Lattice materials can be designed through their microstructure while concurrently considering fabrication feasibility. Here, we propose two types of composite lattice materials with enhanced resistance to buckling: (a) hollow lattice... more
Effect of cooperative grain boundary sliding and migration on crack growth in nanocrystalline solids
A new mechanism of fracture toughness enhancement in nanocrystalline metals and ceramics is suggested. The mechanism represents the cooperative grain boundary (GB) sliding and stress-driven GB migration process near the tips of growing... more
EuCARD-2 is a project partly supported by FP7-European Commission aiming at exploring accelerator magnet technology for 20 T dipole operating field. The EuCARD-2 collaboration is liaising with similar programs for high field magnets in... more
The nitrogen-doped diamond films have been successfully synthesized by using urea as the nitrogen source. Selected-area deposition of diamond nuclei was formed by using a SiO 2 layer as the masking material. Diamond pads, around 9 mm in... more
A previously synthesized hyperbranched poly(butylene adipate) (HPBA) polymer was compared with a commercial dendritic polyol (HPOH) as a toughening agent for a commercial one-part epoxy resin. Both modifiers were added in weight... more
In this investigation, the effect of coloring voltage and thickness on optical and also electrochromical properties of WO 3 thin films has been studied. The WO 3 thin films were grown on glass and indium tin oxide coated conducting glass... more
The local surface chemistry of a low-Ni austenitic stainless steel AISI type 304 used for tensile testing in hydrogen atmosphere is characterized by secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). A chemical map on cylindrical austenitic... more
A versatile method for positive-type patterning of polyimide (PI) based on a two-layer photosensitive poly(benzoxazole) (PSPBO) and poly(amic acid) (PAA) film has been developed to provide a promising material in the field of... more
In high-strength steels it is often difficult to distinguish between hydrogen embrittlement and various other brittle failure mechanisms. The objective of this work was to develop a sensitive analytical procedure based on secondary ion... more
Weld cladding is a process for producing surfaces with good corrosion resistant properties by means of depositing/laying of stainless steels on low-carbon steel components with an objective of achieving maximum economy and enhanced life.... more
Silica-potash-lime stained-glasses from medieval age in Northern Europe are found in a poor conserv ation state. Their mechanisms of atmospheric corrosion are still not fully understood and need deeper investigation. A multi-scale... more
This paper deals with the problem of the colorimetric fidelity of digitised colour slides of painted works of art. A six-matrix conversion model was derived that permitted the transformation of any RGB device-dependent measurement on... more
In this study, headspace gas chromatography/mass spectrometry has been used to assess the volatile by-products generated by the ageing of oilimpregnated paper insulation of power transformers. Sealed-glass ampoules were used to age under... more
The paper is a concise digest of works presented during the XIth Symposium on Laser Technology (SLT 2016) [1]. The Symposium is organized since 1984 every three years [2–8]. SLT 2016 was organized by the Institute of Optoelectronics,... more
The aim of this paper is to demonstrate that atomistic simulations can be used to evaluate the structure of mineral surfaces and to provide reliable data for forsterite surfaces up to a plane index of 2 using the code METADISE. The... more
With the anticipated widespread usage of metal matrix composites (MMCs) in the near future, the machinability of high performance MMCs needs to be understood. This paper reports research results obtained from the grinding of... more
The kinetics of abiotic oxidation in the dark and the kinetics of biological mineralization in soil and in a compost environment of thermally oxidized LDPE were studied. It was demonstrated that different activation energies are obtained... more
Novel high hydroxyl number and high functionality polyols were developed using thiol-ene reaction of castor oil with mercaptoethanol or mercaptanized castor oil with allyl alcohol (by photochemical reaction) and 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate... more
Direct foaming of colloidal suspensions is a simple and versatile approach for the fabrication of macroporous ceramic materials. Wet foams produced by this method can be stabilized by longchain surfactants or by colloidal particles. In... more
The structure and thermodynamic properties of atactic and isotactic acrylic and methacrylic polymers containing 16-18 carbon atoms in the n-aliphatic side chains, and of ccpolymers of hexadecyl acrylate with isopropyl acrylate were... more
Nanotechnology has made great strides forward in the creation of new surfaces, new materials and new forms which also find application in the biomedical field. Traditional biomedical applications started benefiting from the use... more
Plasma-substrate interactions in diamond synthesis via microwave plasma-assisted chemical vapor deposition (CVD) are an important issue in CVD reactor optimization. The hot spot formation observed during single-crystal diamond synthesis... more
This article models bubble removal in centrifugal casting of the thermosetting silicone polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Given spin speeds, mold geometry, and resin properties for centrifugal casting, it is possible to predict the amount of... more
A first principles-based model has been developed to simulate the capacity fade of Li-ion batteries. Incorporation of a continuous occurrence of the solvent reduction reaction during constant current and constant voltage ͑CC-CV͒ charging... more
We present an electrode arrangement for the inline measurement of the conductivity of droplets in segmented flow by impedance spectroscopy. We use a thin-walled glass capillary with electrodes contacting the outer surface, so that the... more
A large number of products, both natural and synthetic, have been and are used for the consolidation of flaking or fragile paint layers occurring on paintings, polychrome sculpture, furniture and other cultural objects. Most products in... more
A new colloidal route leading to the production of B99% dense 3-mol% yttria-stabilized zirconia nanostructured ceramics, while retaining a final average grain size of B75 nm, has been developed. The process was based on the production of... more
Nanocomposite films based on poly(lactic acid)-poly(hydroxybutyrate) (PLA-PHB) blends and synthesized cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) or surfactant modified cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), as bio-based reinforcement, were prepared by melt... more
It is the objective of this article to investigate the influence of surface preparation on the cold roll bonding (CRB) process. In this context, the effects of surface preparation parameters consisting of surface preparation method,... more
Fermilab is developing and investigating different high-field magnet designs for present and future accelerators. The magnet R&D program was focused on the 10-12 T accelerator magnets based on Nb 3 Sn superconductor and explored both... more
To prepare miscible polyethylene glycol diacrylate/polyvinylidene fluoride ͑PEGDA/PVdF͒ blend gel polymer electrolytes, low molecular weight (M ϭ 742) liquid PEGDA oligomer was mixed with PVdF-HFP dissolved in ethylene carbonate/dimethyl... more
Standard fused filament fabrication (FFF)-based 3-D printers fabricate parts from thermopolymers, such as polylactic acid (PLA). A new range of metal based PLA composites are available providing a novel range of potential engineering... more
Timber from eucalyptus and pines trees used in contact with the ground requires preservative treatment to prolong their useful life under natural condition. To obtain resistant timber fence posts to xylophagous attack, this research aimed... more
The corrosion resistance of anodized Al 6061 produced by two different anodizing and sealing processes was evaluated using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The scanning electron microscope (SEM) was employed to determine the... more
Effect of Porosity on the Capacity Fade of a Lithium-Ion Battery. [Journal of The Electrochemical Society 151, A1104 (2004)]. Godfrey Sikha, Branko N. Popov, Ralph E. White. Abstract. ... In this model these values are measured from a... more
The photochemical and thermal behaviour of bisphenol-A polycarbonate (PC) and trimethylcyclohexane-polycarbonate (TMC-PC) have been compared. The ageing of films, irradiated at short (l=254 nm) and long (l > 300 nm) wavelengths in the... more
In order to assist researchers explore the full potential of distributed recycling of post-consumer polymer waste, this article describes a recyclebot, which is a waste plastic extruder capable of making commercial quality 3-D printing... more
Reconocer, identificar y conocer las propiedades de los materiales es muy importante en el campo de la ingeniería, ya que son ellos los que aportan las características de resistencia y estabilidad de lo que se va a diseñar. Si no se... more
A series of highly cross-linked polysiloxane was synthesised via hydrosilylation and condensation reaction. Structural identification using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) and 1 H-NMR confirmed their chemical structures. Their thermal... more
Solder paste is used for reflow soldering of Surface Mount Devices (SMDs). In this paper we discuss how the various stages of the stencil printing cycle affect the rheological properties of the solder paste. First the heat generated in... more
The effect of polyaniline (PANI) nanofibers content on the electrochemical properties of composites based on SnO 2 nanoflakes was studied. PANI nanofibers and SnO 2 nanoflakes were synthesized and characterized (SEM, BET, FTIR, XPS, and... more
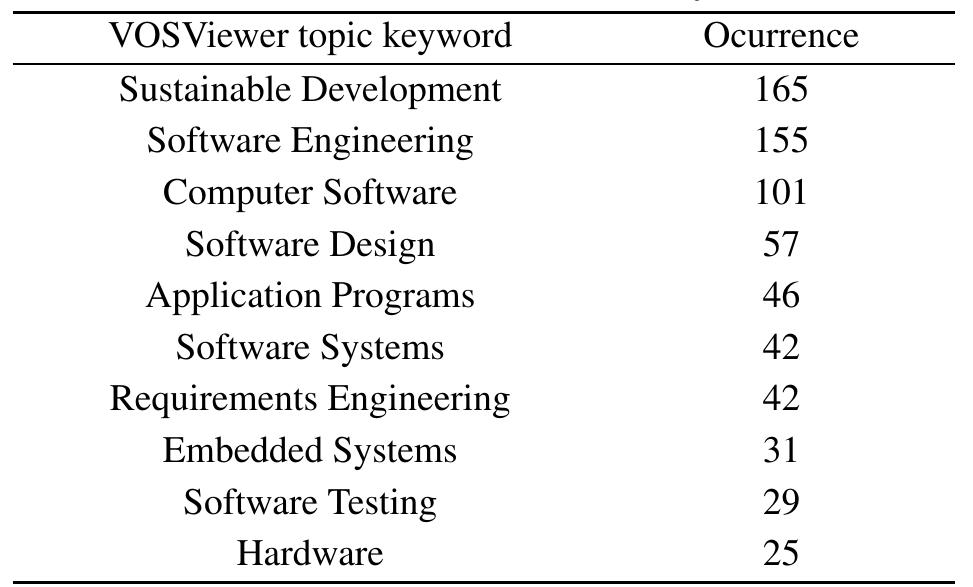
Green and Sustainable Software has emerged as a new and highly active area in the software community. After several years of research and work, we believe that it is now necessary to obtain a general snapshot of how the research in this... more
Materials with the olivine LixMPO4 structure form an important new class of materials for rechargeable Li batteries. There is significant interest in their electronic properties because of the importance of electronic conductivity in... more
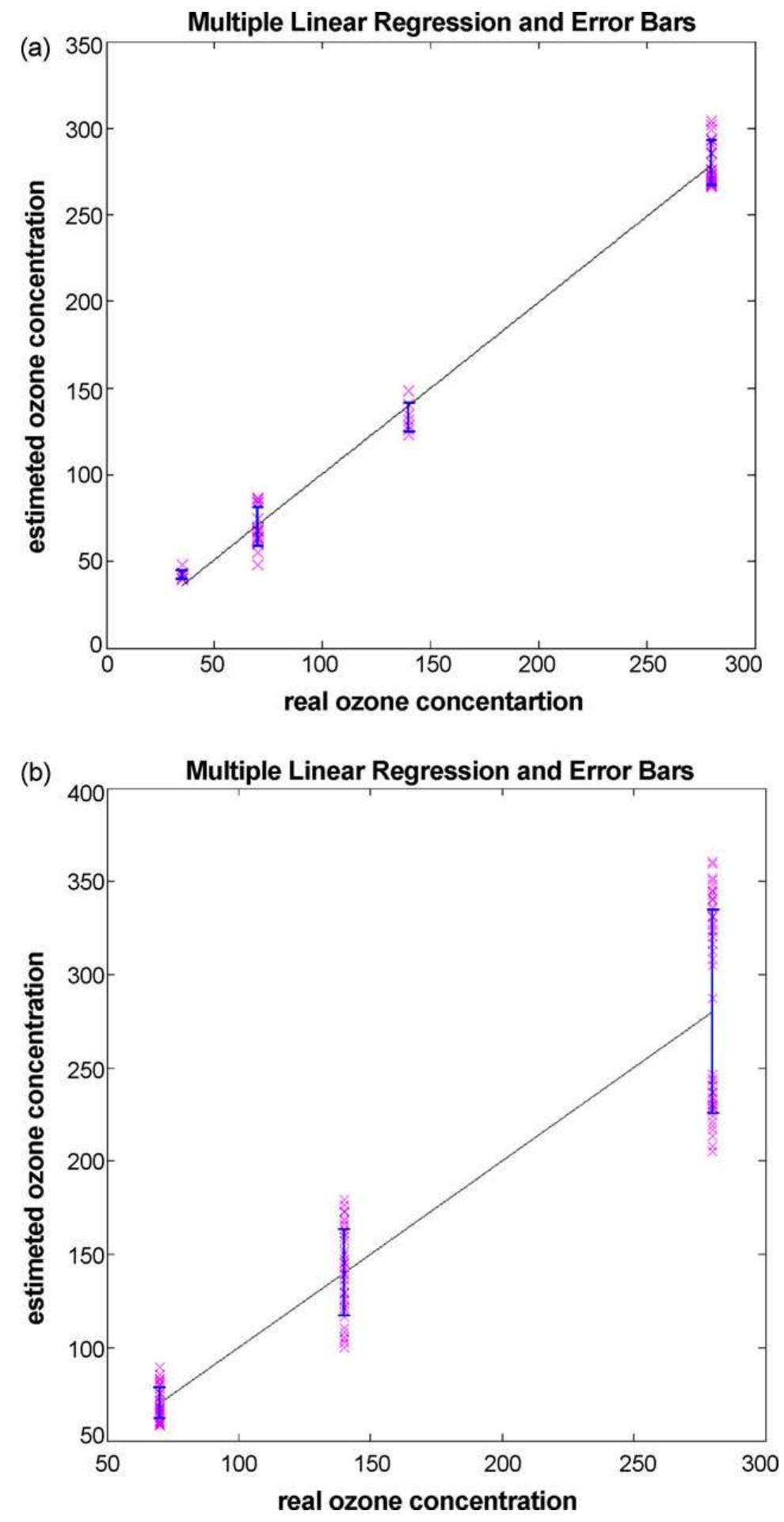
We tested the detection properties of four MOX sensors toward different ozone mixtures to identify sets of sensing layers and interfering compounds concentrations most suitable for a reliable detection of ozone. The measurement campaign... more
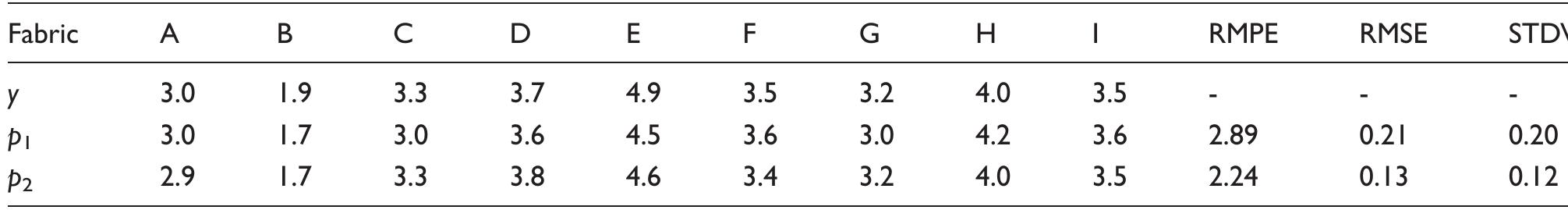
This paper aims to predict the hand values (HVs) and total hand values (THVs) of functional fabrics by applying the fuzzy logic model (FLM) and artificial neural network (ANN) model. Functional fabrics were evaluated by trained panels... more
The application of polymer nanocomposites packaging materials in industrial, food and agricultural products is a superior alternative to traditional packaging materials such as glass, paper, and metals due to their functionalization,... more
Depth sensing indentation is a powerful experimental technique for determining mechanical properties of materials. In this work a computational routine was developed based on Oliver-Pharr method for measuring a more precise values of... more
A 44-pass fiber optic surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor coupled with a field-assist capability for measurement of refractive index change due to positive and negative ions is shown. The field-assist feature forces ions to the SPR... more















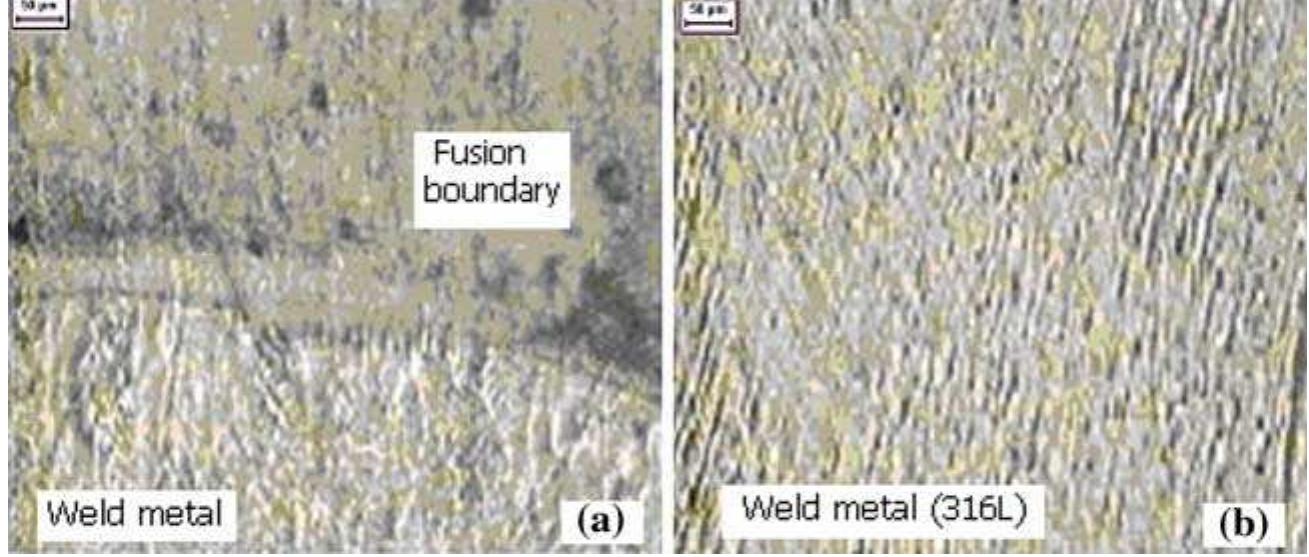
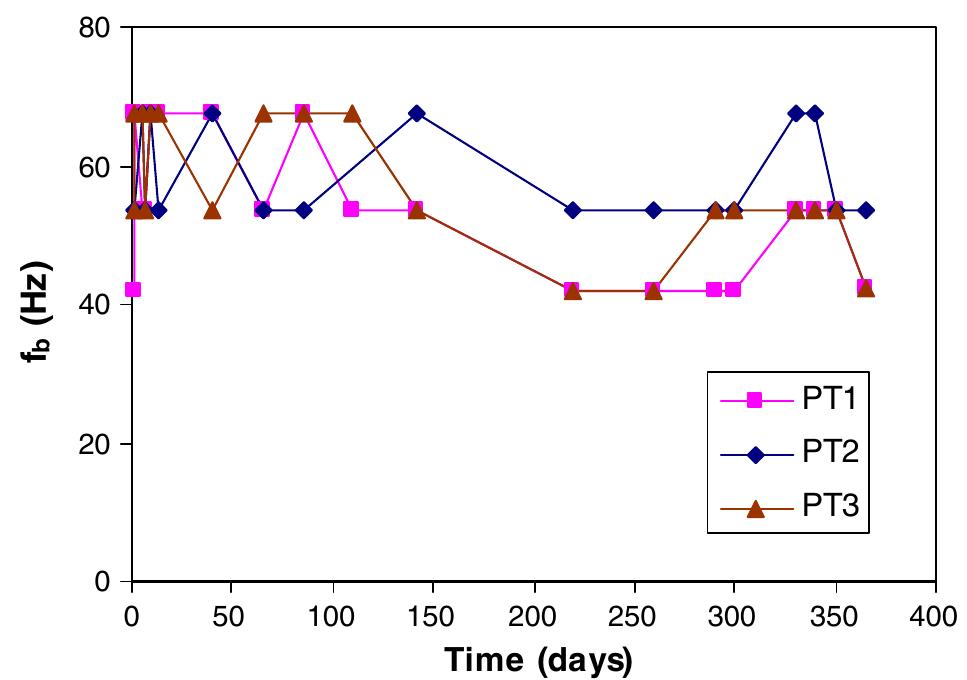
![Fig. 1. Austenitic stainless steel sample after tensile test in hydrogen atmosphere of 40 MPa. (a) Macroscopic image, (b) optical image of the surface and (c) secondary electron image of the rectangular region shown in (b). The sample surface is cylindrical and contains many transverse cracks. An enlarged secondary electron image verifies a cracked and rough surface with a wavy height modulation. In order to obtain a depth profile from oxide layer to bulk region, the solution annealed sample was measured by dual beam mode using 25 keV Ga* for analysis of 150 wm x 150 wm, and 1 keV Ar* or Cs* for sample erosion at 300 wm x 300 wm, to get positive or negative secondary ion profiles, respectively. Details about this setup and analysis modes have been published by Iltgen [16]. After removing the uppermost layer, the intensities of Si2C5H150* and Fe* decrease (Fig. 2b). High intensities are local- ized in special regions. A correlation between the Fe and the SizC5H;50* signals can be seen. After removing about 7nm of surface atoms (Fig. 2c), high intensity regions of Fe*, Ni* and SizC5;H;50* as well as C3F7* are detected, whose positions](https://figures.academia-assets.com/50048800/figure_001.jpg)




![Chemical composition of the austenitic stainless steel AISI type 304 wt%. Table 1 the as-prepared sample is more brittle (RRA = 83.9%) [14]. Focus is put on keeping the sample surface in its original condition which means that no further surface polish is allowed. The samples are, therefore, of cylindrical geometry, that possess surface roughness and surface contamination. We will show that even under these conditions reliable SIMS measurements can be performed. To obtain a depth length scale, the calibration was carried out by taking following parameters into account. These are (i) a known surface area of sputtering, (ii) the number of ion dose as ion current, (iii) density of iron, (iv) sputtering yield and (v) the time required to remove the oxide layer on an as-machined sample with flat surface. This calibration gives the native oxide layer thickness of about 5nm, which is in agreement with the previously reported value [17]. The sputter rate and, consequently, the depth scaling for both samples are based on this calibration. Thus, changes in the sputter rate due to different mechanical hardness of the two samples, related to locally different chemical composition and lattice structures, are neglected.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/50048800/table_001.jpg)
![Scheme 1. Patterning process of two-layer system. N,N-Dimethylacetamide (DMAc) was purified by vacuum distillation. 4,4’-Oxydianiline (ODA) purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd (TCI) was recrystallized from tet- rahydrofuran (THF) under nitrogen. 3,3’,4,4’-Biphenyltetra- carboxylic dianhydride (BPDA) purchased from TCI was dried in vacuo at 180 °C for 12 h before use. The 9,9-bis(4- tert-butoxycarbonyloxypheny]l)fluorene (t-BocBHF), TBMPF and PHA derived from 4,4’-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)- bis(o-aminophenol) and 4,4’-oxybis(benzoic acid) deriva- tives were prepared as described previously [17,24]. The number- and weight-average molecular weight (M, and Firstly, the PAA solution is spin-coated on a silicon wa- fer and baked in the usual way. Then, the thin layer of PSPBO consisting of PHA, TBMPF and PTMA is formed onto the thick PAA film and dried by pre-baking. This film is ex- posed to UV light to generate propanesulfonic acid from PTMA. Upon post-exposure bake (PEB) treatment of the film, the acid deprotects the tert-butyl ester of TBMPF](https://figures.academia-assets.com/70360709/figure_001.jpg)







![Fig. 1. A standard [10] tensile V-notch (TVN) sample made of AISI 4340 steel heat treated to 50-53 Rc](https://figures.academia-assets.com/53459721/figure_001.jpg)



















![Fig. 1. Tensile test results of PLA, PLA-PHB and nanocomposite films: a) Stress-strain curves, b) Young's Modulus (E), c) Tensile strength (TS) and d) Elongation and break (eg) a-dpifferent letters on the bars within the same image indicate significant differences between formulations (p < 0.05). The estimated viscosity molecular weight (My) of PLA and PHB pellets were 95,800 + 4400 g mol” !and 255,300 + 39,000 g mol" !, respectively. It is know that polymers can undergo thermal degradation during processing and diminution of My values for all film formulations with respect of PLA pellet and/or PHB pellet were detected (Table 1). PLA processed into film resulted in a reduction of the M, of PLA around 5%. Further decrease occurred in binary PLA based nanocomposites. While, a reduction of PLA M, value of 10% was detected for PLA-CNC, PLA-CNCs showed a higher reduction of 15%. This results is in accordance with previous work where we showed that the thermal stability of PLA was reduced with the addition of cellulose nanocrystals, particularly for PLA-CNCs [25]. As it can be seen from tensile curves (Fig. 1-a), the neat PLA film showed a characteristic plastic deformation that it was reduced with both, PHB and CNC incorporation. CNC and PHB proved to be effective to increase PLA modulus (Fig. 1-b), but no significant differences were observed between the Young's modulus of PLA-CNCs and PLA films. While CNCs or PHB produced a decrease on the tensile strength (TS) of PLA, the combination of PHB and CNCs produce a nanocomposite (PLA-PHB-CNCs) with comparable TS with respect to PLA. This behaviour can be related with the more efficient dispersion of functionalized cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) [3] resulting in an enhancement in the interfacial adhesion and therefore in a better interaction between PLA and PHB [25]. Moreover, the PLA-PHB-CNCs film revealed the highest deformation at break, showing an increase of 175% with](https://figures.academia-assets.com/43362038/figure_001.jpg)

![Fig. 3. a) Visual appearance of film samples before and after different incubation days under composting conditions. b) Degree of disintegration of films under compostin; conditions as a function of time. Additionally, films for food packaging are required to protect foodstuff from humidity during transport, handling and storage. Thus, water contact angle measurements were carried out to evaluate the hydrophilic/hydrophobic character of films and the results are shown in Fig. 2(c) [37]. It should be noticed that all formulations showed values higher than 65°, being materials acceptable for the intended end-use applications. PHB has a hy- drophobic character due to the poor affinity of the water to the non- polar polymer surface [38]. In this way, the PLA-PHB blend showed significant increased water resistance in comparison with neat PLA, in good accordance with a previous reported work [12]. The pres- ence of CNC in PLA and PLA-PHB caused an increase in wettability, while functionalized CNCs did not significantly change PLA or PLA- PHB wettability. The positive effect of cellulose nonocrystal chemical modification in the wettability of PLA and PLA-PHB films is mainly due to the presence of sulphate groups with low polarity on the surface that increase the surface hydrophobicity of the final material. Fig. 3 (a) shows the visual appearance of PLA, PLA-PHB and cellulose nanocrystal based nanocomposites after different time of disintegration in composting conditions where it is possible to confirm the biodegradable character of all the formulations stud- ied. After only 1 day of incubation, films become smaller, with the exception of PLA-PHB blend, which started the film size reduction on the second day of incubation. After 7 days of incubation binary and ternary formulation films became breakable and small pieces of films were recovered. It also could be noticed that they changed their colour and became more opaque after 7 days. When the degradation process of the polymer matrices started, a change in the refraction index of the materials was observed as a result of water absorption and/or presence of products formed by the hy- drolytic process [39]. Additionally, the films disintegrability was evaluated in terms of mass loss as a function of incubation time (Fig. 3 (b)), in which the line at 90% of disintegration represents the goal of disintegrability test [4]. Unmodified cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) speed up the disintegration of PLA and PLA-PHB blend from 14 days to 21 days, respectively, to 10 days. Comparable findings were previously reported for PLA nano-biocomposite films with functionalized cellulose nanocrystals and silver nanoparticles [40]. Accordingly, after 10 days CNC incorporated films were visibly disintegrated (Fig. 3 (a)), while CNCs incorporated counterparts reached between 50 and 60% of disintegrability and need 14 days to reach the goal of the disintegrability test (Fig. 3 (b)). Itis known that](https://figures.academia-assets.com/43362038/figure_003.jpg)

![Fig. 5. Optical micrographs (20x) of PLA, PLA-PHB and nanocomposite films and their EDF-z profiles. Fig. 7(a) shows the typical Py-GC/MS chromatogram of PLA- PHB-CNCs obtained by pyrolysing the film at 1000 °C for 0.5 s. The pyrolysis of all PLA based films is characterized by the presence of two peaks with very similar mass spectra (m/z = 32, 43, 45 and 56) in which the peak at 17 min corresponds to meso-lactide and the peak at 18 min with the highest signal intensity in all samples to (L) and/or (D)-lactide [32]. Films with PHB showed the broad peak The chemical changes of nanocomposite films before and after 1, 2 and 3 days in composting were followed by FTIR analysis. At](https://figures.academia-assets.com/43362038/figure_005.jpg)
![of crotonic acid (6.7 min, m/z = 39, 41, 68, 69, and 86) [12,36], while nanocomposte films showed a peak at 22.5 min assigned to thermal degradation products of the cellulose structure (m/z = 55, 69, 87 and 103) [47]. The groups of small peaks appearing at retention times between 19 min and 22 min were assigned to the thermal degradation products of PLA with the characteristic series of signals at m/z = 56 + (n x 72) attributed to PLA degradation products such as dimers (n = 2) and trimers (n = 3) [32]. In general, the intensity of peaks decreased with composting time. However, the meso- lactide intensity showed a lower decrease with respect to the (D,L)- lactide equivalent. The ratio meso-lactide:lactide has been used as a semi-quantitative sign of the degradation of PLA [12,32,36,48,49]. ig 7(b) shows the reduction of (D,L)-lactide with respect to meso- lactide after the pyrolysis of the recovered samples. No significant differences were observed between PLA and PLA-PHB blend until 7 days in composting, but after 10 days, the PLA relationship [lactide; meso-lactide;_10 days/lactide/meso-lactide;_o days] highly decreased Nanocomposites showed similar reduction in 3 days of composting, but higher times revealed higher reduction for unfunctionalized nanocomposites (PLA-CNC and PLA-PHB-CNC). The estimated reduction of the (D,L)-lactide form with respect to the meso-lactide followed a similar tendency that the disintegrability test. In this sense, PLA-CNC and PLA-PHB-CNC showed the highest degradation rate suggestive of the polymer shortening by the hydrolysis](https://figures.academia-assets.com/43362038/figure_006.jpg)

![PLA and PLA-PHB nanocomposite film formulations and their viscosity molecular weight (My). Table 1 (EasyDrop-FM140, KRUSS GmbH, Hamburg, Germany) equipped with a camera and Drop Shape Analysis SW21; DSA1 software was used to test the water contact angle (6°) at room temperature. The contact angle was determined by randomly putting 5 drops of distilled water (~2 wL) with a syringe onto the film surfaces and, after 30 s, the average values of ten measurements for each drop were used. The maximum standard deviation in the water contact angle measurements did not exceed +3% [30]. the final film formulations were expressed taken into account the proportion reported in Table 1. The intrinsic viscosity [yn] of samples was determined to estimate the viscosity molecular weight by means the Mark—Houwink relation:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/43362038/table_001.jpg)











![Fig. 4. Equivalent circuit for the analysis of the impedance spectra for different anodized Al samples. The impedance spectra were fitted to the equivalent circuit (EC) shown in Fig. 4 using the software ANODAL [6,21]. G, and C,, are the capacitance of the inner barrier layer and the outer porous layer, respectively and R, is the resistance of the barrier layer. Zpo = K(ja)", where K and n are fit parameters and w = 2nf, is a con- stant phase element that is used to account for the variations of the properties of the pores in the outer porous layer such as pore diam- eter, pore depth and degree of sealing [22]. The fit parameter K is used as a measure of the pore resistance Ryo.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/43171421/figure_002.jpg)



















![* Calculated based on molar ratio monomer I and monomer II, r = [EC/Da]. > Measured using gel permeation chromatography (GPC). © Obtained from Ubbelohde solution viscometer using toluene as the solvent. Feed molar ratio of hydride terminated PDMS which have been synthesised. Table 1](https://figures.academia-assets.com/45895214/table_002.jpg)

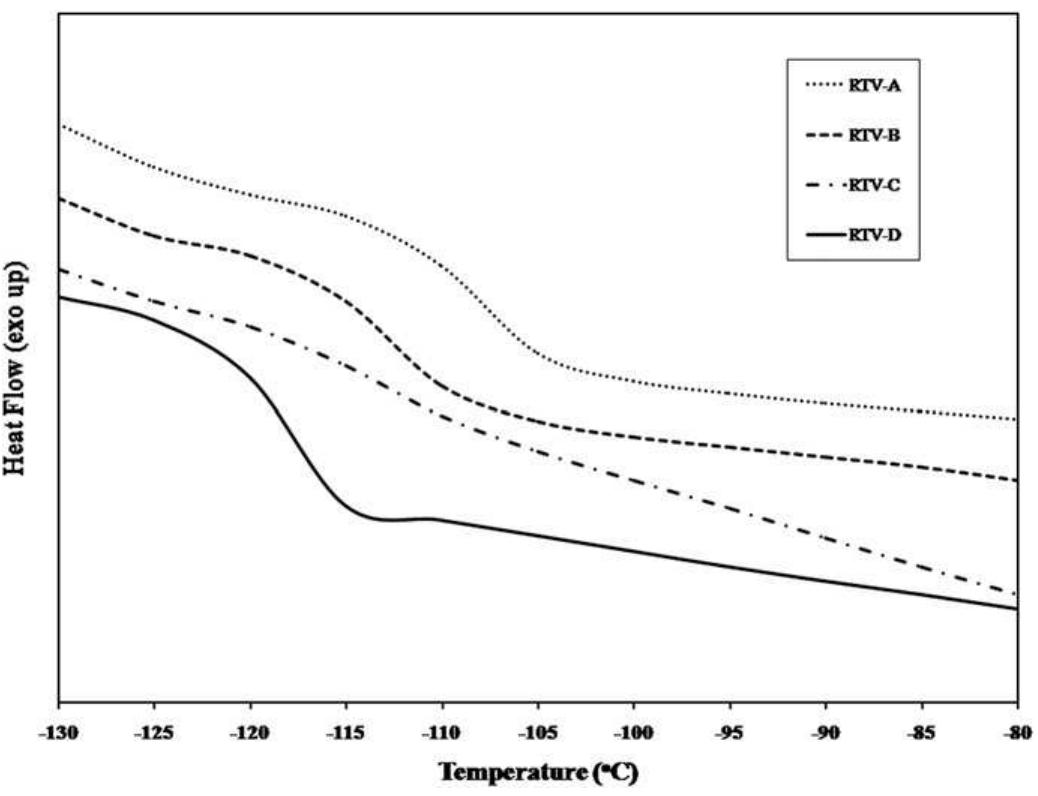
![* Calculated using Krevelen method [15]. Effect of cross-link density on free volume and glass transition temperature. Table 4](https://figures.academia-assets.com/45895214/table_004.jpg)




![Figure 5 Size distribution of particles in paste C. der paste. The following phenomena have been ob- served in dense suspension rheology (see, ¢g., Ref. [15]): be slightly higher than is shown in Table 2. The large variation in irregular particles between pastes E(1) and E(2) is unexpected and is in part due to the relatively small sample sizes from which observations for these pastes were made. Itis known that non-Newtonian boundary effects play a major role in determining suspension flow patterns. Wall slip is a well-documented phenomenon, and plays an; important role in aperture emptying for sol- The evidence for the occurrence of (2) in aperture emptying is now outlined. When skipping occurs, much of the.time, only a very thin layer of paste is](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42720604/figure_005.jpg)




![Figure 9 Schematic representation of a figure in Ref. [17] which examines how the apparent relative viscosity of a suspension in a cylinder ‘varies as the ratio of cylinder diameter to particle dia- meter is decreased. TABLE II Average diameter of particles, standard deviation of particle diameters, and percentage of irregularly shaped particles, with the total number of particles measured for each paste. Six pastes were analysed; pastes E(1) and E(2) were from the same manufacturer](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42720604/figure_010.jpg)




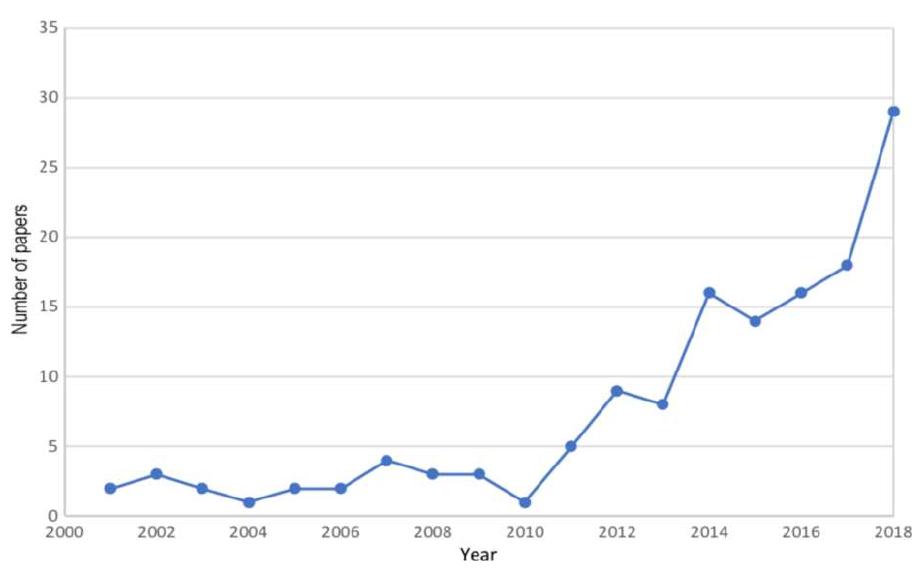



![The growth in the number of publications is shown in Table 2. As will be noted, the number of papers published has increased considerably since 2011, from 81 publications until 2010 (an average of 7 per year), to 461 between 2011 and 2018 (an average of 57 per year, if 2018 is considered to be a complete year). This confirms what is indicated in Ref. [27], Calero identifies 2011 as the point at which Green in Software Engineering in particular, and Green in Software in general, began to be dealt with as research topics, with the publication of the GREENSOFT model by](https://figures.academia-assets.com/67383281/table_001.jpg)

















































![Figure 2. Packaging life cycle. i © as Glass packaging is ena instance, exclusive design fication for wine and s bling brands to have a versatile range of design line [42]. For s peculiar to glass packaging facilitate unique product identi- pirits brands. Glass bottles composed of thickened bases, decoration and embossing work in conjunction with labeling designs in hindering a coordinated, high-quality image which provides shelf-presence and effectively repre- sents the brand and product message. In addition, glass is eco-benign and due to its](https://figures.academia-assets.com/86618660/figure_002.jpg)

![Figure 4. Morphological images, elemental constitution, and phase dispersive detection of zein thin films with crystals inclusion. (a) Visual image; (b) SEM image-facade; (c) SEM image-profile; (d) EDX analysis; (e) EDX mapping on N; (f) EDX mapping on Zn; the antibacterial activity of zein-conjugated ZnO crystals with varying concentrations against (g) 5. aureus and (h) E. coli using the disc diffusion technique. The antibacterial activity of a thin film of zein with inclusion of ZnO crystals after dipping in an aqueous solution at various times. (i) S. aureus and (j) E. coli [236].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/86618660/figure_004.jpg)



![Figure 9. Optical micrographs of ABA films fabricated via masterbatch with MFI = 34 g/10 min. The masterbatches were fabricated via ultrasound-assist technique V-U. (a) 0.1 wt% MWCNT and (b) 1.0 wt% MWCNT in the A-layers. Photograph of ABA films: (c) reference film, 0 wt% MWCNT, (d) film with 1 wt% MWCNT (fabricated with masterbatch: iPP MFI = 2.5, F-U), and (e) film with 0.01 wt% MWCNT (fabricated with masterbatch: iPP MFI = 2.5, V-U). TEM micrographs for ABA film containing 1.0 wt% MWCNT in the A-layers fabricated using masterbatch with MFI = 34 g/10 min with ultrasound-assist method V-U. (f) MWCNTs near to each other, (g) MWCNTs touching to each other, and (h) SEM micrographs for ABA film containing 1.0 wt% MWCNT in the A-layers fabricated using masterbatch with MFI = 34 g/10 min with ultrasound-assist method V-U. The optical attributes of films composed of MWCNTs did not exhibit significant variations in comparison to the reference film at MWCNT concentrations below 0.1 wt%. However, improved brightness was observed, and ascribed to well-arranged iPP molecules engulfing the MWCNTs [175].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/86618660/figure_008.jpg)


![Figure 12. Cryo-fractured cross-sectional high-resolution scanning electron microscope (HR-SEM) images of (a) pristine PP and (b) PP/(HNTs-carvacrol) films. Various HNTs are inked with arrows for clarification. The HNTs are evenly distributed within the PP matrix. The inset reveals a micrograph, showing HNTs extending from the PP matrix. The HNTs exhibit peculiar morphology of cylindrical tubes, with an exterior diameter of up to 100 nm [65]. (c) Antimicrobial influence of pristine PP, PP/ carvacrol, and PP/(HNTs-carvacrol) films exhibited in the micro-atmosphere diffusion assays, i.e., without direct contact between the studied films and the microbial cultures. Top panel: Petri dishes containing the E. coli after incubation with the films for 12 h at 37 C (the margins of the inhibition zone are marked for clarity). Bottom panel: Petri dishes containing A. alternata following 7 days of incubation at 25 C in the dark [65].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/86618660/figure_011.jpg)


![Figure 15. (a) Photographic image of the specimen cut in circular disks within diameter of 1 cm; SEM micrographic images derived using BSE detector for: (b) PE-0.5% Ag; (c) PE-1% Ag; (d) PE-2% Ag and (e) magnification of (c) to show the size of the domains (where PE represents polyethylene) [5].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/86618660/figure_014.jpg)


![Figure 18. (a) TEM of Ag-MMT, (b) TEM and EDS of Ag-OMMT, (c) SEM micrograph of MMT, and (d) Ag-MMT [85].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/86618660/figure_017.jpg)
![Figure 19. FESEM image of varying composite laminates: (a) BA-ph; (b) BA-ph/PEN blends with 20 wt % PEN constitution; (c) zoomed image of (b,d) BA-ph/PEN blends composed of 40 wt% PEN; the arrows depict the gaps between matrix and GF in Figure 19(a), in addition to adhesion properties in Figure 19(b-d); the cycles depict GF rough surface and the smooth surface of the matrix; the rectangles represent the zoomed image of the adhering attributes of the composites in a specific zone [270].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/86618660/figure_018.jpg)
![dispersion in thermosetting matrices can undergo improvement devoid of any surface modification [91]. CNT distribution can be enhanced through functionalization of the CNTs surface [170]. These modifications enhance interfacial interactions with the matrix. Three routes are feasible via chemical functionalization of covalent bonds [171]. Varying techniques abound for chemical functionalization of CNTs for intro- duction of carboxylic acid groups on the surface. This UV/O3 treatment enhances distribution and interfacial bonding of CNTs to the epoxy matrix. Surface functiona- lization of CNT can occur with amines [170-172]. The amine can form covalent bonding with the epoxy matrix; functionalization using silanes [173]. CNTs undergo oxidation on exposure to UV, in the presence of ozone, which reduces to hybrid aluminum-lithium solution followed by silanization. Silane functionalization enhances CNTs distribution in matrix. CNTs distribution in a thermosetting matrix can be enhanced via non-covalent physical treatments, with the benefit of not damaging CNT, or exposure to defects. CNTs can also be functionalized through surfactant inclusion [91,170]. The physical adsorption of surfactant on CNTs surface reduces its surface tension, thereby hindering agglomerates formation [170]. Studies of the surface sizing modified MWCNTs and its influence on the wettability, cf «8 WY . 1a Cw etarToomMi](https://figures.academia-assets.com/86618660/figure_019.jpg)








![Figure 4. a) Vickers indenter: A (d) = d’/2; B [= (180 - 20)/2]= 22°; and d = 2a. b) Under loading, the apex for Vickers indenter, 2% is equal to 148°.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/86423879/figure_003.jpg)










