Anthropogenic pressures on the Earth System have reached a scale where abrupt global environmental change can no longer be excluded. We propose a new approach to global sustainability in which we define planetary boundaries within which... more
‘The Hellenistic Near East,’ in: W. Scheidel, I. Morris, R. Saller eds., The Cambridge Economic History of the Greco-Roman World (Cambridge 2007) 409-433.
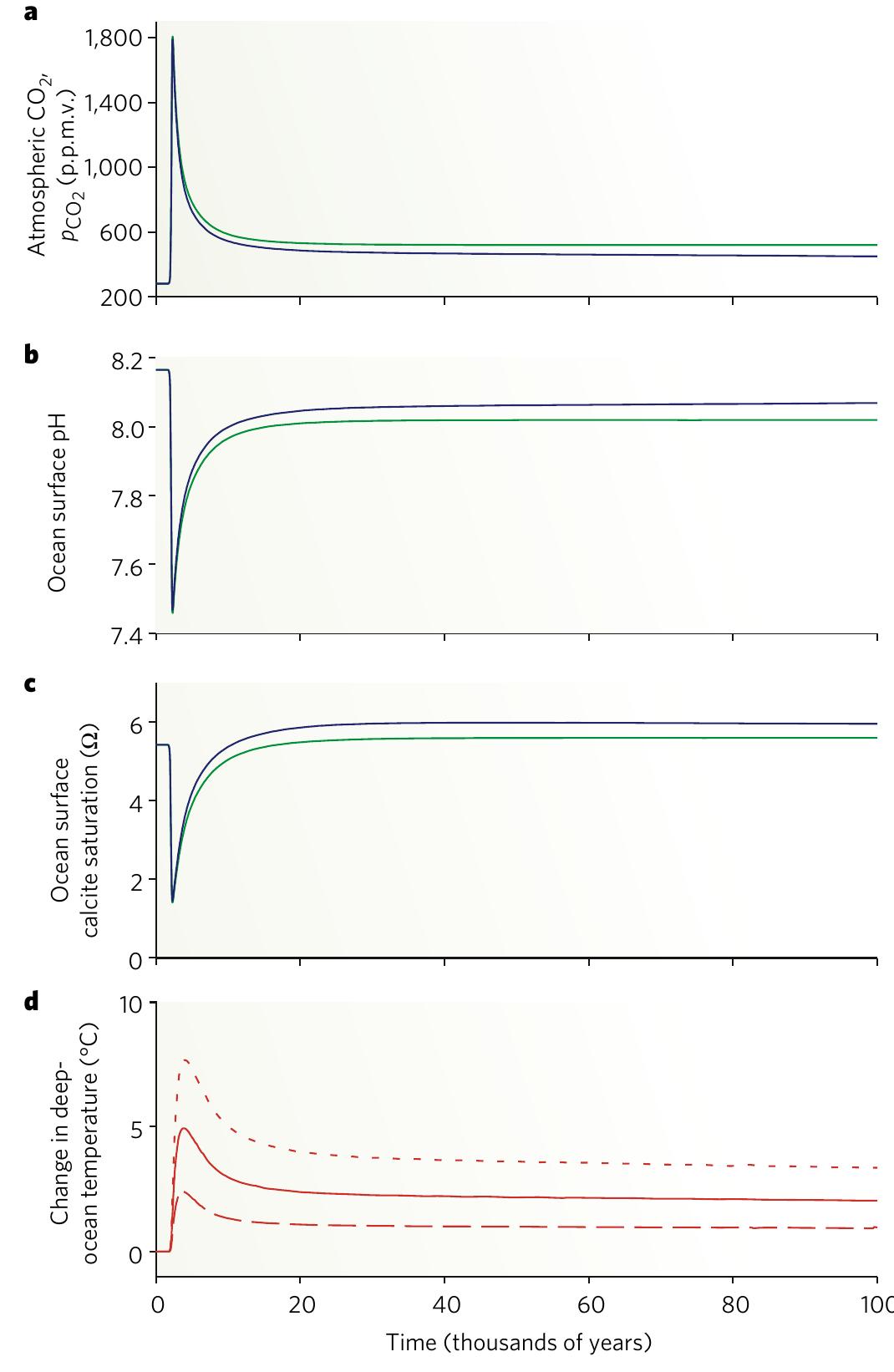
Past episodes of greenhouse warming provide insight into the coupling of climate and the carbon cycle and thus may help to predict the consequences of unabated carbon emissions in the future.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), the most severe form of acute lung injury, is a devastating clinical syndrome with a high mortality rate (30-60%) (refs 1-3). Predisposing factors for ARDS are diverse 1,3 and include sepsis,... more
The discovery of antibiotics more than 70years ago initiated a period of drug innovation and implementation in human and animal health and agriculture. These discoveries were tempered in all cases by the emergence of resistant microbes.... more
Striding bipedalism is a key derived behaviour of hominids that possibly originated soon after the divergence of the chimpanzee and human lineages. Although bipedal gaits include walking and running, running is generally considered to... more
Johnson, Scott Fitzgerald. 2014. “Real and Imagined Geography.” In The Cambridge Companion to the Age of Attila, edited by Michael Maas, 394–413. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
The covariation of carbon dioxide (CO(2)) concentration and temperature in Antarctic ice-core records suggests a close link between CO(2) and climate during the Pleistocene ice ages. The role and relative importance of CO(2) in producing... more
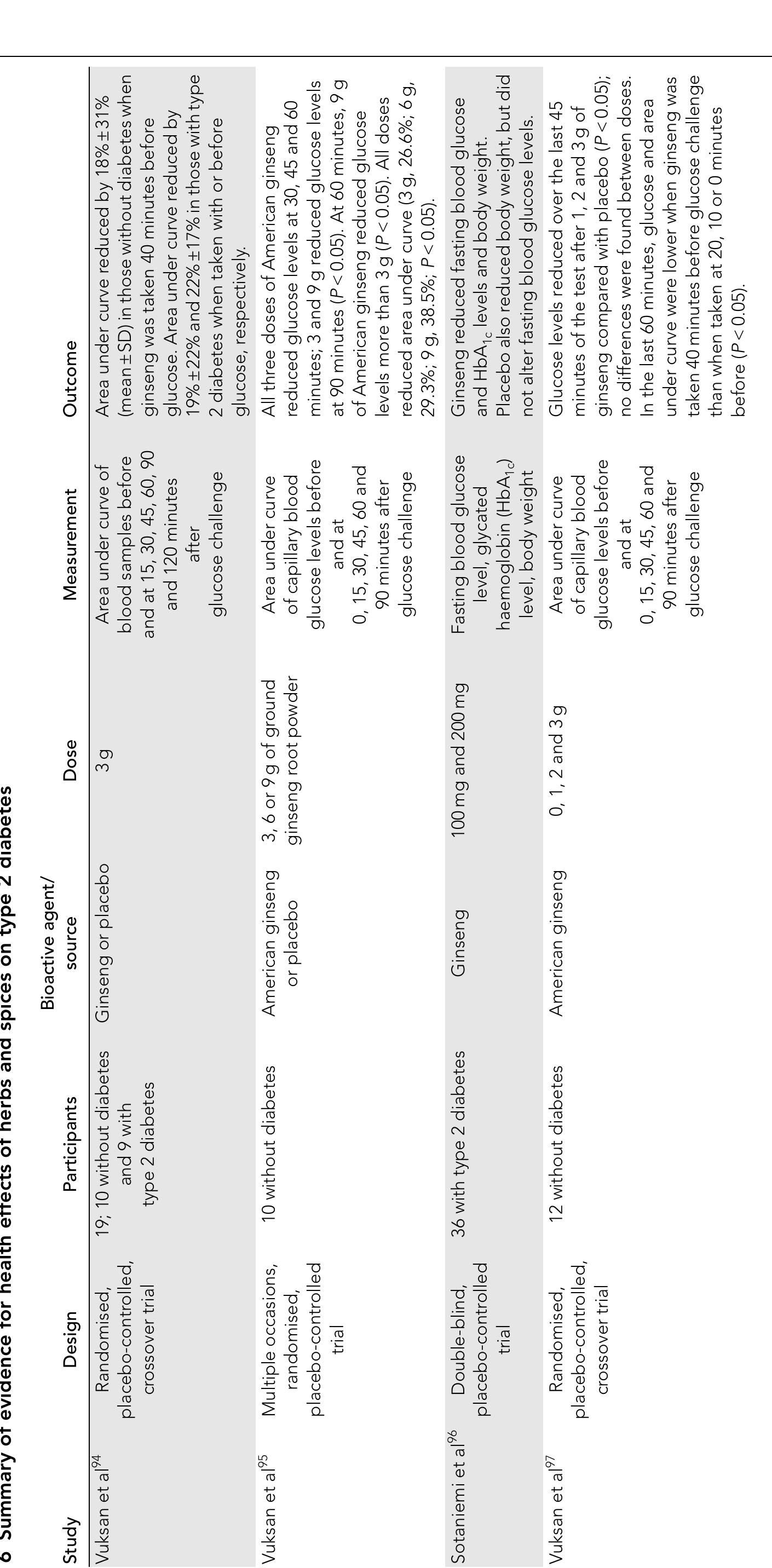
Herbs and spices have a traditional history of use, with strong roles in cultural heritage, and in the appreciation of food and its links to health. Demonstrating the benefits of foods by scientific means remains a challenge, particularly... more
In 1967 the Kibish Formation in southern Ethiopia yielded hominid cranial remains identified as early anatomically modern humans, assigned to Homo sapiens. However, the provenance and age of the fossils have been much debated. Here we... more
RYah mdP Gtd amd p Hm d ud qx gntrd ne Bgqhrsh] mr hs hr md d cetk sg] s sgd qd ad ] uhqfhm) Enq sgd r] ku] shnm ne sgd gntrd hr sghr nmd uhqfhm-%Or-,?sg] m] rhtr) b Ym ( R hm f kdg n n c hm Pn lW m Df w o s hm W Bn lo W pW shu d... more
Currently, it is widely accepted that only one hominin genus, Homo, was present in Pleistocene Asia, represented by two species, Homo erectus and Homo sapiens. Both species are characterized by greater brain size, increased body height... more
High-throughput direct sequencing techniques have recently opened the possibility to sequence genomes from Pleistocene organisms. Here we analyze DNA sequences determined from a Neandertal, a mammoth, and a cave bear. We show that purines... more
The past decade has witnessed a quantum leap in our understanding of the origins, diffusion, and impact of early agriculture in the Mediterranean Basin. In large measure these advances are attributable to new methods for documenting... more
Loss of seed shattering was a key event in the domestication of major cereals. We revealed that the qSH1 gene, a major quantitative trait locus of seed shattering in rice, encodes a BEL1-type homeobox gene and demonstrated that a... more
Warfare and dislocation are obvious features of the break-up of the late Roman West, but this crucial period of change was characterised also by communication and diplomacy. The great events of the late antique West were determined by the... more
There is intense debate about whether all Native Americans stem from one migration or multiple waves of migration from Asia. In addition, little is known about the principal settlement routes and patterns of population diversification... more
Biomaterials, traditionally defined as materials used in medical devices, have been used since antiquity, but recently their degree of sophistication has increased significantly. Biomaterials made today are routinely information rich and... more
Global climate and the atmospheric partial pressure of carbon dioxide (p CO atm 2 ) are correlated over recent glacial cycles, with lower p CO atm 2 during ice ages, but the causes of the p CO atm 2 changes are unknown. The modern... more
We show that DNA molecules amplified by PCR from DNA extracted from animal bones and teeth that vary in age between 25 000 and over 50 000 years carry C→T and G→A substitutions. These substitutions can reach high proportions among the... more
Methadone, a full mu-opioid agonist, is the recommended treatment for opioid dependence during pregnancy. However, prenatal exposure to methadone is associated with a neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) characterized by central nervous... more
In face recognition tasks, the dimension of the sample space is typically larger than the number of the samples in the training set. As a consequence, the within-class scatter matrix is singular and the Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)... more
has clear implications for our understanding of the tempo and mode of important transitions in evolution. But the controversy over the molecular clock is not just the concern of evolutionary theorists: the practical benefits of the... more
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
The grape is one of the earliest domesticated fruit crops and, since antiquity, it has been widely cultivated and prized for its fruit and wine. Here, we characterize genome-wide patterns of genetic variation in over 1,000 samples of the... more
Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine research is being aggressively pursued in attempts to develop biological substitutes to replace lost tissue or organs. Remarkable degrees of success have been achieved in the generation of a... more
The histories of crop domestication and breeding are recorded in genomes. Although tomato is a model species for plant biology and breeding, the nature of human selection that altered its genome remains largely unknown. Here we report a... more
Modern economics tantalizes historians, promising them a set of simple verbal and mathematical formulas to explain and even retrospectively predict historical actions and choices. Colin P. Elliott challenges economic historians to rethink... more
Role of basal ganglia: Vesalius and Piccolomini distinguished subcortical nuclei from cortex and white matter in the 16th century. Willis' mistaken concept in the late 17th century that the corpus striatum was the seat of motor power... more





































 slip in the deep upper mantle) challenge the two traditional interpretations for regions in the deep Earth of weak seismic anisotropy; (1) that they represent zones of poor deformation coherence at the seismic length scale, or (2) that the dominant deformation mechanism (for example, diffusion creep) in these regions does not produce CPO. Indeed, transition from dominant [100] to [001] slip at high pressure may explain the variation with depth of the anisotropy patterns of P and S waves, even if the entire upper mantle deforms coherently with a dominant horizontal shearing component (as expected in a con- vective system with large-scale plates at the surface, like the Earth’s mantle).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42422873/table_001.jpg)






![Figure 1| Temporal trends in Mo enrichment in black shales. Black circles are euxinic examples; grey diamonds refer to non-euxinic, organic-rich shales. The gradient represents the diffuse stage 1-2 boundary as defined in the text. The arrow marks the Mount McRae ‘whiff interval’; the dashed area is the Great Oxidation Event as defined by the multiple sulphur isotope record’. Stratigraphic and chronological details are provided in the Supplementary Information. From our record of [Mo] and Mo/TOC we delineate three stages 0 Mo cycling (Figs 1 and 2) based on marked shifts in the magnitudes o enrichment and Mo/TOC. During stage 1, [Mo] and Mo/TOC are typically variable but low, requiring only small amounts of dissolved Mo in the ocean. A prominent enrichment of Mo is recorded in the 2,500-Myr Mount McRae shale’, but Mo/TOC rises to only ~3p.p.m. per wt% during this event, relative to a background o ~1.5 p.p.m. per wt%, suggesting that dissolved Mo concentrations remained well below those of the modern deep Black Sea. Such enrichments may reflect mild oxidative weathering of continenta. materials during the Archaean eon, including transient events o slightly elevated O, in the surface ocean and atmosphere, consistent with evidence for the presence of oxygenic photosynthesis by 2,700 Myr ago”. Anbar et al.’ proposed recently that continenta pyrite and molybdenite could have been oxidized even at the very low partial pressure of oxygen (pO) suggested for the atmosphere at this time (less than 10° ° of the present level) on the basis of tempora distributions of non-mass-dependent sulphur isotope fractiona- tions*®. Other possibilities include submarine oxidative weathering in shallow photosynthetic hotspots or ephemeral atmospheric](https://figures.academia-assets.com/49869067/figure_001.jpg)
![Figure 2 | Temporal trends in Mo/TOC ratios in euxinic black shales. Symbol and boundary descriptions as in Fig. 1. With [Mo] and Mo/TOC from Black Sea sediments’” as our ana- logue for Proterozoic black shales, we estimate that the concentration of dissolved Mo remained less than 10-20% of the modern ocean for at least 800 Myr following the initiation of intense Mo cycling at about 2,200 Myr. Considering arguments for an increase in weath- ering of Mo-bearing sulphides on the continents during the Proterozoic'’”* and corresponding increase in riverine Mo flux to the ocean, we interpret the suppressed size of the oceanic reservoir as reflecting the persistence or even expansion of sulphidic sinks as opposed to a decrease in the riverine flux. It is important to stress that pervasive euxinia (that is, a sulphidic water column) is not required to exhaust the oceanic Mo reservoir. With a modern riverine flux, expansion of sulphidic pore waters, commonly found below weakly oxygenated bottom waters, to 10% of the sea floor would deplete the oceanic reservoir by 90% in ~200,000 yr (see Supple- mentary Information). This interpretation of the modern Mo budget does not preclude a more common occurrence of euxinic conditions during the Proterozoic*” but demonstrates that less extreme condi- tions are required to explain the Mo record. Indeed, global euxinia](https://figures.academia-assets.com/49869067/figure_002.jpg)










![spatial patterns of the subclades within the common hap- logroups A2, B2, Cib, C1c, C1d, and D1. Indeed, haplogroup D4h3a and X2a did not enter into the Americas alone. Thus, if some internal subclades of the pan-American haplogroups [7] arose before the expansion into the continent, their geographic distribution patterns should parallel those reported here for haplogroups X2a and D4h3a.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/45013871/figure_003.jpg)
![* The p estimate was computed as average number of base substitutions in the mtDNA coding region (between nps 577 and 16,023) from the ancestral sequence type, with a o error derived from an estimate of the genealogy [18]. Table 1. Divergence Estimates for Haplogroups D4h3 and X2 and Their Subclades](https://figures.academia-assets.com/45013871/table_001.jpg)
![*The average number of base substitutions in the mtDNA coding region (between positions 577 and 16,023) from the root sequence type. © Standard error calculated from an estimate of the genealogy [18]. ° Estimate of the time to the most recent common ancestor of each cluster, using a corrected age estimate of approximately 4610 years per substitutior the whole coding region and approximately 7650 years per synonymous transition (see Experimental Procedures). q Including A2, B2, C1b, Cic, C1d, D1, D4h3a, and X2a. Table 3. Averaged Substitution Distance from Relevant Nodes in the Native American Phylogeny of Figure 2](https://figures.academia-assets.com/45013871/table_002.jpg)

![Fig. 1. Clonal relationships within the USDA grape germplasm collection. (A) Number of clonal relationships was evaluated for each of the 950 vinifera accessions. Most of the accessions [551 (58%) of 950 accessions] have a clonal relationship with at least 1 other accession. (B) Degree of clonal relatedness among all 950 vinifera accessions is represented as a set of clusters. The 399 accessions that do not have a clonal relationship with another accession are shown as lone black dots. Accessions with six or fewer clonal relationships are grouped together with their clones and shown in gray. Clusters of clones with >7 accessions are colored, and their names are indicated in the legend. Names listed in the legend are the prime names from the Vitis International Variety Catalogue (http:/www.vivc.de/).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/46065609/figure_001.jpg)










