NEURORADIOLOGIA DE EMERGENCIA
Abstract
AI
AI
This text discusses the role of neuroradiology in emergency situations, particularly focusing on cerebrovascular emergencies like stroke. It emphasizes the importance of timely imaging to differentiate between ischaemic and haemorrhagic events. The chapter highlights the necessity for neuroradiologists to provide comprehensive morphological and functional information to aid in acute clinical decision-making, especially with the advent of fibrinolytic treatments that enhance the potential for effective interventions.
Figures (500)
References (611)
- Atlas SW: MR angiography in neurologic disease. Radiolo- gy 193:1-16, 1994.
- Barber PA, Darby DG, Desmond PM et al: Prediction of stroke outcome with echoplanar perfusion and diffusion weighted MRI. Neurology 51:418-426, 1998.
- Brant-Zawadzki M, Gould R: Digital subtraction cerebral angiography. AJR 140:347-353, 1983.
- De Boer JA, Folkers PJM: MR perfusion and diffusion im- aging in ischaemic brain disease. Medica Mundi 41:20, 1997.
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C et al: Intravenous thrombol- ysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemisferic stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA 274:1017-1025, 1995.
- Hankey GJ, Warlow CP, Molyneux AJ: Complications of cerebral angiography for patients with mild carotid terri- tory ischaemia being considered for carotid endarterecto- my. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53:542-548, 1990.
- John C, Elsner E, Muller A et al: Computed tomographic diagnosis of acute cerebral ischemia. Radiologe 37(11): 853-858, 1997.
- Koening M, Klotz E, Luka B et al: Perfusion CT of the brain: diagnostic approach for early detection of ischemic stroke. Radiology 209(1):85-93, 1998.
- Li TQ, Chen ZG, Hindmarsh T: Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of acute cerebral ischemia. Acta Radiologica 39:460-473, 1998.
- Lovblad KO, Laubach HJ, Baird AE et al: Clinical experi- ence with diffusion-weighted MR in patients with acute stroke. AJNR 19:1061-1066, 1998.
- Lutsep HL, Albers GW, DeCrespigny A et al: Clinical util- ity of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol 41:574- 580, 1997.
- Marks MP, Homgren EB, Fox A et al: Evaluation of early computed tomography findings in acute ischemic stroke 30(2):389-392, 1999.
- Mattews VP, Barker PB, Blackband SJ et al: Cerebral metabolities in patients with acute and subacute strokes: a serial MR and proton MR spectroscopy study. AJR 165:633-638, 1995.
- Pressman BD, Tourse EJ, Thompson JR et al: An early CT sign of ischemic infarction: increased density in a cerebral artery. AJR 149:583-586, 1987.
- Schellinger PD, Jansen O, Frebach JB et al: A standard- ized MRI stroke protocol: comparison with CT in hypera- cute intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 30(4):765-768, 1999.
- Von Kummer R, Allen KL, Holle R et al: Acute stroke: use- fulness of early CT findings before thrombolytic therapy. Radiology 205:327-333, 1997.
- Bahner ML, Reith W, Zuna I et al: Spiral CT vs incremen- tal CT: is spiral CT superior in imaging of the brain ? Eur Radiol 8(3):416-420, 1998.
- Bozzao L, Angeloni V, Bastianello S et al: Early angio- graphic and CT findings in patients with haemorrhagic in- farction in the distribution of the middle cerebral artery. AJNR 2:1115-1121, 1991.
- Bozzao L, Bastianello S, Ternullo S: Imaging anatomo-fun- zionale dell'ischemia encefalica. In: Pistolesi GF, Beltra- mello A: "L'imaging endocranico", Gnocchi Editore, Na- poli, 1997:211-304.
- Caillè JM, Guibert F, Bidabè AM et al: Enhancement of cerebral infarcts with CT. Comput Tomogr 4:73, 1980.
- Constant P, Renou AM, Caillè JM et al: Cerebral ischemia with CT. Comput Tomogr 1:235, 1977.
- Fisher CM: Lacunar strokes and infarcts: a review. Neuro- logy 32:871, 1982.
- Ford K, Sarwar M: Computed tomography of dural sinus thrombosis. AJR 2:539, 1981.
- Gaskill-Shipley MF: Routine evaluation of acute stroke. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 9(3):411-422, 1999.
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C et al: Intravenous throm- bolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemisferic stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA 274:1017-1025, 1995.
- John C, Elsner E, Muller A et al: Computed tomographic diagnosis of acute cerebral ischemia. Radiologe 37(11): 853-858, 1997.
- Kendall BE, Pullicini P: Intravascular contrast injection in ischaemic lesions. II. Effect on prognosis. Neuroradiology 19:241, 1980.
- Klozt E, Konig M: Perfusion measurements of the brain: using dynamic CT for the quantitative assessment of cerebral ischemia in acute stroke. Eur J Radiol 30(3),170-184, 1999.
- Koenig M, Klotz E, Luka B et al: Perfusion CT of the brain: diagnostic approach for early detection of ischemic stroke. Radiology 209(1):85-93, 1998.
- Lutman M: Diagnosi precoce dell'infarto cerebrale: l'iper- densità dell'arteria cerebrale media come primo segno TC di lesione ischemica. Radiol Med 77:171-173, 1989.
- Marks MP, Homgren EB, Fox A et al: Evaluation of early computed tomographic findings in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 30(2):389-392, 1999.
- Motto C, Ciccone A, Aritzu E et al: Haemorrhage after an acute ischemic stroke. MAST-I Collaborative Group. Stroke 30(4):761-764, 1999.
- Moulin T, Tatu L, Vuillier F et al: Brain CT scan for acute cerebral infarction: early signs of ischemia. Rev Neurol 1555(9):649-655, 1999.
- Perrone P, Landelise L, Scotti G et al: CT evaluation in pa- tients with transient ischemic attack. Correlation between clinical and angiographic findings. Eur Neurol 18:217, 1979.
- Pressman BD, Tourje EJ, Thompson JR: An early CT sign of ischemic infarction: increased density in a cerebral ar- tery. AJR 149:583-586, 1987.
- Rao KCVG, Knipp HC, Wagner EJ: Computed tomo- graphic findings in cerebral sinus and venous thrombosis. Radiology 140:391, 1981.
- Reichenbach JR, Rother J, Jonetz-Mentzel L et al: Acute stroke evaluated by time-to-peak mapping during initial and early follow-up perfusion CT studies. AJNR 20(10):1842-1850, 1999.
- Schellinger PD, Jansen O, Fiebach JB et al: A standardized MRI stroke protocol: comparison with CT in hyperacute intracerebral haemorrhage. Stroke 30(4):765-768, 1999.
- Scott JN, Buchan AM, Sevich RJ: Correlation of neurolo- gic dysfunction with CT findings in early acute stroke. Can J Neurol Sci 26(3):182-189, 1999.
- Skriver ED, Esbach O: Transient disappearance of cere- bral infarct on CT scan, the so-called fogging effect. Neu- roradiology 22:61, 1981.
- Ueda T, Yuh WT, Taoka T: Clinical application of perfu- sion and diffusion MR imaging in acute ischemic stroke. J Magn Reson Imaging 10(3):305-309, 1999.
- Vonofakos D, Artmann H: CT findings in haemorragic ce- rebral infarct. Comput Radiol 7:75, 1983.
- von Kummer R, Allen KL, Holle R et al: Acute stroke: use- fulness of early CT findings before thrombolytic therapy. Radiology 205:327-333, 1997.
- von Kummer R, Meyding-Lamadè U, Forsting M et al: Sensitivity and prognostic value of early CT in occlusion of the middle cerebral artery trunk. AJN 15:9-18, 1994.
- Wing SD, Normann D, Pollack JA et al: Contrast enhan- cement of cerebral infarcts in computed tomography. Ra- diology 121:89,1976.
- Yock DH: CT demonstration of cerebral emboli. J Com- put Assist Tomogr 5:190-196, 1981.
- Zulck KJ, Esbach O: The interhemisferic steal syndromes. Neuroradiology 4:179-185, 1972.
- Andrews BT, Chiles W, Olsen W et al: The effect of in- tracerebral hematoma location on the risk of brainstem compression and clinical outcome. J Neurosurg 69:518- 522, 1988.
- Bagley LJ: Imaging of neurological emergencies: trauma, hemorrhage, and infections. Semin Roentgenol 34:144- 159, 1999.
- Blankenberg FG, Loh NN, Bracci P et al: Sonography, CT, and MR imaging: a prospective comparison of neonates with suspected intracranial ischemia and hemorrhage. AJNR 21:213-218, 2000.
- Boulin A: Les affections vasculaires. In: Vignaud J, Boulin A: Tomodensitométrie cranio-encéphalique. Ed Vigot Paris, 1987.
- Broderick JP, Brott TG, Tomsick T et al: Ultra-early eval- uation of the intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 72:195-199, 1990.
- Cirillo S, Simonetti L, Sirabella G et al: Patologia vasco- lare. In: Dal Pozzo G (ed): Compendio di Tomografia Computerizzata (pp. 127-147). USES Ed. Scientifiche Flo- rence, 1991.
- Grossman CB: Magnetic resonance imaging and comput- ed tomography of the head and spine (pp. 145-183). Williams & Wilkins Baltimore, 1990.
- Juvela S, Heiskanen O, Poranen A et al: The treatment of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 70:755-758, 1989.
- Kase C: Diagnosis and treatment of intracerebral hemor- rhage. Rev Neurol 29:1330-1337, 1999.
- Loncaric S, Dhawan AP, Broderick J et al: 3-D imaging analy- sis of intra-cerebral brain hemorrhage from digitized CT films. Comput Method Programs Biomed 46:207-216, 1995.
- Mader TJ, Mandel A: A new clinical scoring system fails to differentiate hemorrhagic from ischemic stroke when used in the acute care setting. J Emerg Med 16:9-13, 1998.
- Masdeu JC, Fine M: Cerebrovascular disorders. In: Gon- zalez CF, Grossman CB, Masdeu JC (eds) Head and spine imaging (pp. 283-356). John Wiley & Sons New York, 1985.
- Miller JH, Warlaw JM, Lammie GA: Intracerebral haemor- rhagic and cerebral amyloid angiopathy: CT features with pathological correlation. Clin Radiol 54:422-429, 1999.
- Modic MT, Weinstein MA: Cerebrovascular disease of the brain. In: Haaga JR, Alfidi RJ (eds) Computed tomogra- phy of the brain, head and neck (pp. 136-169). The C.V. Mosby Co. St. Louis, 1985.
- Novelline RA, Rhea JT, Rao PM et al: Helical CT in emer- gency radiology. Radiology 213:321-339, 1999.
- Ross DA, Olsen WL, Ross AM et al: Brain shift, level of consciouness and restoration of consciousness in patients with acute intracranial hematoma. J Neurosurg 71:498- 502, 1989.
- Scarano E, De Falco R, Guarnieri L et al: Classificazione e trattamento delle emorragie cerebrali spontanee. Ricerca Neurochirurgica 1-2:21-32, 1990.
- Sellier N, Lalande G, Kalifa G: Pathologie vasculaire. In: Montagne JP, Couture A: Tomodensitométrie pédiatrique (pp. 70-90). Ed. Vigot Paris, 1987.
- Takasugi S, Ueda S, Matsumoto K: Chronological changes in spontaneous intracranial hematoma -an experimental and clinical study. Stroke 16:651, 1985.
- Tuhrim S, Horowitz DR, Sacher M et al: Volume of ven- tricular blood is an important determinant of outcome in supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage. Crit Care Med 27:617-621, 1999.
- Waga S, Miyazaki M, Okada M et al: Hypertensive putam- inal haemorrhage: analysis of 182 patients. Surg Neurol 26:159-166, 1986.
- Weisberg LA, Nice C: Cerebral computed tomography. A text atlas (pp. 133-162) W.B. Saunders Co. Philadelphia, 1989.
- Zazulia AR, Diringer MN, Derdeyn CP et al: Progression of mass effect after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 30:1167- 1173, 1999.
- Zhu XL, Chan MS, Poon WS: Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage: which patients need diagnostic cerebral an- giography? A prospective study of 206 cases and review of the literature. Stroke 28:1406-1409, 1997. REFERENCES
- Andrioli G, Cavazzani P: Differential diagnosis of sub- arachnoid hemorrhage. Minerva Anestesiol 64:141-144, 1998.
- Boecher-Schwartz HG, Fries G, Mueller-Forell W et al: Cerebral blood flow velocities after subarachnoid haemor- rhage in relation to the amount of blood clots in the initial computed tomography. Acta Neurochir 140:573-578, 1998.
- Botia E, Vivancos J, Leon T et al: Predictive mortality fac- tors and the development of major complications in non- traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage. Rev Neurol 24:193- 198, 1996.
- Brouwers PJ, Dippel DW, Vermeulen M et al: Amount of blood on computed tomography as an independent pre- dictor after aneurysm rupture. Stroke 24:809-814, 1993.
- Brown BM, Soldevilla F: MR angiography and surgery for unruptured familiar intracranial aneurysms in persons with a family history of cerebral aneurysms. AJR 173:133- 138, 1999.
- Cesarini KG, Hardemark HG, Persson L: Improved sur- vival after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: review of case management during a 12-year period. J Neurosurg 90:664-672, 1999.
- Chan BS, Dorsch NW: Delayed diagnosis in subarachnoid haemorrhage. Med J Aust 154:509-511, 1991.
- Cirillo S, Simonetti L, Sirabella G et al: Patologia vascolare. In: Dal Pozzo G: Compendio di Tomografia Computerizza- ta (pp. 127-147) USES Edizioni Scientifiche Florence, 1991.
- Duong H, Melancon D, Tampieri D et al: The negative an- giogram in subarachnoid haemorrhage. Neuroradiology 38:15-19, 1996.
- Germanson TP, Lanzino G, Kongable GL et al.: Risk clas- sification after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg Neurol 49:155-163, 1998.
- Gilbert JW, Lee C, Young B: Repeat cerebral panangiog- raphy in subarachnoid hemorrage of unknown etiology. Surg Neurol 33:19-21, 1990.
- Gruber A, Dietrich W, Richling B: Recurrent aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: bleeding pattern and inci- dence of posthaemorrhagic ischaemic infarction. Br J Neu- rosurg 11:121-126, 1997.
- Hijdra A, van Gijn J, Nagelkerke NJ et al: Prediction of delayed cerebral ischaemia, rebleeding, and outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrage. Stroke 19:1250- 1256, 1988.
- Kallmes DF, Kallmes MH: Cost-effectiveness of angiogra- phy performed during surgery for ruptured intracranial aneurysms. AJNR 18:1453-1462, 1997.
- Kassel NF, Sasaki T, Colohan AR et al: Cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal SAH. Stroke 15:562, 1985.
- Kingsley DP: Extravasation of contrast-enhanced blood into the subarachnoid space during computed tomogra- phy. Neuroradiology 18:259-262, 1979.
- Kistler JP, Crowell RM, Davis KR: The relation of cerebral vasospasm to the extent and location of subarachnoid blood visualized by CT scan: a prospective study. Neurol- ogy 33:424, 1983.
- Lenhart M, Bretschneider T, Gmeinwieser J et al: Cerebral CT angiography in the diagnosis of acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Radiol 38:791-796, 1997.
- Leonardi M: Diagnosis and general assessment of acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. Minerva Anestesiol 64:145- 147, 1998.
- Modic MT, Weinstein MA: Cerebrovascular disease of the brain. In: Haaga JR, Alfidi RJ (eds): Computed tomogra- phy of the brain, head and neck (pp. 136-169) The CV Mosby Company St. Louis 1985.
- Noguchi K, Ogawa T, Seto H et al: Subacute and chronic sub- arachnoid hemorrhage: diagnosis with fluid attenuated inver- sion recovery MR imaging. Radiology 203:257-262, 1997.
- Ohkawa M, Tanabe M, Toyama Y et al: CT angiography with helical CT in the assessment of acute stage of sub- arachnoid hemorrhage. Radiat Med 16:91-97, 1998.
- Roos YB, Beenen LF, Goen RJ et al: Timing of surgery in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: re- bleeding is still the major cause of poor outcome in neuro- surgical units that aim at early surgery. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63:490-493, 1997.
- Sames TA, Storrow AB, Finkelstein JA et al: Sensitivity of new-generation computed tomography in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acad Emerg Med 3:16-20, 1996.
- Schwartz TH, Solomon RA: Perimesencephalic nona- neurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: review of the litera- ture. Neurosurgery 39:433-440, 1996.
- Sidman R, Connolly E, Lemke T: Subarachnoid hemor- rhage diagnosis: lumbar puncture is still needed when the computed tomography scan is normal. Acad Emerg Med 3:827-831, 1996.
- Sobal D: Cisternal enhancement after subarachnoid he- morrage. AJNR 2:549-552, 1981.
- Terbrugge KG, Rao KC, Lee SH: Cerebral vascular anom- alies. In: Lee SH, Rao KC (eds): Cranial Computed To- mography and MRI (pp. 607-641) Mc Graw-Hill Book Company New York, 1987.
- van der Jagt M, Hasan D, Bijvoet HW et al: Validity of pre- diction of the site of ruptured intracranial aneurysms with CT. Neurology 52:34-39, 1999.
- Vale FL, Bradley EL, Fisher WS: The relationship of sub- arachnoid hemorrhage and the need for postoperative shunting. J Neurosurgery 86:462-466, 1997.
- Vermeij FH, Hasan D, Vermeulen M et al: Predictive fac- tors for deterioration from hydrocephalus after subarach- noid hemorrhage. Neurology 44:1851-1855, 1994.
- Yock DH, Larson DA: Computed Tomography of he- morrage from anterior communicating artery aneurysms with angiographic correlation. Radiology 134:399-407, 1980.
- Yoshimoto Y, Wakai S: Cost-effectiveness analysis of screen- ing for asymptomatic, unrupted intracranial aneurysms. A mathematical model. Stroke 30:1621-1627, 1999.
- Weisberg LA, Nice C: Cerebral Computed Tomography: A text atlas (pp. 163-179). WB Saunders Philadelphia, 1989.
- Zimmerman RD, Yurberg E, Leeds NE: The falx and in- terhemispheric fissure on axial computed tomography: I. Normal anatomy. AJNR 3:175-180, 1982.
- Adams RD, Victor M: Principles of Neurology. McGraw- Hill, Inc., New York: 1985, 508-572.
- Awad L, Modic M et al: Focal parenchymal lesions in TIA: correlation of CT and MRI. Stroke 17:399-403, 1986.
- Bastianello S, Brughitta G, Pierallini A et al: Neuroradiolo- gical findings in acute cerebral ischemia. In: Ottorino Ros- si Award Conference. Zappoli F, Martelli A. (eds). Edizio- ni del Centauro, Udine, 131-140, 1992.
- Bozzao L, Angeloni U et al: Early angiographic and CT fin- dings in patients with hemorragic infarction in the distribu- tion of the middle cerebral artery. AJNR, 12:1115-1121, 1991.
- Brant-Zawadzki M, Pereira B et al: MRI of acute experi- mental ischemia in rats. AJNR 7:7-11, 1986.
- Brierley JB: Cerebral hypoxia. In: Blackwood W, Corsellis JAN (eds). "Greenfield's Neuropathology" Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers 43-85, 1976.
- Bryan RN, Whitlow WD, Levy LM: Cerebral infarction and ischemic disease. In: Atlas SW (ed). "MRI of brain and spine". New York: Raven Press 411-437, 1991.
- Duchen LW: General pathology of neurons and neuroglia. In: "Greenfield's neuropathology" Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers 1-68, 1992.
- Garcia JH, Anderson ML: Circulatory disorders and their ef- fects on the brain. In: Textbook of Neuropathology. Davis RL & Robertson DL. (eds). William&Wilkins, Baltimore, 1997.
- Graham DI: Hypoxia and vascular disorders. In: "Green- field's Neuropathology" Chicago:Year Book Medical Publi- shers 153-268, 1992.
- Gullotta F: Vasculopatie cerebrali. In: Schiffer D ed. "Neu- ropatologia" Roma: Il pensiero scientifico, 1980:155-178.
- Kendall B: Cerebral ischemia. Rivista di Neuroradiologia 3 (suppl. 2):35-38, 1990.
- Mathews WP, Witlow WD, Bryan RN: Cerebral Ischemia and Infarction. In: MRI of brain and spine. (ed). Atlas SW Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, 1997.
- Savoiardo M, Sberna M, Grisoli M: RM e patologia vasco- lare del sistema nervoso centrale. Rivista di Neuroradiolo- gia 1 (suppl. 1):95-100, 1988.
- Simonetti L, Cirillo S, Menditto M: Hemorrhagic infarcts of arterial origin: physiopathological aspects and MR semeio- logy. In: Ottorino Rossi Award Conference. Zappoli F, Mar- telli A. (eds). Edizioni del Centauro, Udine 141-145, 1992.
- Von Kummer R: Changing role of the neuroradiologist in the investigation of acute ischemic stroke. In: Syllabus of 7 th Advanced Course of the ESNR. Byrne JW. (ed). Edizioni del Centauro, Udine 41-44, 1997.
- Adams RD, Victor M: Principles of Neurology. New York: McGraw-Hill, Inc. 508-572, 1985.
- Brott T, Broderick J et al: Early hemorrhage growth in pa- tients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 28(1):1-5, 1997.
- Cirillo S, Di Salle F, Simonetti L et al: La RM nell'emorra- gia sub-aracnoidea: I. Studio in vitro. Rivista di Neurora- diologia 2:211-217, 1989.
- Cirillo S, Simonetti L, Di Salle F et al: La RM nell'emorra- gia sub-aracnoidea: II. Studio in vivo. Rivista di Neurora- diologia 2:219-225, 1989.
- Davis JM, Davis KR, Cromwell RM: SAE secondary to rup- tured of intracranial aneurysms. AJNR (1):17-21, 1980.
- Gardeur D: Pathologie vasculaire. Ellipse, Paris, 1982.
- Gomori JM, Grossman RI et al: Variable appearances of sub-acute intracranial hematomas on high fields SE MR. AJR 150:171-178, 1985.
- Gomori JM, Grossman RI et al: Intracranial hematomas imaging by high field MR. Radiology 157:87-93, 1985.
- Gullotta F: Vasculopatie cerebrali. In: Schiffer D (ed). "Neu- ropatologia" Roma: Il pensiero scientifico 155-178, 1980.
- Noguchi K, Ogawa T et al: Subacute and chronic subara- chnoid hemorrhage: diagnosis with fluid-attenuated in- version-recovery MR imaging. Radiology 203(1):257-62, 1997.
- Noguchi K, Ogawa T, Inugami et al: Acute subarachnoid hemorrhage: MR imaging with fluid-attenuated inversion recovery pulse sequences. Radiology 1963:773-777, 1995.
- Ogawa T, Inugami A, Fujita H et al: MR diagnosis of suba- cute and chronic subarachnoid hemorrhage: comparison with CT. AJR 165(5):1257-1262, 1995.
- Osborne AG: Diagnostic Neuroradiology. Chapter 10. Mo- sby-Year Book, St. Louis, 1994.
- Patel MR, Edelman RR, Warach S: Detection of hyperacu- te primary intraparenchymal hemorrhage by magnetic reso- nance imaging. Stroke 27(12):2321-2324, 1996.
- Savoiardo M, Sberna M, Grisoli M: RM e patologia vasco- lare del sistema nervoso centrale. Rivista di Neuroradiolo- gia 1 (suppl. 1):95-100, 1988.
- Thulborn KR, Atlas SW: Intracranial hemorrage. In: Atlas SW (ed). "MRI of brain and spine". II Edition. Lippincott- Raven Publishers. Philadelphia, 265-313, 1996.
- Triulzi F: Cerebral hemorrage: CT and MRI. Rivista di Neuroradiologia 3 (suppl.2): 39-44, 1990.
- Vignaud J, Buolin A: Tomodensitometrie cranio-encefali- que. Ed Vigot Paris, 1987.
- Zimmerman RA, Leeds NE, Naidich TP: Ring blush associa- ted with cerebral hematoma. Radiology 122:707-711, 1977. REFERENCES
- Bazzocchi M, Quaia E, Zuiani C et al: Transcranial Dop- pler: state of the art. Eur J Radiol 27:141-148, 1998.
- Bendick PJ, Brown OW, Hernandez D et al: Three-Dimen- sional Vascular Imaging using Doppler Ultrasound. Am J Sur 176:183-7, 1998.
- Bonita R: Epidemiologia dell'ictus. The Lancet 9:387-390, 1992.
- Dauzat M: Pratique de l'ultrasonographie vasculaire. Ed. Vigot Paris, 1986.
- Postert T, Braun B, Pfundtner N et al: Echo contrast- enhanced three-dimensional Power Doppler of intracranial arteries. Ultrasound Med Biol 7:953-956, 1998.
- Rabbia C, De Lucchi R, Cirillo R: Eco-Color-Doppler Va- scolare. Ed. Minerva Medica, 91-94, 1995.
- Steinke W, Meairs S, Ries S, Hennerici M: Sonographic As- sesment of Carotid Artery Stenosis, comparison of Power Doppler Imaging and Color Doppler Imaging. Stroke 27(1):91-4, 1996.
- Tonarelli A: Diagnostica per Immagini della carotide extra- cranica: Ecografia ed Eco-Doppler. Rivista di Neuroradio- logia 9 (suppl. 2):11-26, 1996.
- Anderson CM, Edelman RR, Turki PA: Clinical Magnetic Resonance Angiography. Raven Press New York, 1993.
- Atlas SW: MR angiography in neurologic disease. Radio- logy 193:1-6, 1994.
- Atlas SW, Sheppard L, Godberg HI et al: Intracranial aneurysms: detection and characterization with MR angio- graphy with use of an advanced post-processing technique in a blinded-reader study. Radiology 203:807-814, 1997.
- Atkinson D, Brant-Zawadzki M, Gilliam G et al.: Improved MR angiography: magnetization transfer suppression with variable flip angle excitation and increased resolution. Ra- diology 190:890-894, 1994.
- Bowen BC, Quencer RM, Margosian P et al.: MR angio- graphy of occlusive disease of the arteries in the head and neck: current concepts. AJR 162: 9-18, 1994.
- Edelman RR, Ahn SS, Chien D et al.: Improved time-of- fligth MR angiography of the brain with magnetization transfer contrast. Radiology 184: 395-399, 1992
- Furst G, Hofer M, Steinmetz H et al.: Intracranial stenooc- clusive disease: MR angiography with magnetization tran- sfer and variable flip angle. AJNR 17:1749-1757, 1996.
- Heiserman JE, Drayer BP, Keller PJ et al.: Intracranial vascu- lar stenosis and occlusion: evaluation with tree-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography. Radiology 185:667-673, 1992.
- Kim JK, Farb RI, Wright GA: Test bolus examination in the carotid artery at dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MR angio- graphy. Radiology 206:283-289, 1998.
- Korogi Y, Takahashi M, Mabuchi N: Intracranial aneury- sms: diagnostic accuracy of MR angiography with evalua- tion of maximum intensity projection and surce images. Ra- diology 199:199-207, 1996.
- Korogi Y, Takahaski M, Nakagawa T et al.: Intracranial va- scular stenosis and occlusion: MR angiography findings. AJNR 18:135-143, 1997.
- Levy C, Laissy JP, Raveau V: Carotid and vertebral artery dissections: three dimensional time of fligth MR angio- graphy and MR versus conventional angiography. Radio- logy 190:97-103, 1994.
- Levy RA, Prince MR: Arterial-phase three-dimensional contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the carotid arteries. AJR 167:211-215, 1996.
- Litt AW, Eidelman EM, Pinto RS et al.: Diagnosis of caro- tid artery stenosis: comparison of 2D time of fligth MR an- giography with contrast angiography in 50 patients. AJNR 12:149-154, 1991.
- Mathews VP, Elster AD, King JC et al: Combined effects of magnetization transfer and gadolinium in cranial MR ima- ging and MRA. AJR 164:167-172, 1995.
- Mattle HP, Wentz KU et al: Cerebral venography with MR. Radiology 178:453-458, 1991.
- Mohr JP, Biller J, Hilal SK et al: Magnetic resonance ima- ging in acute stroke. Stroke 26:807-812, 1995.
- Parker DL, Blatter DD: Multiple thin slab magnetic reso- nance angiography. Neuroimag Clin North AM 2:677-692, 1992.
- Provenzale JM: Dissection of the internal carotid and ver- tebral arteries: imaging features. AJR 165:1099-1104, 1995.
- Prince MR, Grist TM, Bebatin JE et al: 3D contrast MR an- giography. Springer-Verlag (New-York) 1997.
- Ruggeri PM, Poulos N, Masaryk TJ et al: Occult intracra- nial aneurysms in polycystic kidney disease: screening with MR angiography. Radiology 191:33-39, 1994.
- Sardanelli F, Zandrino F et al: MR angiography of internal- carotid arteries:breath-hold gd-enhanced 3D fast imaging with steady-state precession versus unenhanced 2D and 3D time-of-fligth techniques. J Cat 23:208-215, 1999.
- Scarabino T, Carriero A et al: MR angiography in carotid stenosis: a comparison of three techniques. Eur J Radiol 28:117-125, 1998.
- Sorensen AG, Buonanno FS, Gonzales RG et al: Hypera- cute stroke: evaluation with combined multisection diffu- sion-weighted and hemodynamically weighted echoplanar MR imaging. Radiology 199:991-401, 1996.
- Stock KW, Wetzel S, Kirsch E et al: Anatomic evaluation of the circle of Willis: MR angiography versus intraarte- rial digital subtraction angiography. AJNR 17:1495-1499, 1996.
- Warach S, Gaa J et al: Acute human stroke studied by who- le brain echo planar diffusion-weithted magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 37:231-241, 1995.
- Borgey WM, Demasi RJ, Tripp MD, et al: Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for subclavian artery stenosis. The American Surgeon 60: 103-106, 1994.
- Bozzao L, Fantozzi LM, Bastianello S et al: Ischaemic su- pratentorial stroke: angiographic findings in patients exa- mined in the very early phase. J Neurol. 236: 340-342, 1989.
- Edwards MT, Murphy MM, Geraghty JJ et al: Intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke in a com- munity hospital. AJNR 20: 1682-1687, 1999.
- Elliot JP, Newell DW, Lam DJ et al: Comparison of balloon angioplasty and papaverine infusion for the treatment of vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrha- ge. J Neurosurg 88: 277-284, 1998.
- Florio F, Balzano S, Nardella M et al: Terapia translumina- le delle lesioni stenosanti dei tronchi epiaortici. Radiol. Med 86, 302-307, 1993.
- Florio F, D'Angelo V, Nardella M et al: Displasia fibromu- scolare dell'arteria carotide interna: angioplastica percuta- nea. Radiol. Med 84, 796-801, 1992.
- Gonner F, Remonda L, Mattle H et al: Local intra-arterial thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 29: 1894- 1900,1998.
- Grzyska U, Freitag J, Zeumer H: Selective cerebral intraar- terial DSA. Complication rate and control of risk factors. Neuroradiology 32: 296-299, 1990.
- Guglielmi G, Vinuela F: Intracranial aneurysms Guglielmi electrothrombotic coils. Neurosurg. Clinics North America 3: 427-435, 1994.
- Henry M, Amor M, Henrry I et al: Percutaneous translu- minal angioplasty of the subclavian arteries. In: Tenth in- ternational course book of peripheral vascular intervention. Europa Edition. Paris, pp. 617-627, 1999.
- Henry M, Amor M, Henry I et al: Angioplasty and Stenting of the Extracranial Carotid Arteries. In: Carotid angiopla- sty and stenting. ISCAT ed. Europea pp. 267-280, 1998.
- Higashida RT, Tsai FY, Halbach VV et al: Transluminal an- gioplasty for atherosclerotic disease of the vertebral and ba- silar arteries. J Neurosurg 78: 192-198, 1993.
- Livigstone K et al: Intraarterial papaverine as on adjunct to transluminal angioplasty for vasospasm induced by subara- chnoid haemorrage. AJNR 14: 346-347,1993.
- Milburn JM, Moran CJ, Cross DT et al: Effect of intraarte- rial papaverine on cerebral circulation time. AJNR 18: 1081-1085, 1997.
- Moret J, Boulin A, Castaings L: Endovascular treatment of berry aneurysms by endosaccular occlusion. In: Nacci G, Scialfa G: Atti 3°meeting neuroradiologico potentino: Neuroradiologia terapeutica, pp. 10-14, Ed. C.S.E. Potenza 1991.
- Murayama Y, Vinuela F, Duckwiler GR: Embolization of incidental cerebral aneurysms by using the Guglielmi deta- chable coil system. J Neurosurg 90: 207-214, 1999.
- Polin RS, Coenen VA, Hansen CA: Efficacy of transluminal angioplasty for the management of symptomatic cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrha- ge. J Neurosurg 92: 284-290, 2000.
- Redfern RM, Zygmunt S, Pickard JD et al: The natural hi- story of subarachnoid haemorrhage with negative angio- graphy: a prospectie study and 3 year follow-up. Br J Neu- rosurg 2: 33-41, 1998.
- Sivaguru A, Venables GS, Beard JD et al: European carotid angioplasty trial. J Endovasc Surg 3: 16-20, 1996.
- Smith TP: Radiologic intervention in the acute stroke pa- tient. J Vasc Intervent Radiol 7: 627-40, 1996.
- Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Mawad M: Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of acute intracranial aneurysm: periope- rative anatomical and clinical outcome in 403 patients. J Neurosurg 86:475-482, 1997.
- Zeumer H, Freitag HJ, Grzyska U et al: Local intraarterial fibrinolysis in acute vertebrobasilar occclusion. Neurora- diology 31: 336-340, 1989 REFERENCES
- Frankowski RF, Annegers JF, Whitman S. Epidemiological and descriptive studies. Part I: The descriptive epidemio- logy of head trauma in the United States. In: Becker DP, Polishock J, eds. Central Nervous System Trauma Status Report. Bethesda, MD National Institute of Health, 33-51, 1985.
- French BN, Dublin AB: The value of computerized tomo- graphy in the management of 1000 consecutive head inju- ries. Surg Neurol 7:171-183, 1977.
- Gentry LR, Godersky JC, Thompson BH: Prognosis after severe head injury: MRI correlation with Glasgow outco- me scale. (Submitted).
- Gentry LR: Head trauma. In: Atlas SW:Magnetic resonan- ce of the brain and spine.(2 nd ed.), Lippincott-Raven, Phi- ladelphia, pp. 611-647, 1996.
- Gentry LR: Imaging of closed head injury. Radiology 191:1-17, 1994.
- Grumme T, Kluge W, Kretzschmar K et al: Head Trauma. In: Cerebral and spinal computed tomography. Blackwell Science, Berlin pp. 49-69, 1998.
- Johnson MH, Lee SH: Computed tomography of acute ce- rebral trauma. Radiol Clin N Am 30:325-352, 1992.
- Kanal E, Shellock FG: Patient monitoring during clinical MR imaging. Radiology; 185:623-629, 1992.
- Keskil S, Baykaner K, Ceviker N et al: Clinical significan- ce of acute traumatic intracranial pneumocephalus. Neu- rosurg Rev. 21(1):10-3, 1998.
- Klufas RA, Hsu L, Patel MR: Unusual manifestations of head trauma. AJR 166:675-681, 1996.
- Kuntz R, Skalej M, Stefanou A: Image quality of spiral CT versus conventional CT in routine brain imaging. Eur J Ra- diol. 26(3):235-40, 1998.
- Lanksch W, Grumme T, Kazner E: Computed tomography in head injuries Springer, Berlin, 1979.
- Lee TT, Aldana PR, Kirton OC et al: Follow-up computeri- zed tomography (CT) scans in moderate and severe head injuries: correlation with Glasgow Coma Scores (GCS), and complication rate. Acta Neurochir Wien. 139(11):1042-7; discussion 1047-8, 1997.
- Leidner B, Adiels M, Aspelin P et al: Standardized CT exa- mination of the multitraumatized patient. Eur Radiol. 8(9):1630-8, 1998.
- Lloyd DA, Carty H, Patterson M et al: Predictive value of skull radiography for intracranial injury in children with blunt head injury. Lancet. 22; 349(9055):821-4, 1997
- Macpherson BCM, Macpherson P, Jennett B: CT inciden- ce of intracranial contusion and hematoma in relation to the presence, site and type of skull fracture. Clin Radiology 42:321-326, 1990.
- Mogbo KI, Slovis TL, Canady AI et al: Appropriate ima- ging in children with skull fractures and suspicion of abu- se. Radiology. 208(2):521-4, 1998.
- Mohanty SK, Thompson W, Rakower S: Are CT scan for head injury patients always necessary? J Trauma 31:801- 805, 1991.
- Nagy KK, Joseph KT, Krosner SM et al: The utility of head computed tomography after minimal head injury. J Trau- ma. 46(2):268-70, 1999.
- Osborn A: Craniocerebral trauma. In Osborn A: Diagno- stic neuroradiology. St Louis, pp 199-247, 1994.
- Parizel PM, Ozsarlak P, Van-Goethem JW et al: Imaging findings in diffuse axonal injury after closed head trauma. Eur Radiol. 8(6):960-5, 1998.
- Pellicanò G, Bartolozzi A: La TC nei traumi cranioencefa- lici. Edizioni del Centauro, Udine,1996.
- Petitti N, Williams DW 3 rd : CT and MR imaging of nonacci- dental pediatric head trauma. Acad Radiol. 5(3):215-23, 1998.
- Rhea JT, Rao PM, Novelline RA: Helical CT and three-di- mensional CT of facial and orbital injury. Radiol Clin North Am 37:489-513, 1999.
- Shane SA, Fuchs SM: Skull fractures in infants and pre- dictors of associated intracranial injury. Pediatr Emerg Ca- re. 13(3):198-203, 1997.
- Snoek J, Jennet B, Adams JH: Computerized tomography after recent severe head injury in patients without acute in- tracranial hematoma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 42:215- 225, 1979.
- Stein SC, Ross SE: The value of computed tomographic scans in patients with low-risk head injuries. Neurosurgery 26:638-640, 1990.
- Teasdale G, JennettB: Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness: a practical scale. Lancet 2:81-84, 1974.
- Weisberg L., Nice C.: Cerebral computed tomography. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 321-343, 1989.
- Williams DH, Levin HS, Eisenberg HM: Mild head injury classification. Neurosurgery, 27:422-428, 1990.
- Wilson AJ: Gunshot injuries: what does a radiologist need to know? Radiographics 19:1358-1368, 1999.
- Wysoki MG, Nassar CJ, Koenigsberg RA et al: Head trau- ma: CT scan interpretation by radiology residents versus staff radiologists. Radiology. 208(1): 125-8, 1998.
- Zee CS, Go JL: CT of head trauma. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 8(3): 525-39, 1998. REFERENCES
- Bahner ML, Reith W, Zuna I et al: Spiral CT vs incremen- tal CT: is spiral CT superior in imaging of the brain? Eur Radiol. 8(3): 416-20, 1998.
- Frankowski RF, Annegers JF, Whitman S: Epidemiological and descriptive studies. Part I: The descriptive epidemiology of head trauma in the United States. In: Becker DP, Poli- shock J, eds. Central Nervous System Trauma Status Report. Bethesda, MD National Institute of Health, 33-51, 1985.
- Gentry LR: Head trauma. In: Atlas SW:Magnetic resonan- ce of the brain and spine.(2 nd ed.), Lippincott-Raven, Phi- ladelphia, pp 611-647, 1996.
- Gentry LR: Imaging of closed head injury. Radiology 191:1-17, 1994.
- Grumme T, Kluge W, Kretzschmar K et al: Head trauma. In: Cerebral and spinal computed tomography. Blackwell Science, Berlin pp 49-69, 1998.
- Hymel KP, Rumack CM, Hay TC et al: Comparison of in- tracranial computed tomographic (CT) findings in pedia- tric abusive and accidental head trauma. Pediatr Radiol. 27(9):743-7, 1997.
- Johnson MH, Lee SH: Computed tomography of acute ce- rebral trauma. Radiol Clin N Am 30:325-352, 1992.
- Keskil S, Baykaner K, Ceviker N et al: Clinical significan- ce of acute traumatic intracranial pneumocephalus. Neu- rosurg Rev. 21(1):10-3, 1998.
- Klufas RA, Hsu L, Patel MR: Unusual manifestations of head trauma. AJR 166:675-681, 1996.
- Kuntz R, Skalej M, Stefanou A: Image quality of spiral CT versus conventional CT in routine brain imaging. Eur J Ra- diol. 26(3): 235-40, 1998.
- Lanksch W, Grumme T, Kazner E: Computed tomography in head injuries Springer, Berlin, 1979.
- Lee SH, Rao KL: Cranial computed tomography. MC Graw-Hill, New York, 1983.
- Lee TT, Aldana PR, Kirton OC et al: Follow-up compute- rized tomography (CT) scans in moderate and severe head injuries: correlation with Glasgow Coma Scores (GCS) and complication rate. Acta Neurochir Wien. 139(11): 1042-7; discussion 1047-8, 1997.
- Leidner B, Adiels M, Aspelin P et al: Standardized CT examination of the multitraumatized patient. Eur Radiol. 8(9):1630-8, 1998.
- Lerner C: Detecting acute extraaxial blood with bone al- gorithm CT images. AJR 17:1707, 1998.
- Lloyd DA, Carty H, Patterson M et al: Predictive value of skull radiography for intracranial injury in children with blunt head injury. Lancet. 22; 349(9055): 821-4, 1997.
- Mogbo KI, Slovis TL, Canady AI et al: Appropriate ima- ging in children with skull fractures and suspicion of abu- se. Radiology. 208(2): 521-4, 1998.
- Nagurney JT, Borczuk P, Thomas SH: Elderly patients with closed head trauma after a fall: mechanisms and out- comes. J Emerg Med. 16(5): 709-13, 1998.
- Nagy KK, Joseph KT, Krosner SM et al: The utility of head computed tomography after minimal head injury. J Trau- ma. 46(2): 268-70, 1999.
- Osborn A: Craniocerebral trauma. In Osborn A: Diagno- stic neuroradiology. St Louis, pp 199-247, 1994.
- Parizel PM, Ozsarlak P, Van-Goethem JW et al: Imaging findings in diffuse axonal injury after closed head trauma. Eur Radiol. 8(6): 960-5, 1998.
- Pellicanò G, Bartolozzi A: La TC nei traumi cranioencefa- lici. Edizioni del Centauro, Udine ,1996.
- Petitti N, Williams DW 3 rd : CT and MR imaging of no- naccidental pediatric head trauma. Acad Radiol. 5(3): 215- 23, 1998.
- Rhea JT, Rao PM, Novelline RA: Helical CT and three-di- mensional CT of facial and orbital injury. Radiol Clin North Am 37:489-513, 1999.
- Shane SA, Fuchs SM: Skull fractures in infants and pre- dictors of associated intracranial injury. Pediatr Emerg Ca- re. 13(3):198-203, 1997.
- Weisberg L., Nice C: Cerebral computed tomography. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 321-343, 1989.
- Wilson AJ: Gunshot injuries: what does a radiologist need to know? Radiographics 19:1358-1368, 1999.
- Wysoki MG, Nassar CJ, Koenigsberg RA et al: Head trau- ma: CT scan interpretation by radiology residents versus staff radiologists. Radiology. 208(1):125-8, 1998.
- Zee CS, Go JL: CT of head trauma. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. Aug; 8(3):525-39, 1998.
- Atlas SW, Mark AS, Grossman RI et al: Intracranial he- morrhage gradient-echo MR imaging at 1.5 T. Comparison with spin-echo imaging and clinical applications. Radio- logy 168:803-807, 1988.
- Cirillo S, Simonetti L, Di Salle F et al: La RM in ematolo- gia con particolare riguardo all'emorragia intracranica. In: Trattato delle malattie del sangue. Ed. P. Larizza pp. 563- 568. Piccin, Padova, 1990.
- Cirillo S, Simonetti L, Di Salle F et al: La RM nell'emorra- gia sub-aracnoidea: Parte 2, studio in vivo. Rivista di Neu- roradiologia, 2:219-225, 1989.
- Cirillo S, Simonetti L, Elefante R et al: La RM nell'emor- ragia sub-aracnoidea: Parte 1, studio in vitro. Rivista di Neuroradiologia, 2:211-217, 1989.
- Elefante R, Cirillo S, Simonetti L et al: Confronto TC ed RM in patologia encefalica. In: La TC in Neuroradiologia, Microart's, Genova pp. 169-174, 1991.
- Espagno J, Manelfe C, Bonsique JY et al: Interet et valeur prognostique de la TDM en traumatologie cranio-cerebra- le. J Neuroradiol 7:121-32, 1980.
- Espagno J, Tremoulet M, Espagno C: The prognosis of brainstem lesions in patients with recent head injuries. J Neurosurg Sci 20:33-50, 1976.
- Fohlen ES, Grossman RI, Atlas SW et al: MR characteri- stics of subdural hematomas and hygromas at 1.5 T. Am J Neuroradiol 10:687-693, 1989.
- Gallucci M, Bozzao A, Maurizi Enrici R: La Risonanza Magnetica nei traumi acuti. In: Pellicanò G, Bartolozzi A (eds): La TC nei traumi cranio-encefalici. Ed. del Centau- ro, Udine, pp. 129-153, 1996.
- Gentry LR, Godersky JC, Thompson B et al: Prospective comparative study of intermediate-field MR and CT in the evaluation of closed head trauma. Am J Neuroradiol 9:91- 100, 1985.
- Gentry LR: Head trauma. In: Atlas S.W. Magnetic Reso- nance imaging fo the brain and spine. Lippincott Raven Press, Philadelphia 661-647, 1996.
- Gentry LR: Imaging of closed head injury. Radiology 191:1-17, 1994.
- Gentry LR, Godersky JC, Thompson B: MR imaging of head trauma: review of distribution and radiopathologic feature of traumatic lesions. Am J. Neuroradiol 9:101-110, 1985.
- Gallucci M, Splendiani A, Bozzao A: Valutazione compa- rata RM-TC nel traumatizzato cranico. Eido Electa, 11-21, 1985.
- Hesselink JR, Dowel CF, Healy ME et al: MR imaging of brain contusions: a comparative study with CT. Am J Neu- roradiol 9:269-278, 1985.
- Kelly AB, Zimmerman RD, Snow RB et al: Head trauma: comparison of MR and CT-experience in 100 patients. AJNR 9:269-78, 1988.
- Lanksch W, Grumne T, Kazner E: Correlation between cli- nical symptoms and CT findings in closed head injuries. In: Frowein, Wilcke, Karini (eds): Advances in neurosurgery Vol 5: Head injuries. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 27-29, 1975.
- Levin HS, Amparo E, Eisemberg HM et al: MR and CT in relation to the neurobehavioral sequelae of mild and mo- derate head injuries. J Neurosurg 6:706-713, 1987.
- Ogawa T, Sekino H: Comparative study of MR and CT scan in cases of severe head injury. Acta Neurochir 55:8- 10, 1992.
- Orlandi B, Cardone G, Minio Paluello GB et al: Sequenze standard e sequenze veloci: bilancio di utilità su fantoccio ed in vivo. In: Neuroradiologia 1995, a cura di L. Bozzao. Ed del Centauro, Udine, 161-166, 1995.
- Osborn AG: Diagnostic Neuroradiology. Mosby Year Book, St. Louis 1994. Cap. 8.
- Passariello R: Elementi di tecnologia in radiologia e dia- gnostica per immagini. Cromac, Roma 1990.
- Pierallini A, Pantano P, Zylberman R et al: Valutazione RM con sequenze FLAIR e FFE del carico lesionale in pazien- ti affetti da gravi traumi cranici chiusi. Rivista di Neurora- diologia 10:57-60, 1997.
- Piovan E, Beltramello A, Alessandrini F et al: La Risonan- za Magnetica nei traumi sub-acuti e cronici. In: Pellicanò G, Bartolozzi A (eds): La TC nei traumi cranio-encefalici. Ed. del Centauro, 153-171, Udine 1996.
- Scotti G, Pieralli S, Righi C et al: Manuale di neuroradio- logia diagnostica e terapeutica.
- Sklar EM, Quencer RM: MR application in cerebral injury. RCNA 30(2):353-56, 1992.
- Splendiani A, Gallucci M, Bozzao A et al: Ruolo della Ri- sonanza Magnetica nello studio dei traumi cranici acuti e cronici: studio comparativo con tomografia computerizza- ta. In: Pardatscher K.: Neuroradiologia 1989. Ed. del Cen- tauro, Udine 1989.
- Yoon HC, Lufkin RS, Vinuela F et al: MR of acute suba- rachnoid hemorrhage. Am J Neuroradiol 9:404-5, 1988.
- Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk L, Gennarelli T et al: Cranial CT in the diagnosis and management of acute head trau- ma. Am J Radiol 131:27-34, 1975.
- Zimmerman RD, Heier LA, Snow RB et al: Acute intra- cranial hemorrage. Intensity changes on sequential MR scans at 0.5 T. Am J Neuroradiol 9:47-57, 1985. REFERENCES
- Beirne JC, Butler PE, Brady FA: Cervical spine injuries in patients with facial fractures: a 1-year prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofa Surg, 24(1 Pt):26-29, 1995.
- Buitrago-Tellez CH, Wachter R, Ferstl F et al: 3-D CT for the demonstration of findings in compound skull injuries. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr, 160(2):106-112, 1994.
- Gentry LR, Manor WF, Turski PA et al: High-resolution CT analysis of facial struts in trauma: 2. Osseous and soft- tissue complications. AJR , 140(3):533-541, 1983.
- Kassel EE, Noyek AM, Cooper PW: CT in facial trauma. J Otolaryngol, 12(1):2-15, 1983.
- Kirshenbaum KJ, Nadimpalli SR, Fantus R et al: Unsuspected upper cervical spine fractures associated with significant head trauma: role of CT. J Emerg Med, 8(2):183-198, 1990.
- Mauriello JA Jr, Lee HJ, Nguyen L: CT of soft tissue injury and orbital fractures. Radiol Clin North Am, 37(1):241- 252, 1999.
- Maya MM, Heier LA: Orbital CT. Current use in the MR era. Neuroimaging Clin N Am, 8(3):651-683, 1998.
- Novelline RA, Rhea JT, Rao PM et al: Helical CT in emer- gency radiology. Radiology, 213(2):321-339, 1999.
- Nunez DB Jr, Zuluaga A, Fuentes-Bernardo DA et al: Cervi- cal spine trauma: how much more do we learn by routinely using helical CT? Radiographics, 16(6):1307-1318, 1996.
- Perugini S, Bonetti MG, Ghirlanda S et al: Technical note: CT scout views of the cervical spine in severely head-inju- red patients. Skeletal Radiol, 25:247-249, 1996
- Rhea JT, Rao PM, Novelline RA. Helical CT and three-di- mensional CT of facial and orbital injury. Radiol Clin North Am, 37(3):489-513, 1999.
- Thai KN, Hummel RP 3 rd , Kitzmiller WJ et al: The role of computed tomographic scanning in the management of facial trauma. J Trauma, 43(2):214-217, 1997. REFERENCES
- Butler AB, McLone DG: Hydrocephalus. In Grossmann, Hamilton eds.: Principles of Neurosurgery, pp. 165-177. Raven Press, New York, 1991.
- De Myer W: Tecnica dell'esame neurologico, pp. 415-429. Piccin ed., Padova, 1980.
- Duus P: Diagnosi di sede in Neurologia. Casa ed. Am- brosiana, pp. 337-353, Milano, 1988.
- Langfitt TW, Weinstein JD, Kassel NF et al: Trasmission of increased intracranial pressure. I. Within craniospinal axis. J Neurosurg. 21:989-997, 1964.
- Lundberg N: Continuous recording and control of ventric- ular fluid pressure in neurosurgical practice. Acta Psychiat. Scand. 36 (S 149):1-193, 1960.
- Mascalchi M, Ciraolo L, Tanfani G et al.: Cardiac-gated phase MR imaging of aqueductal CSF flow. J. C.A.T. 12:923-926, 1988.
- Pagni CA: Lezioni di neurochirurgia. Cap. 13: Fisiopatologia e clinica della sindrome di ipertensione endocranica nei tumori cerebrali, pp. 203-214. Ed. Libreria Cortina, Torino, 1978.
- Pagni CA: Lezioni di neurochirurgia. Cap. 11: L'idrocefalo, pp. 161-196. Ed. Libreria Cortina, Torino, 1978.
- Papo I: Ruolo dell'ipertensione endocranica nella patoge- nesi del coma cerebrale traumatico. In Papo, Cohadon, Massarotti eds: Le coma traumatique, pp. 111-127. Liviana ed., Padova, 1986.
- Pollock LJ, Boshes B: Cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 36:931-974, 1936.
- Rao KCVG: The CSF spaces (Hydrocephalus and Atro- phy). In Lee, Rao, Zimmermann eds.: Cranial MRI and CT. 3rd ed., pp. 227-294, McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York, 1992.
- Staab EV: Radionuclide cisternography. In Freeman, John- son eds.: Clinical radionuclide imaging, pp. 679-703. Grune and Stratton, New York, 1986.
- Weisberg L, Nice C: Cerebral computed tomography. A text atlas. Cap. 13: Increased intracranial pressure, pp. 241- 253. 3rd ed. W.B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, 1989. REFERENCES
- Atlas SW, Grossman RI, Gomori JM: Hemorragic intracra- nial malignant neoplasms: spin-echo MR imaging. Radiol 164:71, 1987.
- Atlas SW: MRI of the brain and spine. Spell Checking, The- saurus and Dictionaries, 1994.
- Bayston R: Hydrocephalus shunt infection. Chapman and Hall Medical, London, 1989.
- Blinkov SM, Smirnov NA: Brain displacements and defor- mations. Plenum Press, New York-London, 1971.
- Cittadini G: Manuale di Radiologia clinica, 2nd. ECIG, Ge- nova, 1983.
- Davis JM, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT: Metastases to the central nervous system. Radiol Clin North Am 20:417, 1982.
- Destian S, Sze G, Krol G et al: MR imaging of hemorragic intracranial neoplasms. AJNR 9:1115, 1988.
- Gatenby RA, Coia LR, Richter MP: Oxygen tension in hu- man tumors: in vivo mapping using CT-guided probes. Ra- diology 156:211, 1985.
- Horwit NH, Rizzoli HV: Postoperative complications in in- tracranial neurological surgery. Williams and Wilkins, Bal- timore-London, 1982.
- Leeds NE, Elkin CM, Zimmerman RD: Gliomas of the brain. Semin Roentgenol 19:27, 1984.
- Little JR, Dial B, Belanger G, et al: Brain hemorrhage from intracranial tumor. Stroke 10:283, 1979.
- Mandybur TI: Intracranial hemorrhage caused by metasta- tic tumors. Neurology 27:650, 1977.
- Marano P: Diagnostica per immagini, II vol. Casa Editrice Ambrosiana, Milano, 1994.
- Neill JM: Studies on the oxidation-reduction of hemoglo- bin and methemoglobin. III. The formation of methemo- globin during the oxidation of autooxidizable substances. J Exper Med 41:551, 1925.
- Neill JM: Studies on the oxidation-reduction of hemoglo- bin and methemoglobin. IV. The inhibition of spontaneous methemoglobin. J Exper Med 41:561, 1925.
- Osborne AG: Diagnostic Neuroradiology. Mosby Year Book, Inc, 1994.
- Pagni CA: Lezioni di neurochirurgia. Edizioni Libreria Cortina, Torino, 1984.
- Potts DG, Abbott OF, von Sneidern JV: National Cancer Institute Study: evaluation of computed tomography in the diagnosis of intracranial neoplasms. III. Metastatic tumors. Radiol 136:657, 1980.
- Russel DS, Rubinstein LJ: Pathology of tumors of the ner- vous system, 5th ed. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore-Lon- don, 1989.
- Scott M: Spontaneous intracerebral hematoma caused by cerebral neoplasm: report of eight verified cases. J Neuro- surg 42:338, 1975.
- Sze G, Krol G, Olson WL et al: Hemorragic neoplasms: MRI mimics of occult vascular malformations. Am J Radiol 149:1223, 1987.
- Zimmerman H: The pathology of primary brain tumors. Se- min Roentgenol 19:129, 1984.
- Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT: Computed tomography of acute intratumoral hemorrhage. Radiol 135:355, 1980.
- Zulch KJ: Brain Tumors. Their Biology and Pathology, 3rd ed. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1986.
- Brant-Zawadki M, Gould R et al: Lane B.: Digital sub- traction cerebral angiography by intrarterial injection: comparison with conventional angiography. AJR 140, 347- 353, 1983.
- Chilcote WA, Modic MT, Pavlicek WA et al.: Digital sub- traction angiography of the carotid arteries: a comparative study in 100 patients. Radiology 130, 287-295, 1981.
- Davis PC, Hoffman JC: Intraarterial digital subtraction an- giography: evaluation in 150 patients. Radiology 148, 9-15, 1983.
- Kelly W, Brant-Zawadzki M, Pitts LH: Arterial injection-di- gital subtraction angiography. J. Neurosurg. 58, 851-856, 1983.
- Leeds NE, Rosenblatt R: Arterial wall irregularities in intra- cranial neoplams: the shaggy vessel brought into focus. Ra- diology 103, 121-124, 1972.
- Modic MT, Weinstein MA, Chilcote WA et al.: Digital sub- traction angiography of the intracranial vascular system: comparative study in 55 patients. AJR 138, 299-306, 1982.
- Newton TH, Potts DG: Radiology of the skull and brain: angiography. Volume two/book 4. The CV Mosby Com- pany Saint Louis 1974.
- Weinstein MA, Pavlicek WA, Modic MT et al: Intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography of the head and neck. Ra- diology 147, 717-724, 1983.
- Antunez E, Estruch R, Cardenal C: Usefulness of CT and MR imaging in the diagnosis of acute Wernicke's encepha- lopathy. AJR 171:1131-37; 1998.
- Bracard S, Claude D et al: Computerized tomography and MRI in Marchiafava-Bignami disease. J Neuroradiol 13:87- 94; 1986.
- Brunner JE, Redmond JM et al: Central pontine myeli- nolysis and pontine lesions after rapid correction of hypo- natremia: a prospective MRI study. Ann Neurol 27:61-7; 1990.
- Chang KH, Cha SH et al: Marchiafava Bignami disease: se- rial changes in corpus callossum on MRI. Neuroradiology 34:480-2; 1992.
- Debaere C, Stadnik T, De Maeseneer M: Diffusion-weigh- ted MRI in cyclosporin A neurotoxicity for the classifica- tion of cerebral edema. Eur Radiol 9(9):1916-8; 1999.
- Dietrich RB, Bradley WG: Iron accumulation in the basal ganglia following severe ischemic-anossic insult in chil- dren. Radiology 168:203-6; 1988.
- Diez-Tejedor E, Frank A, Gutierrez M et al: Encephalo- pathy and biopsy-proven cerebrovascular inflammatory changes in a cocaine abuser. Eur J Neurol 5(1):103-7; 1998.
- Donnal JF, Heinz ER, Burger PC: MR of reversible thala- mic lesions in Wernicke syndrome. AJNR 11:893-5; 1990
- Fazio C, Loeb C: Neurologia, Società Editrice Universo, Roma, 1994.
- Gallucci M, Amicarelli I, Rossi A et al: MR imaging of whi- te matter lesions in uncomplicated chronic alcoholism, J Comp Asst Tomogr 13:395-398, 1989.
- Gallucci M, Bozzao A, Splendiani A et al: Wernicke en- cephalopathy: MR findings in five patients, AJNR 11:887- 892, 1990.
- Gallucci M, Caulo M et al: L'encefalopatia alcolica. Atti Meeting Scienze Neurologiche. Selva di Val Gardena, 1999.
- Genevresse I, Dietzman A et al: Subacute encephalopathy after combination chemotherapy including moderate-dose methotrexate in a patient with gastric cancer. Anticancer Drug 10(3):293-4; 1999.
- Horowitz AL, Kaplan R: Carbon monoxide toxicity: MR imaging in the brain. Radiology 162:787-8; 1987.
- Ikeda M, Tsukagoshi H: Encephalopathy due to toluene sniffing. Report of a case with Magnetic Resonance Ima- ging. Eur Neurol 30(6):347-9; 1990.
- Jansen O, Krieger D et al: Cortical hyperintesity on proton density-weighted images: an MR sign of cyclosporine-rela- ted encephalopathy. AJNR 17(2):337-44; 1996.
- Kubo M, Azuma E, Arai S et al: Transient encephalopathy following a single exposure of high-dose methotrexate in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 9(2):157-65; 1992.
- Laubenberger J, Schneider B, Ansorge O et al: Central pontine myelinolysis: clinical presentation and radiologic findings. Eur. Radiol. 6:177-83; 1996.
- Lohr JW: Osmotic demyelination syndrome following cor- rection of hyponatremia: association with hypokalemia. Am J Med 96:408-12; 1994.
- Lovblad K, Kelkar P et al: Pure methotrexate encephalo- pathy presenting with seizures: CT and MRI features. Pe- diatr Radiol 28(2):86-91; 1998.
- Maschke M, Fehlings T, Kastrup O et al: Toxic leukoen- cephalopathy after intravenous consumption of heroine and cocaine with unexpected clinical recovery. J Neurol 246(9):850-1; 1999.
- Mayer JW, De Liége P, Netter JM: Computerized tomo- graphy and nuclear magnetic resonance in Marchiafava-Bi- gnami disease. J Neuroradiol 14:152-8; 1987.
- Osborne AG: Diagnostic Neuroradiology. Mosby ed. St. Louis, Missouri, 1992.
- Schwartz BR, Bravo MS, Klufas RA et al: Cyclosporine neu- rotoxicity and its relationship to hipertensive encephalopathy: CT and MR findings in 16 cases. AJR 165:627-31; 1995.
- Shogry MEC, Curnes JT: Mamillary body enhancement on MR as the only sign of acute Wernicke encephalopathy. AJNR 15:172-4; 1994.
- Silverman CS, Brenner J et al: Hemorragic necrosis and va- scular injury in carbon monoxide poisoning: MR demon- stration. AJNR 14:168-70; 1993.
- Thuomas KA, Moller C, Odkvist LM et al: MR imaging in solvent-induced chronic toxic encephalopathy. Acta Ra- diol 37(2):177-9; 1996.
- Valk J, van der Knaap: Toxic encephalopathy. AJNR 13 (2):747-60; 1992.
- Valk J, van der Knaap MS: Magnetic resonance of myelin, myelination and myelin disorders. Springer edition 1995. REFERENCES
- Aaslid R, Lindegaard KF: Cerebral hemodynamics in tran- scranial doppler sonography. Aaslid R., Ed. Wien Springer- Verlag 60-85, 1986.
- Aaslid R, Markwalder TM, Nornes H: Noninvasive tran- scranial doppler ultrasound of flow velocity in basal cere- bral arteries. J Neurosurgery 57, 769-774, 1982.
- Ahman PA, Carrigan TA, Carlton D et al: Brain death in children: characteristics common carotid arterial velocity patterns measured with pulsed doppler ultrasound. J. Pe- diatr. 110, 723-728, 1987.
- Castillo M. et al: New techniques in MR neuroimaging. MRI Clinics of North America. Saunders 1998.
- Chan CH, Dearden MN, Miller DJ et al: Transcranial doppler waveform differencies in hyperemic and nonhyperemic pa- tients after severe head injury. Surg. Neur. 38, 433-436, 1992.
- Gean M: Head trauma. Raven Press 1994.
- Gentry LR: Current concepts in Imaging Cranio-facial trauma. Neuroimaging Clinics of North America. Decem- ber 1991.
- Grossmann RI, Younsem DM: Neuroradiology: the requi- sites. Mosby, St. Louis 1994.
- Hachinskj V, Norris JW: Ictus. Athena editrice Roma 1988.
- Masakuni Kameyama, Masanori Tomonaga, Tadashi Aiba: Ce- rebrovascular disease. Igaku-Shoin, Tokjo-New York 1988.
- Hayman LA: Nontraumatic intracranial hemorrhage. Neu- roimaging Clinic of North America 2:1, 1992.
- Kassel NF, Sasaki T, Colohan Art et al: Cerebral vasospasm following aneurismal subarachnoid hemorrage. Stroke 16, 573-581, 1985.
- Osborne A: Diagnostic neuroradiology. Mosby Year Book 1994.
- Osborne A: Handbook of Neuroradiology. Mosby Year Book 1991.
- Scarabino T, Cammisa M: Urgenze cranio-spinali: diagno- stica per immagini. Ed. Liviana 1993.
- Scotti G: Manuale di Neuroradiologia diagnostica e tera- peutica. Masson 1993.
- Seckhar L, Wechsler LR, Yonas H, et al: Value of TCD examination in the diagnosis of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrage. Neurosurg. 22, 813-821, 1988.
- Avogaro F, Zamperetti N, Pellizzari A: Studio del flusso ematico cerebrale. In: Trattato Enciclopedico di Anestesio- logia, Rianimazione e Terapia Intensiva, pp. 51-76. Piccin ed., Padova. 1991.
- Choksey MS, Costa DC, Iannotti F et al: 99mTc-HM-PAO SPECT stuclies in traumatic intracerebral haematoma. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psych. 54: 6-11, 1991.
- Costa DC, Ell PJ, Cullum ID et al: The in vivo distribution of` 99mTcHM-PAO in normal man. Nucl. Med. Com. 7: 647-652, 1986.
- Fayad PB, Brass LM: Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography in cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 26: 950- 954, 1991.
- Giubilei F, Lenzi GL, Di Piero V et al: Predictive value of brain perfusion single-photon emission computed tomo- graphy in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 21: 895-900,1990.
- Haberer JR, Hottier E: Encéphalopathies postanoxiques. Ann. Fr. Anesth. Réan. 9: 212-219, 1990.
- Manni C, Della Corte F, Rossi R et al: La perfusione ce- rebrale in Anestesia e Rianimazione. Atti XLV Congr. Naz.le SIAARTI, pp. 1117-1127, Milano 8-12 ottobre 1991.
- Obrist WD, Gennarelli TA, Segawa H et al: Relation of CBF to neurological status and outcome in head injured pa- tients. J. Neurosurg. 51: 292-297, 1979. REFERENCES
- Bonetti MG, Ciritella P, Valle G et al: 99mTc HM-PAO brain perfusion SPECT in brain death. Neuroradiology 37: 365-369, 1995.
- Bradac GB, Simon RS: Angiography in brain death. Neu- roradiology 7: 25-28, 1974.
- Ducrocq X, Braun M, Debouverie M et al: Brain death and transcranial Doppler: experience in 130 cases of brain death patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 160: 41 -46, 1998.
- Dupas B, Gayet-Delacroix M, Villers D et al: Diagnosis of brain death using two-phase spiral CT. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 19: 641-647, 1998.
- Eelco FM, Wijdicks MD: The diagnosi of brain death. N. Engl. J. Med. Vol. 344, 16: 1215-1221, 2001.
- Facco E, Zucchetta P, Munari M et al: 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT in the diagnosis of brain death.death. Intensive Ca- re Med. 24: 911-917, 1998.
- Flowers WM Jr., Patel BR: Radionuclide angiography as a confirmatory test for brain death: a review of 229 studies in 219 patients. South Med. J. 90: 1091-1096, 1997.
- Hadani M, Bruk B, Ram Z et al: Application of transcranial doppler ultrasonographv for the diagnosis of brain death. Intensive Care Med. 25: 822-828, 1999.
- Heiskanen O: Cerebral circulatory arrest caused by acute increase of intracranial pressure. Acta Neurol. Scand. 40: 7- 59, 1964.
- Johnson DW, Warren AS, et al.: Stable Xenon CT Cerebral Blood Flow Imaging: Rationale for and Role in Clinical De- cision Making. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 12: 201-213, 1991.
- Karantanas AH, Hadjigeorgion GM, Paterakis K: Contri- bution of MRI and MR angiography in early diagnosis of brain death. Eur. Radiol. 12 (11): 1210-6, 2002.
- Kendall MJ, Patrick PB: MR diagnosis of Brain Death. Am. J. Neuradiol. 13: 65-66, 1992.
- Kornig M, Kraus M, et al.: Quantitative Assessment of the Ischemic Brain by means of Perfusion-Related Parameters Derived from Perfusion CT. Stroke 32: 431-437, 2001.
- McL. Black P: Brain Death. N. Eng. J. Med. 299: 338-344, 393-401, 1978.
- Norme per l'accertamento e la certificazione di morte. Leg- ge 29 dicembre 1993. n. 578. Gazzetta Ufficiale della Re- pubblica Italiana, Serie generale -n. 5, of 8/1/94, pp. 4-5.
- Pellizzari A, Digito A, Pellegrin C et al: Accertainento di morte cerebrale: aspetti clinici. In Atti del 19°Corso Na- zionale di Aggiornamento in Rianimazione e Terapia Inten- siva, pp. 11-26. Piccin ed., Padova, 1990.
- Pistoia F, Johnson DW, et al.: The role of Xenon CT mea- surements of cerebral blood flow in the clinical determina- tion of brain death. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 12: 97-103, 1991.
- Regolamento recante le modalità per l'accertamento e la certificazione di morte. Decreto del Ministero della Sanità 22 agosto 1994, n. 582. Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana, Serie generale -n. 245, of 19/10/94, pp. 4-7.
- Reid RH, Gulenchyn KY, Ballinger JR: Clinical use of Te- chnetium-99m I IM-PAO for Determination of Brain Death. J. Nucl. Med. 30: 1621-1626, 1989.
- Salvolini U, Montesi A: Diagnostica angiografica di morte ce- rebrale. Annali Italiani di Chirurgia XLVII: 88-98, 1971-72.
- Yoshikai T, Tahara T, Kuroiwa T et al: Plain CT findings of brain death confirmed by hollow skull sign in brain perfu- sion SPECT. Radiat. Med. 15: 419-424, 1997. REFERENCES
- Barron JT: Lumbar pseudomeningocele. Orthopedics 13:608-609, 1990.
- Bejjani GK, Duong DH, Kalamarides M et al: Cerebral va- sospasm after tumor resection. A case report. Neurochirur- gie 43 (3):164-8, 1997.
- Bejjani GK, Sekhar LN, Yost AM et al: Vasospasm after cranial base tumor resection:pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy. Surg Neurol 52(6):577-84, 1999.
- Bell GR: The anterior approach to the cervical spine. In Ross J,ed. Neuroimaging Clinics of North America: Phila- delphia: WB Saunders 465-480, 1995.
- Blomstedt GC: Craniotomy infections. Neurosurg Clin North Am 3:375-385, 1992.
- Bradley WG: MR appearance of hemorrhage in the brain. Radiology 189:15-26, 1993.
- Brant-Zawadzki M, Pitts LH: The role of CT in evaluation of head trauma. In: Federle MP, Brant-Zawadzki M, eds. Computed Tomography in the evaluation of trauma. Balti- mora: Williams e Wilkins 1-82, 1982.
- Bruce DA, Alavi A, Bilaniuk L et al: Diffuse cerebral swel- ling following head injuries in children: The syndrome of malignant brain edema: J Neurosurg 65:170-178, 1981.
- Castel E, Lazennec JY, Chiras J et al: Acute spinal cord compression due to intraspinal bleeding from a vertebral hemangioma:2 case-report. Eur Spine 8(3):244-8, 1999.
- Connolly PJ, Yuan HA: Anterior instrumentation of the cervical spine. In: White AH,ed. Spine Care. Baltimore: Mosby 1428-1436, 1995.
- De La Paz RL, Davis KR: Postoperative imaging of the po- sterior fossa.In: Taveras JM, Ferrucci JT,eds.Radiology dia- gnosis imaging intervention,vol. 3. Neuroradiology and ra- diology of the head and neck(Cpt 75). Philadelphia: JB Lip- pincott 1-11, 1988.
- Di Rocco C: Is the slit ventricle syndrome always a slit ven- tricle syndrome? Child's Nerv Syst 10:49-58, 1994.
- Djukic S, Lang P, Morris J et al: The postoperative spine: Magnetic resonance imaging. Orthop Clin North Am 28: 341-360, 1990.
- Elster AD, Di Persio DA: Cranial postoperative site: assest- ment with contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 174:93-98, 1990.
- Enevoldsen EM, Torfing T, Kjeldsen MJ, et al: Cerebral in- fart following carotid endarterectomy. Frequency clinical and hemodynamic significance evaluated by MRI and TCD. Acta Neurol Scand 100(2):106-10, Aug 1999.
- Enzmann DR, Britt RH, Yeager AS: Experimental brain abscess evaluation: computed tomographic and neuro- pathologic correlation. Radiology 133:113-122, 1979.
- Epstein F, Lapras C, Wisoff JH: Slit ventricle syndrome: etiology and treatment.Pediatr Neurosc 14(1):5-10, 1988.
- Franke CL, dJonge J, van Swieten JP et al: Intracerebral he- matomas during anticoagulant treatment. Stroke 21:726- 730, 1990.
- Heller JG, Whitecloud TS, Butler JC: Complications of spi- nal surgery. In: Herkowitz HN,Garfin SR Baldeston RA et al, (eds.): The Spine,3rd ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders 385-400, 1995.
- Hyman LA, Pagani JJ, Kirkpatrick JB et al: Pathophysiology of acute intracerebral and subarachnoid hemorrhage: appli- cations to MR imaging: Am J Neuroradiol 10:457-461, 1989.
- Ide T, Aoki N, Miki Y: Slit ventricle syndrome successfully treated by a lumboperitoneal shunt. Neurol Res 17(6):440- 2, Dec 1995.
- Ito H, Shimizu A, Miyamoto T et al: Fracture of the axis af- ter dome-like cervical laminoplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 118 (1-2):106-8, 1998.
- Jeffries BF, Kishore PRS, Simgh KS et al: Postoperative computed tomographic changes in the brain. An experi- mental study. Radiology 135:751-753, 1980.
- Jeffries BF, Kishore PRS, Singh KS et al: Contrast enhance- ment in the postoperative brain. Radiology 139:409-413, 1981.
- Kadson DL, Magruder MR,Stevens EA et al: Bilateral in- terhemispheric subdural hematomas. Neurosurgery 5:57- 59, 1979.
- Karasick D: Anterior cervical spine fusion:struts,plugs,and plates.Skel Radiol 22:85-94, 1993.
- Knauth M, Aras N, Wirtz CR et al: Surgical induced intra- cranial contrast enhancement:potential source of diagnostic error in intraoperative MR imaging.AJNR 20(8):1547-53, Sep 1999.
- Lanzieri CF, Lakins M, Mancall A et al: Cranial postopera- tive site: MR imaging appearance. Am J Neuroradiol 9:27- 34, 1988.
- Lee KS, Hardy IM: Postlamynectomy lumbar pseudomenin- gocele: report of four cases. Neurosurg 30:111-114, 1992.
- Manninen PH, Raman SK, Boyle K et al: Early postopera- tive complications following neurosurgical procedures. Can J Anaesth 46 (1): 7-14, Jan 1999.
- Manski TJ, Wood MD, Dunsker SB: Bilateral vocal cord paralysis following anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Case report. J Neurosurg 89(5):839-43, 1998.
- McLelland H, Couillard P: Postoperative heamatoma di- stant from the surgical site. A case report and review of the literature. Neurochirurgie 43(5):322-4, 1997.
- Mercier P, Donnez MC, Papon X et al: Vascular complica- tions during surgery of lumbar disk herniation. Apropos of 3 personal cases and 37 cases from a national investigation. Neurochirurgie 42(4-5):202-8, 1996.
- Miller JD, Stanek A, Langfitt TW: Concepts of cerebral perfusion pressure and vascular compression during intra- cranial hypertension. Pro Brain Rse 35:411-32, 1972.
- Pillet JC, Pillet MC, Braesco J et al: Vascular complica- tions of lumbar disk surgery.Report of two cases and re- view of the literature on 122 cases. J Mal Vasc 20(3):219- 23, 1995.
- Rajaraman V, Schulder M: Postoperative MRI appearance after transsphenoidal pituitary tumor resection. Surg Neu- rol 52(6):598-9, 1999.
- Rao CVGK, Kishore PRS, Barlett J: Computed tomography in the postoperative patient. Neuroradiology 19:257-263, 1980.
- Rapana A, Lamaida E, Pizza V et al: Multiple postoperati- ve intracerebral haematomas from the site of craniotomy.Br J Neurosurg 12(4):364-8, Aug 1998.
- Rastogi H, Baazan III C, da Costa Leite C et al: The po- sttherapeutic cranium. In: Randy Jinkins J edt. Posthtera- peutic neurodiagnostic imaging. Philadelphia: JB Lippin- cott 3-39, 1997.
- Richardson WJ, Spinner RJ: Surgical approaches to the cer- vical spine. In: White AH, ed. Spine Care. Baltimore: Mo- sby 1335-1350, 1995.
- Ross JS, Masaryk TJ, Schrader M et al: MR imaging of the postoperative lumbar spine: assesment with gadapentate di- meglumine. Am J Roentgenol 155:867-872, 1990.
- Samii C, Mobius E, Weber W et al: Pseudo Chiari type I malformation secondary to cerebrospinal fluid leakage. J Neurol 246(3):162-4, Mar 1999.
- Sato N, Bronen RA, Sze G et al: Postoperative changes in the brain:MR imaging findings in patients without neopla- sms. Radiology 204(3):839-46, Sep 1997.
- Scarabino T, Giannatempo GM, Perfetto F et al: Mielogr- fia con Risonanza Magnetica con sequenze Fast Spin Echo. La Radiol Med 91:202-206, 1996.
- Scarabino T, Perfetto F, Giannatempo GM et al: Riduzione degli artefatti ferromagnetici mediante sequenza Fast Spin Echo nella valutazione post-operatoria delle malattie degene- rative del rachide cervicale. La Radiol Med 91:174-176, 1996.
- Scarabino T, Poponara G, Perfetto F et al: Studio RM fast Spin Echo dei traumi midollari acuti. La Radiol Med 9:565- 571, 1996.
- Shafaie FF, Bundschuh C, Jinkins R: The posttherapeutic Lumbar spine. In: Randy Jinkins J edt. Posthterapeutic Neurodiagnostic imaging. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott 223- 243, 1997.
- Shimizu S, Tachibana S, Maezawa H et al: Lumbar spinal subdural hematoma following craniotomy: case report. Neurol Med Chir Takio 39(4):299-301, Apr 1999.
- Slone MR, MacMillan M, Montgomery WJ et al: Spinal fixation: Part 2. Fixation techniques and hardware for the thoracic and lombosacral spine. Radiographics 13:521-543, 1993.
- Slone MR, MacMillan M, Montgomery WJ et al: Spinal fixation: Part 3. Complications of spinal instrumentation. Radiographics 13:797-816, 1993.
- Spetzler RF, Wilson CB, Weinstein P et al: Normal perfu- sion pressure breakthough theory. Clin Neurosurg 25:651- 72, 1978.
- Taber KH, Ford JJ, Hayman LA: Magnetic resonance ima- ging appearance of hemarrhage:sources of imaging contra- st. Neuro Clin North Am 2:61-741, 1992.
- Takahashi M, Korogi Y: Sovratentorial neoplasm: post- opertive changes. In: Taveras JM, Ferrucci JT, (eds.): Ra- diology Diagnosis, Imaging, Intervention, vol. 3. Neurora- diology and Radiology of the Head and neck (Cpt 56). Phi- ladelphia: JB Lippincott 1-10, 1988.
- Tartaglino LM, Flanders AE, Vinitski S et al: Metallic arti- facts on the MR images of the postoperative spine: reduc- tion with fast spin echo techniques. Radiology 190:565-569, 1994.
- TeplicK JG, Haskin MR: Intravenous contrast-enhanced CT of the postoperative lumbar spine: improved identifica- tion of recurrent disc herniation, scar arachnoiditis and di- sckitis: Am J Roent 143:845-855, 1984.
- Thompson J, Smith M, Castillo M et al: The posttherapeu- tic cervicothoracic spine. In: Randy Jinkins J edt. Posthte- rapeutic Neurodiagnostic imaging. Philadelphia: JB Lip- pincott 193-221, 1997.
- Tjan TG, Aarts NJM: Bifrontal epidural haematoma after shunt operation and posterior fossa exploration. Report of a case with survival. Neuroradiology 19:51-53, 1980.
- van Calembergh F, Goffin J, Plets C: cerebellar hemorrha- ge complicating supratentorial craniotomy: report of two cases: Surg Neurol 40:336-338, 1993.
- Walenga JM, Mamon JF: Coagulophaties associated with intracranial haemorrhage. Neuroimag Clin North Am 2:137-152, 1992.
- Winslow CP, Meyers AD: Otolaryngologic complications of the anterior approach to the cervical spine. Am J Otolaryn- gol 20(1):16-27, Jan-Feb 1999.
- Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT, Dolinskas C et al: Computed tomography of pediatric head trauma: Acute general swel- ling. Radiology 126:403-408, 1978.
- Baleriaux DL: Spinal cord tumors. Eur Radiol 9(7):1252- 1258,1999.
- Brant-Zawadzki M, Miller EM, Federle MP: CT in the eva- luation of spinal trauma. AJR 136:369-375, 1981.
- Han JS, Kaufman B, El Youse SJ et al: NMR imaging of the spine. AJNR 4:1151-1159, 1983.
- Kaiser JA, Holland BA: Imaging of the cervical spine. Spi- ne 23(24):2701-712, 1998.
- Keiper MD, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT: MRI on the as- sessment of the supportive soft tissue of the cervical spine in acute trauma in children. Neuroradiology 40(6):359-363, 1998.
- Klein GR, Vaccaro AR, Albert TJ: Efficacy of magnetic re- sonance imaging in the evaluation of posterior cervical spi- ne fractures. Spine 24(8):771-774, 1999.
- Kretzschmar K: Degenerative disease of the spine: the role of myelography and myelo-CT. Eur J Radiol 27(3):229-234, 1998.
- Lee CP, Kazam E, Newman AD: Computed tomography of the spine and spinal cord. Radiology 128:95-102, 1978.
- Modic MT, Weinstein MA, Paulicek W et al: MRI of the spine. Radiology 148:757-762, 1983.
- Paleologos TS, Fratzoglou MM, Papadopoulos SS et al: Po- sttraumatic spinal cord lesions without skeletal or discal and ligamentous abnormalities: the role of MR imaging. J Spinal Disord 11(4):346-349, 1998.
- Wilmink JT: MR imaging of the spine: trauma and degene- rative disease. Eur Radiol 9(7):1259-1266, 1999. REFERENCES
- Berne JD, Velmahos GC, El-Tawil Q et al: Value of com- plete cervical helical computed tomographic scanning in identifying cervical spine injury in the unevaluable blunt trauma patient with multiple injuries: a prospective study. J Trauma, 47(5):896-902, 1999.
- Berquist TH: Spinal trauma. Da: Trauma Radiology. Edited by Mc Cort -Churchill Livingstone: 31-74, 1990.
- Berquist TH, Cabanella ME: The spine. Da: Imaging of the orthopedic trauma. Edited by TH Berquist -Raven Press: 93-206, 1992.
- Cusmano F, Ferrozzi F, Uccelli M et al: Upper cervical spine fracture: sources of misdiagnosis. Radiol Med, 98(4):230-235, 1999.
- Daffner RH, Deeb ZL, Goldeberg AL et al: The radiologi- cal assessment of post-traumatic vertebral stability. Skeletal Radiol, 19:103-108, 1990.
- Denis F: The three column spine and its significance in the classification of the acute thoraco-lumbar spinal injuries. Spine, 8:817-831, 1983.
- Denis F: Spinal instability as defined by three-column spine concept in acute spinal trauma. Clin Orthop, 189:65-73, 1984.
- El-Khoury GY, Kathol MH, Daniel WW: Imaging of acute injuries of the cervical spine: value of plain radiography, CT, and MR imaging. AJR, 164(1):43-50, 1995.
- Guareschi B: Le lesioni traumatiche vertebrali. Da A.P.C.: Rivisitiamo la radiologia tradizionale. L'urgenza radiologi- ca, pp. 39-50.
- Katz MA, Beredjiklian PK, Vresilovic EJ et al: Computed tomographic scanning of cervical spine fractures: does it influence treatment? J Orthop Trauma, 13(5):338-343, 1999.
- LeBlang SD, Nunez DB Jr: Helical CT of cervical spine and soft tissue injuries of the neck. Radiol Clin North Am, 37(3):512-532, 1999.
- Leite CC, Escobar BE, Bazan C 3 rd et al: MRI of cervical fa- cet dislocation. Neuroradiology, 39(8):583-588, 1997.
- Mace SE: Emergency evaluation of cervical spine injuries: CT versus plain radiographs. Ann Emerg Med, 14(10):973- 975, 1985.
- Monti C, Malaguti MC, Bettini N et al: La TC nei traumi acuti del rachide. Da: La diagnostica per immagini nelle "urgenze", a cura di Romagnoli e Del Vecchio, Idelson, Na- poli: 191-198, 1991.
- Murphey MD, Batnitzky S, Bramble JM: Diagnostic ima- ging of spinal trauma. Radiol Clin North Am, 27:855-873, 1989.
- Narayan RK: Emergency room management of the head- injured patient. Da: Textbook of head injury. Edited by DP Beker and SK Gaudeman, W.B. Saunders: 23-66, 1989.
- Nuñez DB Jr, Quencer RM: The role of helical CT in the assessment of cervical spine injuries. AJR, 171:951-957, 1998.
- Olsen WL, Chakeres DW, Berry I et al: Traumatismes du rachis et de la moelle. Da: Imagerie du rachis et de la moel- le, Scanner, IRM, Ultrasons. Edited by C Manelfe, Vi- got:387-426, 1989.
- Pistolesi GF, Bergamo Andreis IA: L'imaging diagnostico del rachide. Edizione Libreria Cortina, Verona: 637-706, 1987.
- Schmieder K, Hentsch A, Engelhardt M et al: Results of spiral CT in patients with fractures of the craniocervical junction suspected on conventional radiographs. Eur Ra- diol, 9(5):1008, 1999.
- Tan E, Schweitzer ME, Vaccaro L et al: Is computed tomo- graphy of nonvisualized C7-T1 cost-effective?. J Spinal Di- sord, 12(6):472-476, 1999.
- Tehranzadeh J, Bonk RT, Ansari A et al: Efficacy of limited CT for nonvisualized lower cervical spine in patients with blunt trauma. Skeletal Radiol, 23(5):349-352, 1994. REFERENCES
- Beers GJ, Raque GH, Wagner GG et al: MRI imaging in acute cervical spine trauma. J CAT 12(5):755-761, 1988.
- Beltramello A, Piovan E, Alessandrini F et al: Diagnosi neu- roradiologica dei traumi spinali. In Dal Pozzo G, Syllabus XV congresso nazionale AINR. Centauro, Bologna: 11-18, 1998.
- Carella A, D'Aprile P, Farchi G: Reperti RM nei traumi vertebro-midollari. Studio con tecniche di acquisizione con eco di gradiente. Rivista di Neuroradiologia 3:45-55, 1990.
- Chakeres DW, Flickinger F, Bresnahan JC et al: MRI Ima- ging of acute spinal cord trauma. AJNR 8(1):5-10, 1987
- Curati WL, Kingsley DPE, Kendall BE et al: MRI in chro- nic spinal cord trauma. Neuroradiology 35:30-35, 1992.
- Daffner RH, Deeb ZL, Goldeberg AL et al: The radiologi- cal assessment of post-traumatic vertebral stability. Skeletal Radiology 19:103-108, 1990.
- Davis SJ, Teresi LM, Bradley WG et al: Cervical spine hy- perextension injuries: MRI findings. Radiology 180(1):245- 251, 1991.
- Demaerel P, Van Hover P, Broeders A et al: Rapid lumbar spine MR mielography: imaging findings using a single-shot technique. Rivista di Neuroradiologia 10:181-187, 1997.
- Denis F: The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoraco-lumbar spinal injuries. Spine 8:817-831, 1983.
- Denis F: Spinal instability as defined by the three-column spine concept in acute spinal trauma. Clin Orthop 189:65- 76, 1984.
- Faccioli F: La biomeccanica del trauma vertebro-midollare. In: Dal Pozzo G, Syllabus XV congresso nazionale AINR. Centauro, Bologna: 7-10, 1998.
- Falcone S, Quencer RM, Green BA et al.: Progressive post- traumatic myelomalacic myelopathy. AJNR 15:747-754, 1994.
- Flanders AE, Croul SE: Spinal trauma. In: Atlas SW: Ma- gnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spine. 2°edition. Lippincott-Raven: 1161-1206, 1996.
- Flanders AE, Tartaglino LM, Friedman DP et al: Applica- tion of fast spin-echo MRI imaging in acute cervical spine injury. Radiology 185(P):220,1992.
- Goldberg AL, Rothfus WE, Deeb ZL et al: The impact of magnetic resonance on the diagnostic evaluation of acute cervico-thoracic spinal trauma. Skeletal Radiol 17(2):89-95, 1988.
- Hackney DB, Asato LR, Joseph P et al: Hemorrhage and edema in acute spinal cord compression: demonstration by MRI imaging. Radiology 161:387-390, 1986.
- Hall ED, Braughler JM: Central nervous system trauma and stroke. II. Physiological and pharmacological evidence for involvement of oxygen radicals and lipid peroxidation. Free Radical Biol Med 6:303-313, 1989.
- Hayashi N, Yamamoto S, Okubo T et al: Avulsion injury of cervical nerve roots: enhanced intradural nerve roots at MR Imaging. Radiology 206:817-822, 1998.
- Janssen L, Hansebout RR: Pathogenesis of spinal cord injury and newer treatments. A review Spine 14:23-32, 1989.
- Jones KM, Mulkern RV, Schwartz RB et al: Fast spin-echo MR Imaging of the brain and spine: current concepts. AJR 158:1313-1320, 1992.
- Kakulas BA: Pathology of spinal injuries. CNS Trauma 1:117-129, 1984.
- Kalfas I, Wilberger J, Goldberg A et al: Magnetic resonan- ce imaging in acute spinal cord trauma. Neurosurgery 23(3):295-299, 1988.
- Kwo S, Young W, De Crescito V: Spinal cord sodium, po- tassium, calcium and water concentration changes in rats after graded contusion injury. J Neurotrauma 6:13-24, 1989.
- Levitt MA, Flanders AE: Diagnostic capabilities of magne- tic resonance and computed tomography in acute cervical spinal column injury. Am J Emerg Med 9(2):131-135, 1991.
- Meldrum B: Possible therapeutic applications of anthago- nists of excitatory aminoacid neurotransmitters. Clin Sci 68:113-122, 1985.
- Pellicanò G, Cellerini M, Del Seppia I: Spinal trauma. Rivi- sta di Neuroradiologia 11:329-335, 1998.
- Posse S, Aue WP: Susceptibility artifacts in spin-echo and gradient-echo imaging. J Magn Reson 88:473-492, 1990
- Quencer RM, Sheldon JJ, MJD et al: MRI of the chronical- ly injured cervical spinal cord. AJR 147:125-132, 1986.
- Ramon S, Dominguez R, Ramirez L et al: Clinical and ma- gnetic resonance imaging correlation in acute spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 35:664-673, 1997.
- Rogenbogen VS, Rogers LF, Atlas SW et al: Cervical spinal cord injuries in patients with cervical spondylosis. Am J Ra- diol 146:277-284, 1986.
- Scarabino T, Polonara G, Perfetto F et al: Studio RM Fast Spin-Echo dei traumi vertebro-midollari acuti. Rivista di Neuroradiologia 9:565-571, 1996.
- Tarr RW, Drolshagen LF, Kerner TC et al: MRI Imaging of recent spinal trauma. J CAT 11(3):412-417, 1987.
- Tartaglino LM, Flanders AE, Vinitski S et al: Metallic arti- facts on MRI images of the postoperative spine: reduction with fast spin echo techniques. Radiology 190:565-569, 1994.
- Tator CH, Fehlindgs MJ: Review of the secondary injury theory of acute spinal cord trauma with emphasis on va- scular mechanisms. J Neurosurg 75:15-26, 1991.
- Tien RD: Fat suppression MR imaging in neuroradiology: techniques and clinical application. Am J Roentgenol 158:369-379, 1992.
- Weirich SD, Cotler HB, Narayana PA et al: Histopatholo- gic correlation of magnetic resonance signal patterns in a spinal cord injury model. Spine 15(7):630-638, 1990.
- White AA, Panjabi MM: Clinical biomechanics of the spi- ne. PA JB Lippincott, Philadelphia: 169-275, 1990. REFERENCES
- Baleriaux DL: Spinal cord tumours. Eur Radiol 9 (7):1252- 1258, 1999.
- Chen CJ, Chen CM, Lin TK: Enhanced cervical MRI in identifying intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae with spinal perimedullary venous drainage. Neuroradiology 40: 393-407, 1998.
- Fortuna A, Ferrante L, Acqui M et al: Spinal cord ischemia diagnosed by MRI. J Neuroradiol 22:115-122, 1995.
- Karampekios S: Inflammatory, vascular and demyelinating diseases of the spine and spinal cord. Eur Radiol (S1)10:36, 2000.
- Liou RJ, Chen CY, Chou TY et al: Hypoxic -ischaemic injury of the spinal cord in systemic shock: MRI. Neurora- diology 38:S 181-183, 1996
- Lyclama à Nijeholt GJ, Uitdehaag BMJ et al: Spinal cord magnetic resonance imaging in suspected multiple sclero- sis. Eur Radiol 10:368-376, 2000.
- Obenberg J, Seidi Z, Plas J: Osteoblastoma in lumbar ver- tebral body. Neuroradiology 41:279-282, 1999.
- Rimmelin A, Clouet PL, Salatino S et al: Imaging of thora- cic and lumbar spinal extradural arachnoid cysts: report of two cases. Neuroradiology 39:203-206, 1997.
- Rocca MA, Mastronardo G, Horsfield MA et al: Comparison of three MR sequences for detection of cervical cord lesions in patients with multiple sclerosis. AJNR 20:1710-1716, 1999.
- Silbergleit R Brunberg JA, Patel SC et al: Imaging of spinal intradural arachnoid cysts: MRI, myelography and CT. Neuroradiology 40:664-668, 1998.
- Suzuki K, Meguro K, Wada M et al: Anterior spinal ar- tery syndrome associated with severe stenosis of the ver- tebral artery. AJNR 19:1353-1355, 1998.
- Wilmink JT: MR imaging of the spine: trauma and degene- rative disease. Eur Radiol 9 (7):1259-1266, 1999.
- Yamada K, Shrier DA, Tanaka H et al: A case of subacute combined degeneration: MRI finding. Neuroradiology 40: 398-400, 1998.
- Aicardi J: Diseases of the Nervous System in Childhood. Mac Keith Press, London, 1992.
- Archer BD: Computed Tomography before lumbar punc- ture in acute meningitis: a review of the risks and benefits. Can Med Ass, 148:961-965, 1996.
- Bowerman RA, Donn SM, Di Pietro MA et al: Periven- tricular leukomalacia in the pretem newborn infant: so- nographic and clinical features. Radiology 151:382-388, 1984.
- Bruneel F, Wolff M: Méningites aigues. Encycl Méd Chir. Elsevier SAS, Paris. Neurologie 17-160-C-10, 2000.
- Carson SC, Hertzberg Bs, Bowie JD et al: Value of sono- graphy in the diagnosis of intracranial hemorrhage and pe- riventricular leukomalacia: a postmortem study of 35 cases. AJNR 11:677-683, 1990.
- Chabbert V, Ranjeva JP, Sevely A: Diffusion and magneti- sation transfer-weighted MRI in childhood moya-moya. Neuroradiology 40(4):267-71, 1998.
- Chanalet S, Chatel M, Grellier P et al.: Symptomatologique clinique et diagnostic radiologique des tumeurs intracra- niennes. Editions Techiniques. Encycl. Méd. Chir. (Paris, France). Neurologie 17-210-A60-10, 1994.
- Conway PD: Oechler HW, Kun LE et al.: Importance of hi- stologic condition and treatment of pediatric cerebellar astrocytoma. Cancer 67:2772, 1991.
- Crowe W: Aspects of Neuroradiology of head injury. Neu- rusurg Clin North Am 2:321, 1991.
- Dias Ms, Backstrom J, Falk M, Li V: Serial radiography in the infant shaken impact syndrome. Pediatr Neurosurg 29 (2):77-85, 1998.
- Flodmark O, Lupton B et al.: MR imaging of periventricu- lar leukomalcia in childhood. AJNR 10:111-1118, 1989.
- Ganesan V, Savv YL, Chong WK et al: Conventional cere- bral angiography in children with ischemic stroke. Pediatr Neurol 20(1):38-42, 1999.
- Garcia DM, Latifi AR, Simpson JR et al: Astocytomas of the cerebellum in children. J Neurosurg 71: 661-664, 1995.
- Giusifelli V, Wall M, Siegel PZ: Symptoms and disease as- sociation in idiopathic intracra nial hypertension (pseudo- tumor cerebri) a case-control study. Neurology 41: 239- 2444, 1991.
- Golden GS: Cerebrovascular Diseases. In: Swaiman KF. Pediatric Neurology. Mosby eds. St. Louis, 1994.
- Hadley MN, Sonntag VK, Rekate HC et al: The infant whi- plash-shake injury syndrome: a clinical and pathological study. Neurosurgery 141: 536-540, 1989.
- Hall MC, Barton LL, Johnson ML: Acute disseminated en- cephalomyelitis-like syndrome folllowing group A Beta he- molytic streptococcal infection. J Child Neurol 13, 7:354- 355, 1998.
- Harris BH: Management of multiple trauma. Pediatric Clin North-America 32:175, 1985.
- Horowitz ME, Mulhern RK, Kun LE et al.: Brain tumors in the very young child. Cancer 61:428, 1988.
- Irthum B, Lemaire JJ: Hypertension Intracranienne. Ency- cl. Méd. Chir. (Elsevier, Paris), Neurologie, 17-035-N-10, 8p, 1999.
- Jan M, Aesch B: Traumatismes cranio-encéphaliques. Edi- tions Techiniques-Encycl. Med. Chirurg Paris. Neurologie, 15785 A10, 15 p, 1991.
- Jelink J, Smorniotopulos Db, Parisis JE: Lateral Ventricular Neoplasms of the Brain: differential Diagnosis Based on clinical CT and MR Findings. AJR 11:567-574, 1990.
- Jonsson RT: Acute encephalitis. Clin Infect Dis 23:219-226, 1996.
- Kalifa G, Cohen PA: The radiologic report in battered child syndrome. J Radiol 80(6):563, 1999.
- Kimura M, Hasegawa Y, Yasuda K: Magnetic resonance ima- ging with fluid attenuated inversion recovery pulse sequences in MELAS syndrome Pediatr Radiol 27 (2):153-154, 1997.
- Lanska MJ: Presentation, clinical course, and outcome of childhood stroke. Pediatr Neurol 7:333, 1991.
- Lasjaunias P, Der Brugge K, Lopez-Ibor et al.: The role of dural anomalies in vein of Galen aneurysms: report of six cases and review of the literature. AJNR 8:185-192, 1988.
- Marshall LF, Bowers-Marshall S, Klauber MR et al.: A new classification of head injury based on computerized tomo- graphy. J Neurosurgery 75 (Suppl):S14-20, 1991.
- Merten DF, Osborne DR., Radkowski MA et al: Cranioce- rebral trauma in the child abuse syndrome: radiological ob- servations. Pediatr Radiol 14:272-277, 1984.
- Murgio A, Andrade FA, Sanchez Munoz MA: International Multicenter Study of Head Injury in Children. ISHIP Group. Childs Nerv Syst Jul 15 (6-7):318-21, 1999.
- Pender MP: Acute disseminated encephalomyeilitis. In: Pender MP Mc Combe PM (eds): Autoimmune Neurologi- cal Diseases. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press pp. 155-165, 1995.
- Roach ES, Riela AR: Pediatric cerebrovascular disorders. Futura Publishing Company Mount Kisco eds New York.
- Rosman NP: Acute brain injury. In: Swaiman KF Mosby st Louis eds Pediatric Neurology: principles and practice.
- Schmidbauer M, Podreka L, Wiimberger D et al.: SPECT and MR imaging in herpes simplex encephalitis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 15:811-815, 1991.
- Schoemann J, Hewlett R: MR of childhood tubercolous meningitis. Neuroradiology 30:473-477, 1988.
- Schroth G, Gawehn J, Thron A et al.: Early diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis by MRI. Neurology 37:179- 183, 1987.
- Seidnwurm D, Berenstein A et al.: Vein of Galen malfor- mation: correlation of clinical presentation, arteriography and MR imaging. AJNR 12:347-354, 1991.
- Starshak RJ, Wells RG, Sty JR et al: Testa collo e rachide. Diagnostica per immagini nel bambino. Momento medico, Salerno, 1996.
- Swaiman K: Pediatric Neurology. Principles and practice. Mosby editor, St. Louis, 1994.
- Syrogianopulos GA, Nelson JD. et al.: Subdural collection of fluid in acute bacterial meningitis in young children: a re- view of 136 cases. Pediatr Infect Dis 5:343-352, 1986.
- Tores CF, Rebsamen S, Silber JH et al.: Survellaince scan- ning of children with medulloblastoma. N Engl J Med 330:892, 1994.
- Toutant S, Klauber MR, Marshall L et al.: Absent or com- pressed basal cysterns of the first CT scan: ominous pre- dictors of outcome in severe head injury. J Neurosurg 61: 691-694, 1984.
- Volanne L, Ketonen L., Majander A et al.: Neuradiologic findings in children with mithocondrial disorders AJNR 19 (2):369-377, 1998.
- Whitley RJ, Cobbs GC, Alford CA et al.: Diseases that mi- mic herpes simplex encephalitis. Diagnosis, presentation and outcome. JAMA 262:234-39, 1989.
- Wilihowski E, Pouwels PJ, Frahm J: Quantitative proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of cerebral metabolic di- sturbances in patients with MELAS. Neuropediatrics 30 (5):256-63, 1999.
- Wison JT, Wiedman KD, Hadley DM et al: Early and late magnetic resonance imaging and neuropsycological outco- me after head injury. J Neurol. Neurosurg Psychiatry 51: 391-6, 1988.
 Frannk Christian Veggro Rios
Frannk Christian Veggro Rios




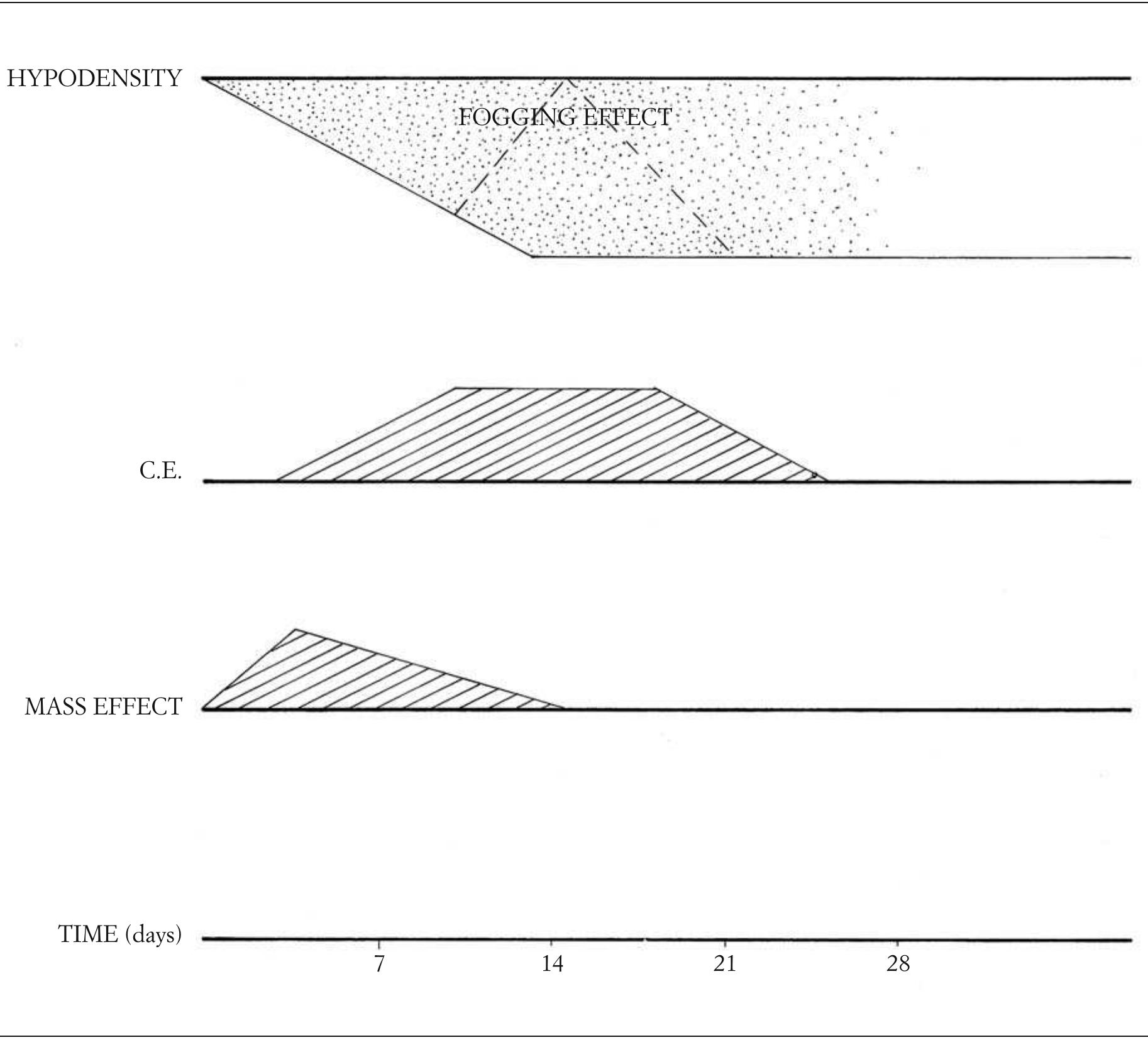














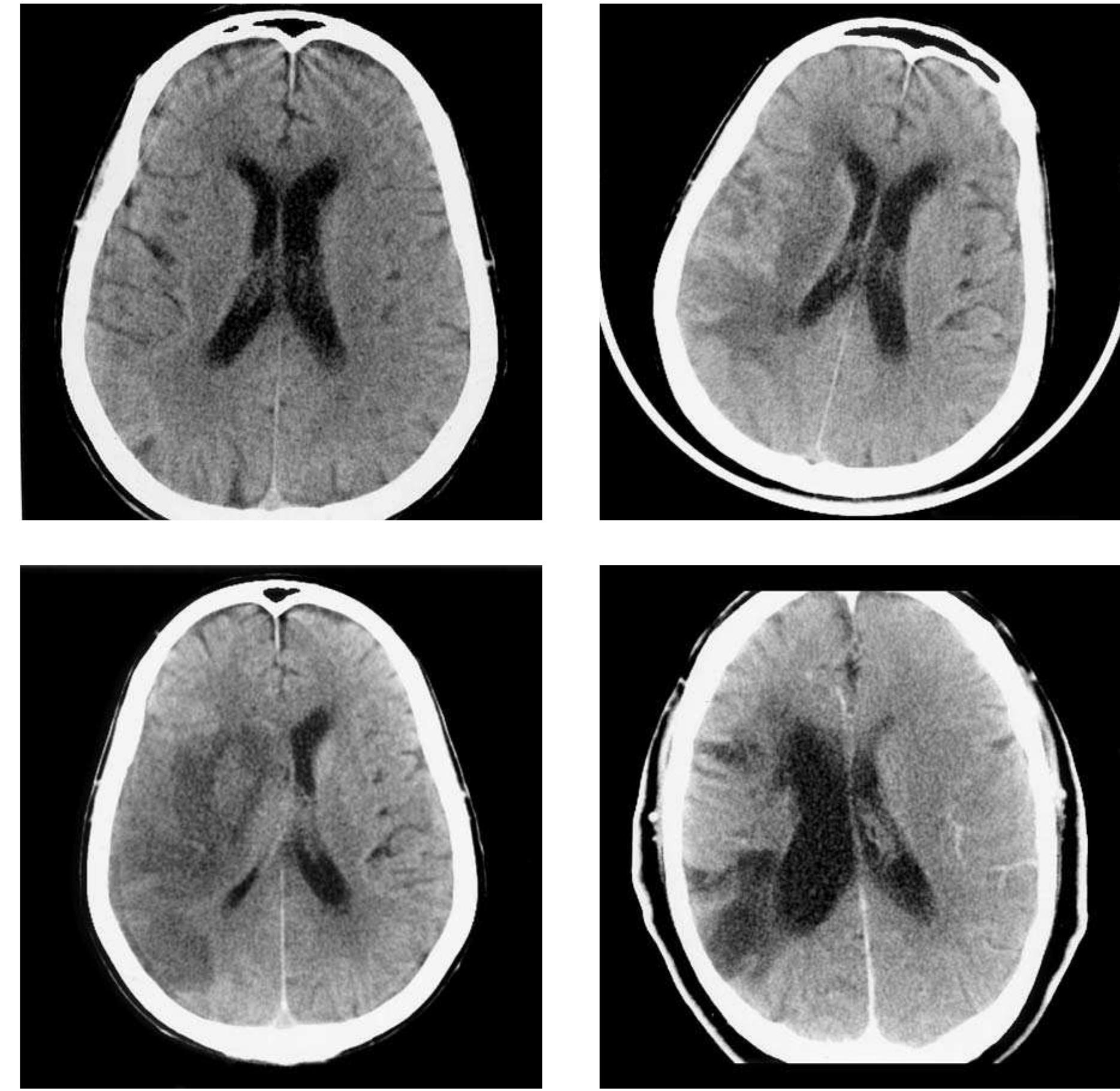


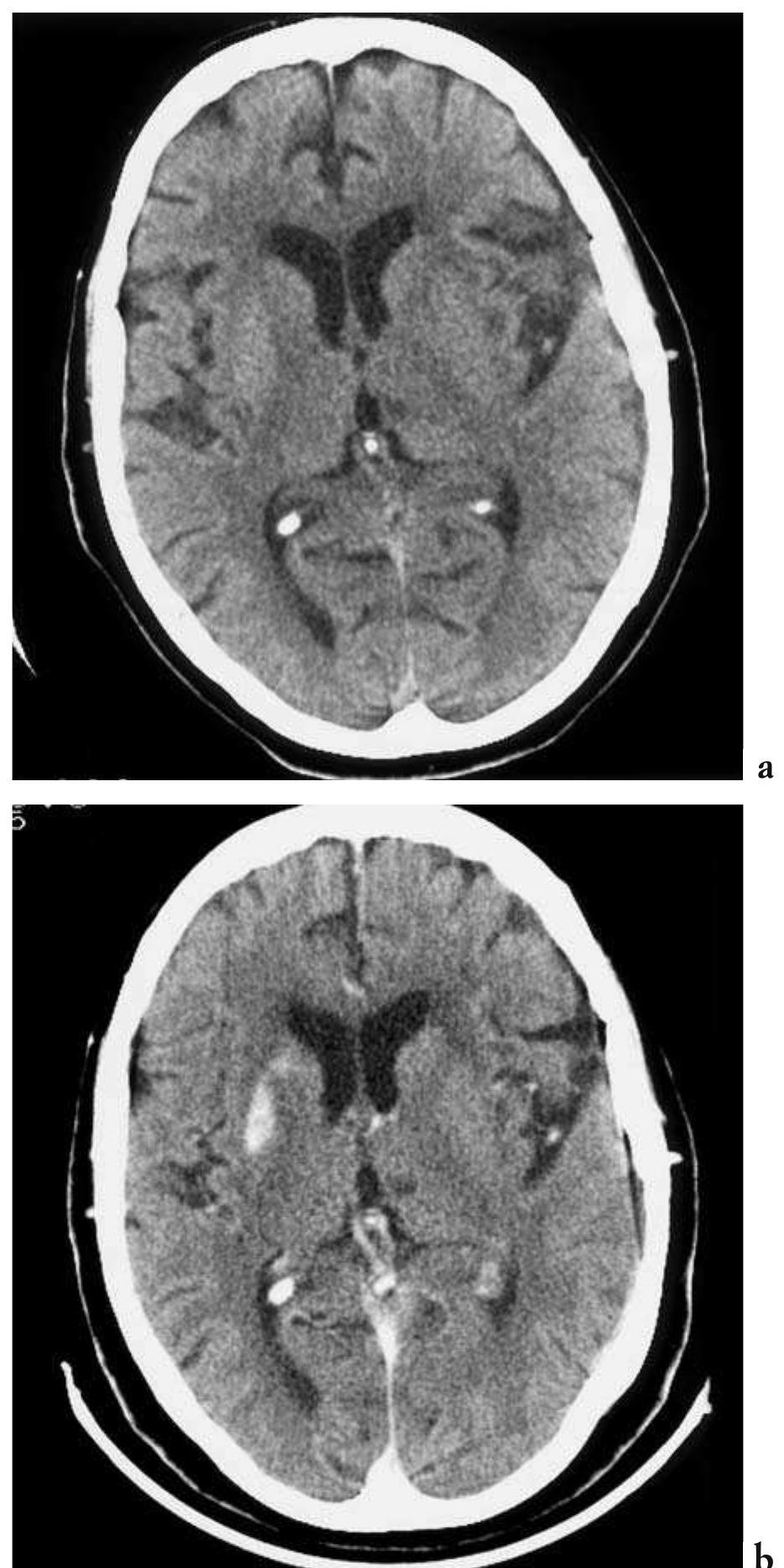




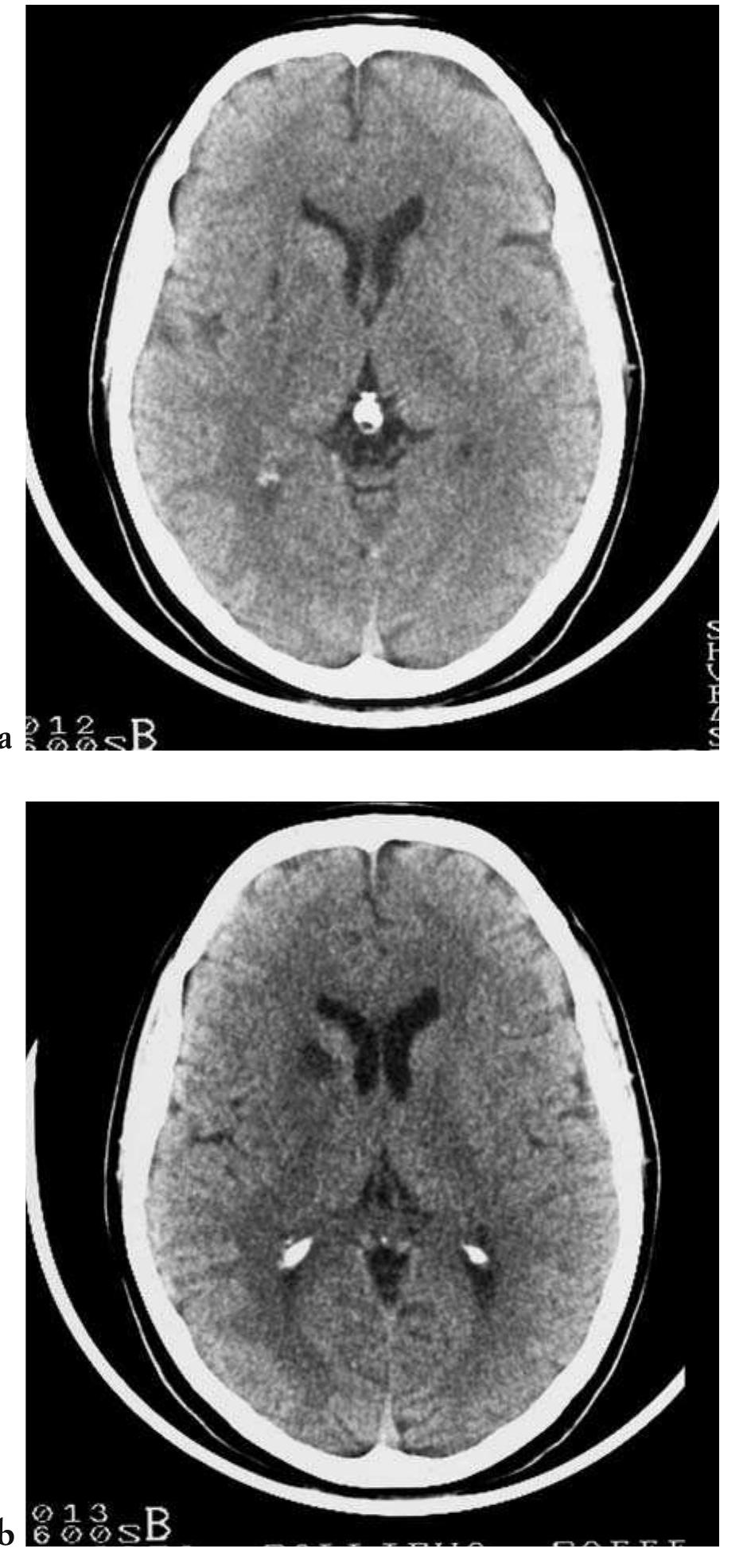

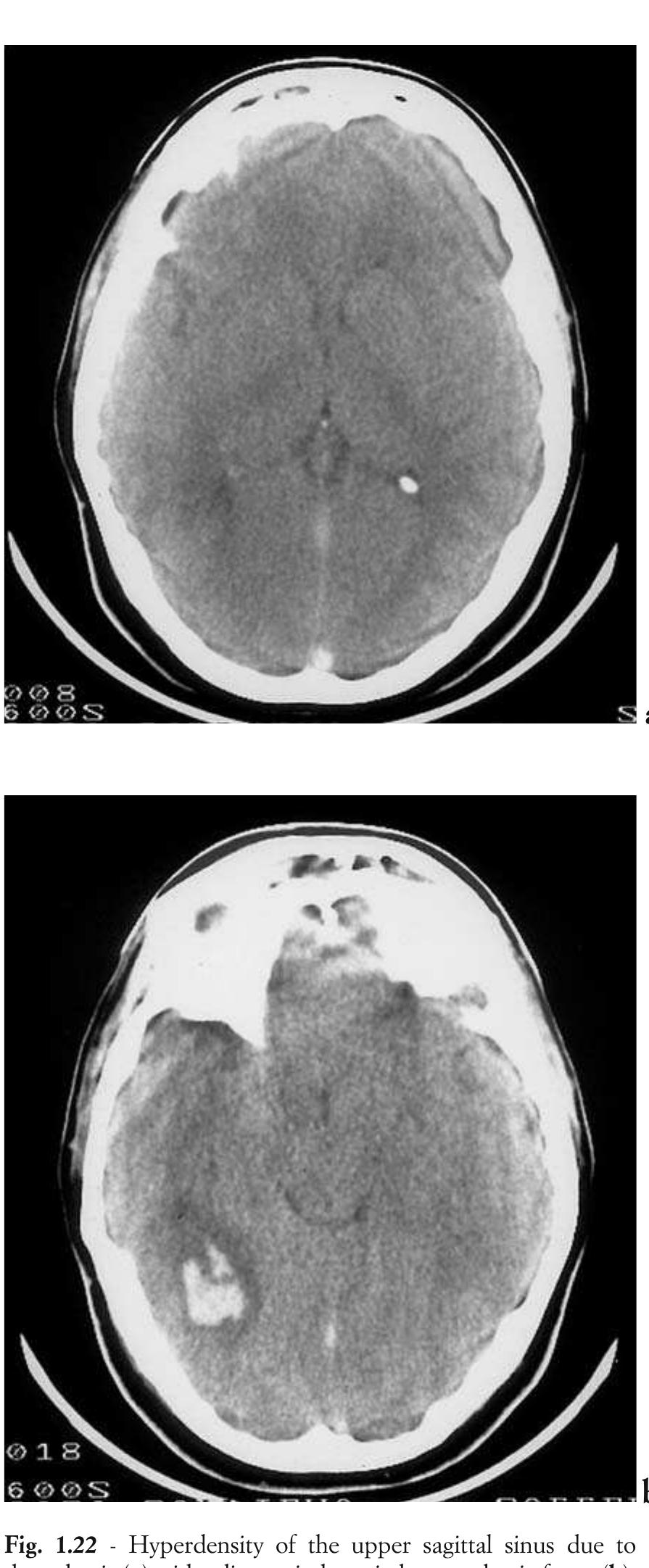


















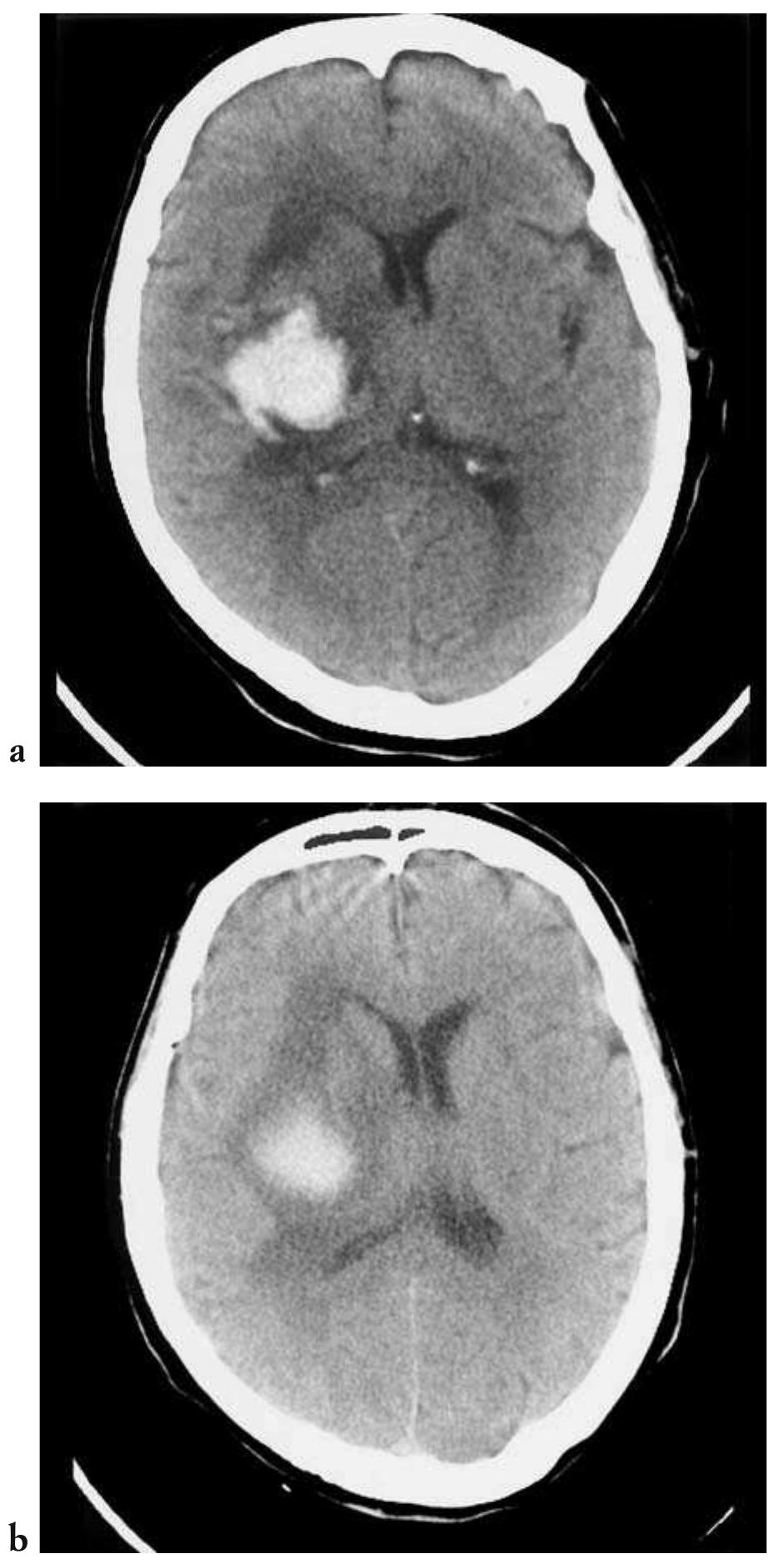


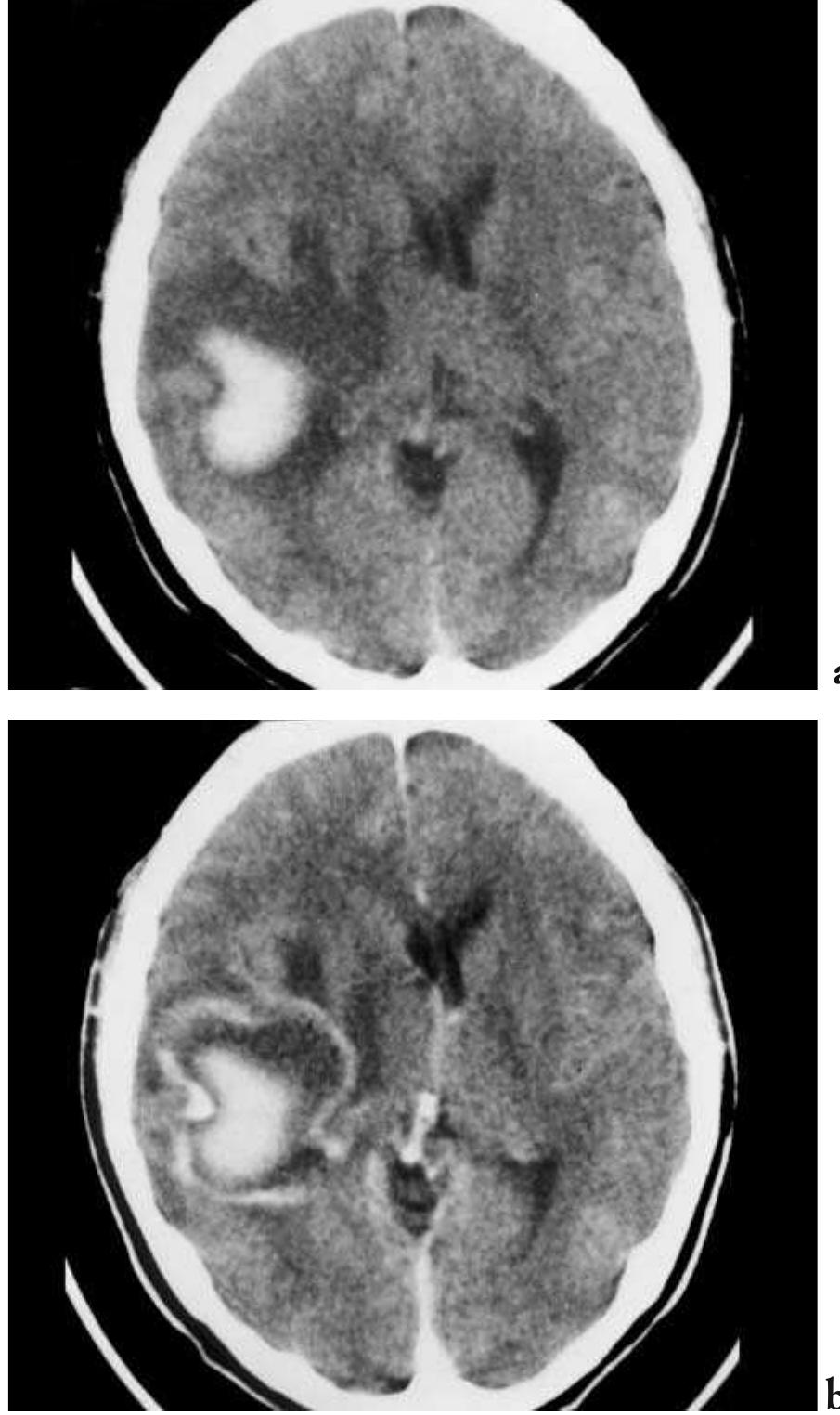











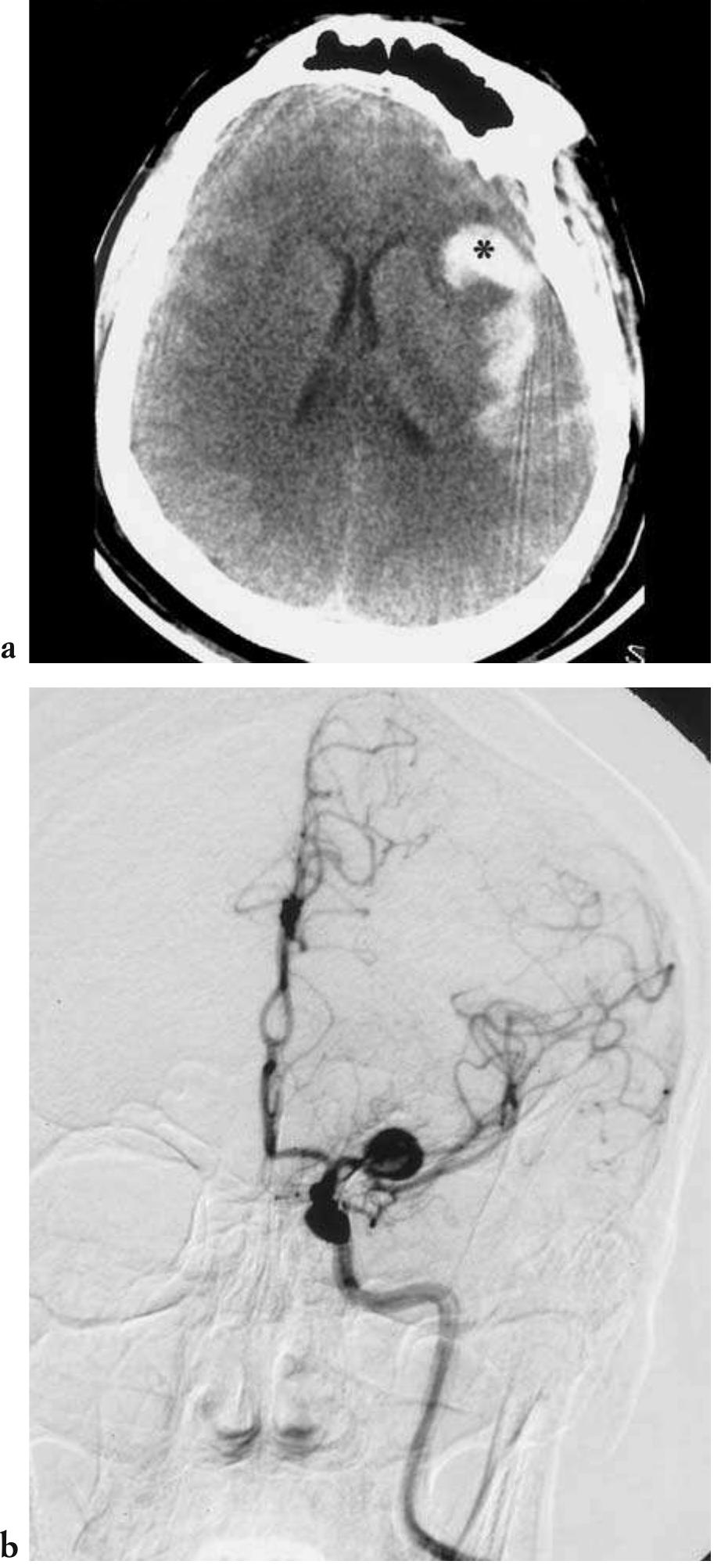













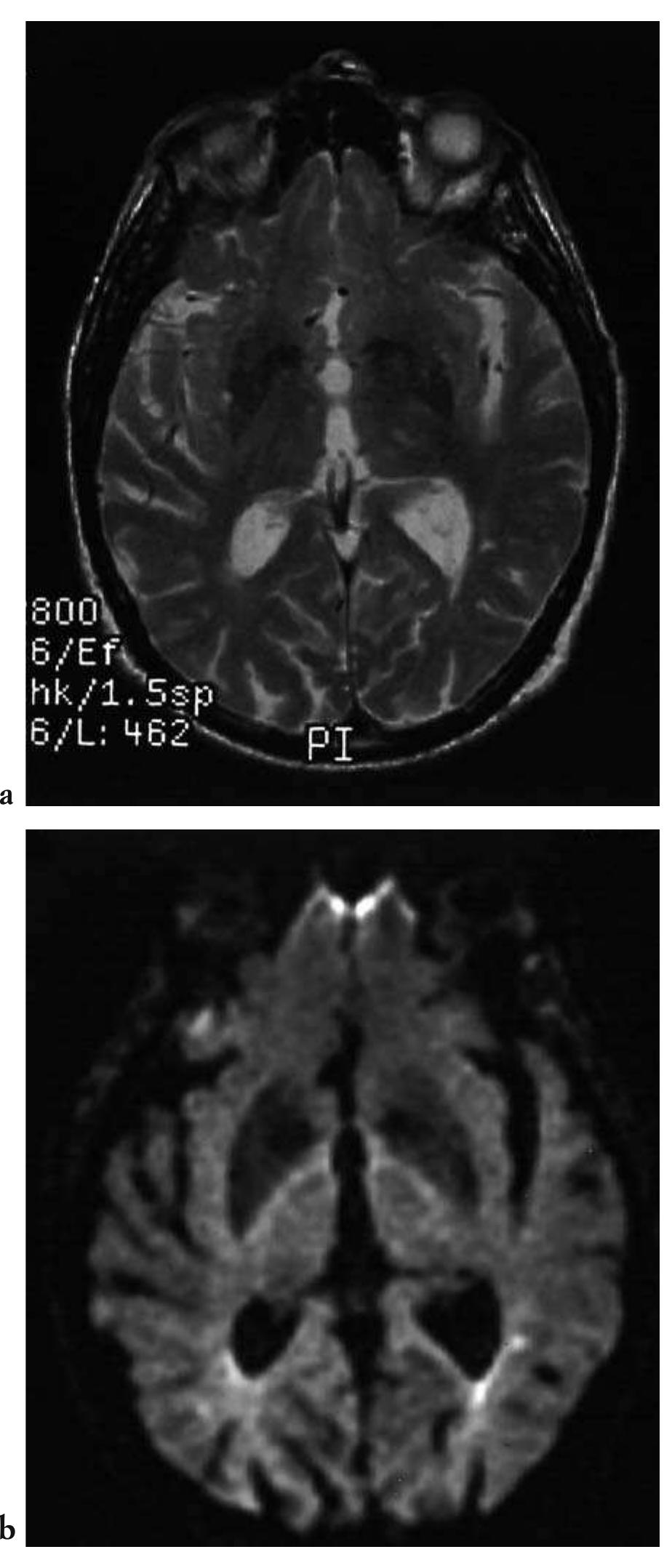










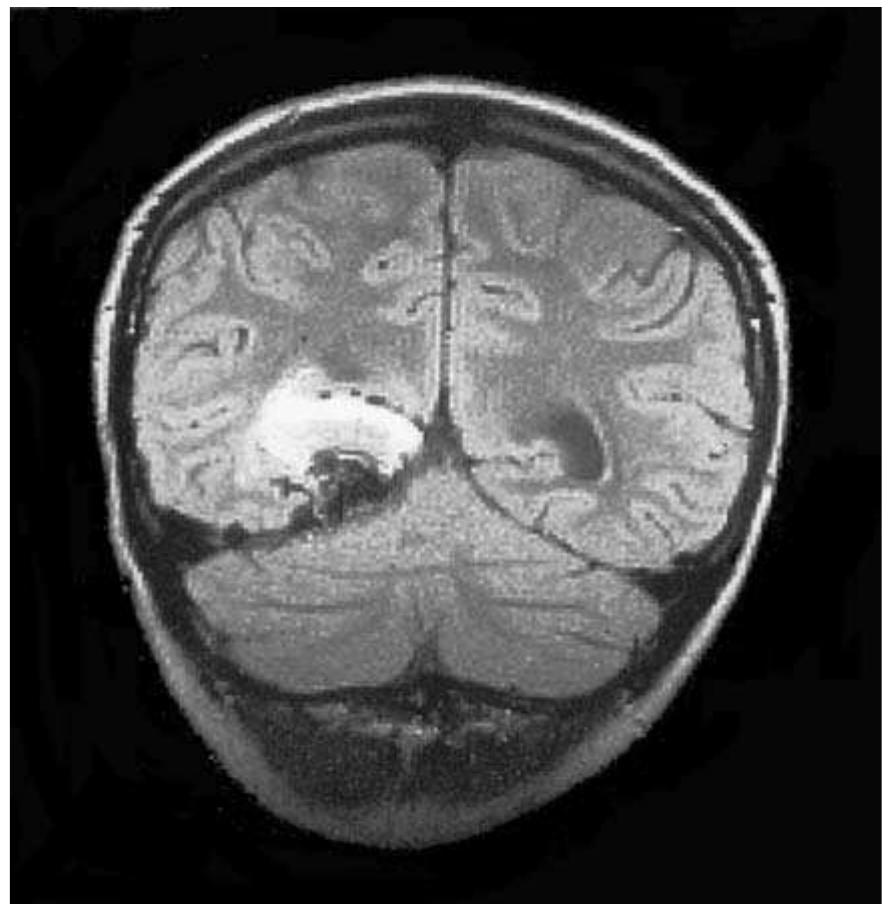

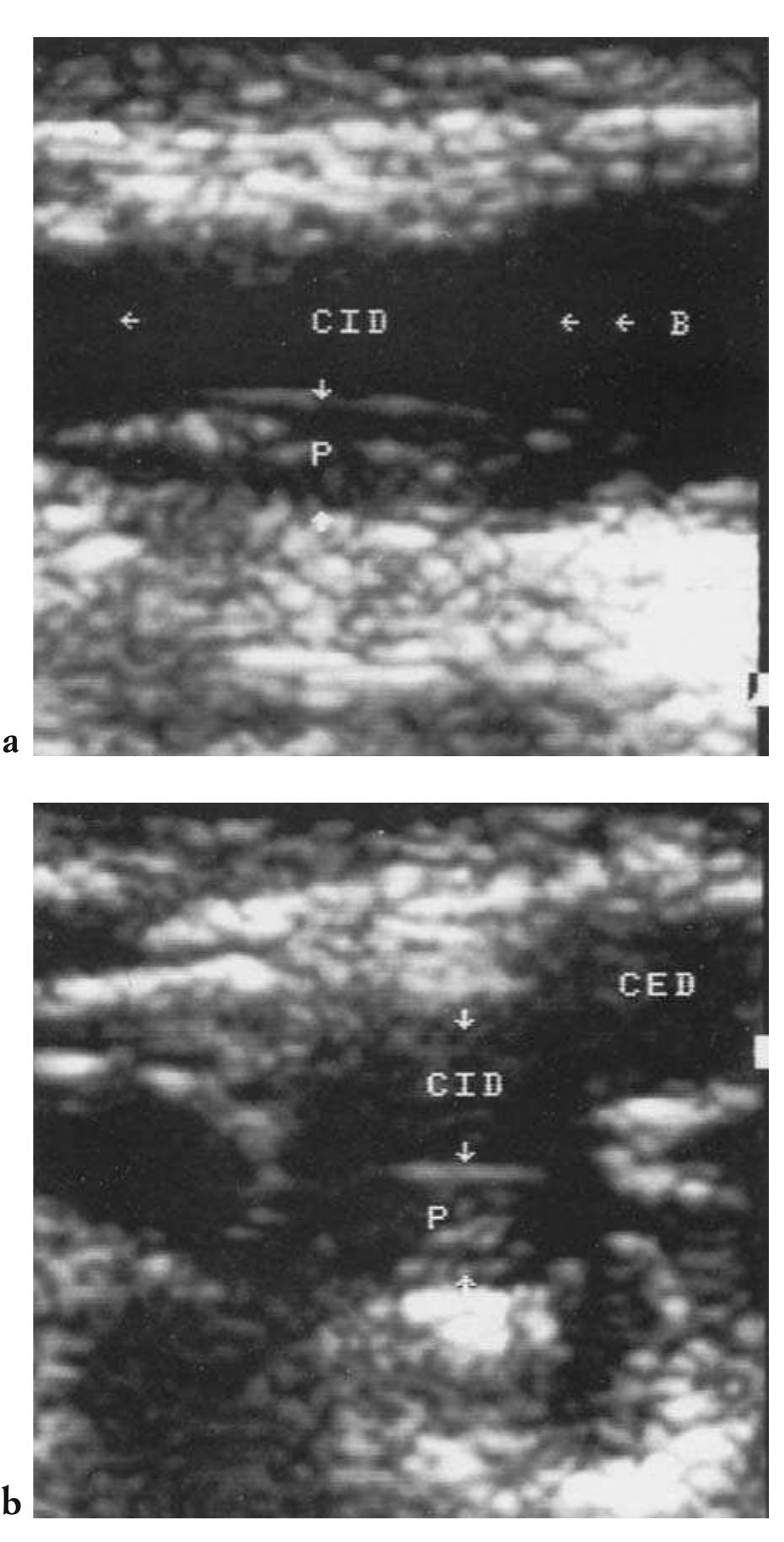

































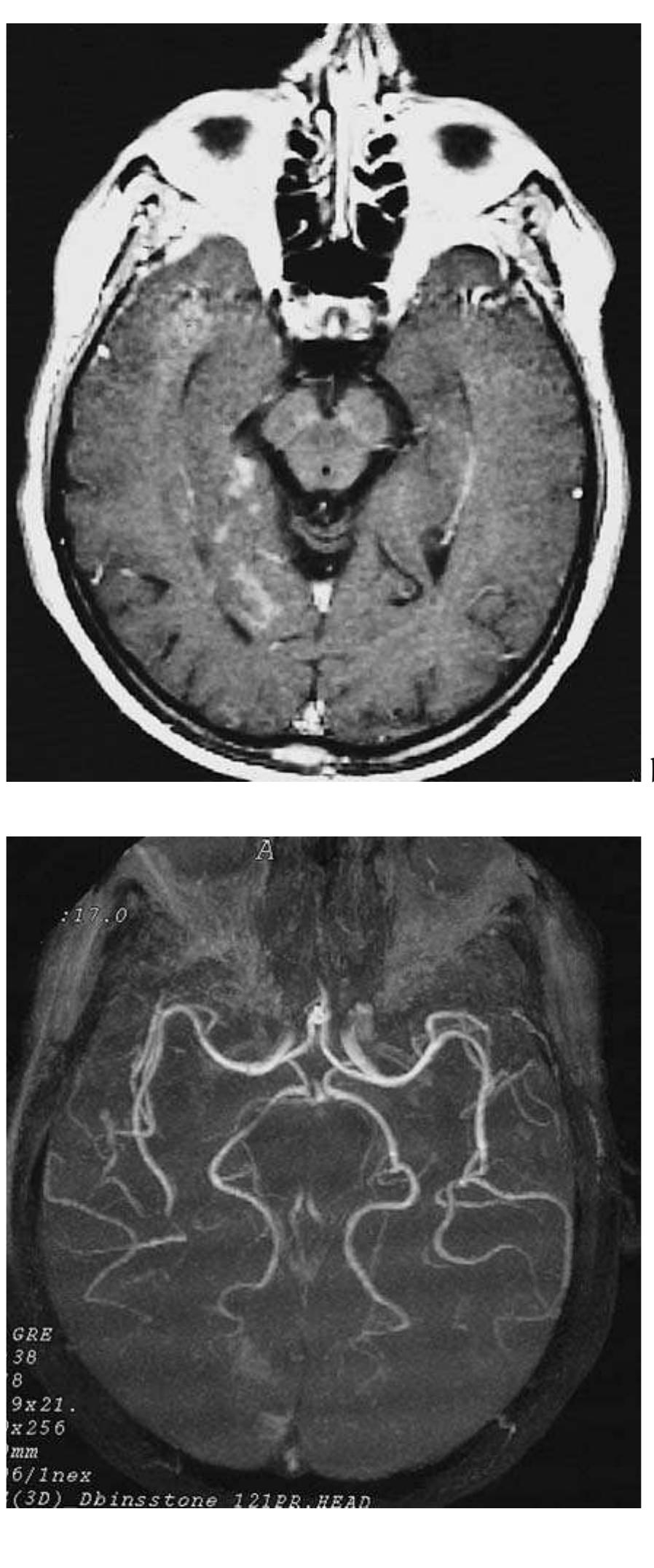



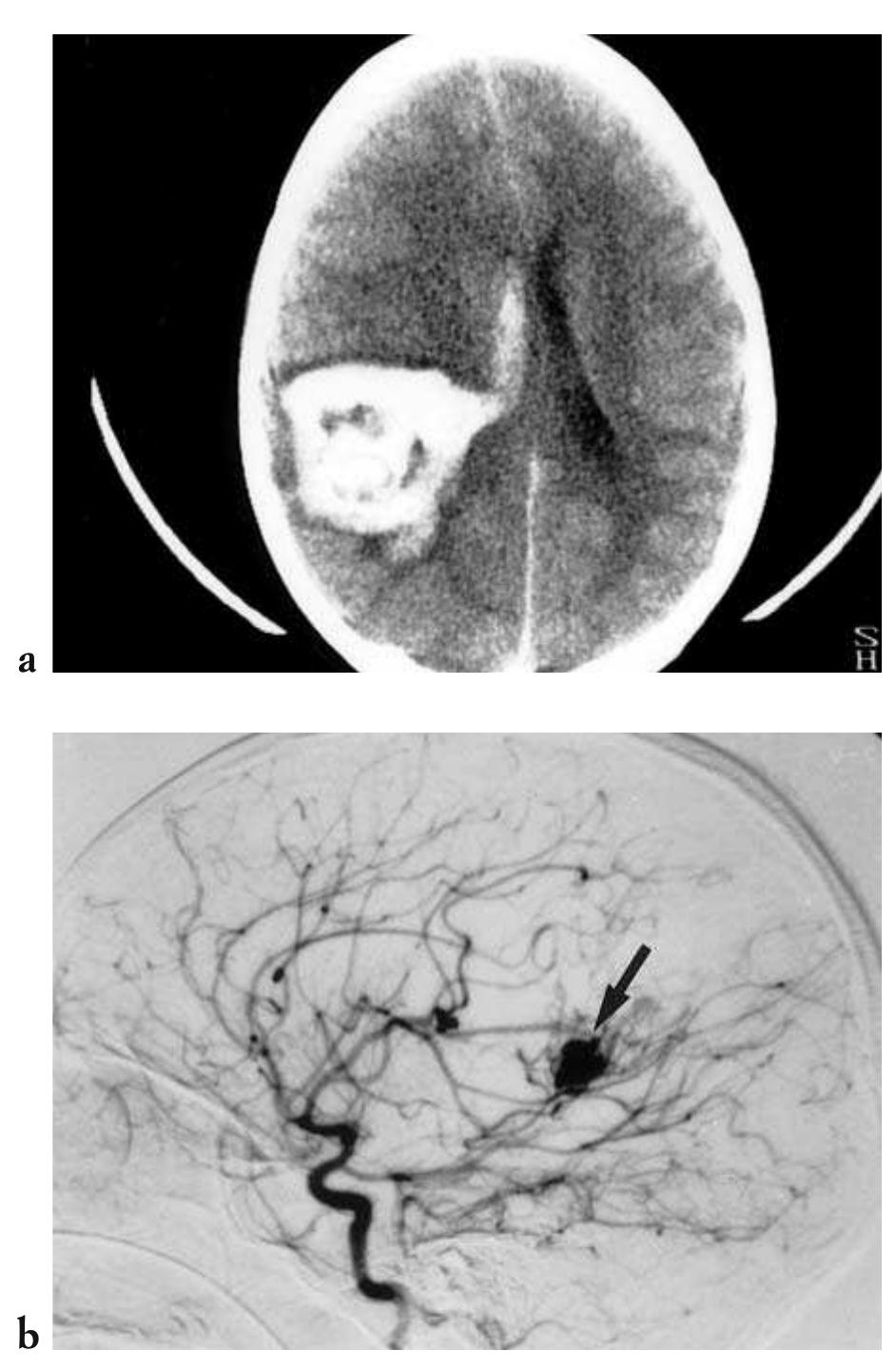



























![Fig. 2.14 - Bilateral subdural haematomas. There is a biloculat- ed acute-subacute subdural haematoma on the right side (a), a heterogeneous appearance of the two haematomas with fluid- fluid levels (b), and presence of haemorrhagic components of different ages. The left sided subacute subdural haematoma is almost isodense as compared to the underlying brain and is therefore somewhat difficult to visualise. [a), b) axial CT].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_152.jpg)
![Fig. 2.13 - Axial CT demonstrates an acute subdural haematoma along the left hemisphere convexity with right shift of the mid- line structures and compression of the left lateral ventricle. [a), b) axial CT].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_153.jpg)

![Fig. 2.16 - Subdural haematoma. Axial CT reveals and unusual appearing left frontoparietal subdural haematoma with a hy- perdense acute haemorrhagic component layering posteriorly. The left lateral ventricle is compressed by the haematoma and the contralateral lateral ventricle is dilated. [a), b) axial CT].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_155.jpg)
![convex lateral margin; however, in the presence of an SDH this margin becomes flattened, con- cave or irregularly distorted. If the cortico- medullary junction is not visible, a bolus injection of contrast medium administered during the scan may be useful in identifying the cortical surface and delineating the border of an isodense SDH. This image enhancement method can document Fig. 2.18 - Subdural haematomas. Axial and coronal CT shows small, chronic subdural haematoma over the convexity of the brain is observed which is better seen on coronal scans. [a) ax- ial CT; b) coronal CT].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_156.jpg)
![Fig. 2.17 - Bilateral subdural haematomas. Axial CT shows bi- lateral hypodense subdural haematomas. [a), b) axial CT].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_157.jpg)


![Fig. 2.21 - Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Hyperdensity is noted within the cortical sulci over the left cerebral hemisphere. Small haemorrhagic cortical contusions are also seen, the largest of which can be observed in the right temporal region (arrow- head). [a), b) axial CT]. SDH’s do not cross the midline because the subdural spaces on the two sides of the crani- um do not communicate. These haematomas are occasionally observed beneath the tempo- ral lobe within the middle cranial fossa and un- der the occipital lobes extending along the ten- torium cerebelli, and are often difficult to see with axial slices alone. In these instances, sup- plemental coronal slices are helpful for visuali- zation.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_160.jpg)
![Fig. 2.22 - Posttraumatic intraventricular haemorrhage, pneumocephalus, and cerebral oedema. Bilateral eyelid haematomas are seet associated with subcutaneous emphysema (a). Intracranially are observed subarachnoid (b) and intraventricular haemorrhage (a), ai bubbles in the CSF spaces (c) and the widespread oedema within the right cerebral hemisphere (d). [a)-d) axial CT].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_161.jpg)

![Fig. 2.24 - Posttraumatic cerebral swelling. The CT demon- strated diffuse posttraumatic cerebral swelling is seen with obliteration of the basal subarachnoid cisterns and superficial cortical sulci, compression of the 3" ventricle and reduction in size of the lateral ventricles. The midline structures are not shifted, and there are no focal haemorrhages are present. [a), b), c) axial CT].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_163.jpg)




![Fig. 2.26 (cont.) - An MRI examination conducted three days later shows an area of hyperintense signal on T1-weighted se- quences (e) and hypointense signal on T2-weighted sequences as a result of haemoglobin breakdown products (i.e., deoxy- haemoglobin). [a), b), ¢) axial CT; d), f) axial T2-weighted MRI; e) axial T1-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_168.jpg)
![Fig. 2.27 - Multiple contusive and lacerative haemorrhagic cere- bral foci in the acute phase. The T2-weighted sequence (a) shows multiple areas of signal hyperintensity within which haemor- rhagic components cannot be distinguished. The long scan time often results in motion artefacts. The echo-planar sequence (b), which is more sensitive to T2*-weighted tissue, enables the iden- tification of areas of hypointense signal caused by the presence of subacute haemorrhage (deoxyhaemoglobin). Motion artefacts can also be reduced by obtaining the acquisition in approxi- mately 500 msec. [a) T2-weighted MRI; T2*-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_169.jpg)
![Fig. 2.28 - Cerebral contusions. T2 fast spin echo (FSE) and FLAIR sequences demonstrate that the latter prove more sensitive in identifying contusive foci, even of very small dimensions. The superior identification of the subdural haematoma with FLAIR se- quences is also noted. [a), c), d) T2-weighted MRI; b) FLAIR MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_170.jpg)

![Fig. 2.29 - Hyperacute cerebral haemorrhage. CT and T2- weighted MRI images show that in the hyperacute phase only CT is capable of showing the haemorrhagic component of the right temporal-insular shear-contusive focus. [a) axial CT; b) axial T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_172.jpg)




![Fig. 2.32 - Haemorrhagic shearing injuries. Unlike FSE T2- weighted sequences, gradient recalled echo sequences which are more sensitive to T2* effects, are able to distinguish the presence of a haemorrhagic components within very small grey- white matter junction shearing injuries. [a) T2-weighted MRI, b) T2*-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_177.jpg)
























![Fig. 3.2 - Vasogenic oedema caused by malignant cavitary glial neoplasm. The MRI study shows extensive oedema involving the white matter surrounding the neoplasm. Note the mass effect upon the lateral cerebral ventricles and the irregular mural contrast enhance- ment. [a), b) T2-weighted, c) unenhanced T1-weighted, d) and T1-weighted MRI following IV gadolinium (Gd) administration].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_203.jpg)



![Fig. 3.5 - Mesencephalic tuberculoma with obstructive hydro- cephalus. The MRI shows a contrast enhancing mass lesion of the posterolateral midbrain resulting in stenosis of the aque- duct of Sylvius and obstructive hydrocephalus. [a) axial T2- weighted and b) sagittal T2-weighted MRI; c) coronal T1- weighted MRI following IV Gd].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_207.jpg)

![Fig. 3.6 - Type II Arnold Chiari malformation with obstructive hydrocephalus The MRI examination demonstrates cerebellar tonsillar ectopia, fourth ventricular outlet obstruction and hy- drocephalus. In addition, there is right occipital encephaloma- lacic porencephalic cyst and cervicothoracic syringohydromyelia. [a) sagittal T1- weighted cranial MRI; b) sagittal T1-weighted cervical MRI; c) axial T2-weighted cranial MRI]. After a certain time, chronic inadequate flu- id reabsorption can produce an enlargement of the ventricles without an attendant increase in fluid pressure (normotensive hydrocephalus). In acute hydrocephalus, the CSF is reabsorbed vicariously by the minor resorption systems, firstly by the transependymal pathway, with the appearance of typical findings of hypodensity on CT and hyperintensity on T2-weighted MRI in the periventricular white matter (Fig. 3.8). This absorption pathway is more permeable than the normal one and permits the passage through the periventricular white matter of even large protein molecules.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_209.jpg)



![Fig. 3.8 - Normotensive communicating hydrocephalus. The MRI images show a thin margin of hyperintensity representing chronic gliosis surrounding the lateral ventricles in a patient with clinically diagnosed chronic normotensive communicating hydrocephalus, not transependymal extravasation of CSF. [a, b) proton density-weighted MRI; c, d) T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_213.jpg)




![Fig. 3.11 - Glioblastoma multiforme. The CT and MRI studies show a large, necrotic left hemispheric glioblastoma associated with extensive perilesional vasogenic oedema resulting mass effect and lateral subfalcian herniation. [a, b) unenhanced axial CT; ¢, d, b) PD-, FLAIR, T2-weighted MRI; f, g) T1-weighted axial and coronal MRI following IV Gd].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_218.jpg)









![Fig. 3.12 (cont.) - h, i) axial and coronal T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_228.jpg)



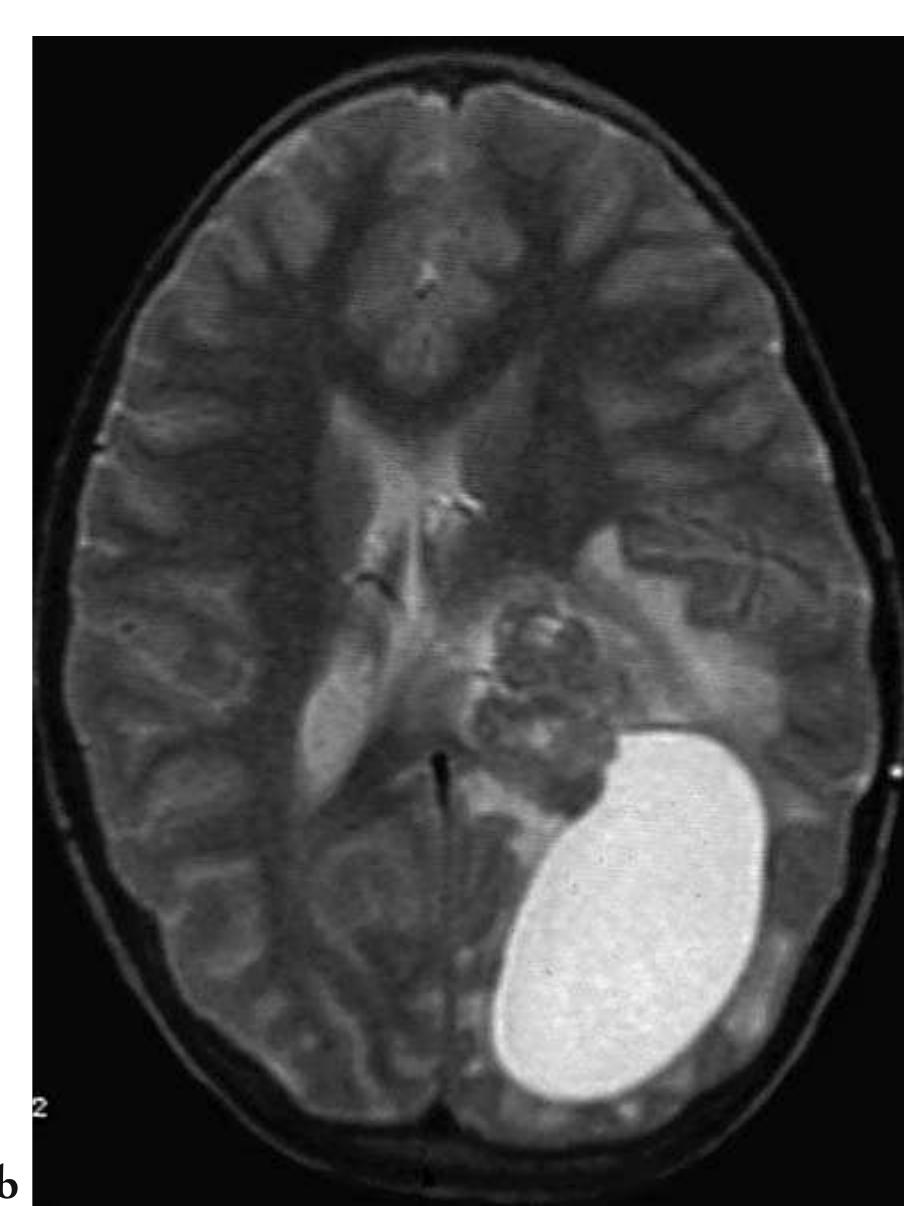




![Fig. 3.15 - Postsurgical infection of surgical site. The surgical cavity demonstrates air with irregular contrast enhancement along the resection margins; hypodensity persists in the adjacent white matter due to persistent vasogenic oedema. The CT findings described are of uncertain significance, as they are still compatible with expected postsurgical alterations, however the associated clinical find- ings (headache and high fever) suggest a probable infection of the surgical site. [a, b) unenhanced axial CT; c, d) axial CT following TV contrast].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_237.jpg)


![Fig. 3.16 - Postsurgical cerebritis. The CT examination shows diffuse hypodensity of the subcortical and deep white matter of the right cerebral hemisphere consistent with oedema, with inhomogeneous contrast enhancement and marked mass effect. The mass re- sults in compression of the ipsilateral ventricle, subfalcian herniation of the midline supratentorial structures and early dilation of the contralateral ventricle caused by obstruction at the level of the foramen of Monro on the left side. The ipsilateral perimesencephalic cistern is obliterated due to downward internal herniation of the uncus of the temporal lobe. [a, b) unenhanced axial CT; c, d) axial CT after IV contrast].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_240.jpg)




![, Fig. 3.17 - Meningioma of the left pterion. The imaging studies reveal a left frontoparietal homogenously enhancing, broad dural based mass with perilesional oedema and neovascularity originating from the left middle meningeal artery. [a) unen- hanced CT; b, c) left external carotid, left middle meningeal ar- teriogram].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_245.jpg)
![Fig. 3.18 - Invasive left frontal region meningioma. The skull x-ray demonstrates a large osteolytic lesion of the left frontal region. The CT shows a hyperdense lesion invading the overlying skull and extracranial soft tissues. The angiogram of the left external carotid ar- tery reveals prominent neovascularity originating from branches of the left superficial temporal and middle meningeal arteries. [a) frontal radiograph; b), ¢) axial CT imaged with bone and soft tissue windows; d) left external carotid arteriogram].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_246.jpg)

![Fig. 3.19 - Olfactory groove meningioma. The right internal carotid arteriogram demonstrates neovascularity associated with a persistent parenchymal blush within a lesion in the ante- rior aspect of the skull base on the right side originating prin- cipally from ethmoid arterial branches. In addition, the right ophthalmic artery in hypertrophied as a result of the increased flow in transit to the neoplasm. [a) frontal projection right in- ternal carotid arteriogram; b) lateral projection right internal carotid arteriogram].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_248.jpg)


![Fig. 3.22 - Right parietal lobe astrocytoma. Contrast enhanced CT shows mural enhancement within a right parietal lobe sub- cortical mass lesion surrounded by much perilesional oedema. The angiogram of the right internal carotid artery demonstrates no hypervascularity. [a) axial CT following IV contrast; b) lat- eral projection right internal carotid arteriogram] OTHER CEREBRAL NEOPLASMS](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_251.jpg)


![Fig. 3.24 - Right temporoparietal parenchymal metastatic neo- plastic disease. Contrast enhanced coronal CT demonstrates an enhancing mass lesion adjacent to the skull on the right side. The right internal carotid arteriogram in the lateral projection reveals an intensely hypervascular cortical lesion associated with a tumor blush and arteriovenous shunting. [a) coronal CT following IV contrast; b, c) lateral projection right internal carotid arteriogram].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_254.jpg)
![Fig. 4.1 - Extrapontine myelinolysis in an alcoholic patient. The MRI demonstrates multiple areas of hyperintensity within the hemispheric subcortical hemispheric white matter, the deep hemispheric white matter and the midbrain. [a) coronal FLAIR MRI; b, c, d) axial T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_255.jpg)

![Fig. 4.2 - Two cases of pontine myelinolysis in alcoholic pa- tients. T2-weighted MRI shows a single hyperintense lesion of the pons in each case. [a, b) axial T2-weighted MRI]. The involvement of the mamillary bodies has been demonstrated in 98% of autopsies per- formed on Wernicke sufferers. Using MRI it is possible to demonstrate the involvement of the mamillary bodies primarily in acute cases in which contrast enhancement of the mamillary bodies is observed. However, this finding is not constant and is probably only present in cases in which there is endothelial necrosis with atten-](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_257.jpg)

![Fig. 4.4 - Wernicke’s encephalopathy in an alcoholic patient. Enhanced MRI shows contrast enhancement within the mamil- lary bodies bilaterally. More craniad T2-weighted scans shows abnormal hyperintensity within the posteromedial aspect of the thalami bilaterally and the hypothalamus. [a), b) T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd; c-e) PD- and T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_259.jpg)



![Fig. 4.8 - Hepatocerebral degeneration in patient with cirrho- sis. The MRI demonstrates an abnormal area of high MRI sig- nal intensity in the globus pallidus bilaterally. [a) axial, b) sagit- tal T1-weighted MRI]. There are a number of sources of methanol, which can be present in solvents, industrial liq- uids, perfumes and counterfeit spirits, thus making methanol intoxication relatively com- mon amongst alcoholics. It manifests clinically as general malaise and headache and may progress to stupor and coma. Necrotic areas are visible in the putamen as hypodense on CT scans and as high signal intensity on T2-de- pendent sequences in MR studies (Fig. 4.9). The appearance of these areas can also be af- fected by the presence of haemorrhagic infarc- tion. Other related necrotic areas can be identi- fied in the subcortical white matter and in the frontal cortex (12, 28, 29).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_263.jpg)


![Fig. 4.11 - Delayed post-hypoxic leukoencephalopathy,. MRI examination performed approximately three hours following admission shows widespread MRI signal hyperintensity of the white matter of the centrum semiovale. Follow up MRI approximately 1 month later shows necrosis within the abnormal hemispheric white matter foci identified on earlier scans. This evolution is consistent with delayed post-hypoxic leukoencephalopathy. As in this case, this phenomenon has been described in heroine addicts following expe- riencing acute cardiorespiratory depression. [a), b) axial T-2 weighted MRI on admission; b) axial T1-weighted MRI on admission; c), one month follow up axial T2-weighted MRI, d) one month follow up T1-weighted MRI]. Intoxication from Methotrexate](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_266.jpg)


![Fig. 4.13 - Acute carbon monoxide intoxication with cerebral necrosis. CT undertaken in the acute phase documents bilateral globus pallidus hypodensity and within the anterior frontal white matter on both sides. CT follow up approximately three weeks later reveals bilateral globus pallidus necrosis; MRI performed the same day as confirms globus pallidus necrosis and the frontal subcortical de- generative alteration. [a, b) acute phase axial CT; c) three week follow up CT; d) three week follow up T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_269.jpg)
![Fig. 4.14 - Acute carbon monoxide intoxication with clinicora- diologic resolution. T2-weighted MRI on patient admission shows swelling of the frontal lobe cortex, more prominent on the right side, resulting from cytotoxic oedema. Follow up MRI performed after clinical resolution reveals regression of the frontal swelling. [a, admission T2-weighted MRI; b) follow up T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_270.jpg)
![Fig. 4.15 - Epidural haematoma. The CT examination shows a biconvex blood collection over the right temporoparietal region asso- ciated with marked mass effect. Note the displacement of the surrounding parenchymal structures associated with leftward midline subfalcian herniation and compression of the right lateral ventricle. In the more caudal scan, ipsilateral downward herniation of the uncus is also clearly visible. In addition, there is a fracture in the right temporal bone, with minor fragment displacement. CT follow up three months later documents encephalomalacia of the posterior temporal lobe, perhaps as a result of infarction secondary com- pression-occlusion of the posterior cerebral artery caused by the uncal herniation. [a,,) initial axial unenhanced CT with brain win- dows; b,,) initial axial CT with bone windows; c) three month follow up axial CT].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_271.jpg)







![— CT is the preferred method of imaging in co- ma patients due to its very rapid examination acquisition speeds, with single or multiple slice scanning times faster than one second in latest generation appliances; in addition to its gener- al diagnostic capabilities, it is also very sensitive in recognizing acute and hyperacute phase in- tracranial haemorrhages, in localizing the cra- nial compartment of the bleed (e.g., subdur- al/epidural, subarachnoid, intraparenchymal); finally it is almost universally available in the Fig. 4.17 - Acute hydrocephalus in a case of spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage. Unenhanced cranial CT shows an intra- ventricular blood clot at the level of the foramina of Monro and the symmetrical subarachnoid haemorrhage. Also note the di- latation of the lateral ventricles, including the temporal horns, as a consequence of the obstructive hydrocephalus. [a-c) unen- hanced axial CT]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_279.jpg)



![Fig. 4.19 - Diffuse axonal injury (damage). Unenhanced cranial CT shows the presence of multiple, small cortical-subcortical junction haemorrhagic foci. These haemorrhages are an ex- pression of axonal shearing, some of which are not visible due to the absence of bleeding. The parenchymal, and therefore functional, damage is often greater than predicted on the basis of CT alone. [a, b) unenhanced axial CT].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_283.jpg)



![Fig. 4.22 - Global hypoperfusion. Unenhanced cranial CT performed 24 hours after a cardiac arrest during heart surgery documents relative isodensity of the lenticular nuclei bilaterally. Axial T2-weighted MRI 48 hours after the event reveals MRI signal hyperinten- sity within the lenticular nuclei. Axial T2-weighted and FLAIR MRI 3 weeks later demonstrates minor dilation of the ventricular sys- tem as a result of resolution of cerebral swelling, and an increase in the hyperintensity of the MRI signal of the lenticular nuclei. The FLAIR image at 3 weeks shows hyperintense cortical-subcortical MRI signal alterations. [a) initial axial CT; b) axial T2-weighted MRI at 48 hours; ¢) axial T2-weighted MRI at 3 weeks; d) axial FLAIR MRI at 3 weeks].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_287.jpg)




















![Fig. 4.34 - Brain death. SPECT scans reveal a complete absence of cerebral and cerebellar perfusion. [a) axial a), sagittal b) and c) coronal SPECT]. doubts have been voiced concerning the use of conventional cerebral angiography for verifying BD (20).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_306.jpg)











![Fig. 4.44 - Postoperative intra-axial haemorrhage. Axial CT (a) shows extensive intraparenchymal haematoma in patient recent- ly operated on for large frontal meningioma (b). [a) postopera- tive unenhanced axial CT; b) preoperative T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_318.jpg)




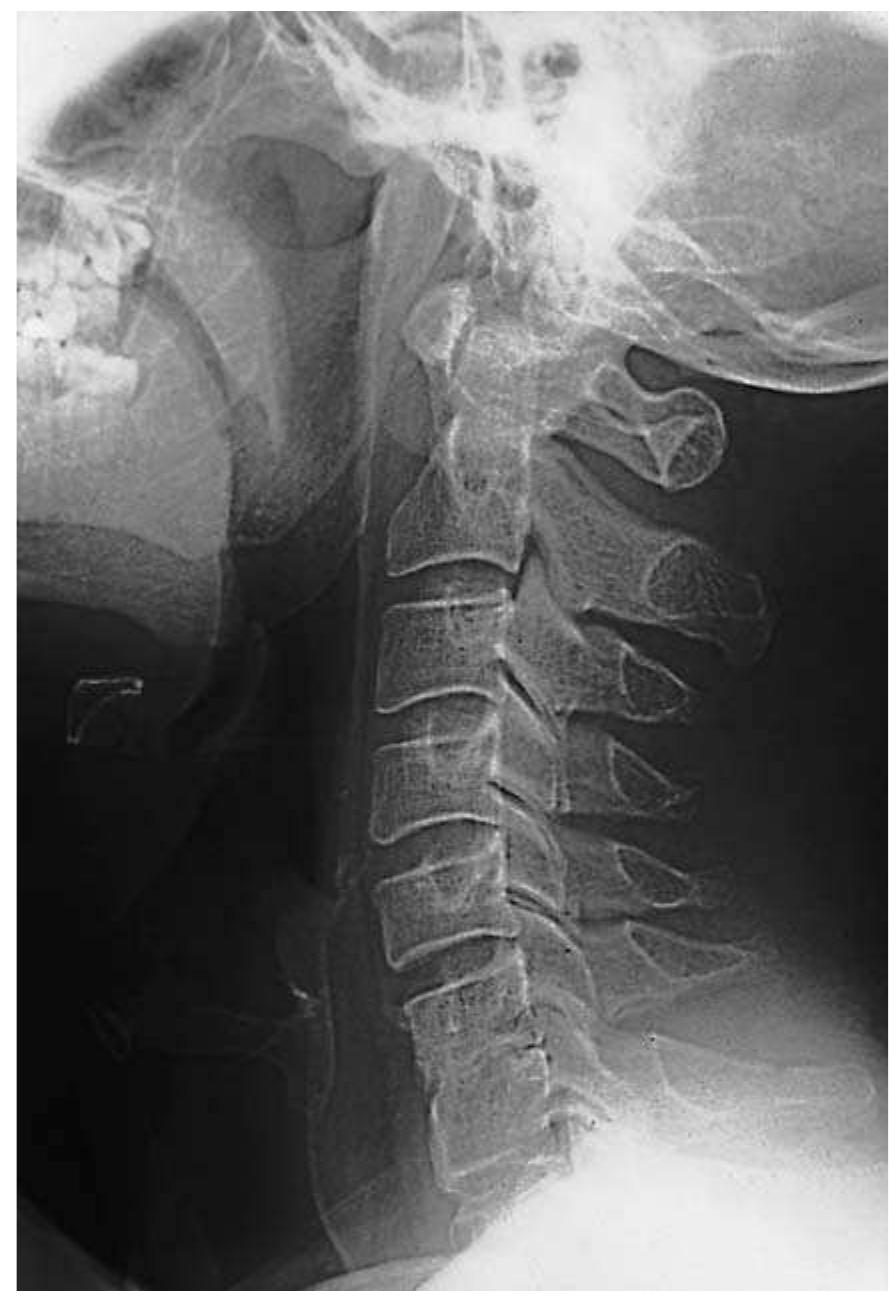
![Fig. 4.51 - Dislocation of surgical appliances following verte- bral collapse in patient with multiple myeloma operated on for posterior stabilisation. [axial CT].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_324.jpg)








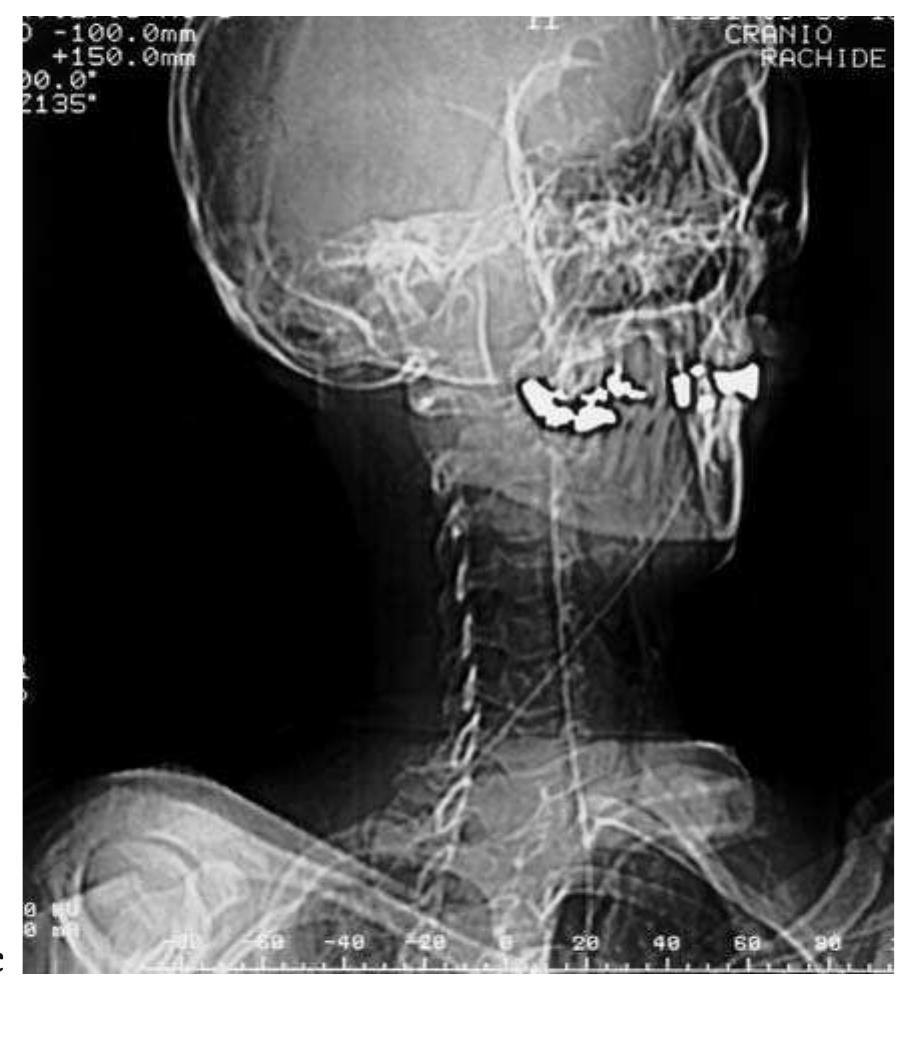



























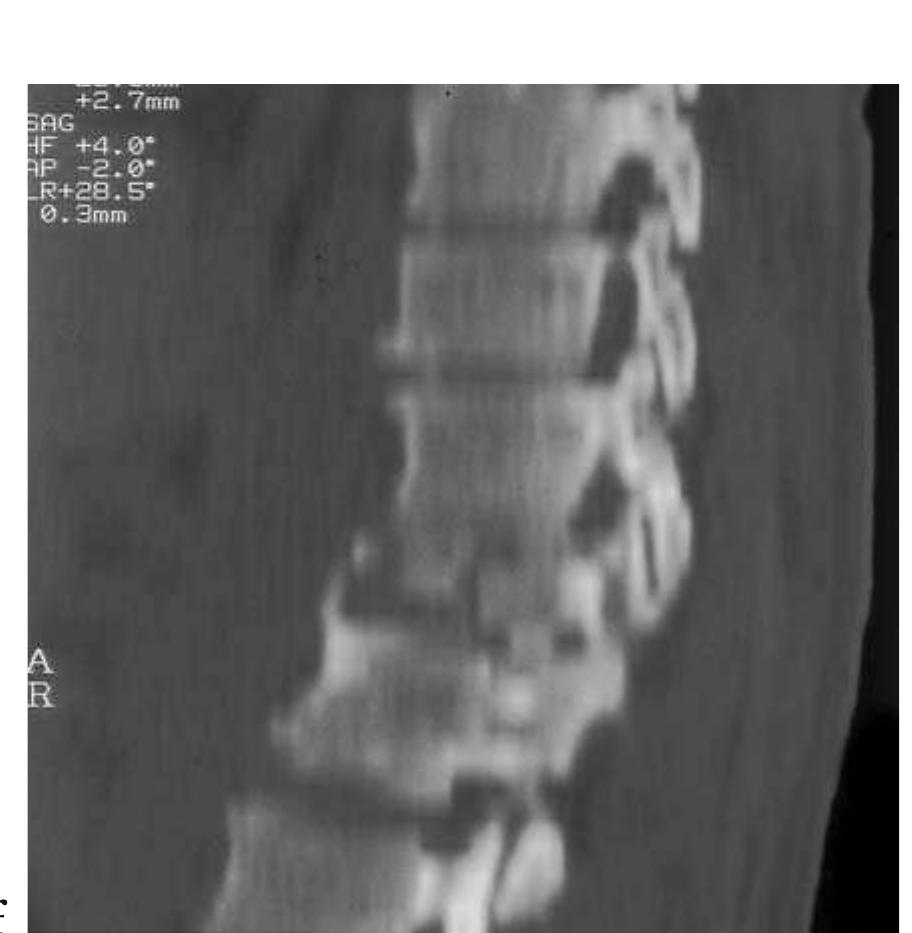
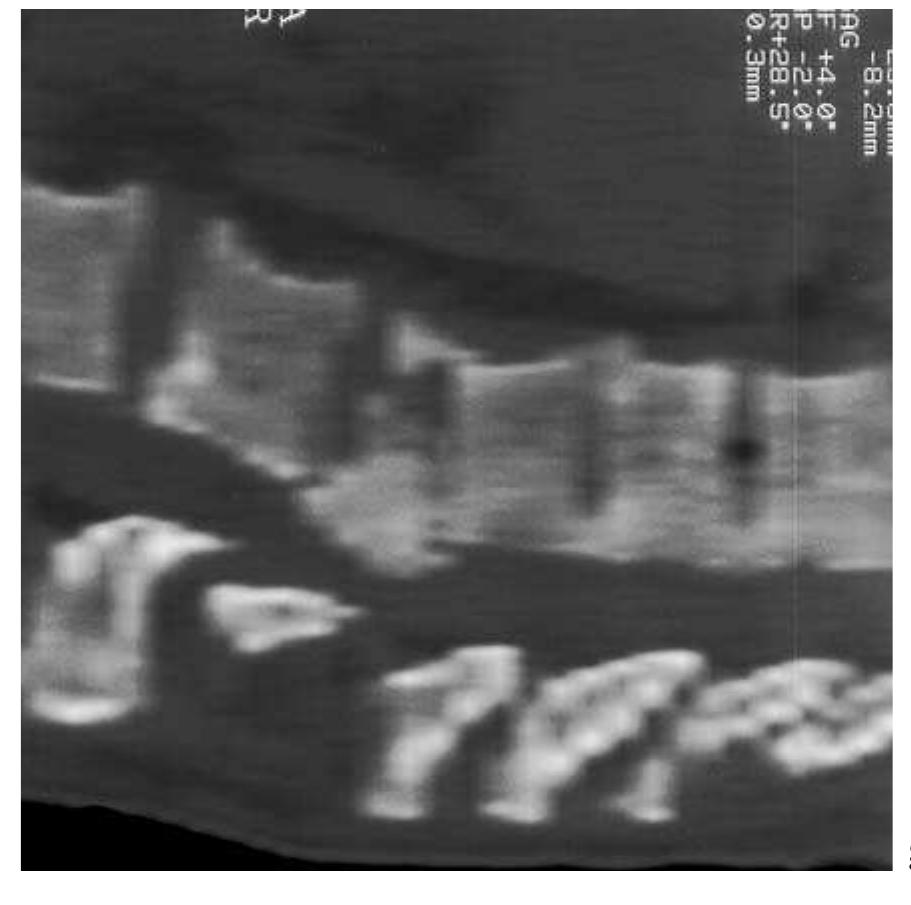


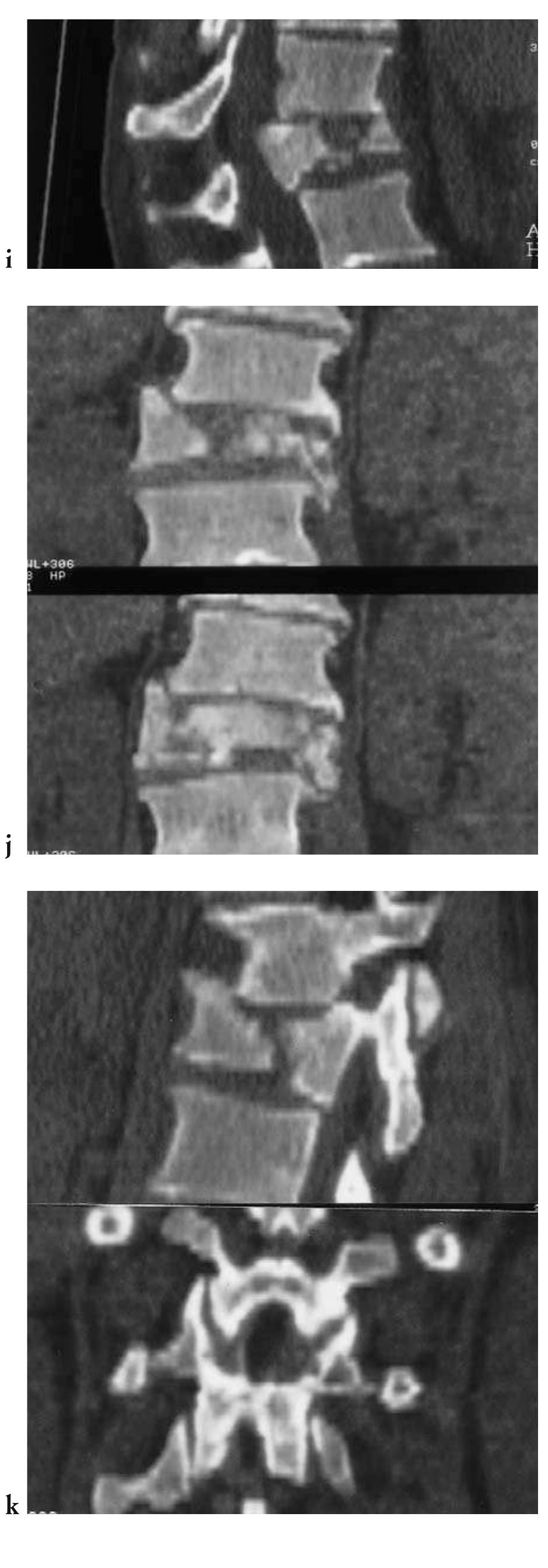






![Fig. 5.8 - Acute thoracic spine trauma. The MRI images show a burst fracture of the T12 vertebral body, with posterior dis- placement of bony fragments into the central spinal canal and resulting stenosis. There are no visible signal alterations of the spinal cord. [a) Sagittal T1-weighted MRI; b, sagittal T2- weighted MRI; c) axial T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_372.jpg)
![Fig. 5.9 - Acute lumbar spine trauma. The MRI reveals an L2 burst fracture with posterior displacement of the upper portion of the vertebral body into the central spinal canal and conse- quent canal stenosis. [a) sagittal Tl-weighted MRI, b) sagittal T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_373.jpg)



![Fig. 5.11 - Acute cervical spine trauma. MRI in a patient with bilateral C2 pedicle fractures (Hangman fracture). a), b) Sagit- tal, axial T2-weighted MRI. Fig. 5.12 - Acute thoracic spine hyperflexion trauma. The MRI study shows a fracture of the T9-10 vertebrae with anterior wedging of the vertebral bodies. There is also evidence of oede- ma of the involved vertebral bone marrow. The spinal cord, al- though deflected by posterior displacement of the T9 vertebra, does not show intrinsic signs of MRI signal alteration. [a) sagit- tal T1-weighted MRI, b) c) sagittal, axial T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_377.jpg)





![Fig. 5.16 - Acute cervical spine flexion trauma. The MRI ex- amination shows anterior dislocation of C6-C7 associated with marked stenosis of the central spinal canal. The spinal cord is severely compressed at this level, revealing oedema and swelling of the cord above and below the compression. [a) sagittal T1-weighted MRI; b) sagittal T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_383.jpg)
![Fig. 5.17 - Acute cervical spine trauma. The MRI images reveal straightening of the physiologic cervical lordotic sagittal spinal curvature. In addition, there is a compression fracture of the C6 vertebral body. The spinal cord is swollen and is hyperintense on T2*-weighted MRI due to oedema associated with cord con- tusion, but no evidence of acute haemorrhage can be identified. [a) sagittal T1-weighted MRI; b) Sagittal T2*-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_384.jpg)

![Fig. 5.18 - Acute cervical spine trauma. The MRI examination shows a loss of the physiologic cervical lordotic sagittal spinal curvature and pre-existent central spinal canal stenosis. A focal area of spinal cord contusion (i.e., oedema and swelling) can be seen on the right side at the C4 level as well as a presumed trau- matic posterior disk herniation associated with underlying spinal cord compression. [a, sagittal T2-weighted MRI; b) axi- al T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_386.jpg)
![Fig. 5.19 - Acute thoracic spine trauma. The MRI acquisitions reveal a compression fracture of the body of T12 associated with T12-L1 anterior subluxation and central spinal canal nar- rowing. In addition, there is a small anterior epidural haematoma at T11. MRI signal hypointensity is present within the spinal cord on the T2* acquisition due to acute haemor- rhagic contusion (deoxyhaemoglobin). a) [sagittal T1-weighted MRI; b) sagittal T2*-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_387.jpg)

![Fig. 5.20 - Chronic spinal cord trauma. MRI images in a case of late follow up of a burst fracture of L1 revealing diffuse spinal cord atrophy and a focal area of myelomalacia within the conus medullaris. [a) sagittal T1-weighted MRI; b) sagittal T2- weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_389.jpg)
![Fig. 5.21 - Chronic spinal cord trauma. MRI in the chronic phase following spinal cord trauma reveals a posttraumatic sy- ringomyelia cavity extending from C6-T1. [a) sagittal T1- weighted MRI; b) sagittal T2-weighted MRI, c) axial T2- weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_390.jpg)
![Fig. 5.22 - Chronic spinal cord trauma. MRI examination sev- eral years following flexion injury and spinal cord contusion shows postsurgical changes and a multisegmental syringohy- dromyelia cavity of the lower thoracic spinal cord. [a) sagittal Tl-weighted MRI; b sagittal T2-weighted MRI, c) axial T2- weighted MRI]. Fig. 5.21 (cont).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_391.jpg)










![Fig. 5.26 - Osteoblastoma of the posterior arch of C5. The MRI examination reveals a hypointense lesion within the posterior arch of C5 on the right. The CT study shows a sclerotic mass lesion of the posterior arch of C5. [a) oblique-sagittal T1- weighted MRI; b) axial T1-weighted MRI; c) axial CT].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_402.jpg)





![Fig. 5.29 - Iatrogenic epidural abscess. The MRI study shows a mass forming posterior epidural lesion that displaces the nerve roots of the cauda equina forwards. There is inhomogeneous enhancement of this process following IV Gd administration. [a) sagittal T2-weighted MRI; b) unenhanced sagittal T1-weighted MRI; ¢) sagittal T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd; d) coronal T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_408.jpg)




![Fig. 5.31 - Subacute spondylodiskitis caused by brucella species. The MRI study shows a simultaneous pathologic involvement of two adjacent vertebrae and the intervening intervertebral disk. There is irregular contrast enhancement in all involved struc- tures following IV Gd administration. The perivertebral soft tis- sues demonstrate limited involvement. [a) unenhanced sagittal T1-weighted MRI; b) sagittal T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd; c) coronal T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_413.jpg)


![Fig. 5.33 - Os odontoideum. The MRI images show anterior subluxation of the C1 vertebral body and adjacent odontoid process in relationship to the vertebral body of C2. In addition, the spinal cord is compressed between the posterior bony arch of C1 and the vertebral body of C2, and the intervening spinal cord is hyperintense indicating underlying myelomalacia. Note the partial reduction of the dislocation in extension. [a): neutral T1- and T2-weighted sagittal MRI; b): flexion T1- and T2-weighted sagittal MRI; c): ex- tension T1- and T2-weighted sagittal MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_416.jpg)
![Fig. 5.34 - Spontaneous subacute epidural haemorrhage in patient with plasmacytopenia. The MRI examination shows mass forming posterior epidural haematoma. IV Gd enhanced MRI shows minor peripheral enhancement around the haematoma. The remaining MRI study reveals hypointensity of the margins of the haematoma consistent with early haemosiderin evolution and anterior spina cord deflection-compression. [a) unenhanced sagittal T1-weighted MRI; b) T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd; c) T2-weighted MRI d) sagittal T2-weighted MRI with fat suppression; e) axial T1-weighted MRI; (f) axial T2-weighted MRI]. The rarer mass-forming lesions of the sub- arachnoid space include (in decreasing order of](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_417.jpg)
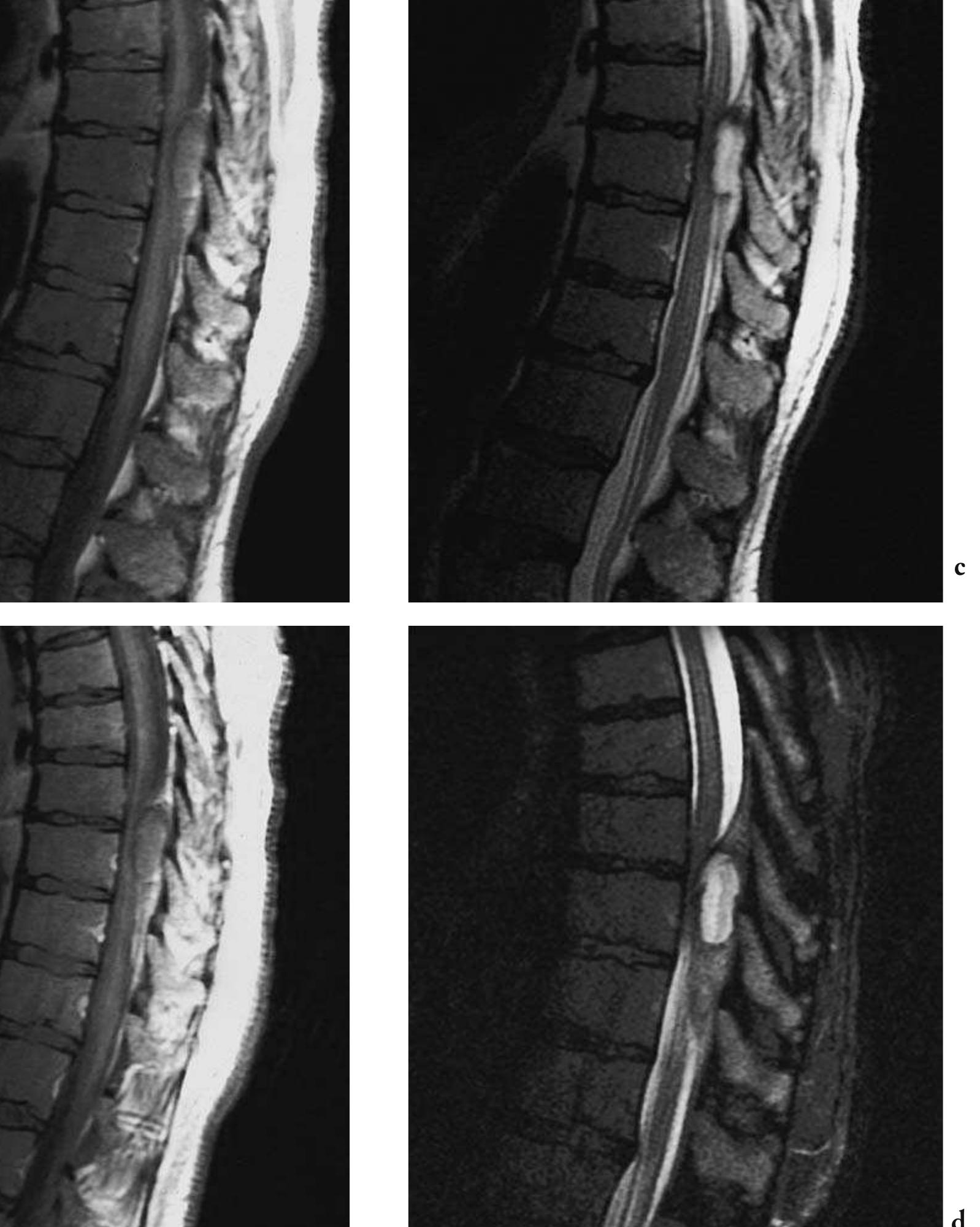

![Fig. 5.35 - Extradural arachnoid cysts. The MRI images show a posterolateral intraspinal mass lesion that has an MRI signal that is slightly higher than that of CSF. There is associated cra- nial and caudal displacement of the supra- and subjacent epidural fat surrounding the mass indicating its epidural loca- tion. There is also minor mass effect upon the thecal sac and ex- tension of the cyst into the contiguous, expanded spinal neural foramen. [a) midline sagittal T2-weighted MRI; b) parasagittal T2-weighted MRI; c) midline T1-weighted MRI; d) coronal T1- weighted MRI; e) midlesion axial T2-weighted MRI; f) subja- cent axial T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_420.jpg)




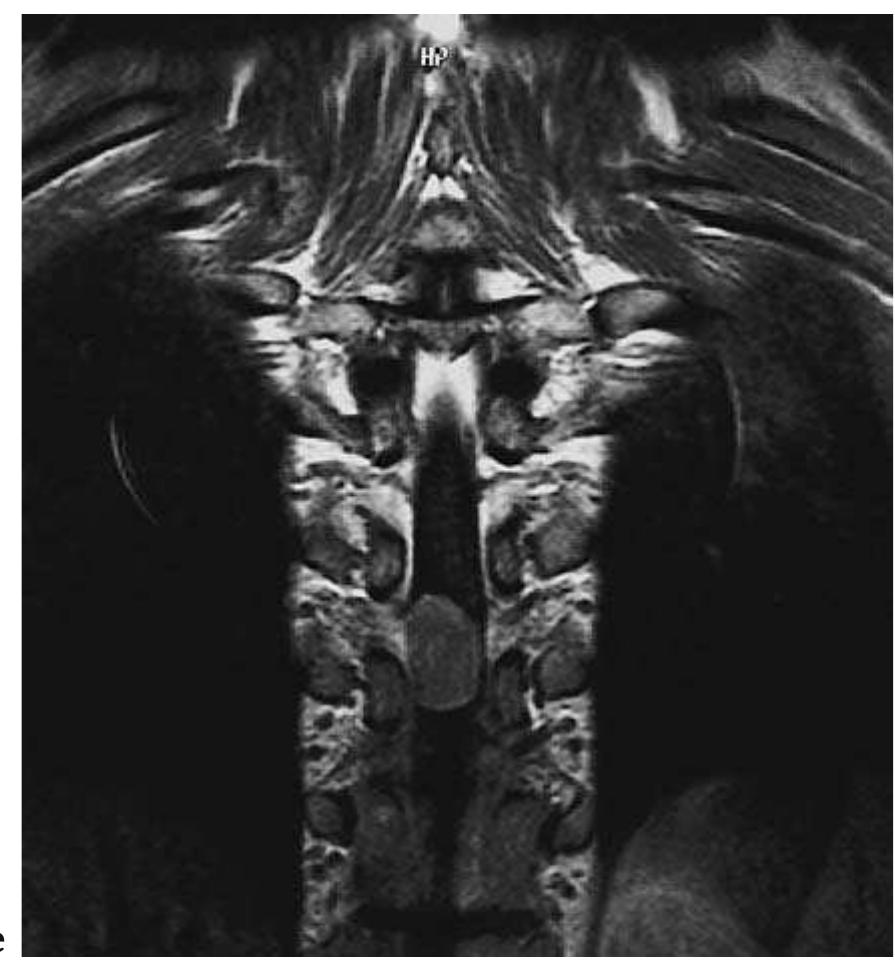
![Fig. 5.37 - Multiple spinal schwannomas in a subject with von Recklinghausen’s disease. The MRI imaging study demonstrates multi- ple intramedullary and intradural-extramedullary masses in the cervicothoracic region, which appear hyperintense on T2-weighted MRI, and show contrast enhancement following IV Gd administration. Also note the multiple perimedullary masses and the numer- ous masses within the nerve roots of the cauda equina. [a) sagittal cervicothoracic T2-weighted MRI; b) sagittal cervicothoracic T1- weighted MRI following IV Gd; c) axial cervical T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd; d) sagittal midthoracic T1-weighted MRI follow- ing IV Gd; e) axial upper thoracic T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd; f): sagittal lumbosacral T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd]. MRI is also useful for the diagnosis of acute spinal cord involvement in multiple sclerosis and sudden onset ischaemic medullary disease. Multiple sclerosis (MS) (6, 9) is a demyelinating disease that most frequently affects females, and which presents with variable neurological](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_426.jpg)



![Fig. 5.38 - Intradural spinal metastasis in a patient with primary intracranial pinealoblastoma. The MRI examination shows that the spinal cord is compressed posterolaterally by an enhancing intradural-extramedullary mass consistent with subarachnoid dissemination of the pinealoblastoma. [a) sagittal T2-weighted MRI, b) sagittal T1-weighted MRI; c) axial T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_430.jpg)




![Fig. 5.42 - Ependymoma of the conus medullaris. The MRI study shows a septated partially cystic mass with a mural nodu- lar area of contrast enhancement. [a) sagittal T2-weighted MRI, b) sagittal T1-weighted MRI following IV Gd].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_435.jpg)




![Fig. 5.44 - Ischaemia of the thoracic spinal cord associated with spinal dural arteriovenous fistula. T-2 weighted MRI demon- strates high signal intensity within the central region of the conus medullaris associated with central medullary hyperinten- sity and vascular flow voids over the posterior surface of the thoracic spinal cord. [a) sagittal T1-weighted MRI; b) axial T2- weighted MRI; c) axial T-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_440.jpg)
![Fig. 5.43 - Thoracic intramedullary multiple sclerosis. T2 weighted MRI shows an area of intramedullary high signal in- tensity at the T8-9 level associated with minor focal swelling of the spinal cord. Contrast enhancement is seen within the area of MRI signal abnormality following IV Gd administration. [a) sagittal T2-weighted MRI; a) sagittal T-1 weighted MRI follow- ing IV Gd].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_441.jpg)

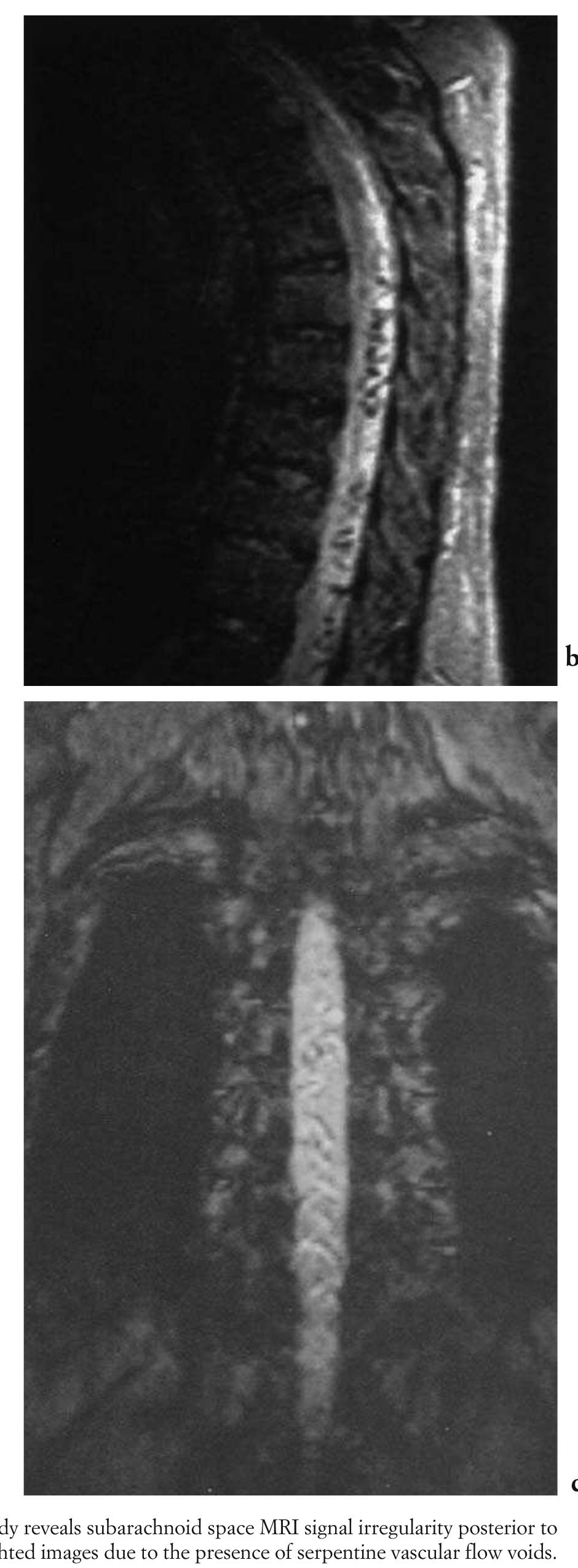

![Fig. 5.45 - Thoracic spinal dural arteriovenous fistula. The MRI study reveals subarachnoid space MRI signal irregularity posterior to the spinal cord, which becomes much more evident on the T2-weighted images due to the presence of serpentine vascular flow voids. [a) sagittal T1-weighted MRI; b) sagittal T2-weighted MRI, c) coronal T2-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_445.jpg)






![Fig. 5.48 - Radiation induced thoracic myelitis/spondylitis three years following radiotherapy. T2-weighted MRI with fat suppression shows hyperintense MRI signal within the thoracic spinal cord and within the bone marrow of several contiguous vertebral bodies, both of which are caused in this case by the preceding radiation therapy. Axial T2*-weighted images demonstrate again the intramedullary location of the patholog- ic process. No contrast enhancement of the intramedullary process can be identified. Note the postsurgical alterations. [a) sagittal T2-weighted MRI; b) sagittal T1-weighted MRI follow- ing IV Gd; c) axial T2*-weighted MRI].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35610716/figure_452.jpg)