Tarek Ahmad - Advanced Reservoir Engineering
Abstract
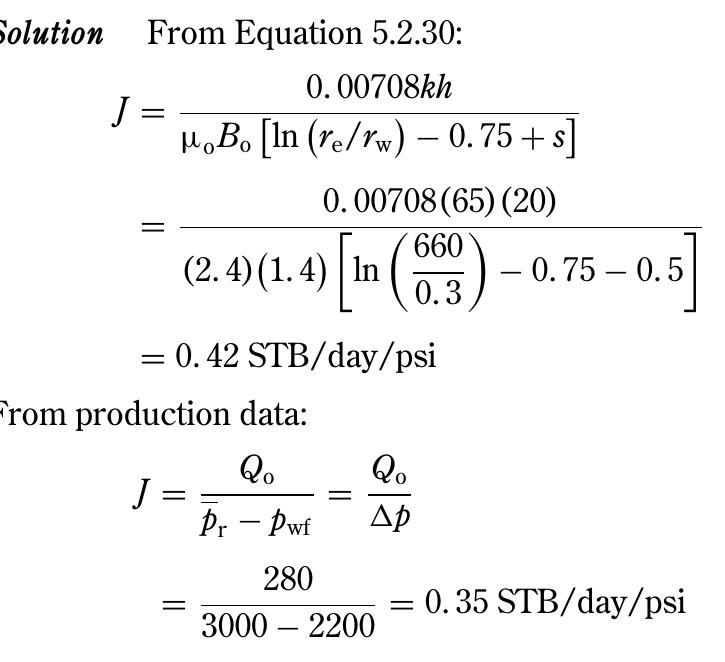
Calculate the bottom-hole flowing pressure after 4 hours by using:
Figures (569)
References (159)
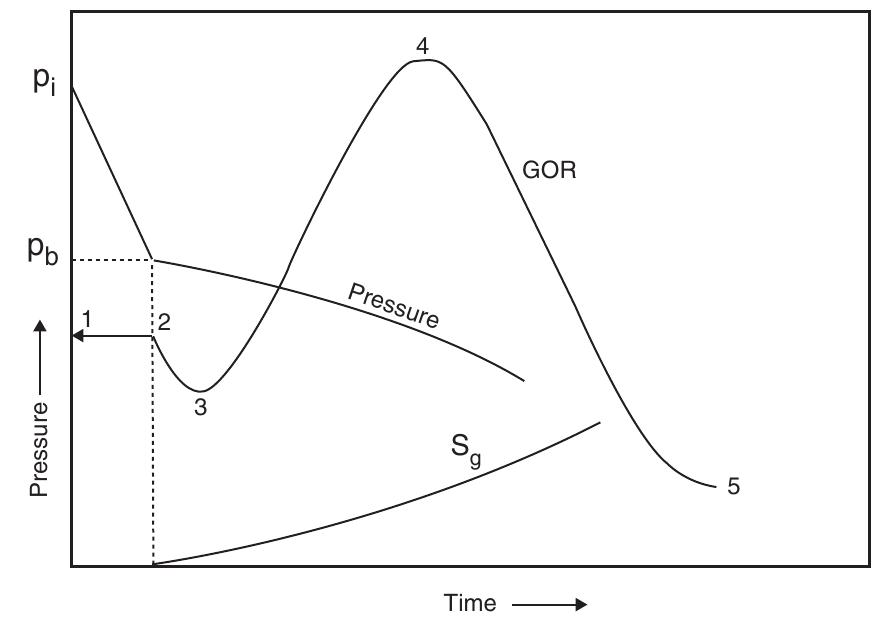
- 4350 1323 49.182 1576 43.6 7.25 4060 1143 58.383 1788 56.8 16.6 3840 1037 64.812 1992 57.3 21.0 3600 958 69.562 2158 56.7 23.8 3480 882 74.572 2383 54.4 25.6 3260 791 78.400 2596 53.5 28.3 3100 734 81.275 2785 51.6 29.2 2940 682 83.879 2953 50.0 29.9 2800 637 86.401 3103 48.3 30.3 Step 2. Calculate the PV at the bubble point pressure from: (PV) b = (N i -N pb )B ob + N i B oi 1 -S References TLFeBOOK REFERENCES
- AGARWAL, R.G. (1980). A new method to account for produc- ing time effects when drawdown type curves are used to analyze pressure buildup and other test data. SPE Paper 9289, Presented at SPE-AIME 55th Annual Technical Conference, Dallas, Texas, Sept. 21-24
- AGARWAL, R.G., AL-HUSSAINY, R., and RAMEY, H.J., JR. (1970). An investigation of wellbore storage and skin effect in unsteady liquid flow: I. Analytical treatment. SPE J., Sept., 279-290
- AGARWAL, R.G., CARTER, R.D., and POLLOCK, C.B. (1979). Eval- uation and performance prediction of low-permeability gas wells stimulated by massive hydraulic fracturing. J. Pet. Technol., Mar., 362-372; also in SPE Reprint Series No.
- AL-GHAMDI, A. and ISSAKA, M. (2001). SPE Paper 71589, Pre- sented at the SPE Annual Conference, New Orleans, LA, 30 Sept.-3 Oct.
- AL-HUSSAINY, R., RAMEY, H.J., JR., and CRAWFORD, P.B. (1966). The flow of real gases through porous media. Trans. AIME, 237, 624
- ALLARD, D.R. and CHEN, S.M. (1988). Calculation of water influx for bottomwater drive reservoirs. SPE Reservoir Eng., May, 369-379
- ANASH, J., BLASINGAME, T.A., and KNOWLES, R.S. (2000). A semi- analytic (p/Z) rate-time relation for the analysis and prediction of gas well performance. SPE Reservoir Eng., 3, Dec.
- ANCELL, K., LAMBERTS, S., and JOHNSON, F. (1980). Analysis of the coalbed degasification process. SPE/DPE Paper 8971, Presented at 1980 Unconventional Gas Recovery Symposium, Pittsburgh, PA, May 18-12, 1980
- ARPS, J. (1945). Analysis of decline curve. Trans. AIME, 160, 228-231
- BEGGS, D. (1991). Production Optimization Using Nodal Analysis (Tulsa, OK: OGCI)
- BEGLAND, T. and WHITEHEAD, W. (1989). Depletion perfor- mance of volumetric high-pressured gas reservoirs. SPE Reservoir Eng, Aug., 279-282
- BENDAKHLIA, H. and AZIZ, K. (1989). IPR for solution-gas drive horizontal wells. Paper SPE 19823, Presented at the 64th SPE Annual Meeting, San Antonio, TX, Oct. 8-11
- BORISOV, JU.P. (1984). Oil Production Using Horizontal and Multiple Deviation Wells, trans. J. Strauss and S.D. Joshi (ed.) (Bartlesville, OK: Phillips Petroleum Co., the R&D Library Translation)
- BOSSIE-CODREANU, D. (1989). A simple buildup analysis method to determine well drainage area and drawdown pressure for a stabilized well. SPE Form. Eval., Sept., pp. 418-420
- BOURDET, D. (1985). SPE Paper 13628, Presented at the SPE Regional Meeting, Bakersfield, CA, Mar. 27-29
- BOURDET, D. and GRINGARTEN, A.C. (1980). Determination of fissure volume and block size in fractured reservoirs by type-curve analysis. SPE Paper 9293, Presented at the 1980 Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Sept. 21-24
- BOURDET, D., WHITTLE, T.M., DOUGLAS, A.A., and PIRARD, Y.M. (1983). A new set of type curves simplifies well test analysis. World Oil, May, 95-106
- BOURDET, D., ALAGOA, A., AYOUB, J.A., and PIRARD, Y.M. (1984). New type curves aid analysis of fissured zone well tests. World Oil, Apr., 111-124
- BOURGOYNE, A. (1990). Shale water as a pressure support mechanism. J. Pet. Sci., 3, 305
- CARSON, D. and KATZ, D. (1942). Natural gas hydrates. Trans. AIME, 146, 150-159
- CARTER, R. (1985). Type curves for finite radial and linear gas- floe systems. SPE J., Oct., 719-728
- CARTER, R. and TRACY, G. (1960). An improved method for calculations of water influx. Trans. AIME, 152
- CHATAS, A.T. (1953). A practical treatment of nonsteady-state flow problems in reservoir systems. Pet. Eng., Aug, B-44-56
- CHAUDHRY, A. (2003). Gas Well Testing Handbook (Houston, TX: Gulf Publishing)
- CHENG, AM. (1990). IPR for solution gas-drive horizontal wells. Paper SPE 20720, Presented at the 65th SPE Annual Meeting, New Orleans, Sept. 23-26
- CINCO, H. LEY and SAMANIEGO, F. (1981). Transient pressure analysis for finite conductivity fracture case versus dam- age fracture case. SPE Paper 10179
- CLARK, N. (1969). Elements of Petroleum Reservoirs (Dallas, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineers)
- COATS, K. (1962). A mathematical model for water movement about bottom-water-drive reservoirs. SPE J., Mar., 44-52
- COLE, F.W. (1969). Reservoir Engineering Manual (Houston, TX: Gulf Publishing)
- CRAFT, B. and HAWKINS, M. (1959). Applied Petroleum Reservoir Engineering (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall)
- CRAFT, B.C. and HAWKINS, M. (Revised by terry, r.e.) (1991). Applied Petroleum Reservoir Engineering, 2nd ed. (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall)
- CULHAM, W.E. (1974). Pressure buildup equations for spherical flow regime problems. SPE J., Dec. 545-555
- CULLENDER, M. and SMITH, R. (1956). Practical solution of gas flow equations for wells and pipelines. Trans. AIME, 207, 281-287
- DAKE, L. (1978). Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering (Ams- terdam: Elsevier)
- DAKE, L.P. (1994). The Practice of Reservoir Engineering (Ams- terdam: Elsevier)
- DIETZ, D.N. (1965). Determination of average reservoir pres- sure from buildup surveys. J. Pet. Technol., Aug., 955-959
- DONOHUE, D. and ERKEKIN, T. (1982). Gas Well Testing, Theory and Practice (Boston: International Human Resources Development Corporation)
- DUGGAN, J.O. (1972). The Anderson 'L' -an abnormally pres- sured gas reservoir in South Texas. J. Pet. Technol., 24, No. 2, 132-138
- EARLOUGHER, ROBERT C., JR. (1977). Advances in Well Test Anal- ysis, Monograph Vol. 5 (Dallas, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineers of AIME)
- ECONOMIDES, C. (1988). Use of the pressure derivative for diag- nosing pressure-transient behavior., J. Pet. Technol., Oct.
- ECONOMIDES, M., HILL, A., and ECONOMIDES, C. (1994). Petroleum Production Systems (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall)
- EDWARDSON, M. et al. (1962). Calculation of formation tem- perature disturbances caused by mud circulation. J. Pet. Technol., Apr., 416-425
- ERCB (1975). Theory and Practice of the Testing of Gas Wells, 3 ed. (Calgary: Energy Resources Conservation Board)
- FANCHI, J. (1985). Analytical representation of the van Everdingen-Hurst influence functions. SPE J., June, 405-425
- FETKOVICH, E.J., FETKOVICH, M.J., and FETKOVICH, M.D. (1996). Useful concepts for decline curve forecasting, reserve estimation, and analysis. SPE Reservoir Eng., Feb.
- FETKOVICH, M., REESE, D., and WHITSON, C. (1998). Applica- tion of a general material balance for high-pressure gas reservoirs. SPE J., Mar., 923-931
- FETKOVICH, M.J. (1971). A simplified approach to water influx calculations -finite aquifer systems. J. Pet. Technol., July, 814-828
- FETKOVICH, M.J. (1973). The isochronal testing of oil wells. Paper SPE 4529, Presented at the SPE Annual Meeting, Las Vegas, Nevada, Sept. 30-Oct.
- FETKOVICH, M.J. (1980). Decline curve analysis using type curves. SPE 4629, SPE J., June FETKOVICH, M.J., VIENOT, M.E., BRADLEY, M.D., and KIESOW, U.G. (1987). Decline curve analysis using type curves -case histories. SPE 13169, SPE Form. Eval., Dec.
- GENTRY, R.W. (1972). Decline curve analysis. J. Pet. Technol., Jan., 38
- GIGER, F.M., REISS, L.H., and JOURDAN, A.P. (1984). The reser- voir engineering aspect of horizontal drilling. Paper SPE 13024, Presented at the 59th SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, TX, Sept. 16-19
- GODBOLE, S., KAMATH, V., and ECONOMIDES, C. (1988). Natural gas hydrates in the Alaskan Arctic. SPE Form. Eval., Mar.
- GOLAN, M. and WHITSON, C. (1986). Well Performance, 2nd ed. (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall)
- GRAY, K. (1965). Approximating well-to-fault distance. J. Pet. Technol., July, 761-767
- GRINGARTEN, A. (1984). Interpretations of tests in fissured and multilayered reservoirs with double-porosity behavior. J. Pet. Technol., Apr., 549-554
- GRINGARTEN, A. (1987). Type curve analysis. J. Pet. Technol., Jan., 11-13
- GRINGARTEN, A.C., RAMEY, H.J., JR., and RAGHAVAN, R. (1974). Unsteady-state pressure distributions created by a well with a single infinite-conductivity vertical fracture. SPE J., Aug., 347-360
- GRINGARTEN, A.C., RAMEY, H.J., JR., and RAGHAVAN, R. (1975). Applied pressure analysis for fractured wells. J. Pet. Technol., July, 887-892
- GRINGARTEN, A.C., BOURDET, D.P., LANDEL, P.A., and KNIAZEFF, V.J. (1979). Comparison between different skin and well- bore storage type-curves for early time transient anal- ysis. SPE Paper 8205, Presented at SPE-AIME 54th Annual Technical Conference, Las Vegas, Nevada, Sept. 23-25
- GUNAWAN GAN, RONALD and BLASINGAME, T.A. (2001). A semi- analytic (p/Z) technique for the analysis of reservoir performance from abnormally pressured gas reser- voirs. SPE Paper 71514, Presented at SPE Annual Technical Conference & Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, Sept.
- HAGOORT, JACQUES and HOOGSTRA, ROB (1999). Numerical solu- tion of the material balance equations of compartmented gas reservoirs. SPE Reservoir Eng., 2, Aug.
- HAMMERLINDL, D.J. (1971). Predicting gas reserves in abnor- mally pressure reservoirs. Paper SPE 3479 presented at the 46th Annual Fall Meeting of SPE-AIME. New Orleans, LA, Oct.
- HARVILLE, D. and HAWKINS, M. (1969). Rock compressibility in geopressured gas reservoirs. J. Pet. Technol., Dec., 1528-1532
- HAVLENA, D. and ODEH, A.S. (1963). The material balance as an equation of a straight line: Part 1. Trans. AIME, 228, I-896
- HAVLENA, D. and ODEH, A.S. (1964). The material balance as an equation of a straight line: Part 2. Trans. AIME, 231, I-815
- HAWKINS, M. (1955). Material Balances in Expansion Type Reservoirs Above Bubble-Point. SPE Transactions Reprint Series No. 3, pp. 36-40
- HAWKINS, M. (1956). A note on the skin factor. Trans. AIME, 207, 356-357
- HOLDER, G. and ANGER, C. (1982). A thermodynamic evaluation of thermal recovery of gas from hydrates in the earth. J. Pet. Technol., May, 1127-1132
- HOLDER, G. et al. (1987). Effect of gas composition and geo- thermal properties on the thickness of gas hydrate Zones. J. Pet. Technol., Sept., 1142-1147
- HOLDITCH, S. et al. (1988). Enhanced recovery of coalbed methane through hydraulic fracturing. SPE Paper 18250, Presented at the SPE Annual Meeting, Houston, TX, Oct. 2-5
- HORN, R. (1995). Modern Test Analysis (Palo Alto, CA: Petroway)
- HORNER, D.R. (1951). Pressure build-up in wells. Proceedings of the Third World Petroleum Congress, The Hague, Sec II, 503-523. Also Pressure Analysis Methods, Reprint Series, No. 9 (Dallas, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineers of AIME), pp. 25-43
- HUGHES, B. and LOGAN, T. (1990). How to design a coalbed methane well. Pet. Eng. Int., May, 16-23
- HURST, W. (1943). Water influx into a reservoir. Trans. AIME, 151
- IKOKU, C. (1984). Natural Gas Reservoir Engineering (New York: John Wiley & Sons)
- JONES, S.C. (1987). Using the inertial coefficient, b, to charac- terize heterogeneity in reservoir rock. SPE Paper 16949, Presented at the SPE Conference, Dallas, TX, Sept. 27-30
- JOSHI, S. (1991). Horizontal Well Technology (Tulsa, OK: Penn Well)
- KAMAL, M. (1983). Interference and pulse testing -a review. J. Pet. Technol., Dec., 2257-2270
- KAMAL, M. and BIGHAM, W.E. (1975). Pulse testing response for unequal pulse and shut-in periods. SPE J., Oct., 399-410
- KAMAL, M., FREYDER, D., and MURRAY, M. (1995). Use of transient testing in reservoir management. J. Pet. Technol., Nov.
- KATZ, D. (1971). Depths to which frozen gas fields may be expected. J. Pet. Technol., Apr.
- KAZEMI, H. (1969). Pressure transient analysis of naturally frac- tured reservoirs with uniform fracture distribution., SPE J., Dec., 451-462
- KAZEMI, H. (1974). Determining average reservoir pressure. SPE. J., Feb., 55-62
- KAZEMI, H. and SETH, M. (1969). Effect of anisotropy on pressure transient analysis. J. Pet. Technol., May, 639-647
- KING, G. (1992). Material balance tec for coal seam and Devo- nian shale gas reservoirs with limited water influx. SPE Reservoir Eng., Feb., 67-75
- KING, G., ERTEKIN, T., and SCHWERER, F. (1986). Numerical sim- ulation of the transient behavior of coal seam wells. SPE Form. Eval., Apr., 165-183
- KLINS, M. and CLARK, L. (1993). An improved method to predict future IPR curves. SPE Reservoir Eng., Nov., 243-248
- LANGMUIR, I. (1918). The constitution and fundamental prop- erties of solids and liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 38, 1918 TLFeBOOK
- LEE, J. (1982). Well Testing (Dallas, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineers of AIME)
- LEE, J. and WATTENBARGER, R. (1996). Gas Reservoir Engineer- ing, SPE Textbook Series, Vol. 5 (Dallas, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineers)
- LEFKOVITS, H., HAZEBROEK, P., ALLEN, E., and MATTHEWS, C. (1961). A study of the behavior of bounded reservoirs. SPE. J., Mar., 43-58
- LEVINE, J. (1991). The impact of oil formed during coalifica- tion on generating natural gas in coalbed reservoirs. The 1991 Coalbed Methane Symposium, The University of Alabama-Tuscaloosa, May 13-16
- MAKOGON, Y. (1981). Hydrates of Natural Gas (Tulsa, OK: Penn Well)
- MATTAR, L. and ANDERSON, D. (2003). A systematic and compre- hensive methodology for advanced analysis of production data. SPE Paper 84472, Presented at the SPE Conference, Denver, CO, Oct. 5-8
- MATTHEWS, C.S. and RUSSELL, D.G. (1967). Pressure Buildup and Flow Tests in Wells, Monograph Vol. 1 (Dallas, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineers of AIME)
- MATTHEWS, C.S., BRONS, F., and HAZEBROEK, P. (1954). A method for determination of average pressure in a bounded reser- voir. Trans. AIME, 201, 182-191; also in SPE Reprint Series, No.
- MAVOR, M. and NELSON, C. (1997). Coalbed reservoirs gas- in-place analysis. Gas Research Institute Report GRI 97/0263, Chicago MAVOR, M., CLOSE, J., and McBANE, R. (1990). Formation evalua- tion of coalbed methane wells. Pet. Soc. CIM, CIM/SPE Paper 90-101
- McLENNAN, J. and SCHAFER, P. (1995). A guide to coal bed gas content determination. Gas Research Institute Report GRI 94/0396, Chicago
- McLEOD, N. and COULTER, A. (1969). The simulation treatment of pressure record. J. Pet. Technol., Aug, 951-960
- MERRILL, L.S., KAZEMI, H., and COGARTY, W.B. (1974). Pressure falloff analysis in reservoirs with fluid banks. J. Pet. Technol., July, 809-818
- MEUNIER, D., WITTMANN, M.J., and STEWART, G. (1985). Interpreta- tion of pressure buildup test using in-situ measurement of afterflow. J. Pet. Technol., Jan., 143-152
- MULLER, S. (1947). Permafrost (Ann Arbor, MI: J.W. Edwards)
- MUSKAT, M. (1945). The production histories of oil producing gas-drive reservoirs. J. Appl. Phys., 16, 167
- MUSKAT, M. and EVINGER, H.H. (1942). Calculations of theoretical productivity factor. Trans. AIME, 146, 126-139
- NAJURIETA, H.L. (1980). A theory for pressure transient analy- sis in naturally fractured reservoirs. J. Pet. Technol., July, 1241-1250
- NEAVEL, R. et al. (1986). Interrelationship between coal com- positional parameters. Fuel, 65, 312-320 1999
- NELSON, C. (1989). Chemistry of coal weathering (New York: Elsevier Science)
- NELSON, R. (1999). Effects of coalbed reservoir property anal- ysis methods on gas-in-place estimates. SPE Paper 57443, Presented at SPE Regional Meeting, Charleston, WV, 21-22 Oct.
- OSTERGAARD, K. et al. (2000). Effects of reservoir fluid produc- tion on gas hydrate phase boundaries. SPE Paper 50689, Presented at the SPE European Petroleum Conference, The Hague, The Netherlands, Oct. 20-22
- PALACIO, C. and BLASINGAME, T. (1993). Decline-curve anal- ysis using type-curves analysis of gas well produc- tion data. SPE Paper 25909, Presented at the 1993 SPE Rocky Mountain Regional Meeting, Denver, CO, Apr. 26-28
- PAPADOPULOS, I. (1965). Unsteady flow to a well in an infinite aquifer. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol., I, 21-31
- PAYNE, DAVID A. (1996). Material balance calculations in tight gas reservoirs: the pitfalls of p/Z plots and a more accurate technique. SPE Reservoir Eng., Nov.
- PERRINE, R. (1956). Analysis of pressure buildup curves. Drill. Prod. Prac. API , 482-509
- PETNANTO, A. and ECONOMIDES, M. (1998). Inflow performance relationships for horizontal wells. SPE Paper 50659, Pre- sented at the SPE European Conference held in The Hague, The Netherlands, Oct. 20-22
- PINSON, A. (1972). Convenience in analysing two-rate flow tests. J. Pet. Techol., Sept., 1139-1143
- PLETCHER, J. (2000). Improvements to reservoir material balance methods. SPE 62882, SPE Annual Technical Conference, Dallas, TX, 1-4 Oct.
- POSTON, S. (1987). The simultaneous determination of for- mation compressibility and gas in place. Presented at the 1987 Production Operation Symposium, Oklahoma City, OK
- POSTON, S. and BERG, R. (1997). Overpressured Gas Reservoirs (Richardson, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineers)
- PRATIKNO, H., RUSHING, J., and BLASINGAME, T.A. (2003). Decline curve analysis using type curves -fractured wells. SPE 84287, SPE Annual Technical Conference, Denver, CO, 5-8 Oct.
- PRATT, T., MAVOR, M., and DEBRUYN, R. (1999). Coal gas resources and production potential in the Powder River Basin. Paper SPE 55599, Presented at the 1999 Rocky Mountain Meeting; Gillette, WY, May 15-18
- RAMEY, H. (1975). Interference analysis for anisotropic forma- tions. J. Pet. Technol., Oct., 1290-1298
- RAMEY, H. and COBB, W. (1971). A general buildup theory for a well located in a closed drainage area. J. Pet. Technol., Dec. RAWLINS, E.L. and SCHELLHARDT, M.A. (1936). Back-pressure Data on Natural Gas Wells and Their Application to Production Practices (US Bureau of Mines Monograph 7)
- REMNER, D. et al. (1986). A parametric stuffy of the effects of coal seam properties on gas drainage. SPE Reservoir Eng., Nov., 633
- RENARD, G.I. and DUPUY, J.M. (1990). Influence of formation damage on the flow efficiency of horizontal wells. Paper SPE 19414, Presented at the Formation Damage Control Symposium, Lafayette, LA, Feb. 22-23
- ROACH, R.H. (1981). Analyzing geopressured reservoirs -a material balance technique. SPE Paper 9968, Society of Petroleum Engineers of AIME, Dallas, TX, Dec.
- RUSSELL, D. and TRUITT, N. (1964). Transient pressure behaviour in vertically fractured reservoirs. J. Pet. Tech- nol., Oct., 1159-1170
- SABET, M. (1991). Well Test Analysis (Dallas, TX: Gulf Publishing)
- SAIDIKOWSKI, R. (1979). SPE Paper 8204, Presented at the SPE Annual Conference, Las Vegas, NV, Sept. 23-25
- SCHILTHUIS, R. (1936). Active oil and reservoir energy. Trans. AIME, 118, 37
- SEIDLE, J. (1999). A modified p/Z method for coal wells. SPE Paper 55605, Presented at the 1999 Rocky Mountain Meeting, Gillette, WY, May 15-18
- SEIDLE, J. and ARRL, A. (1990). Use of the conventional reservoir model for coalbed methane simulation. CIM/SPE Paper No. 90-118
- SHERRAD, D., BRICE, B., and MacDONALD, D. (1987). Application of horizontal wells in Prudhoe Bay. J. Pet. Technol., May, 1417-1421
- SLIDER, H.C. (1976). Practical Petroleum Reservoir Engineering Methods. (Tulsa, OK: Petroleum Publishing)
- SLOAN, D. (1984). Phase equilibria of natural gas hydrates. Paper Presented at the 1984 Gas Producers Association Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, Mar. 19-21
- SLOAN, E. (2000). Hydrate Engineering (Richardson, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineers)
- SMITH, J. and COBB, W. (1979). Pressure buildup tests in bounded reservoirs. J. Pet. Technol., Aug.
- SOMERTON, D. et al. (1975). Effects of stress on permeability of coal. Int. J. Rock Mech., Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr., 12, 129-145
- STANDING, M.B. (1970). Inflow performance relationships for damaged wells producing by solution-gas drive. J. Pet. Technol., Nov., 1399-1400
- STEFFENSEN, R. (1987). Solution-gas-drive reservoirs.
- Petroleum Engineering Handbook, Chapter 37 (Dallas, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineers)
- STEGEMEIER, G. and MATTHEWS, C. (1958). A study of anomalous pressure buildup behavior. Trans. AIME, 213, 44-50
- STROBEL, C., GULATI, M., and RAMEY, H. (1976). Reservoir limit tests in a naturally fractured reservoir. J. Pet. Technol., Sept., 1097-1106
- TARNER, J. (1944). How different size gas caps and pressure maintenance affect ultimate recovery. Oil Wkly, June 12, 32-36
- TERWILLIGER, P. et al. (1951). An experimental and theoreti- cal investigation of gravity drainage performance. Trans. AIME, 192, 285-296
- TIAB, D. and KUMAR, A. (1981). Application of the p D function to interference tests. J. Pet. Technol., Aug., 1465-1470
- TRACY, G. (1955). Simplified form of the MBE. Trans. AIME, 204, 243-246
- UNSWORTH, J., FOWLER, C., and JUNES, L. (1989). Moisture in coal. Fuel, 68, 18-26
- VAN EVERDINGEN, A.F. and HURST, W. (1949). The application of the Laplace transformation to flow problems in reser- voirs. Trans. AIME, 186, 305-324
- VOGEL, J.V. (1968). Inflow performance relationships for solution-gas drive wells. J. Pet. Technol., Jan. 86-92
- WALSH, J. (1981). Effect of pore pressure on fracture perme- ability. Int. J. Rock Mech., Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr., 18, 429-435
- WARREN, J.E. and ROOT, P.J. (1963). The behavior of naturally fractured reservoirs. SPE J., Sept., pp. 245-255
- WATTENBARGER, ROBERT A. and RAMEY, H.J., JR. (1968). Gas well testing with turbulence damage and wellbore storage. J. Pet. Technol., 877-887
- WEST, S. and COCHRANE, P. (1994). Reserve determination using type curve matching and extended material bal- ance methods in The Medicine Hat Shallow Gas Field. SPE Paper 28609, Presented at the 69th Annual Technical Conference, New Orleans, LA, Sept. 25-28
- WHITSON, C. and BRULE, M. (2000). Phase Behavior (Richardson, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineers)
- WICK, D. et al. (1986). Effective production strategies for coalbed methane in the Warrior Basin. SPE Paper 15234, Presented at the SPE Regional Meeting, Louisville, KY, May 18-21
- WIGGINS, M.L. (1993). Generalized inflow performance rela- tionships for three-phase flow. Paper SPE 25458, Pre- sented at the SPE Production Operations Symposium, Oklahoma City, OK, Mar. 21-23
- YEH, N. and AGARWAL, R. (1989). Pressure transient analy- sis of injection wells. SPE Paper 19775, Presented at the SPE Annual Conference, San Antonio, TX, Oct. 8-11
- ZUBER, M. et al. (1987). The use of simulation to determine coalbed methane reservoir properties. Paper SPE 16420, Presented at the 1987 Reservoir Symposium, Denver, CO, May 18-19
 Sorina Dumitrascu
Sorina Dumitrascu











![The above calculations show that g, and q2 are not largely different, which is due to the fact that the liquid is slightly incompressible and its volume is not a strong function of pressure. [1.2.6]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/32148465/figure_012.jpg)




































































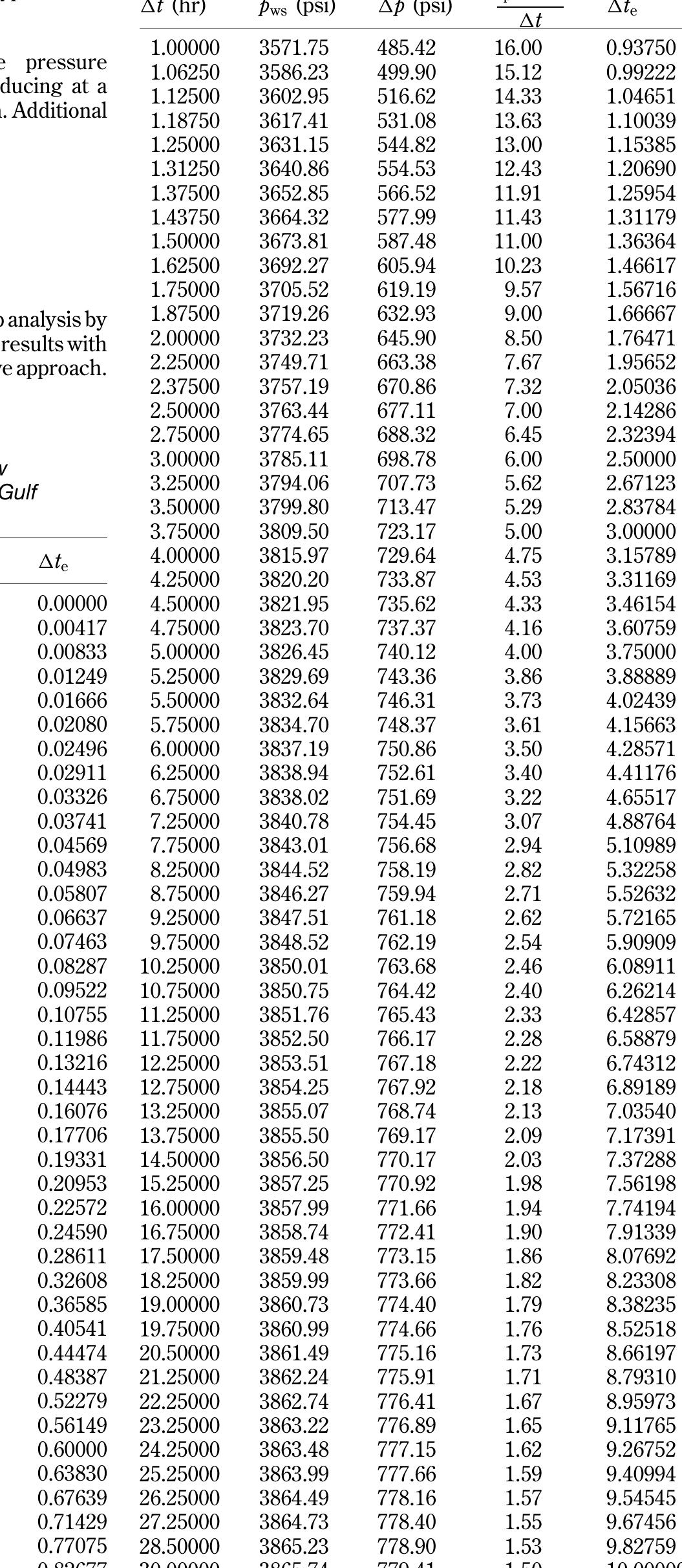















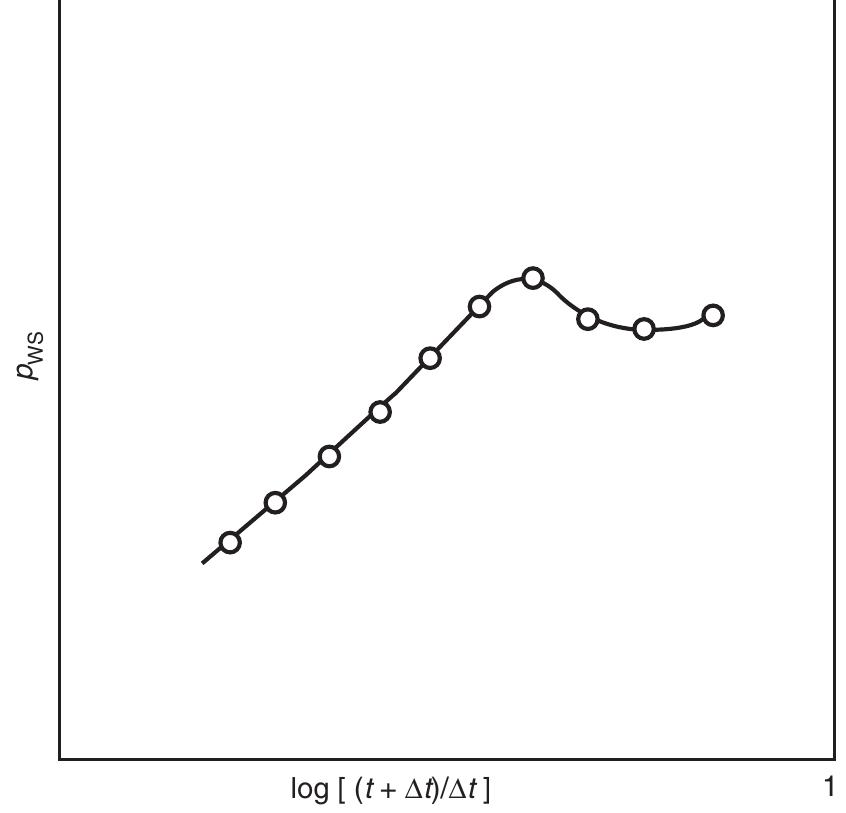






















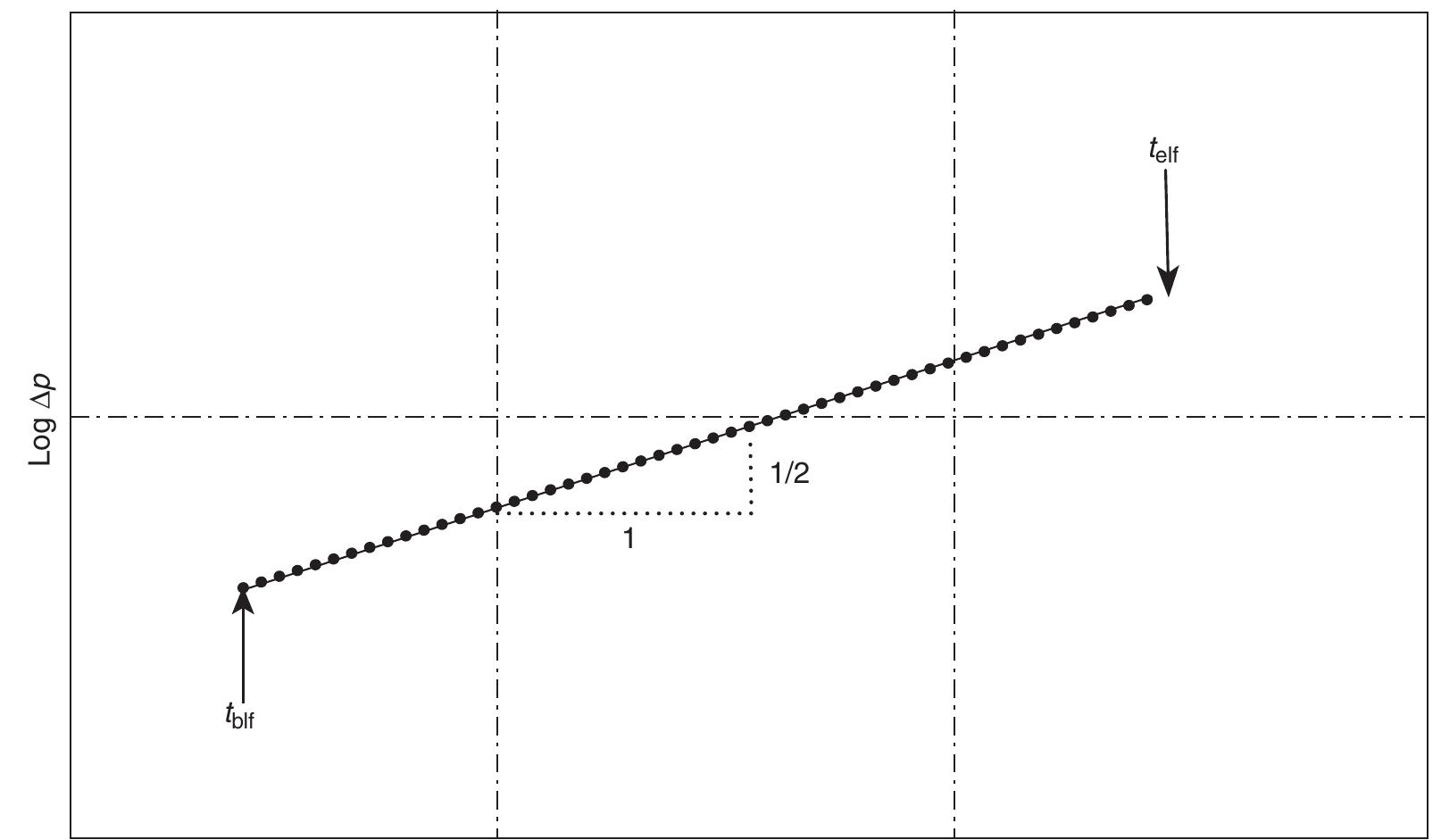



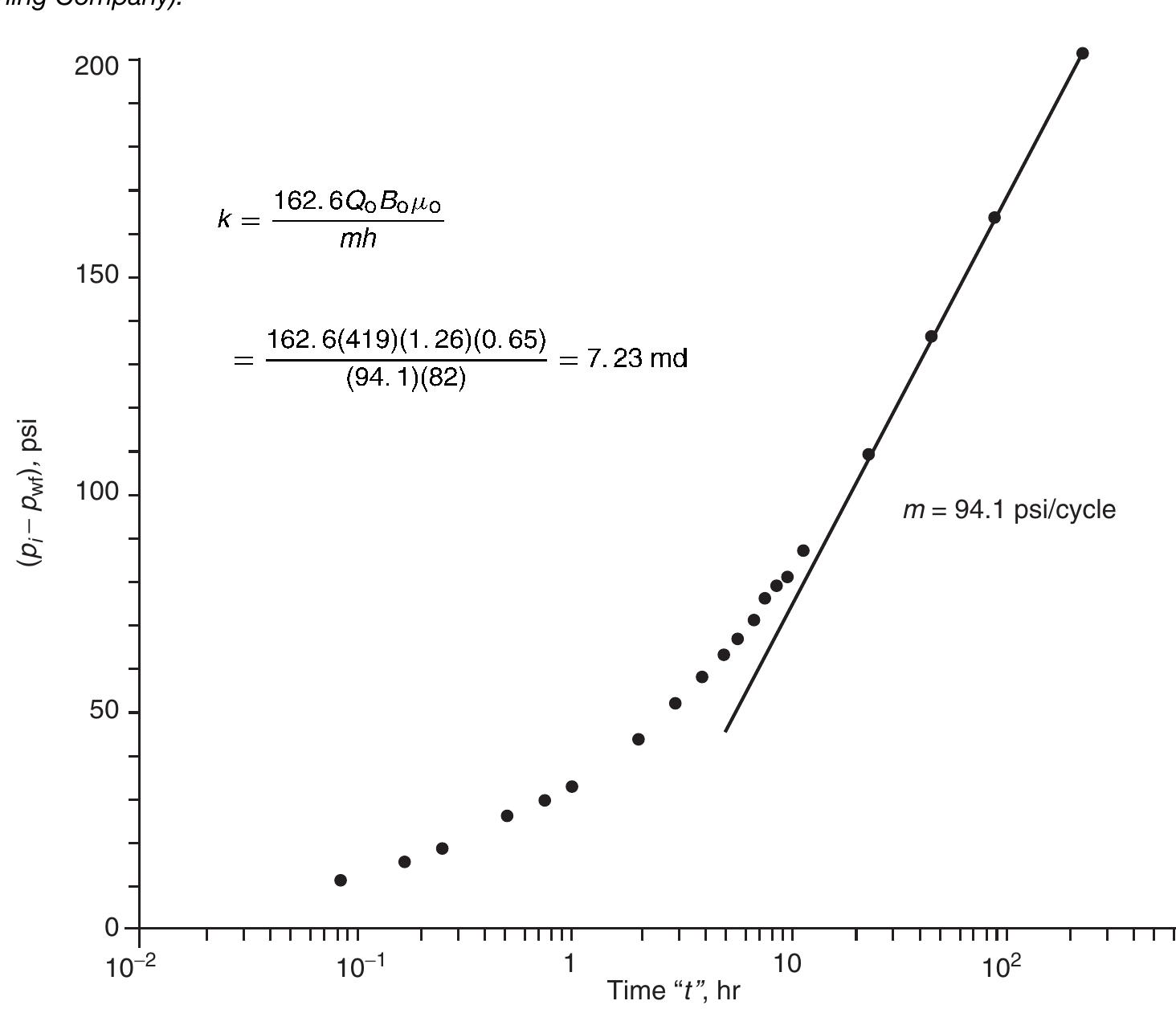






















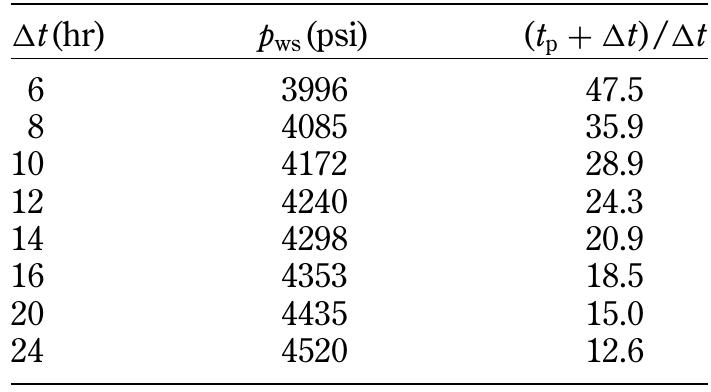






































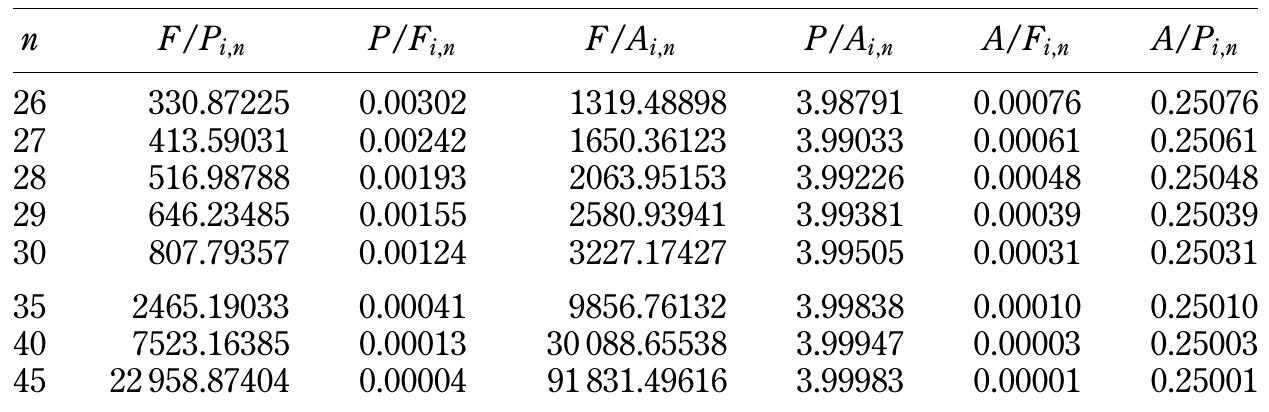
![shown in Figure 1.123, a plot of pys vs. log [ (tp) + At) /At] would form a straight-line portion with an intercept of p* at (t) + At) /At = 1 and a negative slope of m. Solution](https://figures.academia-assets.com/32148465/figure_151.jpg)























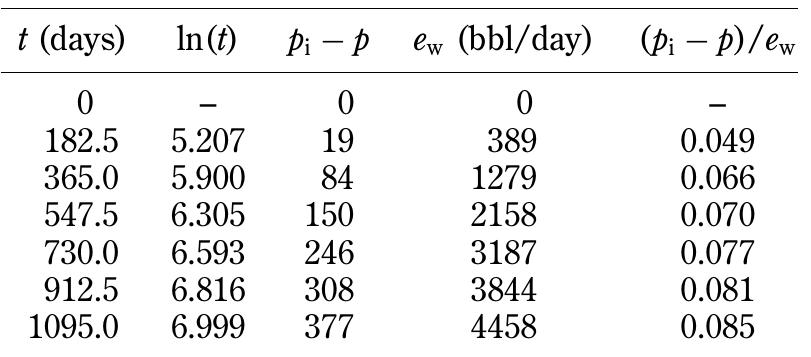







































































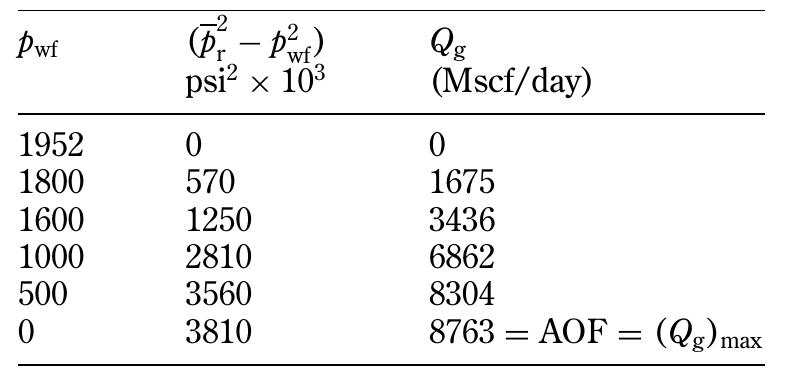





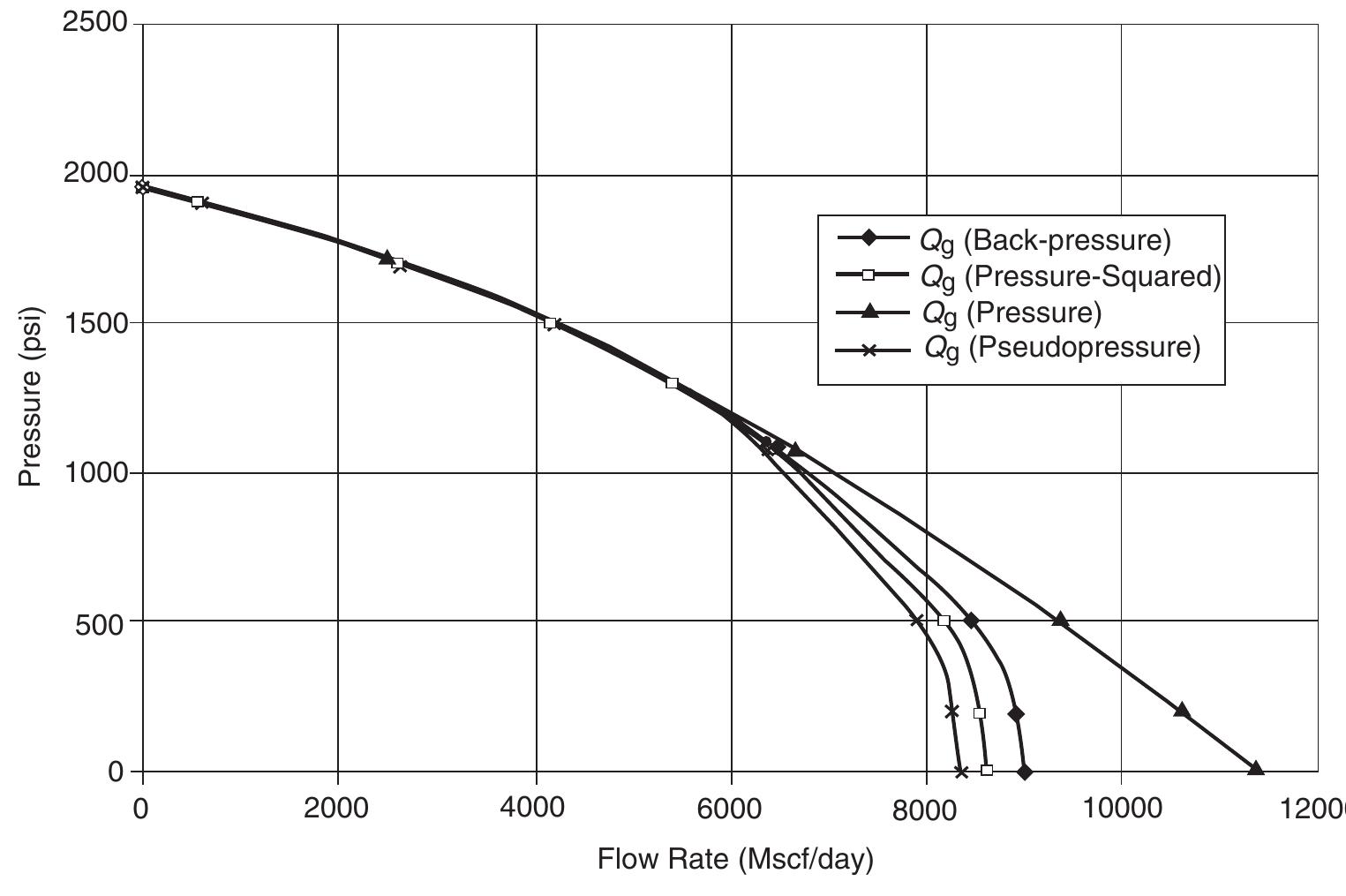




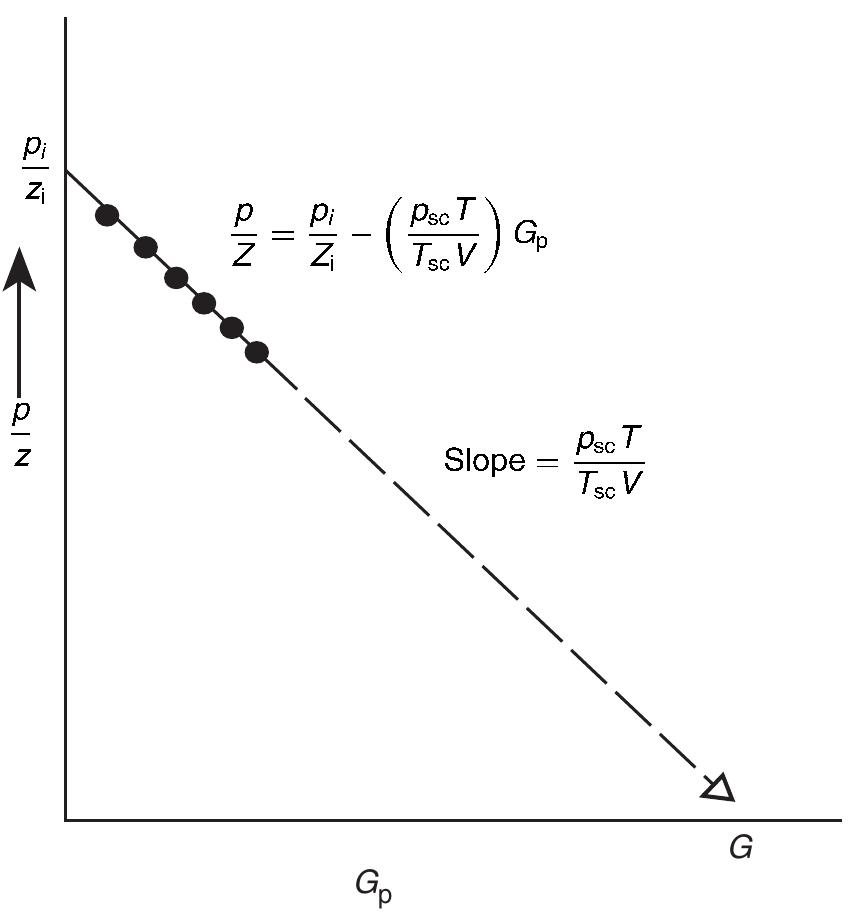





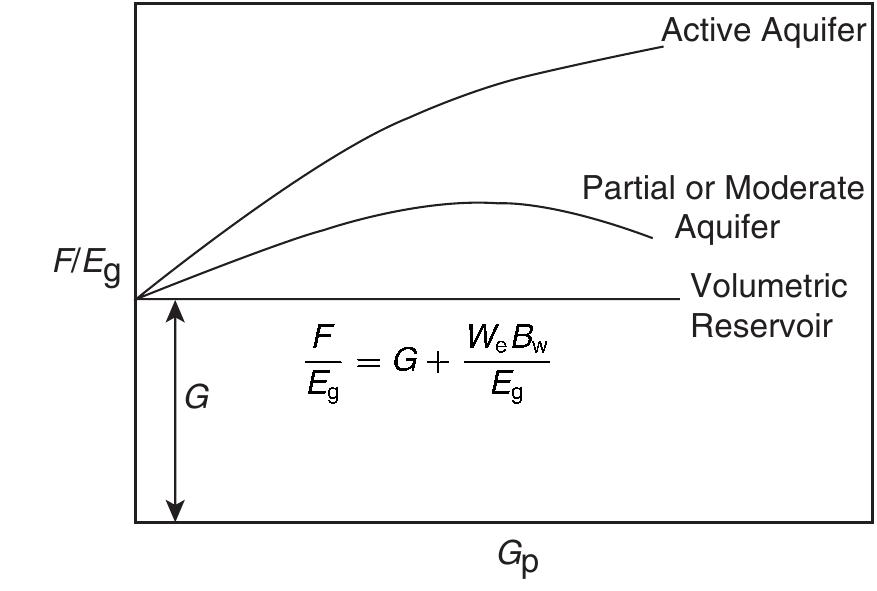








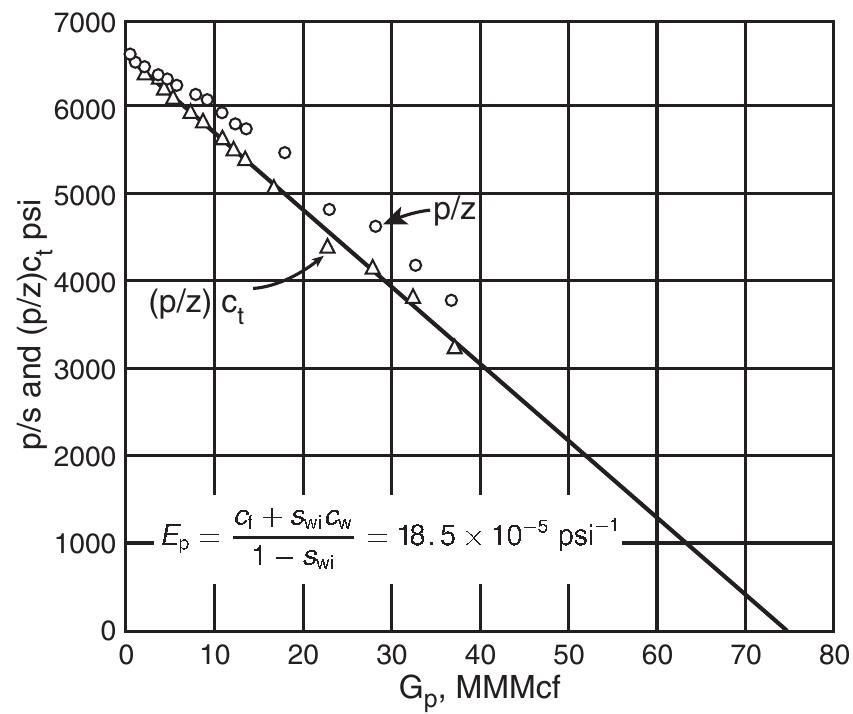






















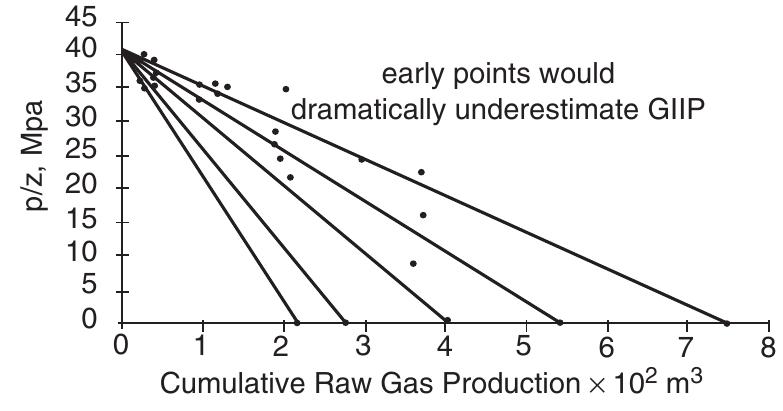
































































































































































![Standing method = 989[1 — 0.52(Py¢/2200) — 0.48 (Pyt/2200)7] Standing (1970) essentially extended the application of the Vogel method to predict the future IPR of a well as a func- tion of reservoir pressure. He noted that Vogel’s equation (Equation 5.2.9) can be rearranged as:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/32148465/table_160.jpg)