In this article, we attempt to distinguish between the properties of moderator and mediator variables at a number of levels. First, we seek to make theorists and researchers aware of the importance of not using the terms moderator and... more
The CES-D scale is a short self-report scale designed to measure depressive symptomatology in the general population. The items of the scale are symptoms associated with depression which have been used in previously validated longer... more
The present article presents an integrative theoretical framework to explain and to predict psychological changes achieved by different modes of treatment. This theory states that psychological procedures, whatever their form, alter the... more
North begins his book by stating that "institutions are the rules of the game in a society or, more formally, are the humanly devised constraints that shape human interaction."(3) That being said North then proposes to examine... more
GOAL PURSUITS . The self-determination continuum, showing the motivational, self-regulatory, and perceived locus of causality bases of behaviors that vary in the degree to which they are self-determined.
Factor analysis, path analysis, structural equation modeling, and related multivariate statistical methods are based on maximum likelihood or generalized least squares estimation developed for covariance structure models. Large-sample... more
The purpose of this article is to determine whether the positive association between social support and well-being is attributable more to an overall beneficial effect of support (main-or direct-effect model) or to a process of support... more
Intrinsic and extrinsic types of motivation have been widely studied, and the distinction between them has shed important light on both developmental and educational practices. In this review we revisit the classic definitions of... more
A science of positive subjective experience, positive individual traits, and positive institutions promises to improve quali~. ' of life and prevent the pathologies that arise when life is barren and meaningless. The exclusive focus on... more
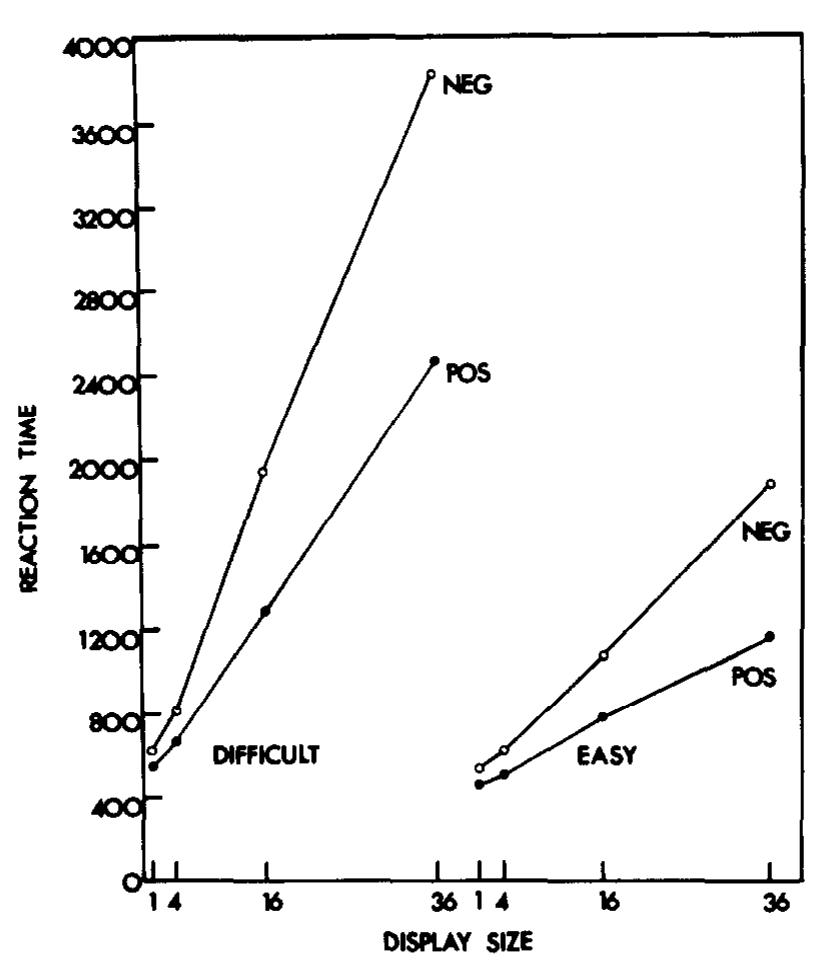
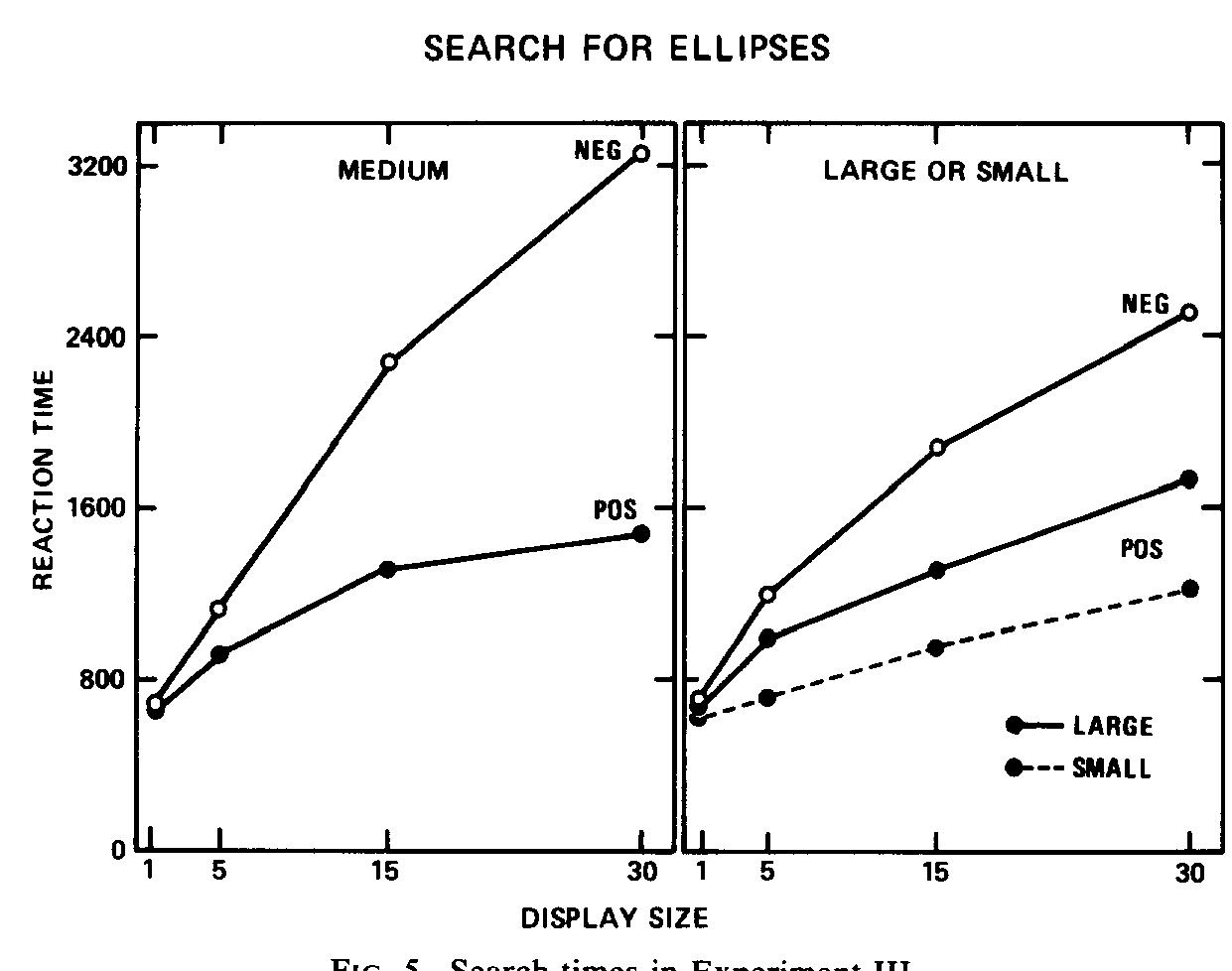
A new hypothesis about the role of focused attention is proposed. The feature-integration theory of attention suggests that attention must be directed serially to each stimulus in a display whenever conjunctions of more than one separable... more
This article examines five common misunderstandings about case-study research: (a) theoretical knowledge is more valuable than practical knowledge; (b) one cannot generalize from a single case, therefore, the single-case study cannot... more
s Abstract The capacity to exercise control over the nature and quality of one's life is the essence of humanness. Human agency is characterized by a number of core features that operate through phenomenal and functional consciousness.... more
Time underlies many interesting human behaviors. Thus, the question of how to represent time in connectionist models is very important. One approach is to represent time implicitly by its effects on processing rather than explicitly (as... more
W. review of the area of subjective well-being (SWB) advanced several conclusions regarding those who report high levels of "happiness." A number of his conclusions have been overturned: youth and modest aspirations no longer are seen as... more
We developed a muRidimensional coping inventory to assess the different ways in which people respond to stress. Five scales (of four items each) measure conceptually distinct aspects of problemfocused coping (active coping, planning,... more
A scale designed to assess various aspects of the burnout syndrome was administered to a wide range of human services professionals. Three subscales emerged from the data analysis: emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and personal... more
Mindfulness is an attribute of consciousness long believed to promote well-being. This research provides a theoretical and empirical examination of the role of mindfulness in psychological well-being. The development and psychometric... more
A Monte Carlo study compared 14 methods to test the statistical significance of the intervening variable effect. An intervening variable (mediator) transmits the effect of an independent variable to a dependent variable. The commonly used... more
The Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) has received considerable attention in the literature. The present study is a quantitative integration and review of that research. From a database of 185 independent studies published up to the end... more
This paper summarizes a stream of research aimed at developing and validating a measure of employee commitment to work organizations.
An integrative model of change was applied to the study of 872 subjects changing their smoking habits on their own. The subjects represented the following five stages of change: precontemplation, contemplation, action, maintenance, and... more
This article describes the development of a new sex-role inventory that treats masculinity and femininity as two independent dimensions, thereby making it possible to characterize a person as masculine, feminine, or "androgynous" as a... more
A framework for hypothesis testing and power analysis in the assessment of fit of covariance structure models is presented. We emphasize the value of confidence intervals for fit indices, and we stress the relationship of confidence... more
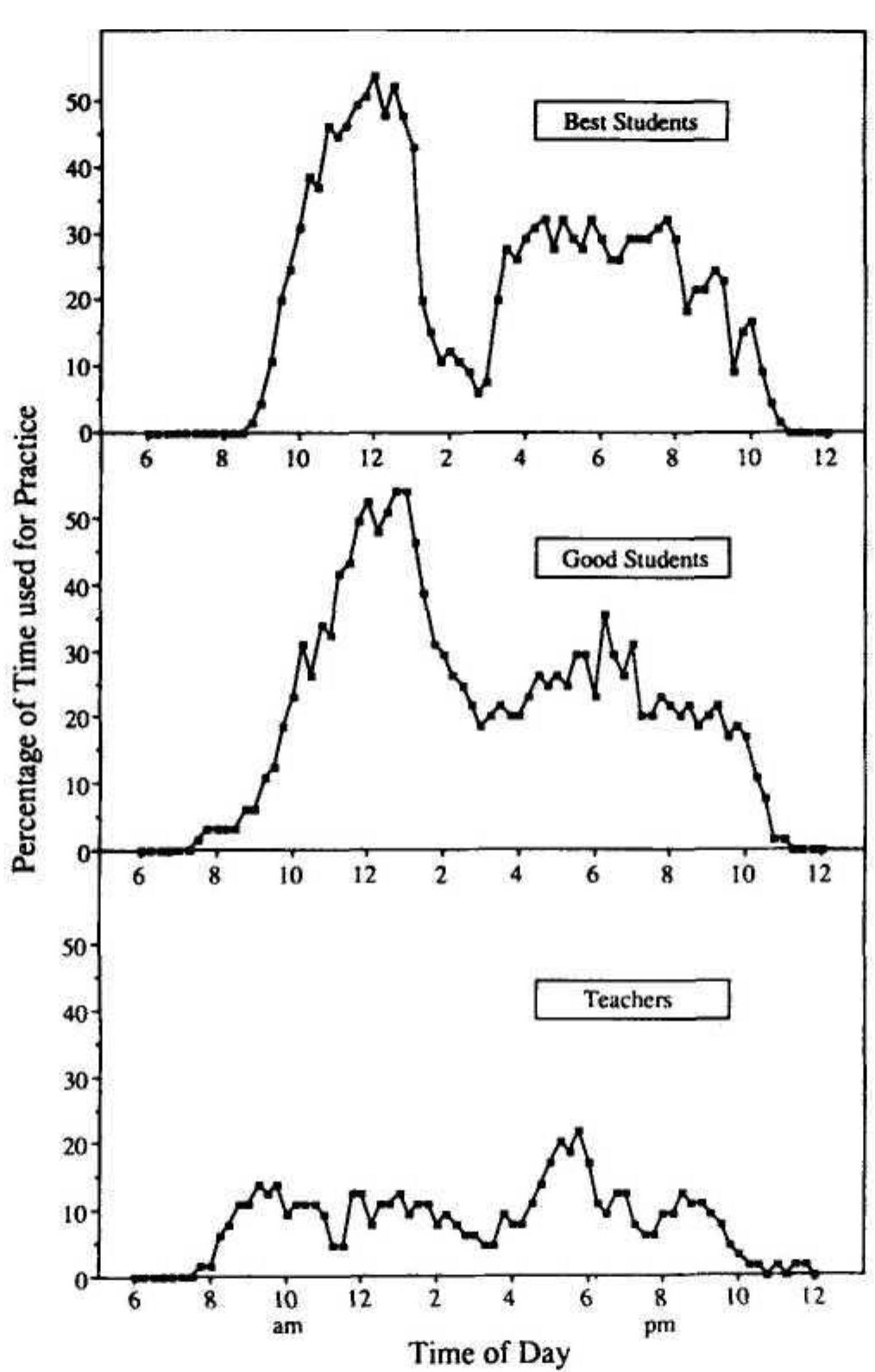
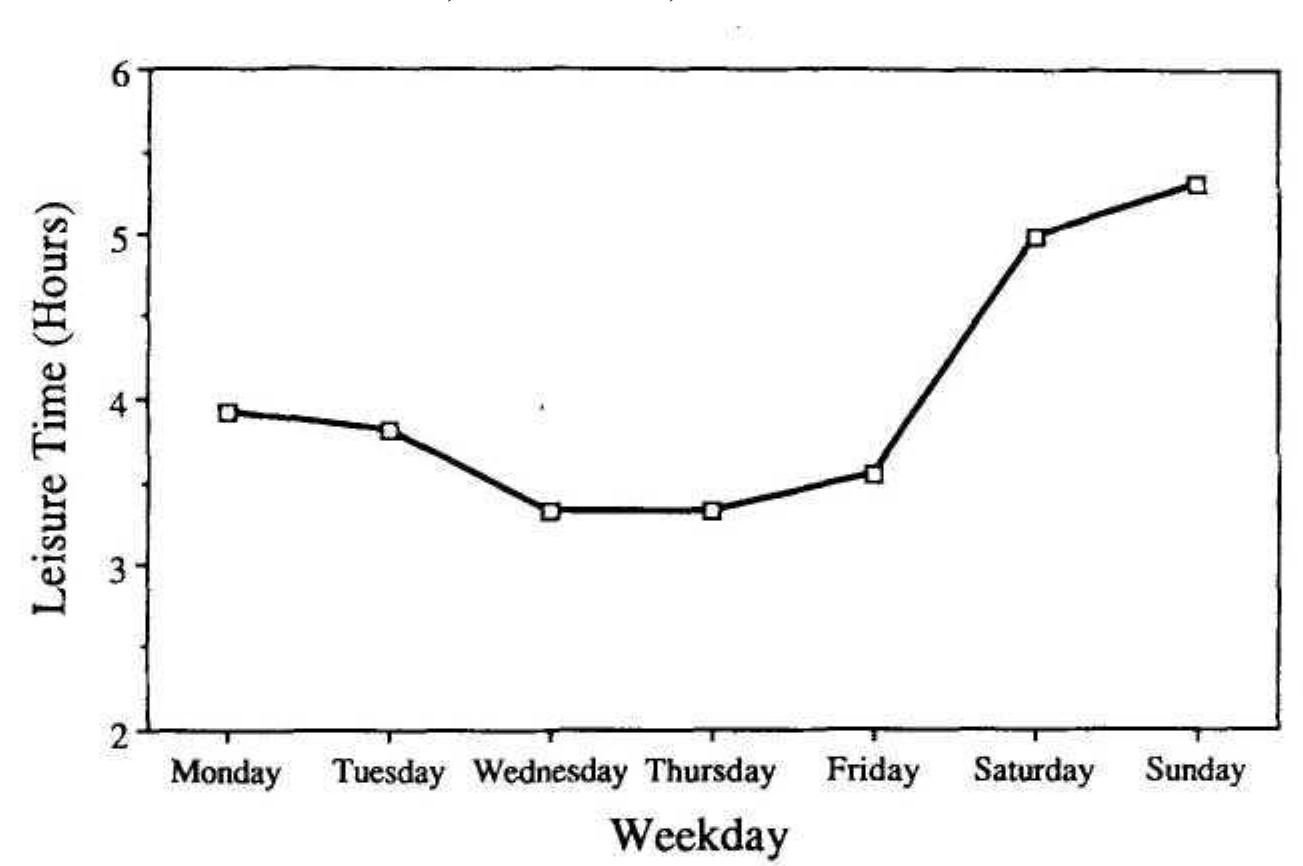
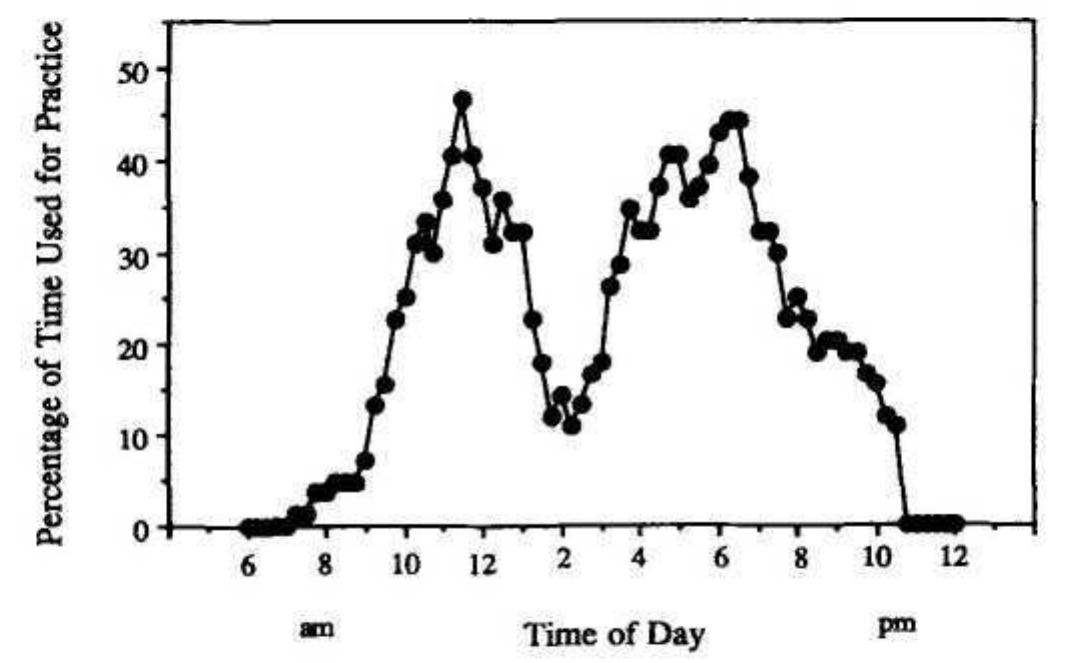
... Citation. Database: PsycARTICLES. [Journal Article]. The role of deliberate practice in the acquisition of expert performance. ... Full Record Display. Unique Identifier 1993-40718-001 Title The role of deliberate practice in the... more
A correlational study examined relationships between motivational orientation, self-regulated learning, and classroom academic performance for 173 seventh graders from eight science and seven English classes. A self-report measure of... more



















![Figure 1. Mean performance attainments as a function of differential levels of perceived self-efficacy. (The left panel shows the performances of groups of subjects whose self-percepts of efficacy were raised to either low, me- dium, or high levels; the right panel shows the perfor- mances of the same subjects at different levels of self- efficacy [Bandura, Reese, & Adams, in press].)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31145911/figure_001.jpg)
![Figure 2. Data from two moderately phobic subjects, illustrating how similar mastery experiences have vari- able effects on perceived self-efficacy over the course of treatment. (PRE represents the subjects’ pretest status; M, the changes produced in perceived self-efficacy by the preparatory modeling alone; and TREATMENT, the changes in subjects’ self-percepts of efficacy measured after each task mastery [Bandura et al., in press].)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31145911/figure_002.jpg)
![Figure 3. Data from two severe phobics, illustrating how similar mastery experiences have variable effects on perceived self-efficacy over the course of treatment. (PRE represents the subjects’ pretest status; M, the changes produced in perceived self-efficacy by the pre- paratory modeling alone; and TREATMENT, the changes in subjects’ self-percepts of efficacy measured after each task mastery [Bandura et al., in press].) In preliminary explorations of the cognitive pro- cessing of enactive experiences, people register notable increases in self-efficacy when their ex- periences disconfirm misbeliefs about what they fear and when they.gain new skills to manage threatening activities. They hold weak self-per- cepts of efficacy in a provisional status, testing their newly acquired knowledge and skills before raising judgments of what they are able to do. If in the course of completing a task, they discover some- thing that appears intimidating about the under-](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31145911/figure_003.jpg)
![Figure 4. Mean performance attainments by different groups of subjects at different levels of perceived self- efficacy (intergroup) and by the same subjects at higher levels of perceived self-efficacy (intrasubject) [Bandura et al., in press].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31145911/figure_004.jpg)
![Figure 5. Level of perceived self-efficacy and coping behavior displayed by subjects toward threats after receiving treatments relying on either enactive, vicarious, emotive, or cognitive modes of influence. (In the posttest phase, level of self-efficacy was measured prior to and after the test of coping behavior. The scores represent the mean performance attainments with similar and generalization threats [Bandura & Adams, 1977; Bandura, Adams, & Beyer, 1977; Bandura, Adams, Hardy, & Howells, 1980].)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31145911/figure_005.jpg)




![Figure 10. Relationship between strength of self-percepts of efficacy and level of anticipatory and performance fear arousal, after enhancement of self-efficacy through enactive, vicarious, emotive, or cognitive influence. (Participant modeling created such strong self-efficacy that there were only a few instances in which subjects receiving this form of treatment displayed self-percepts of efficacy below a strength value of 80 [Bandura, Adams, Hardy, & Howells, 1980].)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31145911/figure_010.jpg)
![Figure 11. Mean intensity of anticipatory and performance fear arousal experienced by different groups of subjects at different levels of perceived self-efficacy (intergroup) and by the same subjects at successively higher levels of perceived self-efficacy (intrasubject). (Self- percepts of efficacy were raised through enactive mastery in the two left panels and through modeling in the two right panels [Bandura et al., in press].)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31145911/figure_011.jpg)