Control System Using a Mechanistic Model,'' MS thesis, California State University, Long Beach, Long Beach, CA.
- ͓9͔ Deshpande, M., and Kar, S., 1981, ''Theoretical Prediction of Characteristics of Certain Flow Control Valves Used in Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems,'' Proceedings of the IFAC Symposium on Pneumatic and Hydraulic Compo- nents and Instruments in Automatic Control, May 20-23, 1980, Warsaw, Po- land, Pergamon Press, New York.
- ͓10͔ Benedict, R., and Wyler, J., 1974, ''A Generalized Discharge Coefficient for Differential Pressure Type Fluid Meters,'' ASME J. Eng. Power, 96, pp. 440- 448. Sonar-Based Wall-Following Control of Mobile Robots Alberto Bemporad Automatic Control Laboratory, ETH Zentrum, ETL I24.2, 8092 Zu ¨rich, Switzerland References ͓1͔ Crowley, J. L., 1985, ''Navigation for an Intelligent Mobile Robot,'' IEEE Trans. Rob. Autom., RA-1, No. 1, pp. 31-41.
- van Turennout, P., Honderd, G., and van Schelven, L. J., 1992, ''Wall- following Control of a Mobile Robot.'' Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Au- tomat., 1, pp. 280-285.
- ͓3͔ Latombe, J. C., 1991, Robot Motion Planning, KAP, Boston.
- Zelinsky, A., 1991, ''Mobile Robot Map Making Using Sonar,'' J. Rob. Syst., 8, No. 5, pp. 557-577.
- ͓5͔ Durrant-Whyte, H., 1992, ''Where Am I?,'' Industrial Robot, 21, No. 2, pp. 11-16.
- Holenstein, A. A., and Badreddin, E., 1994, ''Mobile-Robot Positioning Up- date Using Ultrasonic Range Measurements,'' International Journal of Robot- ics and Automation, 9, No. 2, pp. 72-80.
- ͓7͔ Elfes, A., 1987, ''Sonar-Based Real-World Mapping and Navigation,'' IEEE Trans. Rob. Autom., RA-3, No. 3, pp. 249-265.
- ͓8͔ Bozma, O ¨., and Kuc, R., 1991, ''Building a Sonar Map in a Specular Envi- ronment Using a Single Mobile Sensor,'' IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., RA-13, No. 12, pp. 1260-1269.
- ͓9͔ McKerrow, P. J., 1993, ''Echolocation-From Range to Outline Segments,'' Rob. Auton. Syst., 11, pp. 205-211.
- ͓10͔ Bemporad, A., Di Marco, M., and Tesi, A., 1993, ''Sonar-Based Wall- Following Control of Mobile Robots,'' Research Report DSI-14/97. Diparti- mento di Sistemi e Informatica, Firenze.
- Mayback, P., 1979, Stochastic Models-Estimation and Control, Vol. 1, Aca- demic Press, New York.
- References ͓1͔ Horowitz, I., 1991, ''Survey of Quantitative Feedback Theory ͑QFT͒,'' Int. J. Control, 53, No. 2, pp. 255-291.
- ͓2͔ Borghesani, C., Chait, Y., and Yaniv, O., 1995, Matlab™ Quantitative Feed- back Theory Toolbox, Mathworks Inc.
- Rodrigues, J. M., Chait, Y., and Hollot, C. V., 1997, ''An Efficient Algorithm for Computing QFT Bounds,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 119, pp. 548-552.
- ͓4͔ Horowitz, I., and Sidi, M., 1972, ''Synthesis of feedback systems with large plant ignorance for prescribed time domain tolerances,'' Int. J. Control, 16, pp. 287-309.
- Schwartz, A., 1967, Calculus and Analytic Geometry, Second Edition, Holt, Rinehart, and Winston.
- ͓6͔ Matlab 5.2 Reference, The Math Works Inc., 24 Prime Park Way, Natwick, MA. References ͓1͔ Alleyne, A., and Liu, R., 1999, ''On the Limitations of Force Tracking Control for Hydraulic Servosystems,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 121, No. 2, pp. 184-190.
- ͓2͔ Watton, J., 1989, Fluid Power Systems: Modeling, Simulation, Analog and Microcomputer Control, Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
- ͓3͔ Heinrichs, B., Sepheri, N., Thornton-Trump, A. B., 1997, ''Position-Based Impedance Control of an Industrial Hydraulic Manipulator,'' IEEE Control Syst. Mag., 17, No. 1, pp. 46-52.
- ͓4͔ Niksefat, N., and Sepehri, N., ''Robust Force Controller Design for a Hydrau- lic Actuator Based on Experimental Input-Output Data,'' 1999 American Con- trol Conference, pp. 3718-3722, San Diego, CA, June 1999.
- Alleyne, A., 1996, ''Nonlinear Force Control of an Electrohydraulic Actua- tor,'' Japan/USA Symposium on Flexible Automation, 1, pp. 193-200, Bos- ton, MA, June 1996.
- Merritt, H. E., 1967, Hydraulic Control Systems, Wiley, New York, NY.
- Khalil, H. K., 1996, Nonlinear Systems, 2nd edition, Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
- ͓8͔ Karnopp, D., 1985, ''Computer Simulation of Stick-Slip Friction in Mechani- cal Dynamic Systems,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 107, No. 1, pp. 100-103.
- Armstrong-Helouvry, B., Dupont, P., and Canudas de Wit, C., 1994, ''Friction in Servo Machines: Analysis and Control Methods.'' Appl. Mech. Rev., 47, No. 7.
- Alleyne, A., and Liu, R., 1999, ''Nonlinear Force/Pressure Tracking of an Electro-hydraulic Actuator,'' 1999 IFAC World Congress, Vol. B, pp. 469- 474, Beijing, China, July 1999. References ͓1͔ Meirovitch, L. 1986, Elements of Vibration Analysis, 2nd Edition, McGraw- Hill, Sydney.
- Fraser, A. R., and Daniel, R. W., 1991, Perturbation Techniques for Flexible Manipulators, Kluwer Academic Publishers, MA.
- Alberts, T. E., Colvin, J. A., 1991, ''Observations on the Nature of Transfer Functions for Control of Piezoelectric Laminates.'' J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct., 8, pp. 605-611.
- ͓4͔ Hong, J., Akers, J. C., Venugopal, R., Lee, M., Sparks, A. G., Washabaugh, P. D., and Bernstein, D., 1996, ''Modeling, Identification, and Feedback Control of Noise in an Acoustic Duct,'' IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol., 4, No. 3, pp. 283-291.
- ͓5͔ Bisplinghoff, R. L., and Ashley, H., 1962, Principles of Aeroelasticity, Dover Publications, New York.
- ͓6͔ Clark, R. L., 1997, ''Accounting for Out-of-Bandwidth Modes in the Assumed Modes Approach: Implications on Colocated Output Feedback Control,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 119, pp. 390-395.
- ͓7͔ Zhu, X., and Alberts, T. A., 1998, ''Appending a Synthetic Mode to Compen- sate for Truncated Modes in Coliocated Control,'' Proc. of AIAA GNC, Bos- ton.
- Pota, H. R., and Alberts, T. E., 1995, ''Multivariable Transfer Functions for a Slewing Piezoelectric Laminate Beam,'' ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., Control, 117, pp. 353-359.
- ͓9͔ Alberts, T. E., DuBois, T. V., and Pota, H. R., 1995, ''Experimental Verifica- tion of Transfer Functions for a Slewing Piezoelectric Laminate Beam,'' Con- trol. Eng., 3, pp. 163-170.
- ͓10͔ Pota, H. R., and Alberts, T. E., 1997, ''Vibration Analysis Using Symbolic Computation Software,'' Proc. of the 1997 American Control Conference, Albuquerque, NM, pp. 1400-1401.
- ͓11͔ Moheimani, S. O. R., Petersen, I. R., and Pota, H. R., 1997, ''Broadband Disturbance Attenuation over an Entire Beam,'' Proc. European Control Con- ference, Brussels, Belgium, to appear in the J. Sound. Vib.
- Moheimani, S. O. R., Pota, H. R., and Petersen, I. R., 1999, ''Spatial Balanced Model Reduction for Flexible Structures,'' Automatica, 35, pp. 269-277.
- ͓13͔ Moheimani, S. O. R., Pota, H. R., and Petersen, I. R., 1997, ''Active Vibration Control-A Spatial LQR Approach,'' Proc. Control 97, Sydney, Australia, pp. 622-627.
- Moheimani, S. O. R., Pota, H. R., and Petersen, I. R., 1998, ''Active Control of Noise and Vibration in Acoustic Ducts and Flexible Structures-A Spatial Control Approach,'' Proc. of the 1998 American Control Conference, Phila- delphia, PA, pp. 2601-2605.
- ͓15͔ Lewis, F. L., 1992, Applied Optimal Control and Estimation, Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
- References ͓1͔ Burnham, N. A., Kulik, A., Gremaud, G., and Briggs, G., 1995, ''Nanosubar- monics: The Dynamics of Small Nonlinear Contacts,'' Phys. Rev., 74, pp. 5092-5095.
- Ashhab, M., Salapaka, M., Dahleh, M., and Mezic ´, I., 1997, ''Control of Chaos in Atomic Force Microscopes,'' ACC, Albuquerque, NM.
- Ashhab, M., Salapaka, M. V., Dahleh, M., and Mezic, I., ''Melnikov-based Dynamical Analysis of Microcantilevers in Scanning Probe Microscopy,'' J. Nonlinear Dynam., 20, pp. 197-220.
- ͓4͔ Israelachvili, J. N., 1985, Intermolecular and Surface Forces, Academic Press, New York.
- Wiggins, S., 1990, Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos, Springer-Verlag, New York.
- ͓6͔ Nayfeh, A., and Balachandran, B., 1995, Applied Nonlinear Dynamics, Wiley, New York.
- ͓7͔ Osedelec, V. I., 1968, ''A Multiplicative Ergodic Theorem: Lyapunov Char- acteristic Numbers for Dynamical System'' Trans. Mosc. Math. Soc., 19, p. 197.
- Parker, T. S., and Chua, L. O., 1989, Practical Numerical Algorithms for Chaotic Systems, Springer-Verlag, New York.
- Ott, E., 1993, Chaos in Dynamical Systems, Cambridge University Press, New York.
- Ruelle, D., 1987, Chaotic Evolution and Strange Attractors, Cambridge Uni- versity Press, New York.
- Doedel, E. J., Keller, H. B., and Kernevez, J. P., 1991, ''Numerical Analysis and Control of Bifurcation Problems I: Bifurcations in Finite Dimension,'' Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng., 1, pp. 493-520.
Related papers
Engineering Research Publication ( www.erpublication.org )
Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1976
IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2000
Conference Proceedings
IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2007
 Moshe Shoham
Moshe Shoham
