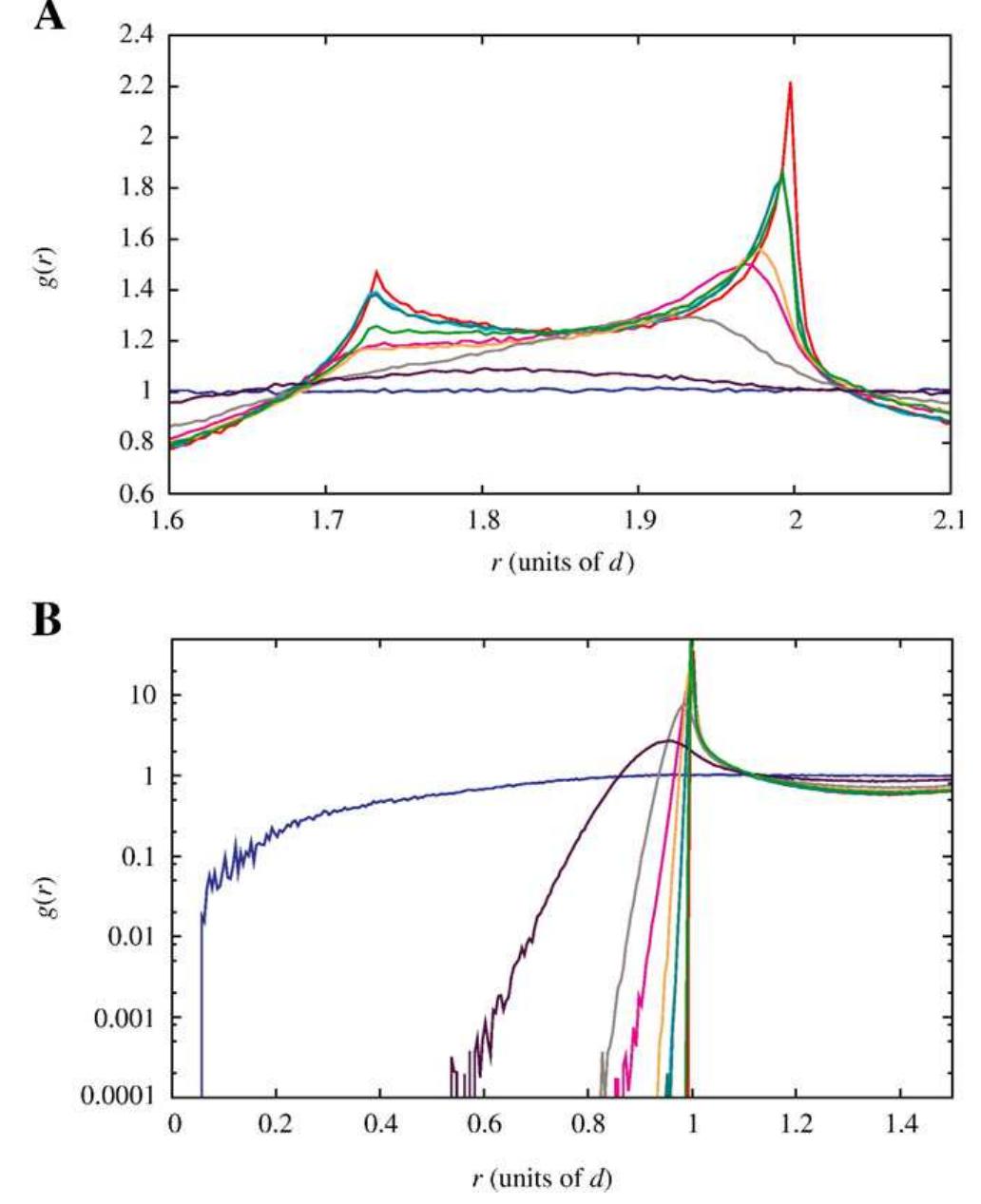
We develop a multiscale simulation method for dense granular drainage, based on the recently proposed spot model, where the particle packing flows by local collective displacements in response to diffusing "spots" of interstitial free... more
Thermodynamic analysis methods, based on an exergy metric, have been developed to improve system efficiency of traditional heat driven systems such as ground based power plants and aircraft propulsion systems. However, in more recent... more
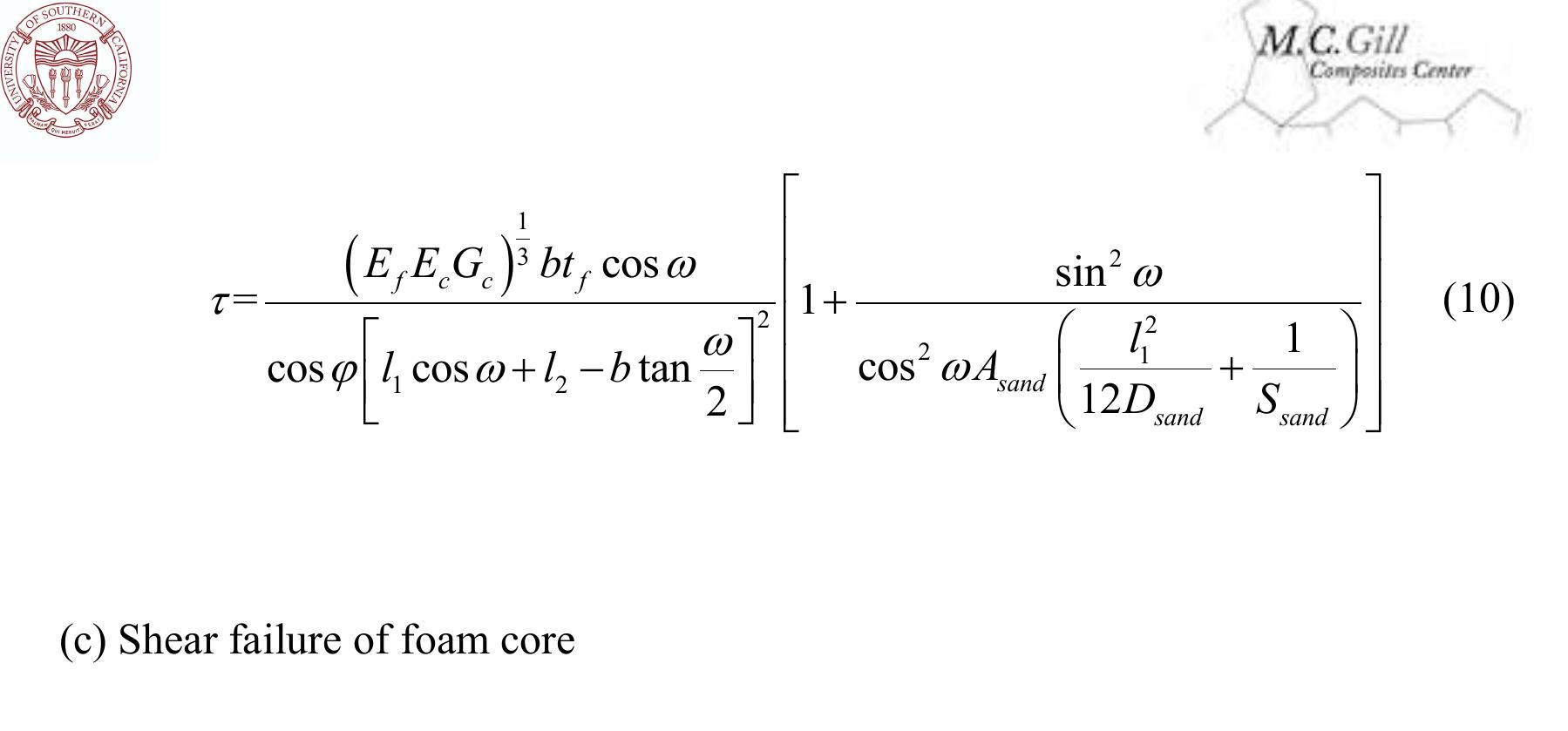
Lattice materials can be designed through their microstructure while concurrently considering fabrication feasibility. Here, we propose two types of composite lattice materials with enhanced resistance to buckling: (a) hollow lattice... more
Effect of cooperative grain boundary sliding and migration on crack growth in nanocrystalline solids
A new mechanism of fracture toughness enhancement in nanocrystalline metals and ceramics is suggested. The mechanism represents the cooperative grain boundary (GB) sliding and stress-driven GB migration process near the tips of growing... more
This work involves the determination of transport coefficients and equation of state of supercritical fluids by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations on parallel computers using the Green-Kubo formulae and the virial equation of state,... more
A previously synthesized hyperbranched poly(butylene adipate) (HPBA) polymer was compared with a commercial dendritic polyol (HPOH) as a toughening agent for a commercial one-part epoxy resin. Both modifiers were added in weight... more
Today, renewable energy sourcese.g. forest biomassare of great importance, not only domestic but also industrialf.i. wood fired power stationutilization is wide spread as well. However, the comminution of such fibrous texture materials... more
This article presents a new format of tool path polynomial interpolation in 5-axis machining. The linear interpolation usually used produces tangency discontinuities along the tool path, sources of decelerations of the machine tool... more
In high-strength steels it is often difficult to distinguish between hydrogen embrittlement and various other brittle failure mechanisms. The objective of this work was to develop a sensitive analytical procedure based on secondary ion... more
In the paper there is presented a dynamic model of the articulated shaft. The model is used for the analysis of critical angular velocities. This model can be rewritten into a computer program to handle rotating parts of gear pumps. Using... more
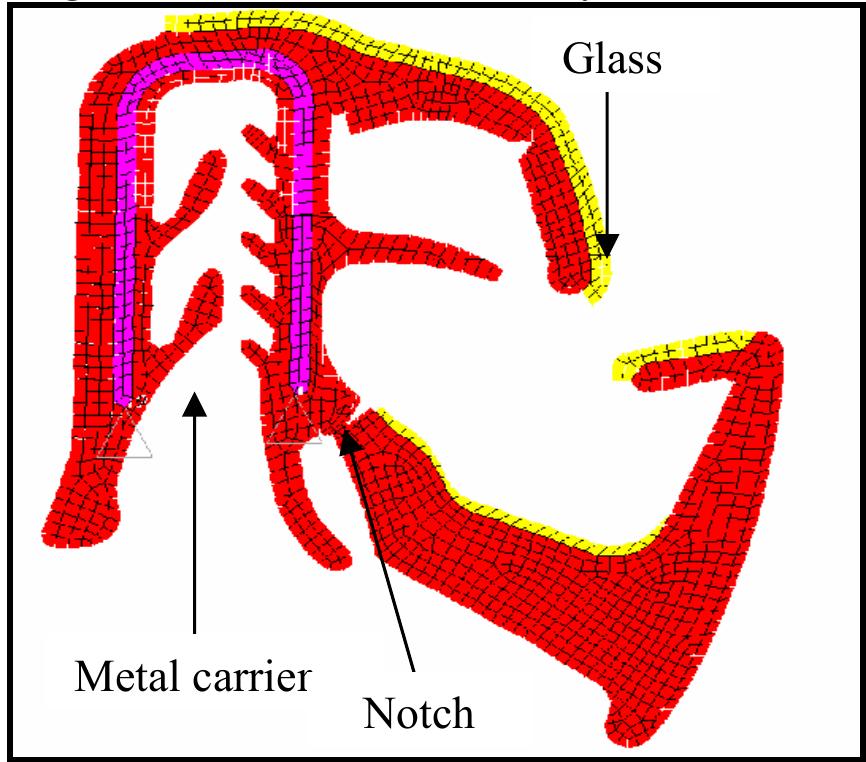
Silica-potash-lime stained-glasses from medieval age in Northern Europe are found in a poor conserv ation state. Their mechanisms of atmospheric corrosion are still not fully understood and need deeper investigation. A multi-scale... more
Background: Tendinopathies represent a serious challenge for orthopaedic surgeons involved in treatment of athletes.
A varied-space grating mounted to both rotate and translate constitutes a practical single element fixed slit monochromator which is in focus at all wavelengths. Monochromators, diffraction gratings, grazing incidence, x-ray optics.
A method for systematic reactor design, described by Hillestad , is applied to the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. The reactor path is sectioned into stages and design functions are optimized to maximize an objective function. Two different... more
International standards highlight the steps required by risk assessment and involving first hazard identification, then risk evaluation and finally, if necessary, risk assessment. To check approach appropriateness to "risk... more
A new method of designing nonimaging concentrators is presented and two new types of concentrators are developed. The first is an aspheric lens, and the second is a lens-mirror combination. A ray tracing of three-dimensional concentrators... more
Rainscreen wall design is still at its infancy stage even after its introduction about four decades ago. Research continues in an effort to set out appropriate design guidelines for rainscreen walls. This paper presents the key results of... more
Frequency modulation (FM) spectroscopy is a new method of optical heterodyne spectroscopy capable of sensitive and rapid measurement of the absorption or dispersion associated with narrow spectral features. The absorption or dispersion is... more
This research presents a new intelligent fault diagnosis and condition monitoring system for classification of different conditions of mechanical equipment that produces distinct thermal signatures for different fault conditions. This... more
A new kinetic model for the fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) riser is developed. An elementary reaction scheme, for the FCC, based on cracking of a large number of lumps in the form of narrow boiling pseudocomponents is proposed. The... more
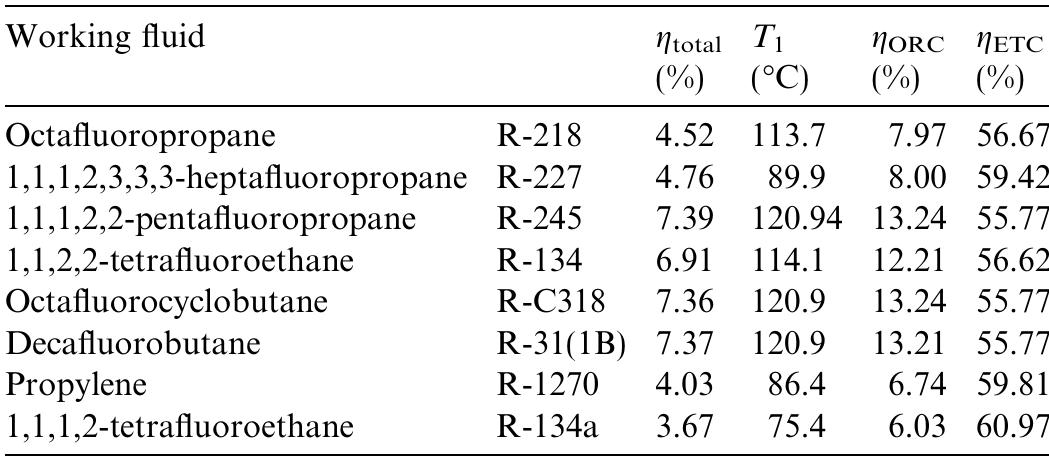
The objective of this paper is to model and optimise solar organic rankine cycle (ORC) engines for reverse osmosis (RO) desalination using currently available solar thermal collectors. The proposed systems are intended to be potentially... more
The goal of this paper is the development of control algorithms for the management of an automated warehouse system. As usual, the implementation of a control algorithm requires three preliminary steps: development of a reliable model;... more
The paper presents the application of ultrasonic guided waves for fatigue crack detection in metallic structures. The study involves a simple fatigue test performed to introduce a crack into an aluminium plate. Lamb waves generated by a... more
ABSTRACT Lean Six Sigma Executive Overview (Case Study) Templates are a guide to Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt, and Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt Projects. Lean Six Sigma Practitioners use the DMAIC (Define,... more
With the anticipated widespread usage of metal matrix composites (MMCs) in the near future, the machinability of high performance MMCs needs to be understood. This paper reports research results obtained from the grinding of... more
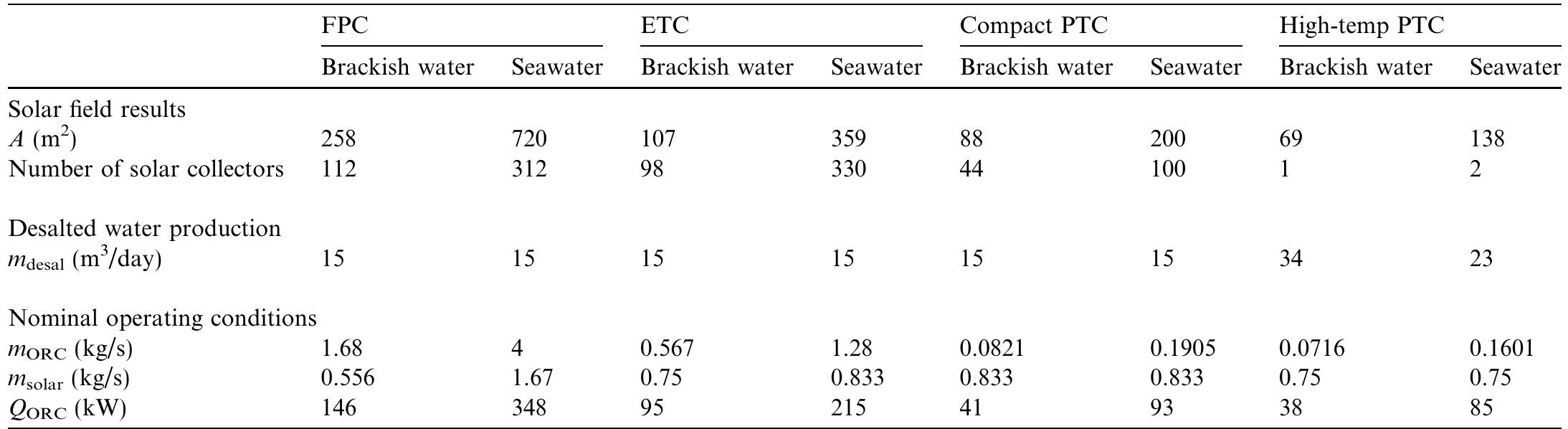
Technological innovation in all areas has led to the appearance in recent years of new metallic and pearlescent materials, yet no exhaustive studies have been conducted to assess their colorimetric capabilities. The chromatic variability... more
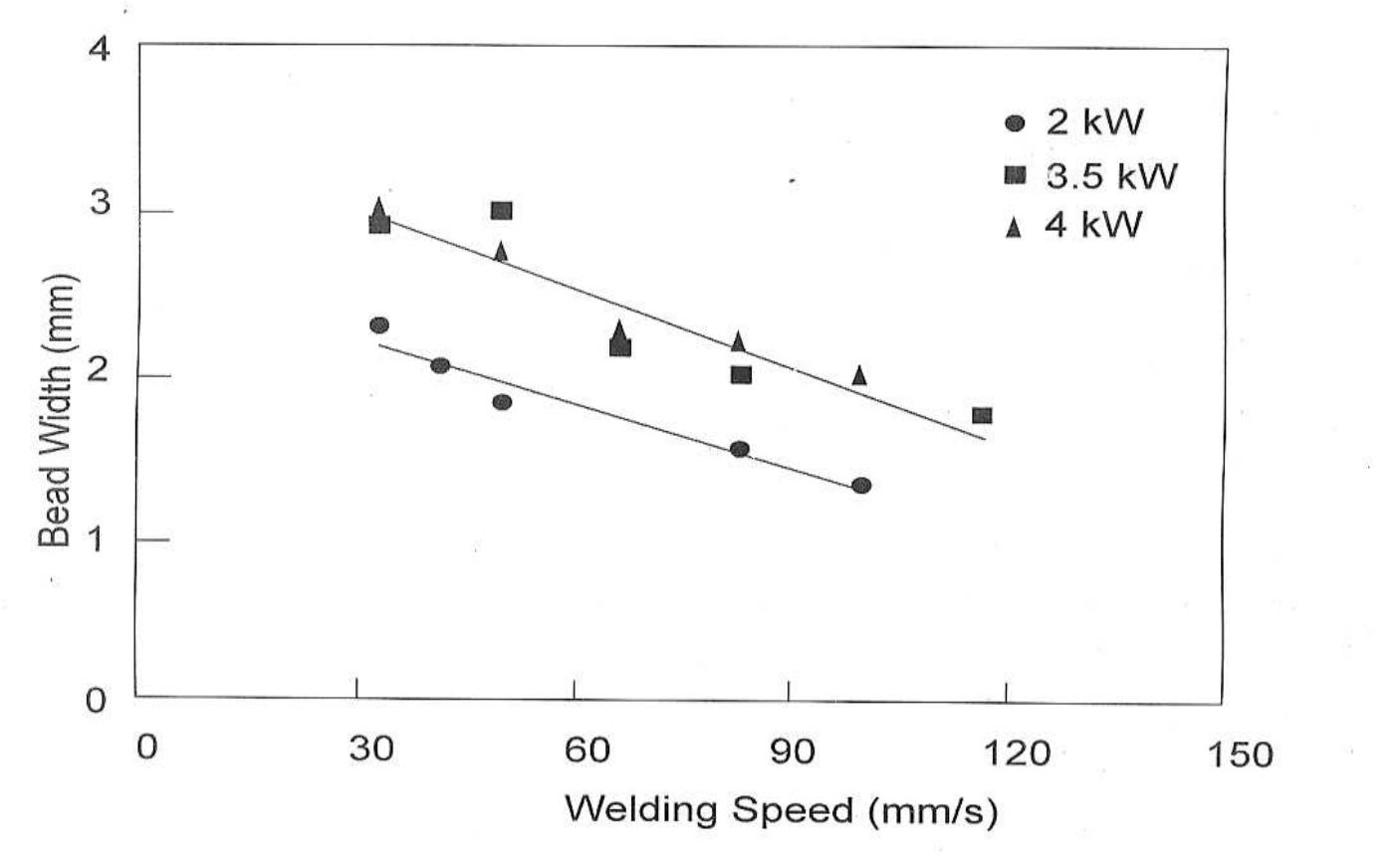
Laser welding will be an important welding process for different applications in aerospace , aircraft , automotive, electronics and other industries, due to its capabilities like minimum heat affected zone, welding of various... more
Feature extraction and dimensionality reduction are important tasks in many fields of science dealing with signal processing and analysis. The relevance of these techniques is increasing as current sensory devices are developed with ever... more
Direct foaming of colloidal suspensions is a simple and versatile approach for the fabrication of macroporous ceramic materials. Wet foams produced by this method can be stabilized by longchain surfactants or by colloidal particles. In... more
A model for predicting the refractive index of sodium iodide (NaI) aqueous solution n N I as a function of temperature T, NaI concentration c and wavelength was determined for moderate parameter variations. The equation accurately... more
The US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Planetary Protection Office, in the Science Mission Directorate, has a long-term initiative under way in communication research and planning. The possibility of extraterrestrial... more
The aim of the present study was to examine an adapted integrated psycho-social model to predict sport injury rehabilitation adherence. A longitudinal prospective design was used whereby 70 patients attending private physiotherapy clinics... more
Passive thermography is a non-contact monitoring approach with a great potential to be used for early bearing fault detection. However, to date, it has only been used to complement vibration-based approaches. However, the vibration-based... more
Digital image correlation (DIC) is assessed as a tool for measuring strains with high spatial resolution in woven-fiber ceramic matrix composites. Using results of mechanical tests on aluminum alloy specimens in various geometric... more
The microbiota of two traditional Iranian cheeses (Lighvan and Koozeh) made of raw ewe's milk or mixtures of ewe's and goat's milk without starter addition was explored by culture-independent and culture-dependent approaches. Three... more
and sharing with colleagues.
One of the most important issues in aircraft noise monitoring systems is the correct detection and marking of aircraft sound events through their measurement profiles, as this influences the reported results. In the recent ISO 20906... more
This project is modeled around reducing the overall drag and lift coefficient by modifying the geometry and comprehending the underlying rootphenomenon for the variation in these drag values. The designing of models used in this project... more
The automotive industry extensively uses elastomers as sealing systems in glass runner, shock absorbers, gaskets and several others. The challenges in the simulation of elastomers are non-linearity in material, geometry, boundary... more
Coordinate metrology is a field of metrology that is becoming increasingly popular in the manufacturing industry. Coordinate metrology enables the three-dimensional measurement to be carried out on complex object in a single setup. The... more
Extrusion-based bioprinting (EBB) is a rapidly growing technology that has made substantial progress during the last decade. It has great versatility in printing various biologics, including cells, tissues, tissue constructs, organ... more
The purpose of the study was to determine the effects of static and dynamic stretching protocols within general and activity specific warm-ups. Nine male and ten female subjects were tested under four warm-up conditions including a 1)... more

![Fig. 1. The mechanism for structural rearrangement in the spot model. The random displacement of a diffusing spot of free volume (dashed circle) causes affected particles to move as a block by an amount (A), followed by a relaxation under soft-core repulsion forces (B); the net co-operative motion combines these two steps (C). (Particle displacements are exaggerated for clarity.) Fioure from Ref [22].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47641182/figure_001.jpg)
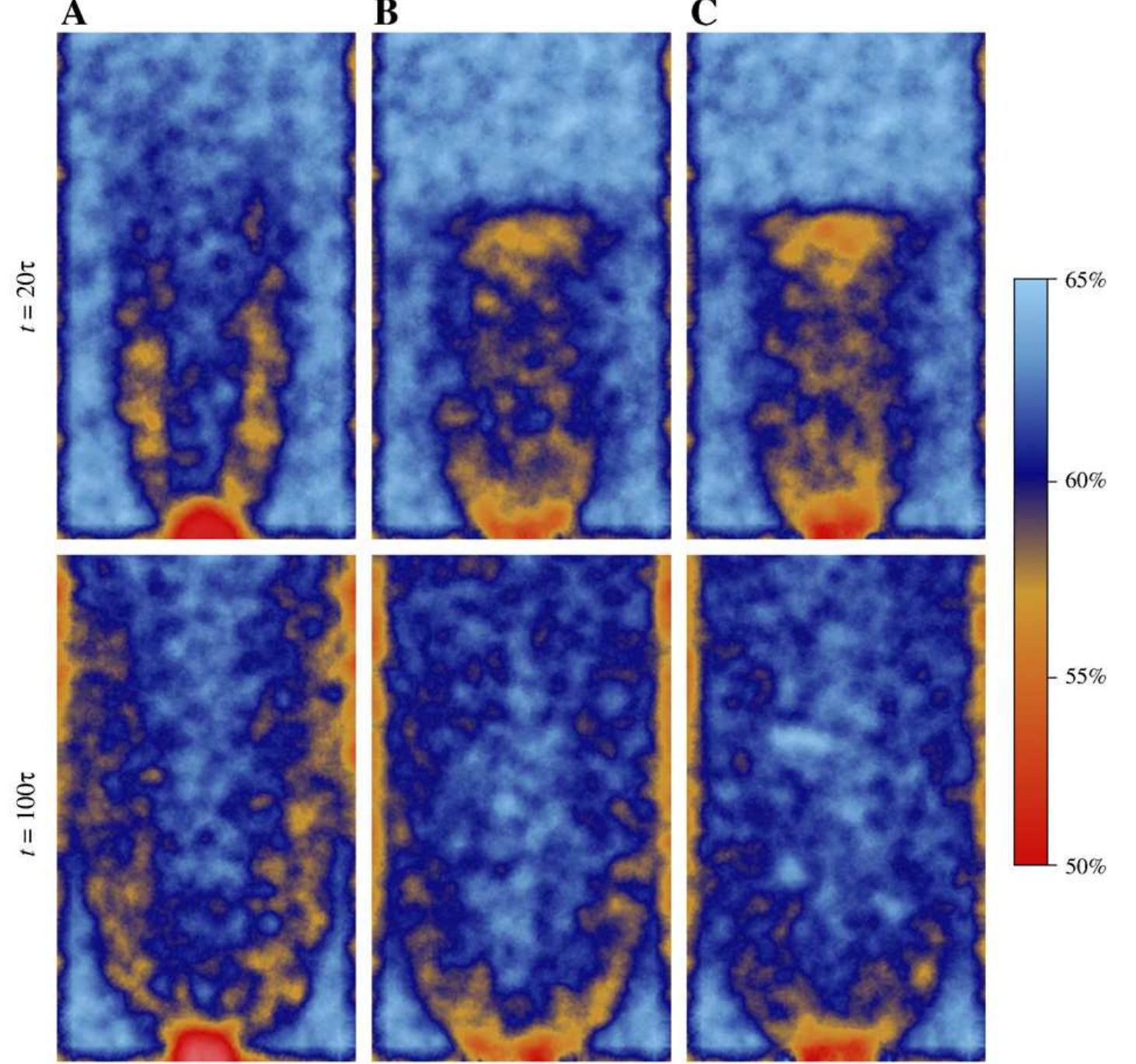
![Fig. 4. Snapshots of (A) DEM simulation, (B) a spot simulation using a random walk with simple biasing, (C) a spot simulation using simple biasing and influence weighting, and (D) spot simulation using adapted biasing (with (= 3) and influence weighting. The snapshots are taken at t= 300r. A further modification to the spot model can be employed to correct for this. In the previous implementation, when a spot moves by VV, then the particles experience a displacement —Vv/w, where w is a fixed quantity. Suppose that a spot is going to influence p particles, each of volume V,,. If spots are thought of as carrying a completely fixed amount of free volume V,, then another possible approach would be to let w=pV,/Vs, so the spot's influence is divided equally among the parti- cles in range. In the bulk, where the particles are roughly at constant In the void model, the evolution of the free surface has been addressed by making use of a very simple modification of the random walk process [11]. In the bulk of the packing, when a void generally has two particles in the lattice points above it, the void moves to each of these sites with equal probability. However, in the case when only one of these two sites is filled with a particle, the void always moves in](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47641182/figure_004.jpg)






![(a) The parameters used in the DEM simulation. (b) The five parameters used in the spot model simulations that were fitted from DEM simulation. All values are taken from Ref. [22]. The spot simulation was implemented in C++, with the main routine being written as part of a class that represents the entire simulation domain. For efficiency, the class divides the simulation up into a rectangular subgrid of regions, and keeps a separate list of position vectors of particles within each region. When particles are added to the container, they are sorted into the correct region. Two key routines are used to implement the spot microscopic mechanism. The first, spot (pV rs) applies the spot motion, by displacing all particles within a distance r, of p’ by an amount V. Table 1](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47641182/table_001.jpg)
































![Fig. 1. A standard [10] tensile V-notch (TVN) sample made of AISI 4340 steel heat treated to 50-53 Rc](https://figures.academia-assets.com/53459721/figure_001.jpg)
















![concentration of CO) at the end of the path is 34.81%. This will increase H,/CO at the end of the reactor path to 5.33. The optimal mixing structure is plug flow [12].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/45642159/figure_003.jpg)

![Staging with optimal distribution of heat transfer area, dis- tribution of syngas, and mixing configuration will increase the profit measure as demonstrated here. The results of this study can serve as initial points for staging of the FT reactor in the overall GTL process with different syngas production config- urations [23].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/45642159/figure_005.jpg)
![Table 1. Kinetic and adsorption parameters in Eqs. (2) and (3) [2].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/45642159/table_001.jpg)













![Fig. 5. Time variation of pressure coefficients. the air barrier is smooth compared to that across the panel. Consequently, the higher-frequency pressure fluctuations have been transferred to the rainscreen. Extensive analysis of the field data in the frequency domain has been recently presented in Ref. [12]. For simplicity, only the pressure coefficients applicable to the panel and rainscreen are discussed; one of the intentions of pressure equalization to reduce pressure load on the rainscreen is another good reason for presenting results in this format.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/66590541/figure_006.jpg)








![Note: ,=porosity of rainscreen, ; =effective porosity of air barrier estimated based on orifice plate- meter equation [10]. Comparison of full-scale measurements with the provisions in ENV 1991-2-4 for rainscreen walls with permeable air barrier](https://figures.academia-assets.com/66590541/table_002.jpg)
![Fig, 2, Frequency domain illustration of FM spectroscopy Fig. 1. A typical experimental arrangement for FM spectroscopy heterodyne) laser absorption spectroscopy with side- bands has been performed by Corcoran et al. [6], Mattick et al. [7], and Mager] et al. [8]. Heterodyne laser spectroscopy with amplitude modulated (AM) sidebands has been accomplished by Szabo [9] and Erickson [10]. Sideband techniques have recently been employed with great success to heterodyne detect signals from resonant degenerate four-wave mixing experiments [11-14]. Wavelength modulation spec- troscopy with lasers, as has been done by Hinkley and Kelley [15] and Tang and Telle [16], can be viewed as heterodyne spectroscopy with very closely spaced FM sidebands. Harris et al. [17] recognized that the ap- pearance of rf beats provides a sensitive indication of distortion of the output of an FM laser. However, the use of widely separated FM sidebands for optical heterodyne spectroscopy has only recently been ac- complished and exploitation of the attendant advan- tages of zero-background signal, rapid response to ransients, and laser limited resolution has only just begun.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/72857977/figure_001.jpg)






























![Fig. 1. An integrated ORC-RO plant modelled with Aspen Plus. perature waste heat, geothermal heat, biomass, or solar energy. Many references to these applications are available in the literature. A couple of facilities with ORC plants using solar thermal energy were constructed in 1978 in Cadarache, France and in 1981 at El Hamrawin, Egypt, but unfortunately there has been little information pub- lished about them [7]. A commercial parabolic trough ORC power plant completed in 2006 in Arizona is of par- ticular interest. It is a 1 MWe plant using n-pentane as the working fluid for the ORC, and is based on plants used in geothermal applications having 10,340 m* of parabolic trough collectors [8]. Studies on ORC applications for desalination are very scarce although a few projects exist and some studies are available. The Vari-Power company, based in California, started to develop an RO-based desa- lination system driven by solar thermal energy [9,10]. A patented direct drive engine (DDE) converts heat to the hydraulic power required by the RO. To our present knowledge, this project is still in the pilot stage. In [11] it is proposed a solar ORC system using R-134a and evacu- ated tube collectors. The system efficiency is low (7%) but the authors considered it comparable to equivalent photo- voltaic desalination systems. The first laboratory test stmu- lating the heat provided by solar collectors has been given by Manolakos et al. [12]. Burgess and Lovegrove [13] dis- cussed the application of solar thermal powered desalina- tion using membrane and distillation technologies. One of their conclusions was that more detailed analyses of solar driven RO are required to determine its costs and applicability. In summary, existing research on solar ORC for desalination is very limited, and few efforts have been reported on determining the most useful working flu- ids for this application.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/44539148/figure_001.jpg)


































![‘ig. 3. (Color online) Differences between the spectral reflectance curves associated with optimal colors and a real color. As goniochromism is the effect of abrupt color depending on the illumination/observation angle, it is interesting to consider whether these color varia- tions are inside or outside the Résch—MacAdam color solid and whether this depends on the pigment type, measurement geometry, or light source used. Provid- ing an answer to these two questions is the main objective of this work, i.e. to analyze the colorimetric characteristics of goniochromatic samples using the theoretical color solid associated with a standard observer and with different light sources associated with normal colors. This will make it possible to On the other hand, according to traditional color science, the colors distinguishable by the hu- man visual system define a three-dimensional (3D) structure called a color solid. The colors that define the limits are known as optimal colors and were stu- died by MacAdam [7,8]. These colors are associated with the normal reflectance/transmittance spectrum (photometric scale from 0 to 100%), with maximum colorfulness for a given luminance factor (Y, lower than 100%). The main characteristic of optimal col- ors is the shape of their reflectance curve. Its possible values are zero and one, with only two possible tran- sitions between these two values throughout the visible spectrum. Two types of optimal colors can therefore be distinguished: type 1, with a mountain- like spectral profile and type 2, with a valleylike spectral profile. However, a recent theorem has been proved from which the number of transitions](https://figures.academia-assets.com/49304167/figure_003.jpg)



















![Fig. 3. RMSE atmospheric temperature profiles (left); surface temperature [K] world map provided by the official ECMWF model, http://www.ecmwf.int/| on March 4, 2008 (middle); and estimated surface temperature maps in California/Mexico area for several methods along with the averaged RMSE across the whole atmospheric column given in brackets.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/49714609/figure_005.jpg)



![MAIN CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DATA SETS THAT COMPOSE THE UCI BENCHMARK AND PERFORMANCE OF THE DIFFERENT (K)MVA FEATURE EXTRACTION METHODS. AS A FIGURE OF MERIT WE USE THE OVERALL ACCURACY (OA, [%]) + THE BINOMIAL STANDARD DEVIATION. BEST RESULTS FOR EACH PROBLEM ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN BOLDFACE. THE NUMBER OF EXTRACTED FEATURES IS INDICATED FOR PCA AND KPCA, WHEREAS ALL OTHER METHODS USE c — 1 FEATURES.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/49714609/table_003.jpg)



![Fig. 3. Forces and moments exciting the pump casing over one meshing period, expressed in reference frame 0,X/Y; at different output pressure values and rotational speec of 3000 rpm. model. In more details, the structural FE model includes the casing, the two end-plates (the lower one is indicated as flange and the upper one as cover), as well as the ergal plate to which the pump is fastened on the test bench and the four force sensors support- ing the plate. The casing and the two end-plates are meshed using tetrahedral elements as indicated in Table 2. The casing and the end-plates have different Young Modulus and density: the casing is in aluminium whereas the end-plates are made of steel. In the actual pump, the three components are fastened to- gether by means of two steel screws (M6, length 65mm) as shown in Fig. 4. The two screws, with proper tightening torque, guarantee the connection between the casing and the end-plates. The two screws are modelled as beam elements having the same cross section area and inertia properties of the actual screws joined to the surrounding mesh of the end-plate by means of interpolation spiders (Card RBE3 in MSC.Nastran [38]) as shown in Fig. 5a. This way, the motion of the two end-points of the beam element is defined as the weighted average of the motions of the surrounding mesh. The screw tightening torque is not applied to the screws in the model because it represents a static torque and therefore it gives no contribution in a dynamic analysis. More- over, the tightening torque produces the effect of joining the cas- ing surface to the end-plate surfaces. Therefore in order to model this effect, rigid spider connections (Card RBE2 in Nastran) are used in order to connect the casing surface with the end-plate surfaces as shown in Fig. 5a. Furthermore, the presence of bearing blocks, oil and relief valve is taken into account. Each of these components is modelled by means of a concentrated mass and an inertia momentum (Card CONM2 in Nastran) located in its centre of mass and connected to the surrounding mesh by means of interpolation spiders (Card RBE3 in Nastran). The ergal plate of the test bench is modelled using tetrahedral elements. The ergal plate is connected to the pump by means of two aluminium screws (Figs. 4 and 5a). These screws are modelled using beam elements - in the same way as for the steel screws - and are connected to the ergal plate and to the pump by means of interpolation spiders. Moreover, rigid spiders are used between the end-plate lower surface and the ergal plate surface for mod- elling the connection between the two surfaces and in order to avoid penetration between the surfaces themselves. Finally, the ergal plate is connected to ground by four triaxial force sensors located under the ergal plate. These sensors are modelled by means of spring elements having the nominal stiffness of each sensor as collected in Table 3; the spring elements are joined to the plate mesh by means of rigid spiders as depicted in Fig. 5b.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/43547903/figure_004.jpg)


![Fig. 6. (a) Input and output points in the FRF analysis and (b) experimental FRF amplitude for tests without oil and with oil at 23 bar with excitation in C and response in I along the X{, direction. Fig. 7 depicts the cavity mesh developed for the pump being studied, which has been coupled to the structural one for the solu- tion of the fluid-structural problem. The properties of the cavity mesh are reported in Table 2. The cavity mesh has the fluid prop- erties of the pumping oil (see Table 1), in particular the oil density and the oil bulk modulus have been introduced in the model in or- der to take into account the distributed mass and stiffness effects, respectively. Moreover the continuity of the mesh between the structural and fluid part has been imposed. In order to verify the effectiveness of the coupled fluid-structural FE model with respect to the genuine structural FE model described above, a numerica FRF analysis (SOL 111 in MSC.Nastran driven by LMS Virtual.Lab [38,41 ]) is carried out with excitation point in C and response point in B, along X‘ direction (see Fig. 6a). The numerical FRFs obtained by the fluid-structural FE model and the structural FE model are compared with the experimental FRF obtained by hammer and accelerometers (see Section 2.2). Fig. 8 depicts such a comparison in the frequency range of interest (1500-3500 Hz), where norma Moreover, on the fluid-structural FE model, a forced response analysis has been carried out (SOL 111 in MSC.Nastran) with the aim at obtaining the vibration level on the entire pump in opera- tional conditions. The excitations are the pressure forces and mo- ments and the bearing reactions exchanged between the gears and the casing (see Section 3.3 and Fig. 3) as well as the variable](https://figures.academia-assets.com/43547903/figure_007.jpg)




















![Fig. 9. Distribution of Laircraft,p Observed by experts, for every acoustic environment. By applying the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test [22,23], the influence of several factors on the data distribution was studied. Afterwards, it was checked if the new variable, error, followed a Normal distribution, so that a parametric approach could be ap- plied for the analysis. The probability distribution of the residuals was analyzed using the Chi-square and the Kolmogorov-Smirnoff tests, and a Normal Probability Plot, It was evidenced that data were not distributed according to a Gaussian distribution, so a non-parametric approach had to be used. Fig. 10 shows the Normal probability plot for the residuals.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41765820/figure_011.jpg)







![CFD Analysis And Optimization Of Geometrical Modifications Of Ahmed Body Manipulation of the rear slant angle of the generic Ahmed body reference model was carried out previously [2], to determine the optimum angle configuration for the least drag coefficient with velocity of air at inlet being 40m/s. The drag coefficient and the corresponding lift coefficient were plotted.The pressure distribution and velocity contours for the various rear slant angles were also investigated to comprehend the aerodynamic behavior around the model.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47212464/figure_001.jpg)













![Fig. 16- Roof camber: Lift vs. H/L ratio Fig. 15- Roof camber: Drag vs. H/L ratio ——'_' OO The analyses of the 22 multifarious models carried out yield optimum configurations for each geometrical modification of the benchmark model — Ahmed body having 10 degree rear slant angle. The values of the aerodynamic parameters obtained for the benchmark model are- Coefficient of drag (C4) = 0.238 and the coefficient of lift (C,) = 0.0848[2]. For all the configurations for a particular modification (obtained by varying the associated geometrical parameter),the drag and lift coefficients are plotted and examined to determine the optimum configuration resulting in least drag and lift coefficients. Furthermore, the underlying root causes are also analysed, comprehended and listed.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47212464/figure_016.jpg)
















![Fig. 2. Bioink types used in EBB: (A) cells loaded in hydrogels, (B) polymer micro-carriers pre-loaded with cells [63], (C) tissue spheroids made of cells and ECM [21], (D) cell pellet in nozzle tip [41], (E) tissue strands [29] and (F) dECM before loading cells [51].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39997046/figure_002.jpg)

![Fig. 4. Bioprinting of vascular and vascularized tissue constructs: (A1) photograph of bioprinted agarose hydrogel filaments representing branched vascular network in a GelM/ hydrogel block and (A2) a high resolution cross-sectional view of GelMA block stained for live and dead cells (reproduced/adapted with permission from Ref. {25]); (B1) sprouting o endothelium (stained with red fluorescent protein) into capillary network (stained with green fluorescent protein) within fibrin gel on day 9 and (B2) a high resolution image of th capillary network on day 14 (reproduced/adapted with permission from Ref. [197]); (C) an image acquired during evacuation of the fugitive ink showing channels in GelMA scaffolt (upper-left) which were later glued with 10T¥ fibroblasts, HUVECs and human dermal fibroblasts (HUDFs) (reproduced/adapted with permission from Ref. |27]); (D1) a scannin, electron microscopy image of directly bioprinted vascular channels embedded in a large alginate construct (D2) showing L929 mouse fibroblasts in green (reproduced/adapted wit! permission from Ref. | 190]); (E1) scaffold-free bioprinting of a branched vascular network using 300 um human skin fibroblast (HSF) spheroids (solid and broken arrows show 1. and 0.9 mm in vascular diameter, respectively), where spheroids (E2) fuse and maturate into tissue after 6 days of deposition (reproduced/adapted with permission from Ref. [21}) (F) fabrication of a perfusable tissue via integration of bioprinted vasculature and fibroblast tissue strands (reproduced/adapted with permission from Ref. [29]), the scare ba corresponds to 2 mm on the right figure. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39997046/figure_004.jpg)

![Fig. 6. 3D printed cyborg ears: (A) bioprinting of anatomically correct cartilage scaffold loaded with chondrocytes along with printing of coil antenna; (B) scaffolds were cultured 10 weeks, resulting in neocartilaginous tissue in alginate matrix, (C) 3D printed complementary ears (right and left) demonstrated the ability to listen to stereophonic audio music (reproduced/adapted with permission from Ref. [218)}). Due to its unique capabilities, EBB has been preferred for fabrication of living tissues and organs, and regulatory issues seem to be down the way as the technology transforms into products for clinics and human-use purposes. Currently, there is no regulations that has been laid down for bioprinting including bioink, bio- printers and bioprinted products such as tissues, and FDA has not imposed any regulatory restrictions on bioprinting technology yet. Cutting-edge technologies such as bioprinting cannot be easily categorized for regulatory purposes while it does not fit into the general classification of “device”, “drug” or “biologic” under FDA regulations. Office of Combination Products (OCP) formed by FDA can handle this situation, where “combination product” is defined in 21 CFR §3.2(e) as “A product comprised of two or more regulated components, i.e., drug/device, biologic/device, drug/biologic or drug/device/biologic, that are physically, chemically, or otherwise combined or mixed and produced as a single entity” [221]. The OCP does not conduct product reviews but assigns combination prod- ucts to the appropriate FDA center (i.e., the Center for Drug Eval- uation and Research (CDER), The Center for Biologics Evaluation One of the major shortcomings of EBB is the lack of high- resolution systems due to the nature of the extrusion process it- self. Although certain errors can be induced due to other system components, such as errors associated with the motion system or the extrusion process itself has an enormous contribution to the low resolution. Although very small nozzle tips can be considered possible, decreasing the nozzle size results in a considerable increase in the shear stress and corresponding cell damage and death. Thus, EBB systems should be modified to alleviate this issue. In addition, lowering the size further increases issues such as nozzle clogging and the need for elevated dispensing pressure levels. Although a low electric field can be applied to reduce the size of the printed fila- ments as widely used in electrohydrodynamic printing [53], cells should be kept away from the electric field to safely deliver them. A recent approach in the application of electrohydrodynamic jetting in inkjet-based bioprinting demonstrates the safe usage of the system with cells; this approach has the potential to be used in EBB [54]. The other potential of increasing the resolution is to use a cone-shaped nozzle (i.e., Taylor cone or regular cone) that has a relatively allevi- ated shear stress, which reaches its maximum at the end of the nozzle tip, affecting cells at a minimum duration. In addition to these approaches, a highly innovative approach might be using a nozzle- free extrusion system that enables the bioink to overcome surface- tension-induced droplet formation.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39997046/figure_006.jpg)



